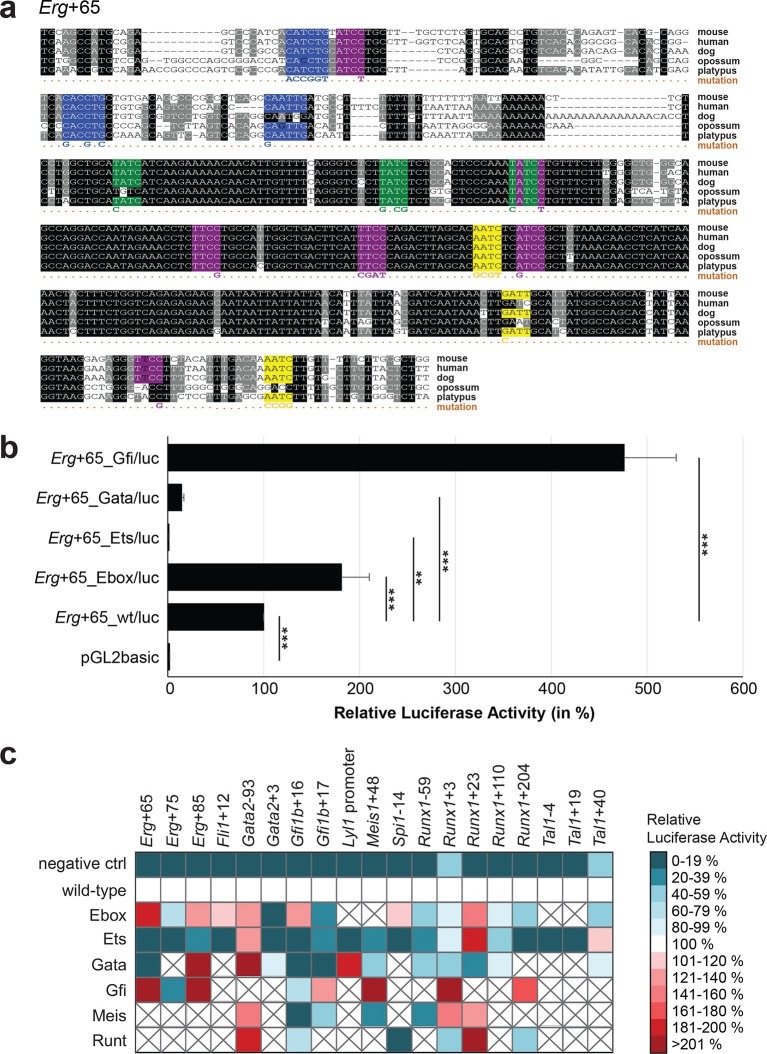
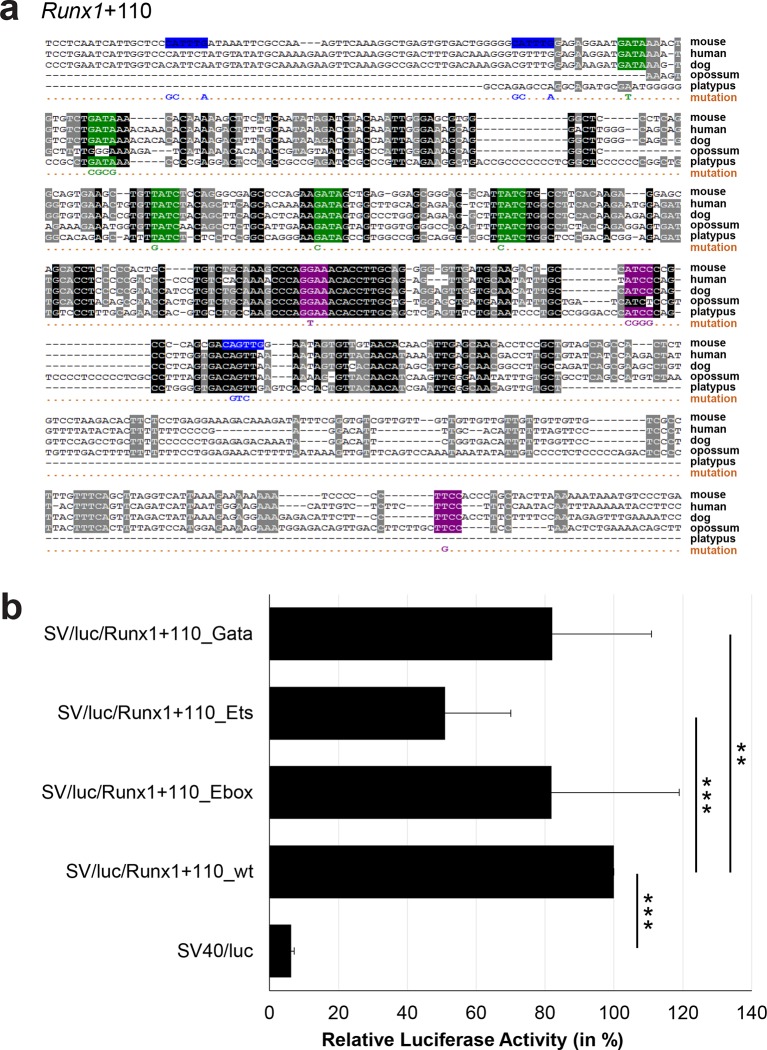
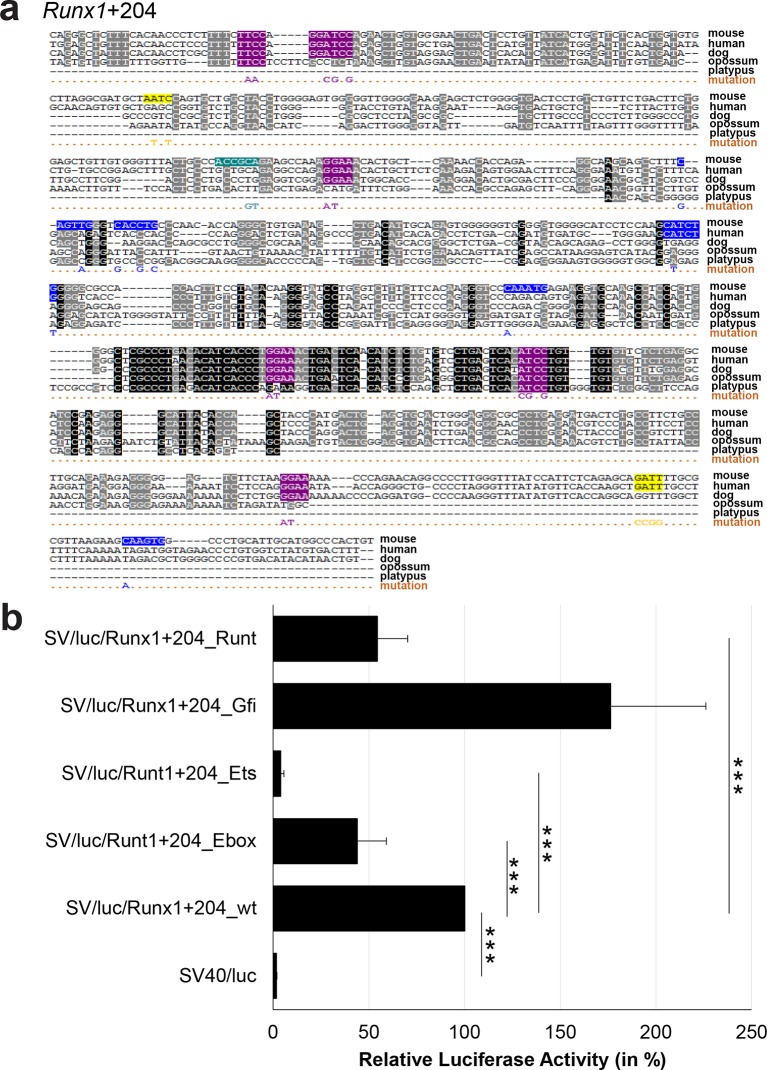
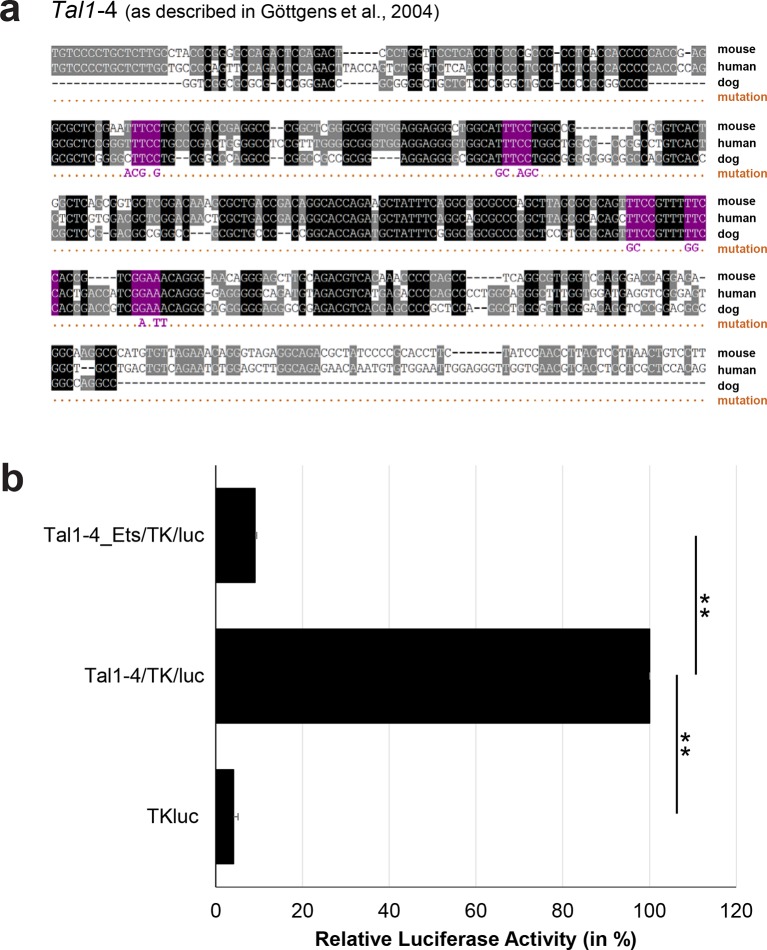
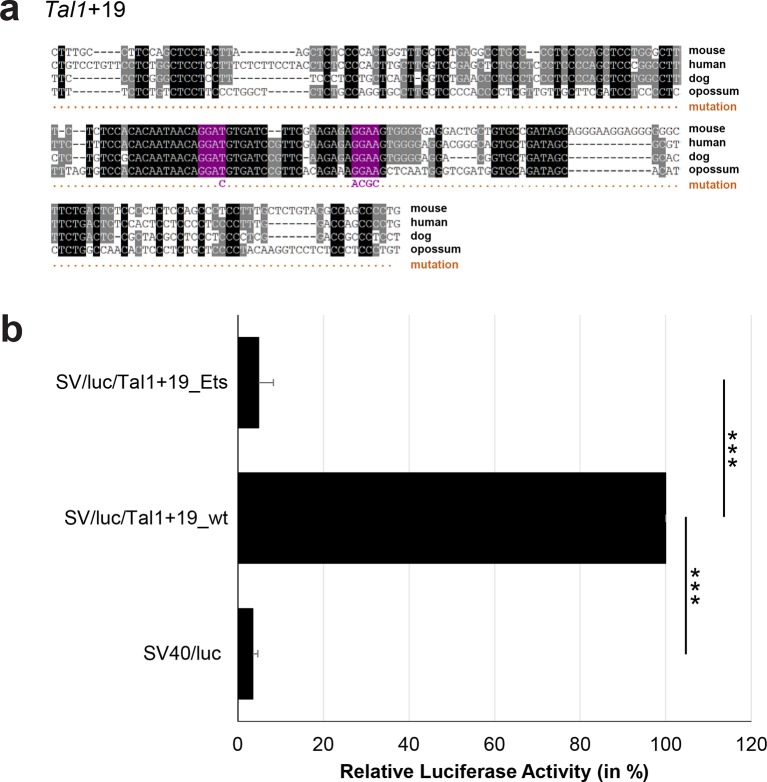
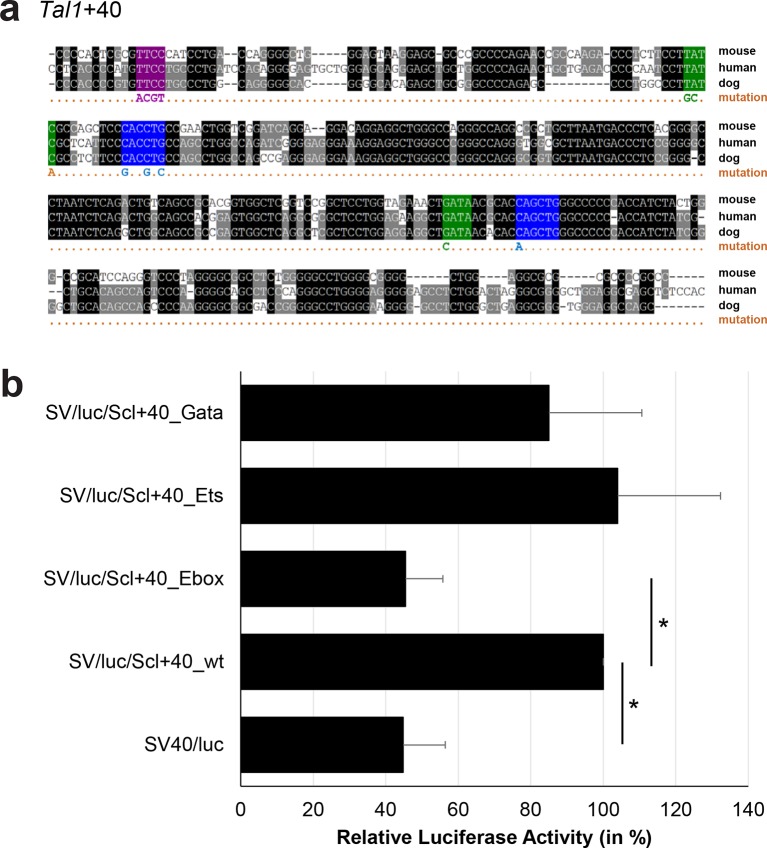
Figure 3. TFBS mutagenesis reveals enhancer-dependent effects of TF binding on gene expression.
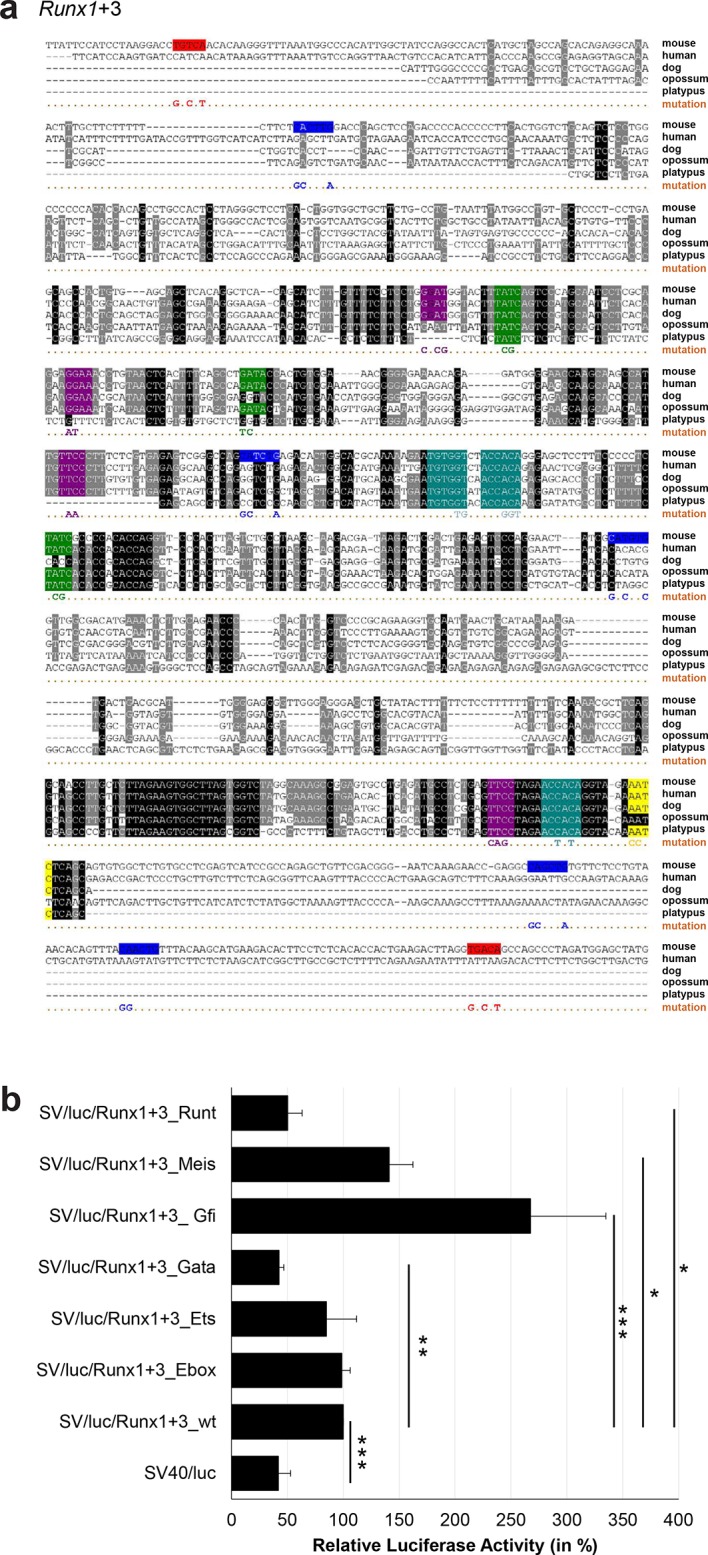
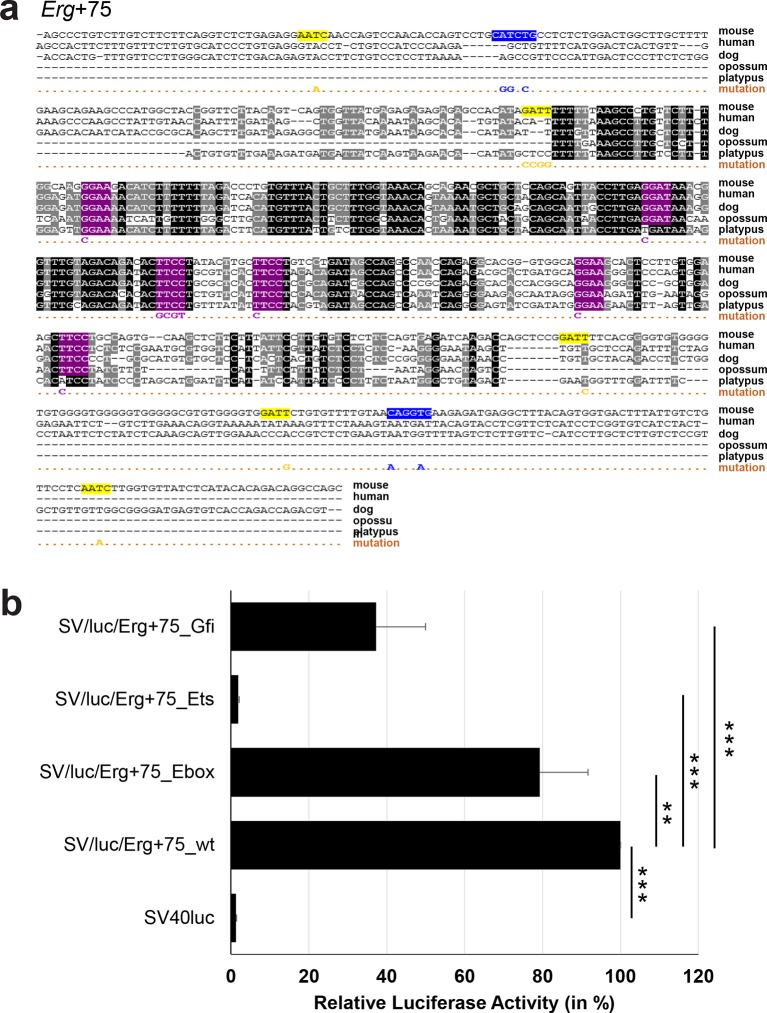
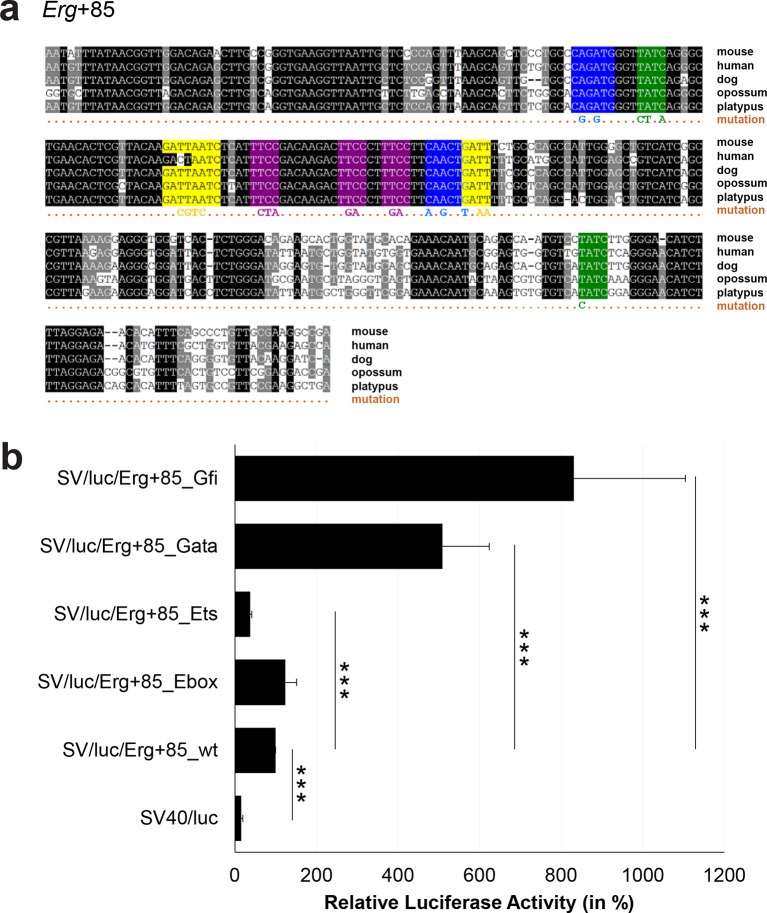
(a) Multiple species alignment of mouse (mm9), human (hg19), dog (canFam2), opossum (monDom5) and