Abstract
Diagnoses of hip and pelvis disorders are based on the detailed medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests, as appropriate for each condition. Plain radiography is still the initial examination of choice and, because of its importance, there is a need to standardize radiographic studies, both in relation to execution and in radiographic series, according to the different pathological conditions. The aim of this paper was to propose standardization for the main radiographic views of the hip and pelvis, and with regard to performing specific series for different pathological conditions, and to provide technical guidance for achieving these aims.
Keywords: Hip/pathogy, Hip/radiography, Pelvis/pathogy, Pelvis/radiography
INTRODUCTION
The diagnosis of hip and pelvic disorders is based on detailed clinical history, physical examination and laboratory tests, as appropriate for each condition.
Plain radiography is still the initial examination of choice, although computed tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance are useful for diagnostic confirmation1, 2.
In view of the importance of radiography, there is a need to standardized radiographic studies, both in relation to execution and in radiographic series, according to the different pathological conditions. The aim of this article is to propose standardization for the main radiographic views of the hip and pelvis, and with regard to performing specific series for different pathological conditions, providing technical guidance for achieving these aims.
RADIOGRAPHIC VIEWS
A) Non-traumatic series
-
1)Anteroposterior (AP) pelvic radiograph:
-
-Patient in supine or orthostatic position;
-
-Beam incident on median line just above the pubic symphysis, feet rotated internally from 15 to 20° (for correction of the neck anteversion angle), so that the greater trochanter does not overlap the femoral neck (Figure 1);
- -
- -
-
-The AP pelvic radiograph is the main view in the radiographic series of the hip and of the pelvis; however, their performance with stress is controversial in literature. Conrozier et al(5) and Vanni et al(6) demonstrated that there is only a decrease of the articular space in patients with coxarthrosis, in a comparison with unstressed radiography. However, in patients with normal hips or in cases of initial arthrosis, the use of stressed radiography is not necessary6, 7, 8.
-
-
-
2)Lequesne's false profile(9):
-
-It is a false profile, as it corresponds to the profile of the head and of the proximal femur, and not of the acetabulum (Figure 4);
-
-Patient in orthostatic position, with the back tilted 65° anteriorly in relation to the film chassis, both lower limbs in external rotation, with the affected limb (limb furthest from the chassis) perpendicular to the chassis and the contralateral limb parallel to the chassis (Figure 5);
-
-When properly executed, observe between the femoral heads the distance corresponding to the diameter of a femoral head (Figure 6); and
- -
-
-
-
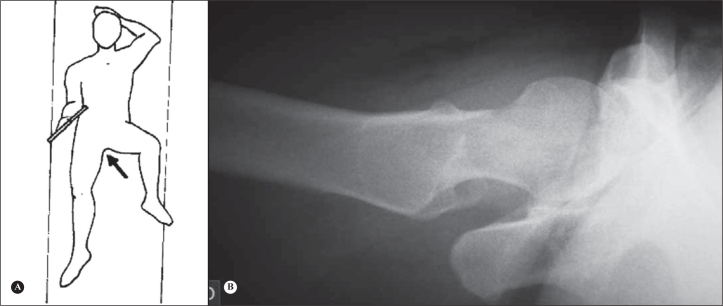
3)Ducroquet's profile:
-
-Patient positioned supine, affected hip with flexion of 90° and abduction of 45° (this radiograph therefore requires good hip mobility) (Figure 7);
-
-Beam centered vertically on the coxofemoral joint;
-
-We can observe the profile of the femoral neck, with good visibility of the anterosuperior region of the femoral head-neck transition, the most frequent site of CAME type femoroacetabular impingement. Besides the neck, we can visualize the acetabular roof and identify the presence of an intra-articular foreign body (Figure 8);
-
-The Dunn view is a similar profile, performed with hip flexion of 45° and abduction of 20°. In this view we can also clearly observe the anterosuperior segment of the femoral head-neck transition; and
-
-It is also possible to measure the alpha angle in both views (angle formed between the longitudinal axis of the femoral neck and a line passing through the center of rotation of the femoral head and through the point of the head-neck junction from where the distance to the center of the head exceeds the radius, i.e., loses sphericity. Its normal value should not exceed 55°)3, 12, 13 (Figure 9).
