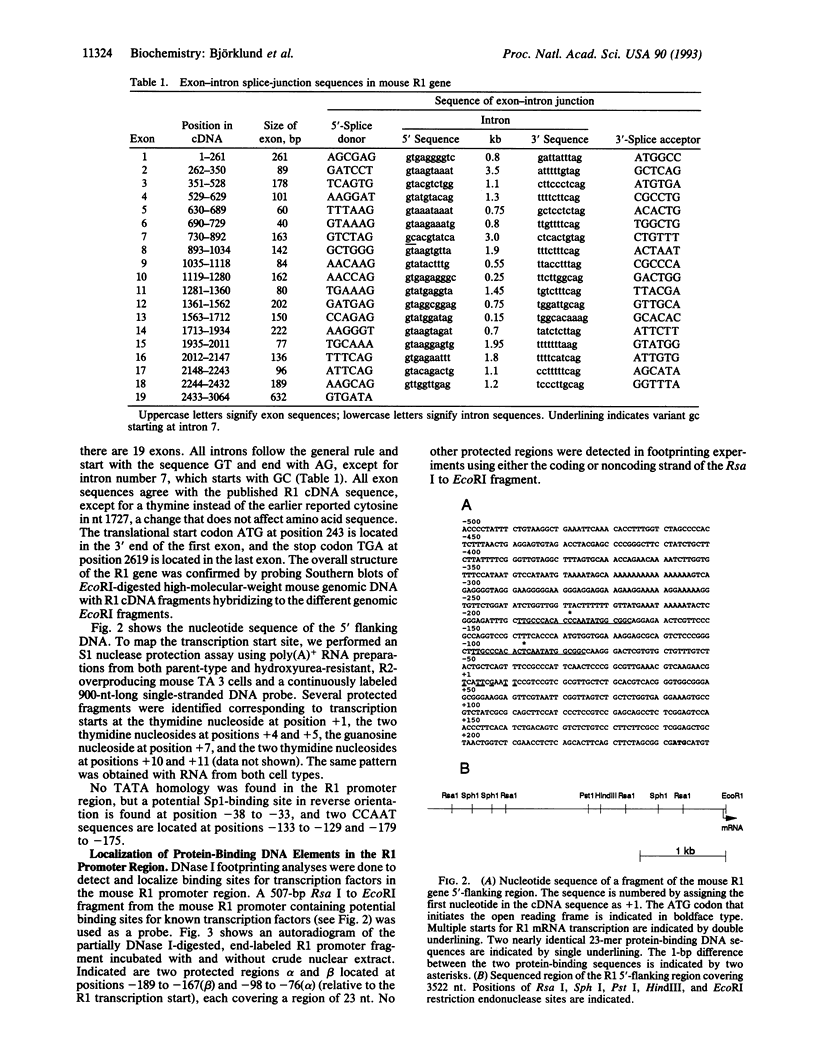
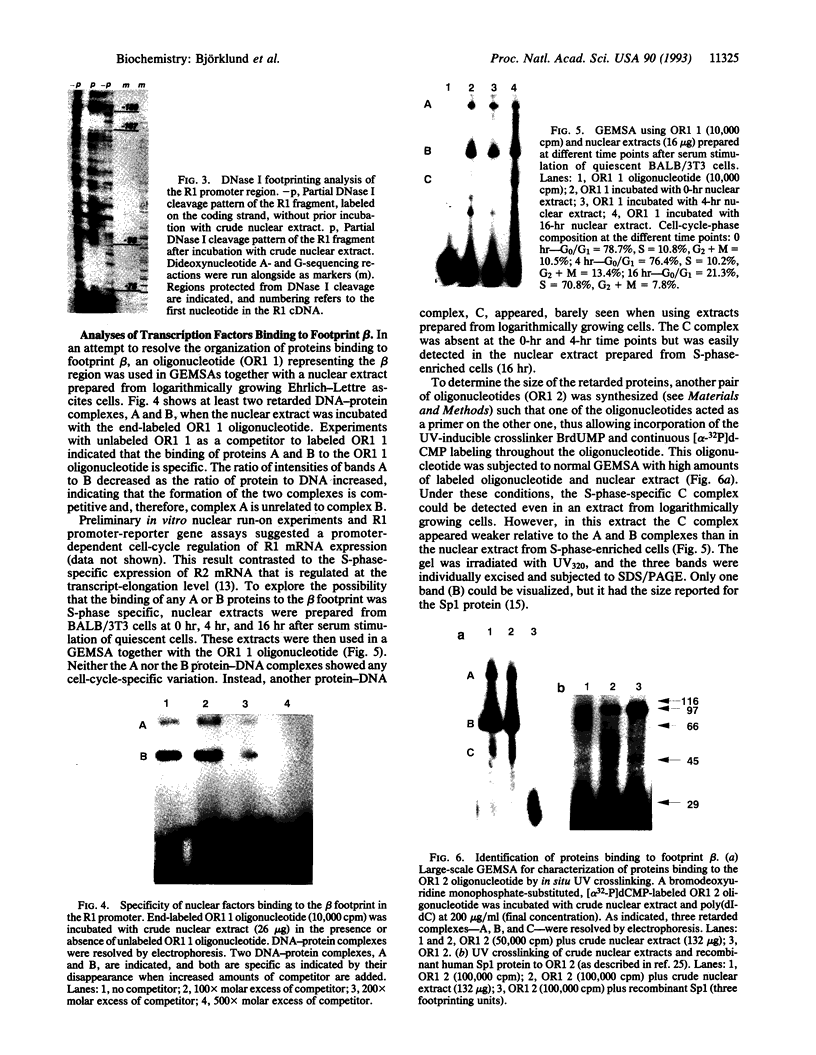
Abstract
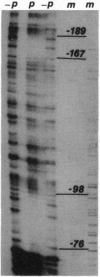
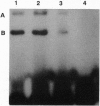
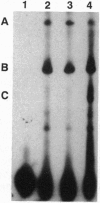
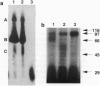
Mammalian ribonucleotide reductase (EC 1.17.4.1) is composed of two nonidentical subunits, proteins R1 and R2, both required for enzyme activity. The structure of the genomic mouse ribonucleotide reductase R1 gene was compiled from a number of overlapping lambda clones isolated from a Charon 4A mouse sperm genomic library. The R1-encoding gene covers 26 kb and consists of 19 exons. All exon-intron boundaries were located by dideoxynucleotide sequencing, showing that intron 7 starts with the variant GC instead of GT. About 3.5 kb of DNA from the 5'-flanking region of the R1-encoding gene were cloned and sequenced, and the transcriptional start site was determined by nuclease S1 mapping of RNA. DNase I footprinting assays on the R1 promoter identified two nearly identical 23-bp-long protein-binding regions. Three protein complexes binding to one of the 23-mer regions were resolved and partially identified by using gel-retardation mobility-shift assays and UV crosslinking. One complex most likely contained Sp1, and another complex showed S-phase-specific binding, suggesting a direct role in the cell-cycle-dependent R1 gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund S., Skog S., Tribukait B., Thelander L. S-phase-specific expression of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 and R2 subunit mRNAs. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5452–5458. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund S., Skogman E., Thelander L. An S-phase specific release from a transcriptional block regulates the expression of mouse ribonucleotide reductase R2 subunit. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4953–4959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissenden J. E., Caras I., Thelander L., Francke U. The structural gene for the M1 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase maps to chromosome 11, band p15, in human and to chromosome 7 in mouse. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):302–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Mapping of gene transcripts by nuclease protection assays and cDNA primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:611–632. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W., Levinson B. B., Fabry M., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloned mouse ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 cDNA reveals amino acid sequence homology with Escherichia coli and herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7015–7022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. Maximal binding levels of an H1 histone gene-specific factor in S-phase correlate with maximal H1 gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4576–4578. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Fridovich-Keil J. L., Pardee A. B. Inducible proteins binding to the murine thymidine kinase promoter in late G1/S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström Y., Eriksson S., Jildevik I., Skog S., Thelander L., Tribukait B. Cell cycle-dependent expression of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. Differential regulation of the two subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9114–9116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Gräslund A., Skog S., Thelander L., Tribukait B. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase. The S phase-correlated increase in subunit M2 is regulated by de novo protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11695–11700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traina-Dorge V., Slagel V., Deininger P. L. Sequence, structure and promoter characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann G. J., Musgrove E. A., Fox R. M., Thelander L. Ribonucleotide reductase M1 subunit in cellular proliferation, quiescence, and differentiation. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 15;48(18):5151–5156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard P. Interactions between deoxyribonucleotide and DNA synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:349–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiser C., Knöfler M., Rudelstorfer I., Haas R., Wintersberger E. Mouse thymidine kinase: the promoter sequence and the gene and pseudogene structures in normal cells and in thymidine kinase deficient mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):185–195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Eriksson S., Akerman M. Ribonucleotide reductase from calf thymus. Separation of the enzyme into two nonidentical subunits, proteins M1 and M2. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7426–7432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander M., Thelander L. Molecular cloning and expression of the functional gene encoding the M2 subunit of mouse ribonucleotide reductase: a new dominant marker gene. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2475–2479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Barton D. E., Thelander L., Lewis W. H., Srinivasan P. R., Francke U. Ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit sequences mapped to four different chromosomal sites in humans and mice: functional locus identified by its amplification in hydroxyurea-resistant cell lines. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerivitz K., Akusjärvi G. An improved nuclear extract preparation method. Gene Anal Tech. 1989 Sep-Oct;6(5):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(89)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]