platypus (ornAna1) sequences for the Erg+65 region. Nucleotides highlighted in black are conserved between all species analysed, nucleotides highlighted in grey are conserved between four of five species. Transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) are highlighted in: blue = Ebox, purple = Ets, green = Gata, yellow = Gfi, red = Meis. The nucleotides that were changed to mutate the TFBSs are indicated below the alignment. All binding sites of one motif family (e.g. all Ebox motifs) were mutated simultaneously. (b) Luciferase assay for the Erg+65 wild-type and mutant enhancer in stably transfected 416b cells. Each bar represents the averages of at least three independent experiments with three to four replicates within each experiment. The results are shown relative to the wild-type enhancer activity, which is set to 100%. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Stars indicate significance: **=p-value <0.01, ***=p-value <0.001. p-values were calculated using t-tests, followed by the Fisher’s method. (c) Summary of luciferase assay results for all 19 high-confidence haematopoietic active regulatory regions. Relative luciferase activity is illustrated in shades of blue (down-regulation) and red (up-regulation). Crossed-out grey boxes indicate that there is no motif for the TF and/or the TF does not bind to the region. Detailed results and corresponding alignments with highlighted TFBSs and their mutations can be found in Figure 3—figure supplements 1–18.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11469.023
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Erg+75.
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Erg+85.