-
-
-
4)Arcelin's surgical profile or cross table view:
-
-Patient in supine position with flexion of 90 degrees of the contralateral hip;
-
-The X-ray tube should be angled 45° cranially in the horizontal plan, towards the thigh root (does not require mobilization of the affected hip, and is ideal for traumatized patients) (Figure 10); and
-
-Observe the femoral neck in profile and the head-neck transition.
-
-
-
5)Lauenstein pelvic radiograph (frog position):
-
-Patient in supine position with double abduction of the lower limbs; beam incident on median line, just above the pubic symphysis, oriented vertically (Figure 11).
-
-
Figure 1.
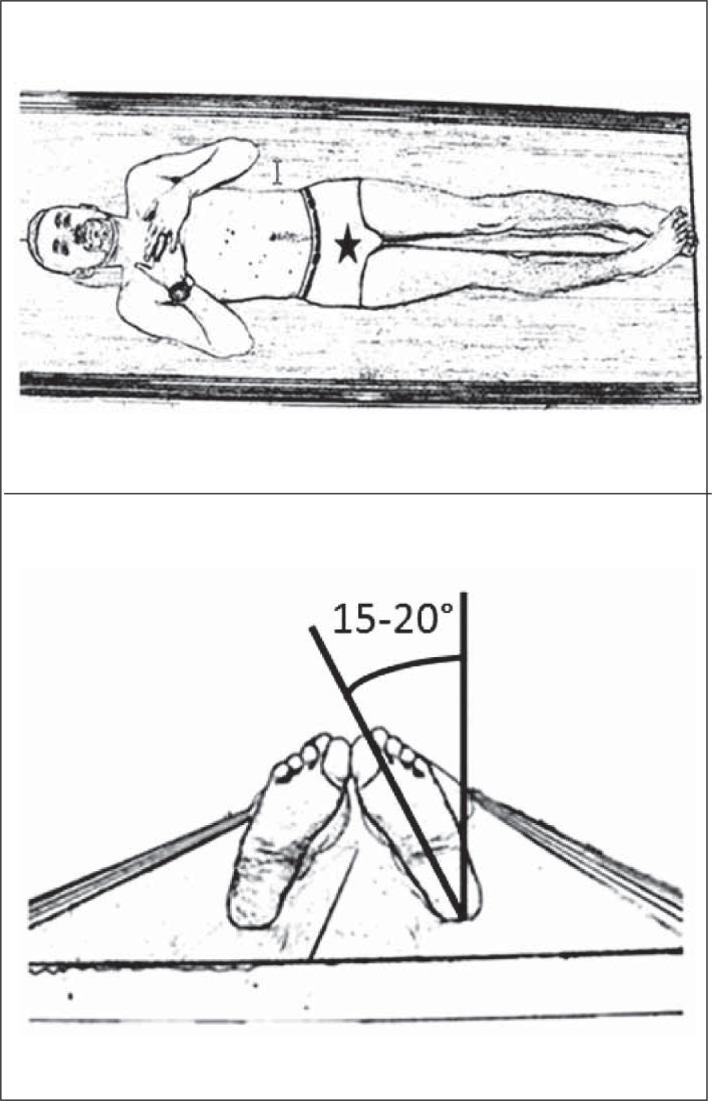
Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph: positioning of patient supine with the lower limbs rotated internally from 15 to 20 degrees; beam incident on the median line, just above the pubic symphysis.
Figure 2.
