Abstract
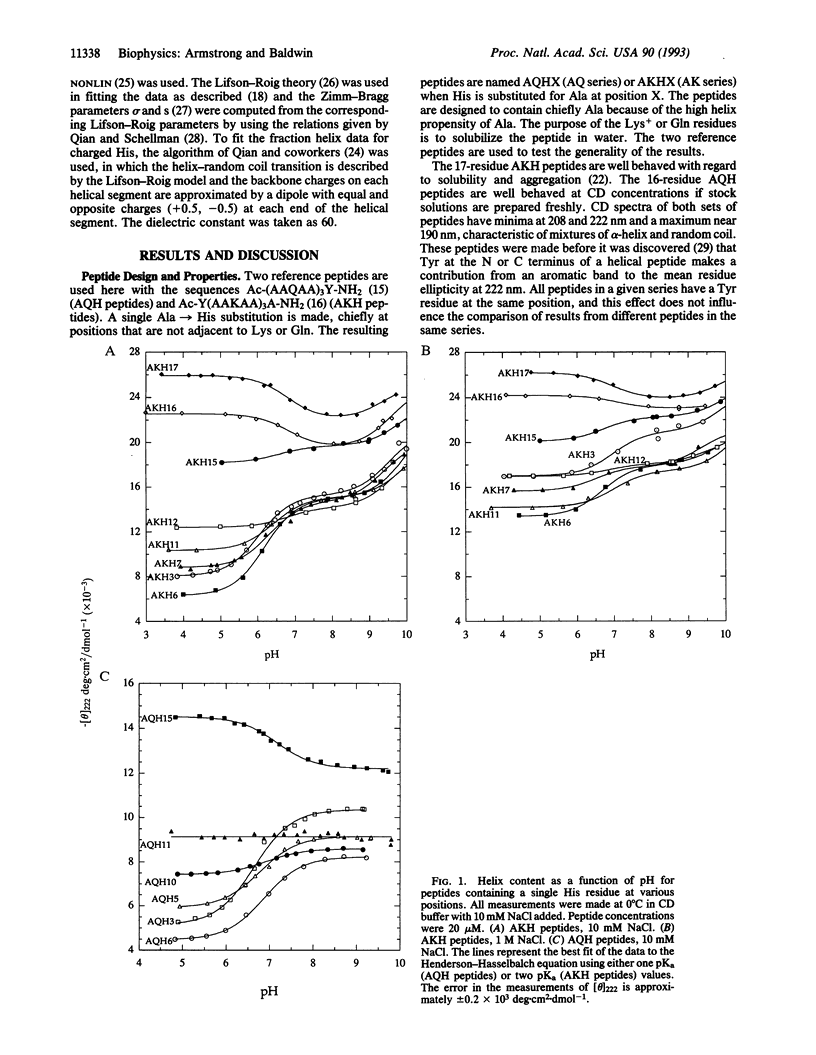
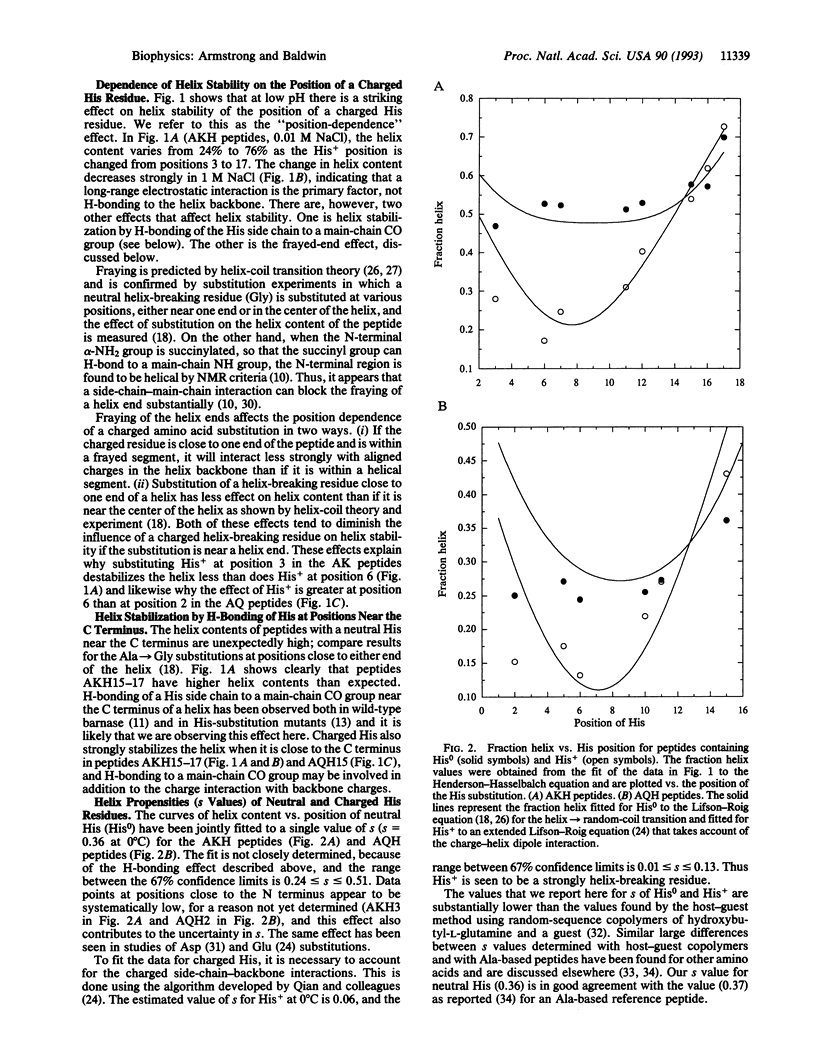
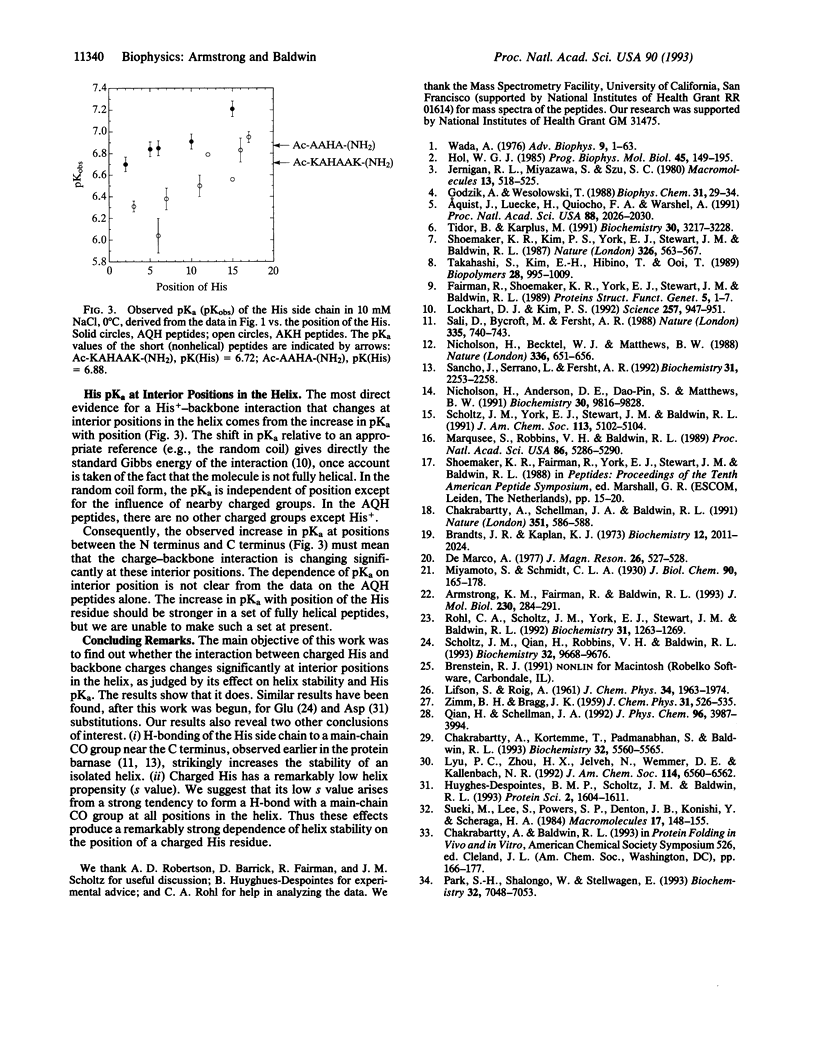
To determine whether a charged histidine side chain affects alpha-helix stability only when histidine is close to one end of the helix or also when it is in the central region, we substitute a single histidine residue at many positions in two reference peptides and measure helix stability and histidine pKa. The position of a charged histidine residue has a major effect on helix stability in 0.01 M NaCl: the helix content of a 17-residue peptide is 24% when histidine is at position 3 compared to 76% when it is at position 17. This dependence of helix content on histidine position decreases sharply in 1 M NaCl, as expected for counterion screening of the charge-helix dipole interaction. Results at interior positions indicate that the position of a charged histidine residue affects helix stability at these positions. Unexpectedly high values of the helix content are found when either neutral or charged histidine is at one of the last three C-terminal positions, suggesting that either form can stabilize an isolated helix by hydrogen bonding to a main-chain CO group.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aqvist J., Luecke H., Quiocho F. A., Warshel A. Dipoles localized at helix termini of proteins stabilize charges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):2026–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong K. M., Fairman R., Baldwin R. L. The (i, i + 4) Phe-His interaction studied in an alanine-based alpha-helix. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):284–291. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Kaplan L. J. Derivative sspectroscopy applied to tyrosyl chromophores. Studies on ribonuclease, lima bean inhibitors, insulin, and pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):2011–2024. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabartty A., Kortemme T., Padmanabhan S., Baldwin R. L. Aromatic side-chain contribution to far-ultraviolet circular dichroism of helical peptides and its effect on measurement of helix propensities. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5560–5565. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabartty A., Schellman J. A., Baldwin R. L. Large differences in the helix propensities of alanine and glycine. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):586–588. doi: 10.1038/351586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman R., Shoemaker K. R., York E. J., Stewart J. M., Baldwin R. L. Further studies of the helix dipole model: effects of a free alpha-NH3+ or alpha-COO- group on helix stability. Proteins. 1989;5(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godzik A., Wesolowski T. On the interactions of charged side chains with the alpha-helix backbone. Biophys Chem. 1988 Aug;31(1-2):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(88)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hol W. G. The role of the alpha-helix dipole in protein function and structure. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;45(3):149–195. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huyghues-Despointes B. M., Scholtz J. M., Baldwin R. L. Effect of a single aspartate on helix stability at different positions in a neutral alanine-based peptide. Protein Sci. 1993 Oct;2(10):1604–1611. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560021006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart D. J., Kim P. S. Internal stark effect measurement of the electric field at the amino terminus of an alpha helix. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):947–951. doi: 10.1126/science.1502559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marqusee S., Robbins V. H., Baldwin R. L. Unusually stable helix formation in short alanine-based peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5286–5290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson H., Anderson D. E., Dao-pin S., Matthews B. W. Analysis of the interaction between charged side chains and the alpha-helix dipole using designed thermostable mutants of phage T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):9816–9828. doi: 10.1021/bi00105a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson H., Becktel W. J., Matthews B. W. Enhanced protein thermostability from designed mutations that interact with alpha-helix dipoles. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):651–656. doi: 10.1038/336651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. H., Shalongo W., Stellwagen E. Residue helix parameters obtained from dichroic analysis of peptides of defined sequence. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 13;32(27):7048–7053. doi: 10.1021/bi00078a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohl C. A., Scholtz J. M., York E. J., Stewart J. M., Baldwin R. L. Kinetics of amide proton exchange in helical peptides of varying chain lengths. Interpretation by the Lifson-Roig equation. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 11;31(5):1263–1269. doi: 10.1021/bi00120a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sali D., Bycroft M., Fersht A. R. Stabilization of protein structure by interaction of alpha-helix dipole with a charged side chain. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):740–743. doi: 10.1038/335740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Serrano L., Fersht A. R. Histidine residues at the N- and C-termini of alpha-helices: perturbed pKas and protein stability. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 3;31(8):2253–2258. doi: 10.1021/bi00123a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz J. M., Qian H., Robbins V. H., Baldwin R. L. The energetics of ion-pair and hydrogen-bonding interactions in a helical peptide. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9668–9676. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker K. R., Kim P. S., York E. J., Stewart J. M., Baldwin R. L. Tests of the helix dipole model for stabilization of alpha-helices. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):563–567. doi: 10.1038/326563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Kim E. H., Hibino T., Ooi T. Comparison of alpha-helix stability in peptides having a negatively or positively charged residue block attached either to the N- or C-terminus of an alpha-helix: the electrostatic contribution and anisotropic stability of the alpha-helix. Biopolymers. 1989 May;28(5):995–1009. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidor B., Karplus M. Simulation analysis of the stability mutant R96H of T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3217–3228. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A. The alpha-helix as an electric macro-dipole. Adv Biophys. 1976:1–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