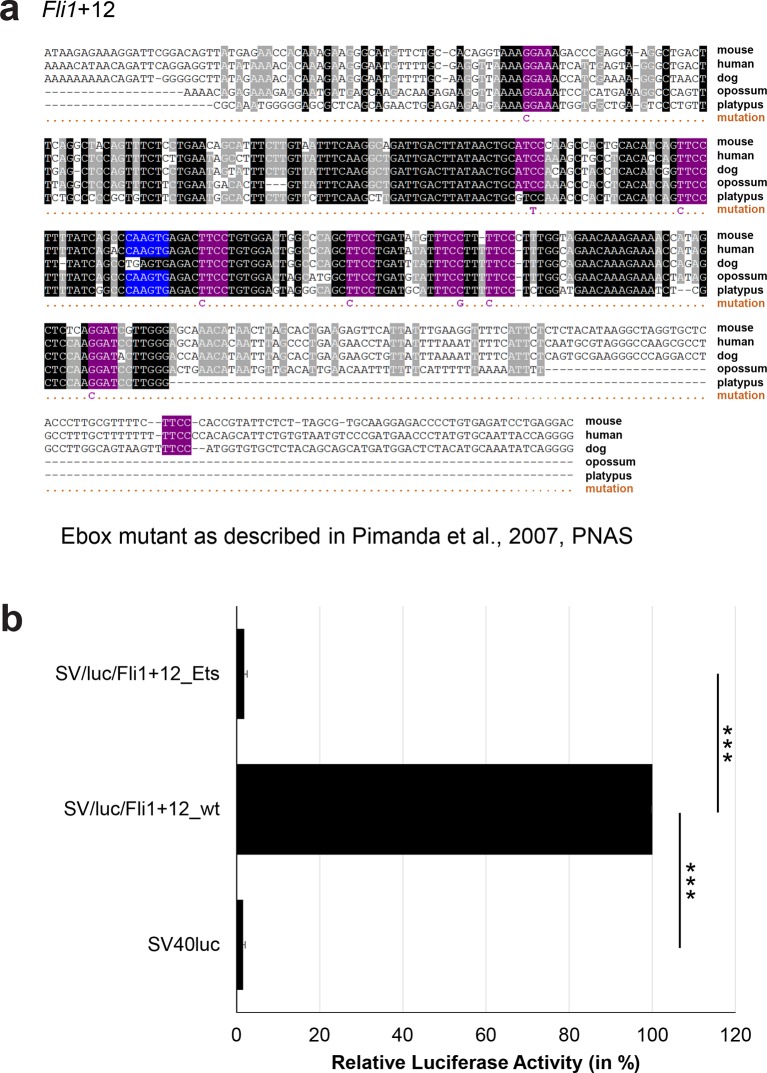
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Fli1+12.
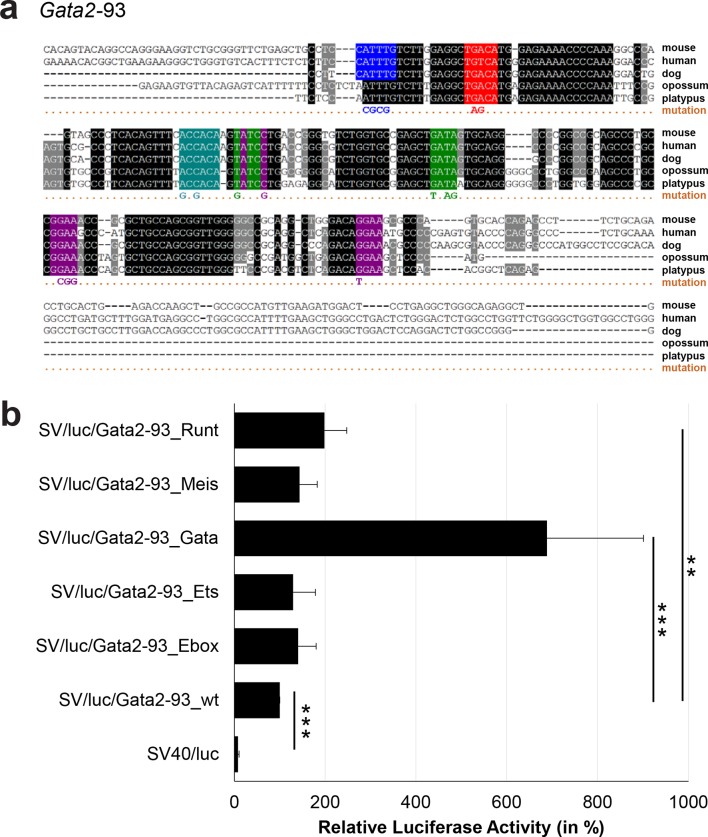
Figure 3—figure supplement 4. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Gata2-93.
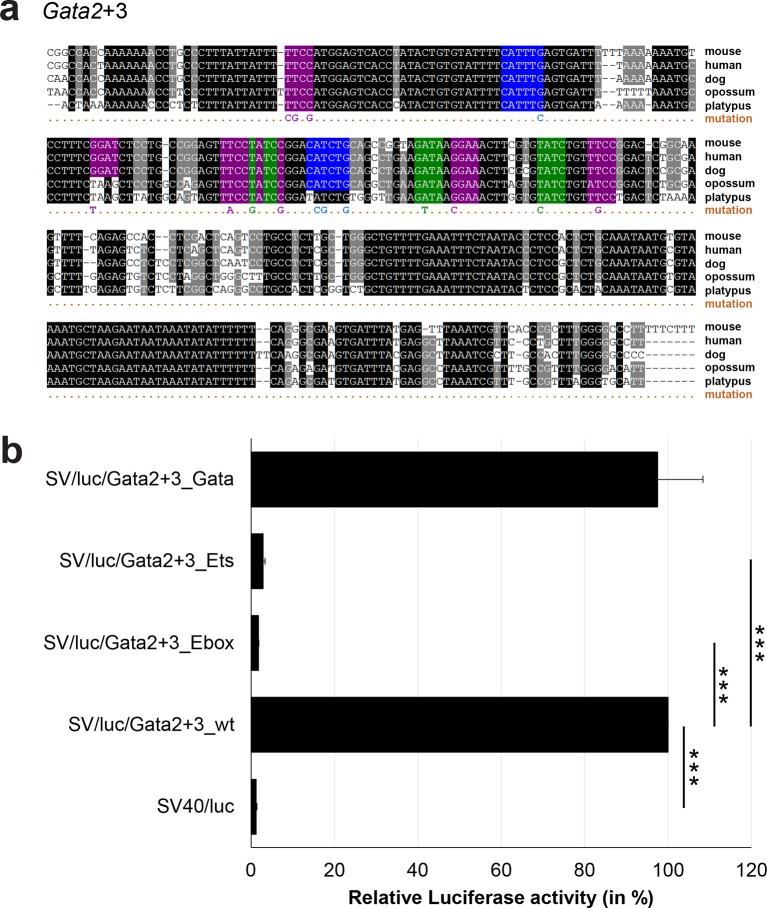
Figure 3—figure supplement 5. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Gata2+3.