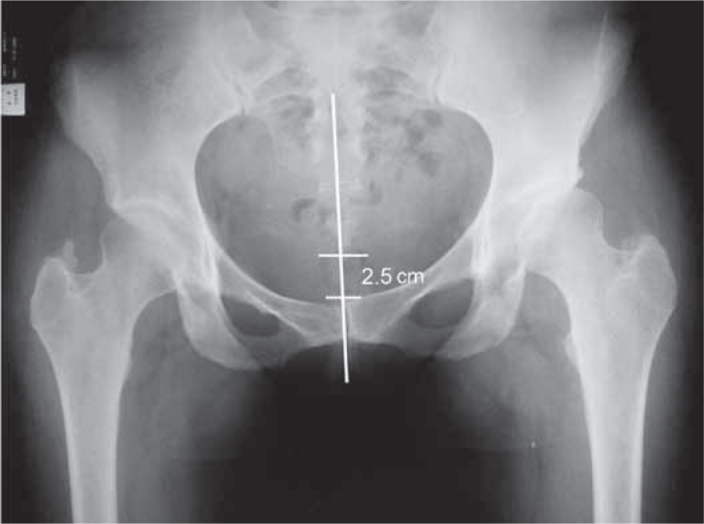
Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph executed with correct technique. Observe the alignment of the coccyx with the pubic symphysis. The coccyx should be located cranially, no further than 2.5cm from the pubic symphysis.
Figure 3.
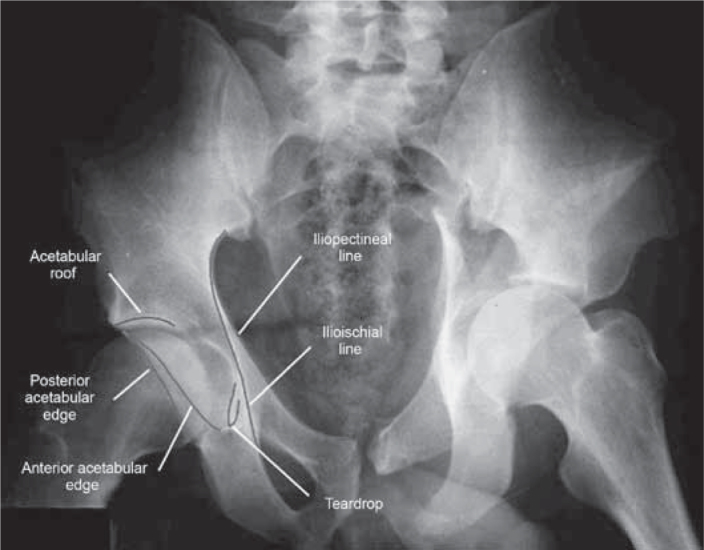
Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph and the main structures identified.
Figure 4.
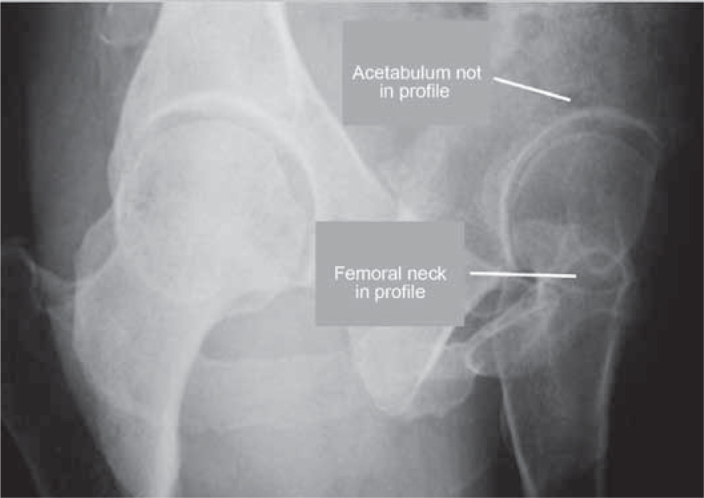
Lequesne's false profile radiograph, called falseprofile as it corresponds to the profile of the head and of the proximal femur, and not of the acetabulum.
Figure 5.
