Abstract
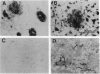
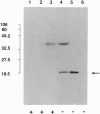
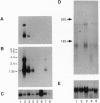
A neuropathological hallmark of Alzheimer disease (AD) is a widespread amyloid deposition. We analyzed the entire amino acid sequences in an amyloid preparation and found, in addition to the major beta/A4-protein (A beta) fragment, two unknown peptides. We raised antibodies against synthetic peptides using subsequences of these peptides. These antibodies immunostained amyloid in neuritic and diffuse plaques as well as vascular amyloid. Electron microscopic analysis demonstrated that the immunostaining was localized on amyloid fibrils. We have isolated an apparently full-length cDNA encoding a 140-amino-acid protein within which two previously unreported amyloid sequences are encoded in tandem in the most hydrophobic domain. We tentatively named this 35-amino acid peptide NAC (non-A beta component of AD amyloid) and its precursor NACP. NAC is the second component, after A beta, identified chemically in the purified AD amyloid preparation. Secondary structure predictions indicate that the NAC peptide sequence has a strong tendency to form beta-structures consistent with its association with amyloid. NACP is detected as a M(r) 19,000 protein in the cytosolic fraction of brain homogenates and comigrates on immunoblots with NACP synthesized in Escherichia coli from NACP cDNA. NACP mRNA is expressed principally in brain but is also expressed in low concentrations in all tissues examined except in liver, suggesting its ubiquitous and brain-specific functions. The availability of the cDNA encoding full-length NACP should help to elucidate the mechanisms of amyloidosis in AD.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyreuther K., Dyrks T., Hilbich C., Mönning U., König G., Multhaup G., Pollwein P., Masters C. L. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and beta A4 amyloid in Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;379:159–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busciglio J., Gabuzda D. H., Matsudaira P., Yankner B. A. Generation of beta-amyloid in the secretory pathway in neuronal and nonneuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2092–2096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi-Miura N. H., Ihara Y., Fukuchi K., Takeda M., Nakano Y., Tobe T., Tomita M. SP-40,40 is a constituent of Alzheimer's amyloid. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;83(3):260–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00296787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikelenboom P., Hack C. E., Kamphorst W., Rozemuller J. M. Distribution pattern and functional state of complement proteins and alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in cerebral beta/A4 deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Res Immunol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):617–620. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(92)80044-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidani L., Goate A. Mutations in APP and their role in beta-amyloid deposition. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;379:195–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Fleming J., Tung Y. C., Lassmann H., Iqbal K., Joshi J. G. Ferritin is a component of the neuritic (senile) plaque in Alzheimer dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(2):105–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00334497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. A., Higgins G. A. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):184–185. doi: 10.1126/science.1566067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Haga S. Complements, microglial cells and amyloid fibril formation. Res Immunol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):614–616. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(92)80043-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Selkoe D. J. The seminal role of beta-amyloid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1992 Spring;6(1):7–34. doi: 10.1097/00002093-199205000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaria R. N., Kroon S. N. Complement inhibitor C4-binding protein in amyloid deposits containing serum amyloid P in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):461–466. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80830-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamholz J., de Ferra F., Puckett C., Lazzarini R. Identification of three forms of human myelin basic protein by cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4962–4966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J., Honda T., Mori H., Hamada Y., Miura R., Ogawara M., Ihara Y. The carboxyl third of tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):827–834. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Cole G. M., Hansen L. A., Mallory M., Albright T., Terry R. D., Saitoh T. Protein kinase C alteration is an early biochemical marker in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1991 Sep;11(9):2759–2767. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-09-02759.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Cole G., Shimohama S., Hansen L., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Saitoh T. Differential involvement of protein kinase C isozymes in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2113–2124. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02113.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald B., Esiri M. M., McIlhinney R. A. A monoclonal antibody that reacts immunohistochemically with amyloid deposits in the brain tissue of Alzheimer patients binds to an epitope present on complement factor 4. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1172–1177. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Selkoe D. J., Kurnit D. M., Kosik K. S. A cDNA for a human microtubule associated protein 2 epitope in the Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangle. Brain Res. 1986 Nov;387(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter L. S., Chui H. C., Saperia D., Athanikar J. Microangiopathy and the colocalization of heparan sulfate proteoglycan with amyloid in senile plaques of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 29;508(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91111-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Cras P., Siedlak S. L., Tabaton M., Kawai M. Beta protein immunoreactivity is found in the majority of neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):283–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. L., Walker L. C., Martin L. J., Sisodia S. S. Amyloidosis in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1992 Oct;141(4):767–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. D. Prediction of chain turns in globular proteins on a hydrophobic basis. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):586–590. doi: 10.1038/272586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozemuller J. M., Stam F. C., Eikelenboom P. Acute phase proteins are present in amorphous plaques in the cerebral but not in the cerebellar cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 30;119(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90759-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Sundsmo M., Roch J. M., Kimura N., Cole G., Schubert D., Oltersdorf T., Schenk D. B. Secreted form of amyloid beta protein precursor is involved in the growth regulation of fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Kamino K., Bryant E. M., Moore D., Bird T. D. Genetic heterogeneity, Down syndrome, and Alzheimer disease. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;379:215–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Esch F., Lee M., Dovey H., Davis D., Sinha S., Schlossmacher M., Whaley J., Swindlehurst C. Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):325–327. doi: 10.1038/359325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Golde T. E., Ghiso J., Cheung T. T., Estus S., Shaffer L. M., Cai X. D., McKay D. M., Tintner R., Frangione B. Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.1439760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Hirai S., Yamaguchi H., Harigaya Y., Ishiguro K., Matsubara E. Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin is present in diffuse senile plaques. A comparative study of beta-protein and alpha 1-antichymotrypsin immunostaining in the Alzheimer brain. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):247–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Mar H., Nochlin D., Kimata K., Kato M., Suzuki S., Hassell J., Wight T. N. The presence of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the neuritic plaques and congophilic angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):456–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Verga L., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Down syndrome as a key to the time sequence of brain changes in Alzheimer disease. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;379:143–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinters H. V., Nishimura G. S., Secor D. L., Pardridge W. M. Immunoreactive A4 and gamma-trace peptide colocalization in amyloidotic arteriolar lesions in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):233–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Mesulam M. M. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. beta-Amyloid and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 26;325(26):1849–1857. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112263252605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]