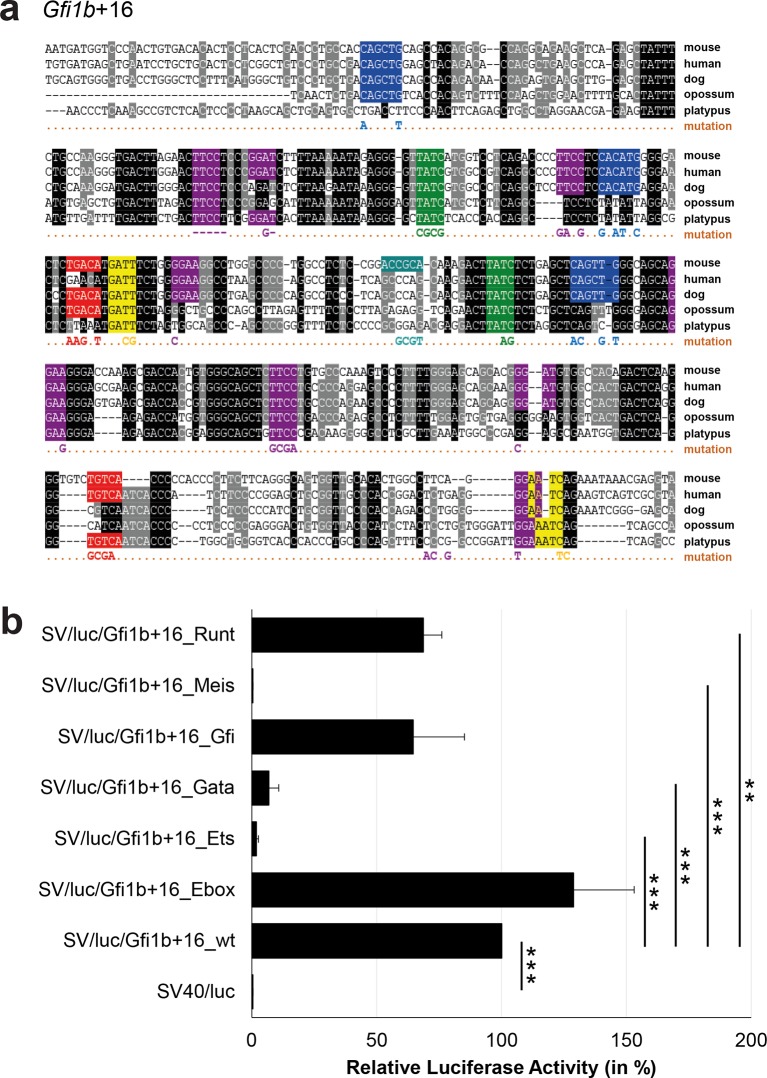
Figure 3—figure supplement 6. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Gfi1b+16.
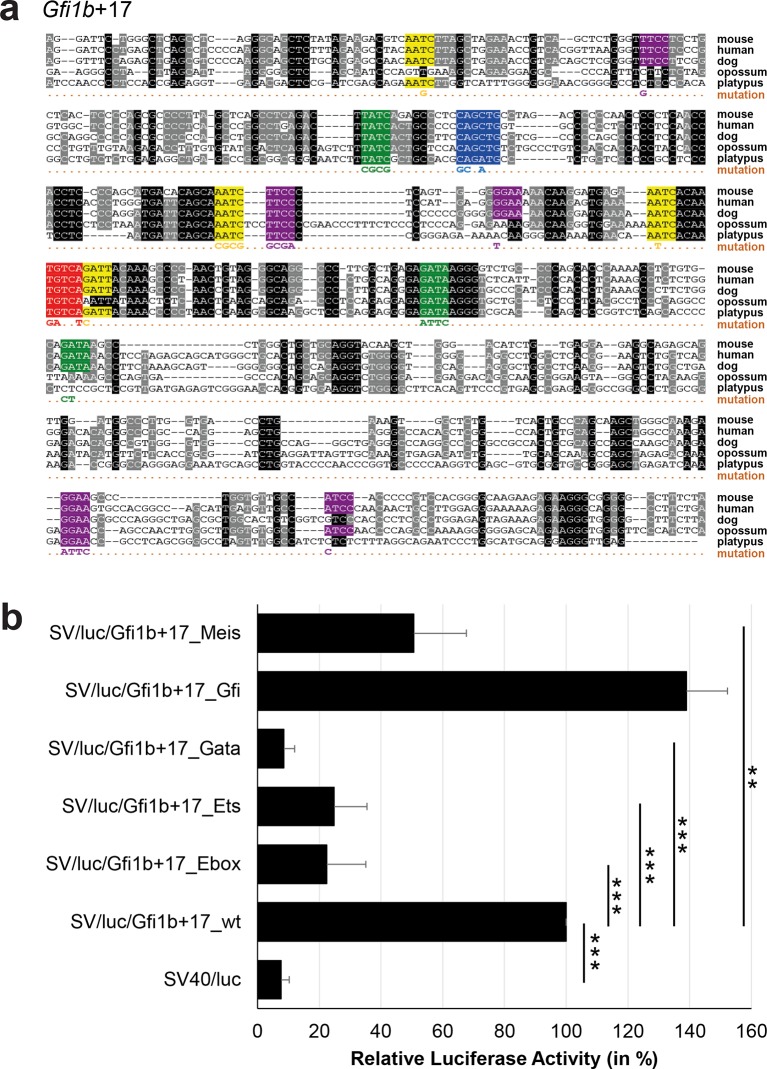
Figure 3—figure supplement 7. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Gfi1b+17.
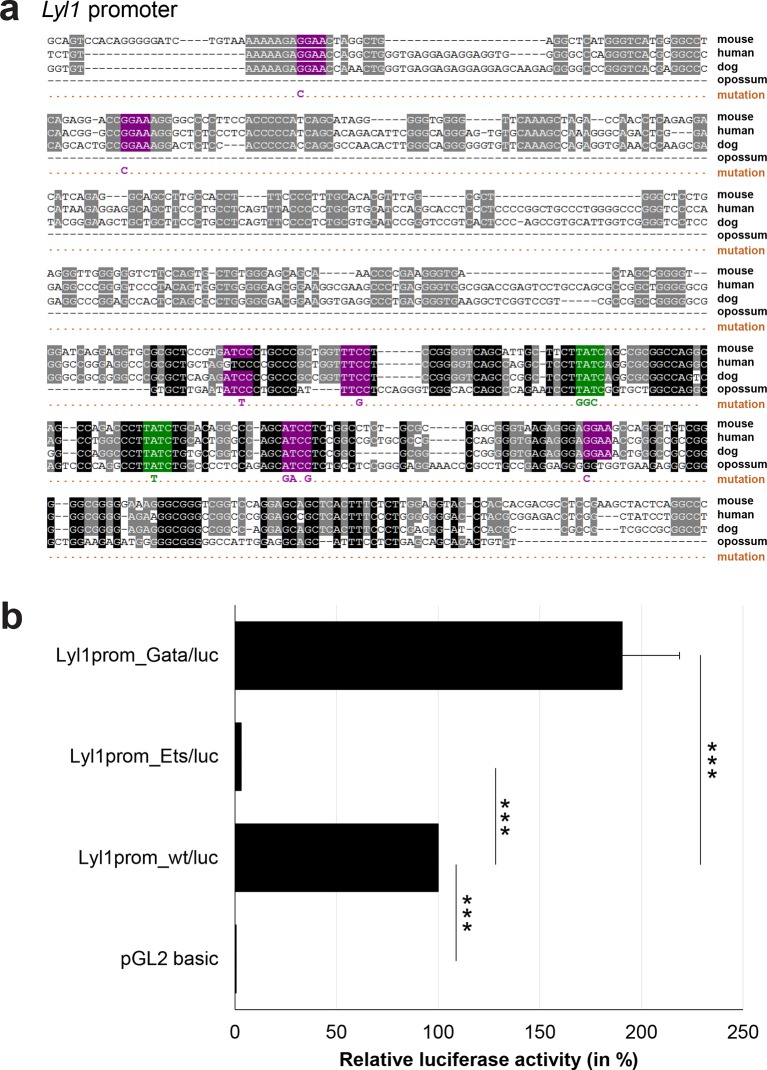
Figure 3—figure supplement 8. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Lyl1 promoter.
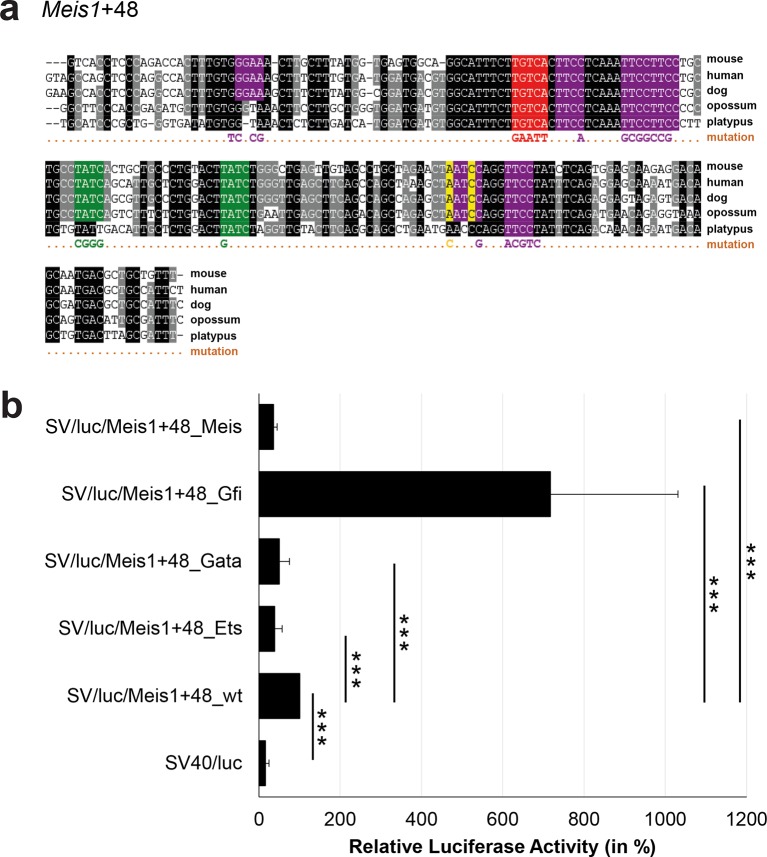
Figure 3—figure supplement 9. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Meis1+48.
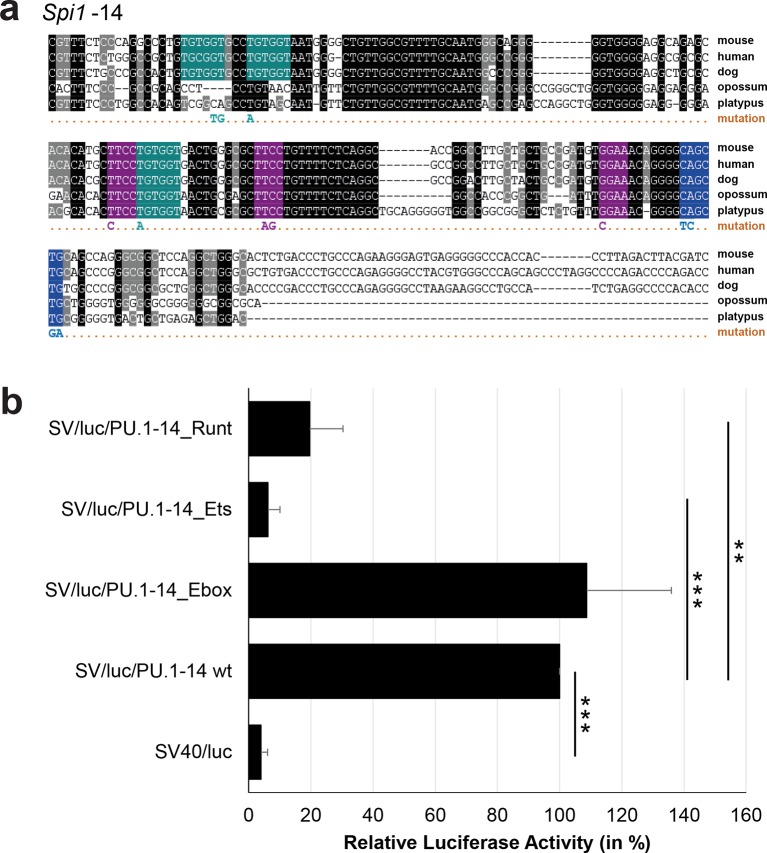
Figure 3—figure supplement 10. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Spi1-14.
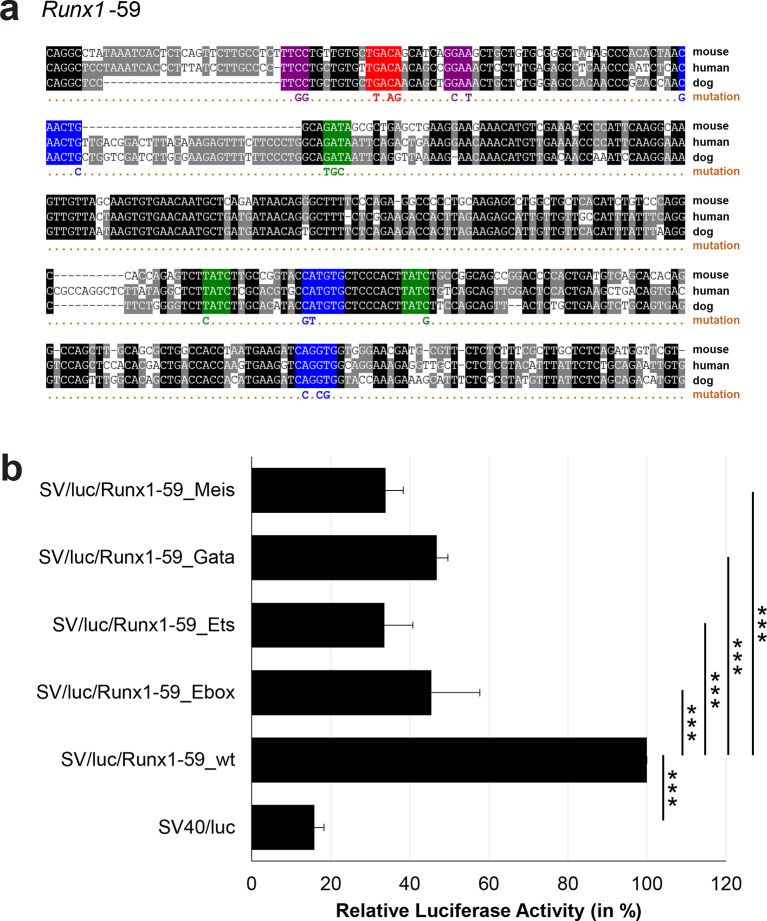
Figure 3—figure supplement 11. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Runx1-59.
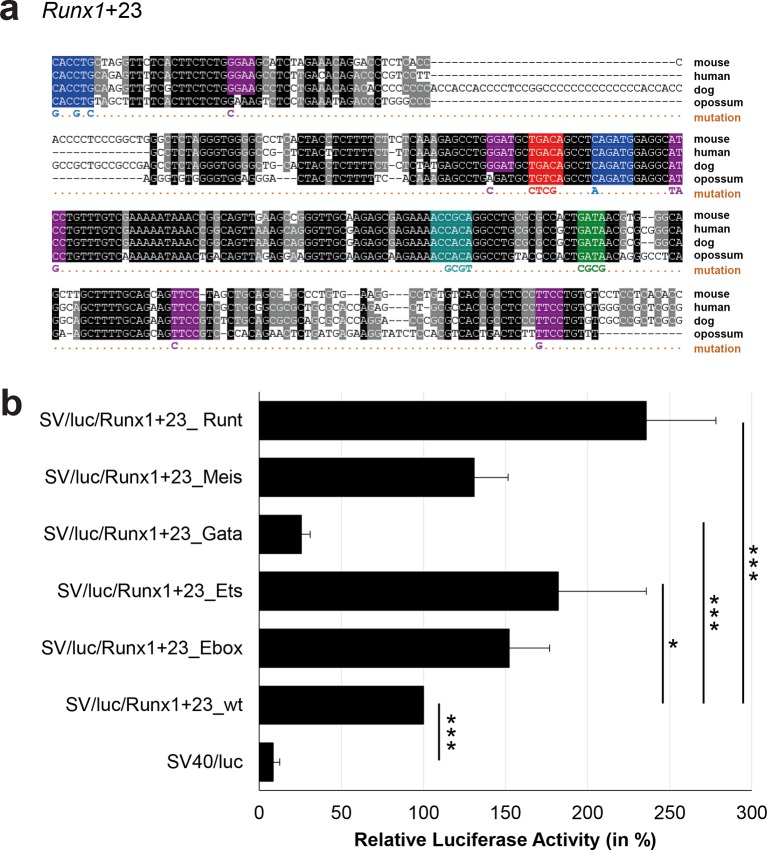
Figure 3—figure supplement 12. Multiple species alignment and luciferase assay results for Runx1+3.