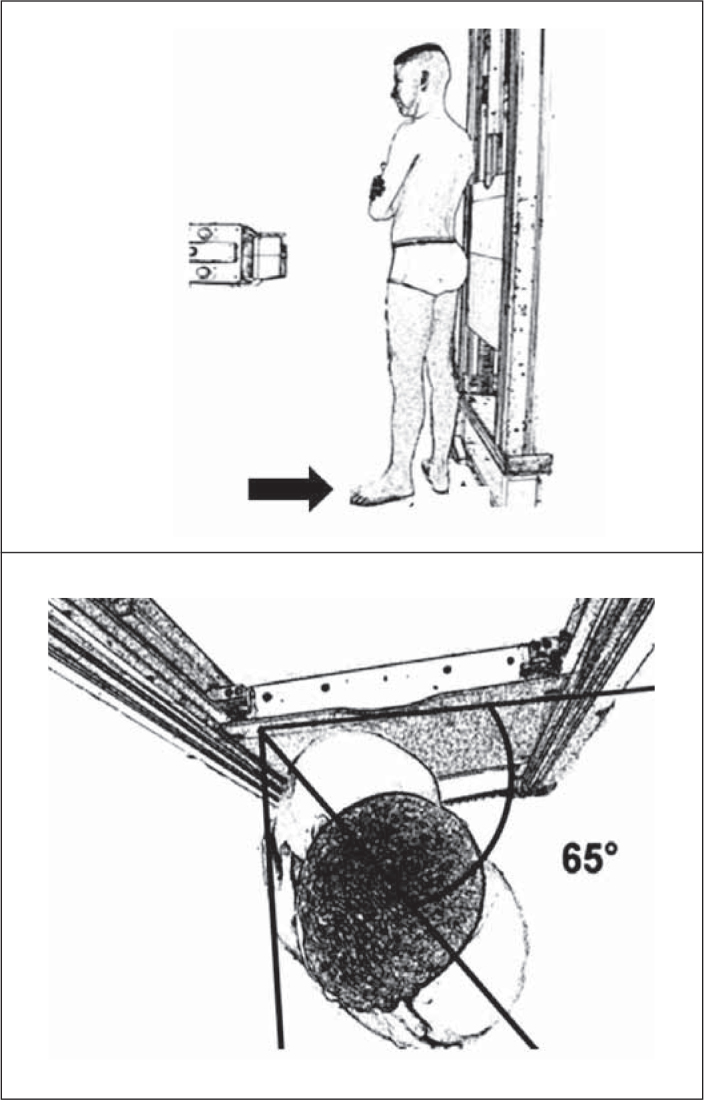
Lequesne's false profile radiograph. Observe patient's positioning with the affected left lower limb further from the chassis. Patient in orthostatic position, with the back tilted 65° anteriorly in relation to the film chassis, both lower limbs in external rotation, with the affected limb perpendicular to the chassis and the contralateral limb parallel to the chassis.
Figure 6.
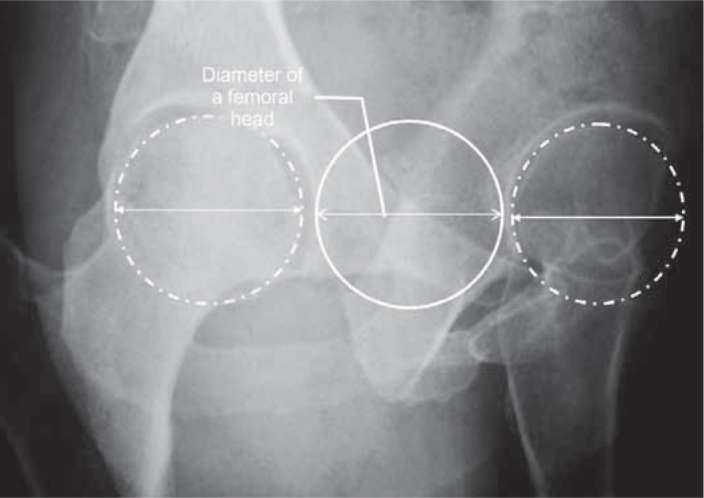
Lequesne's false profile radiograph executed with correct technique. Observe the distance between the two heads corresponding to the diameter of one of them.
Figure 7.
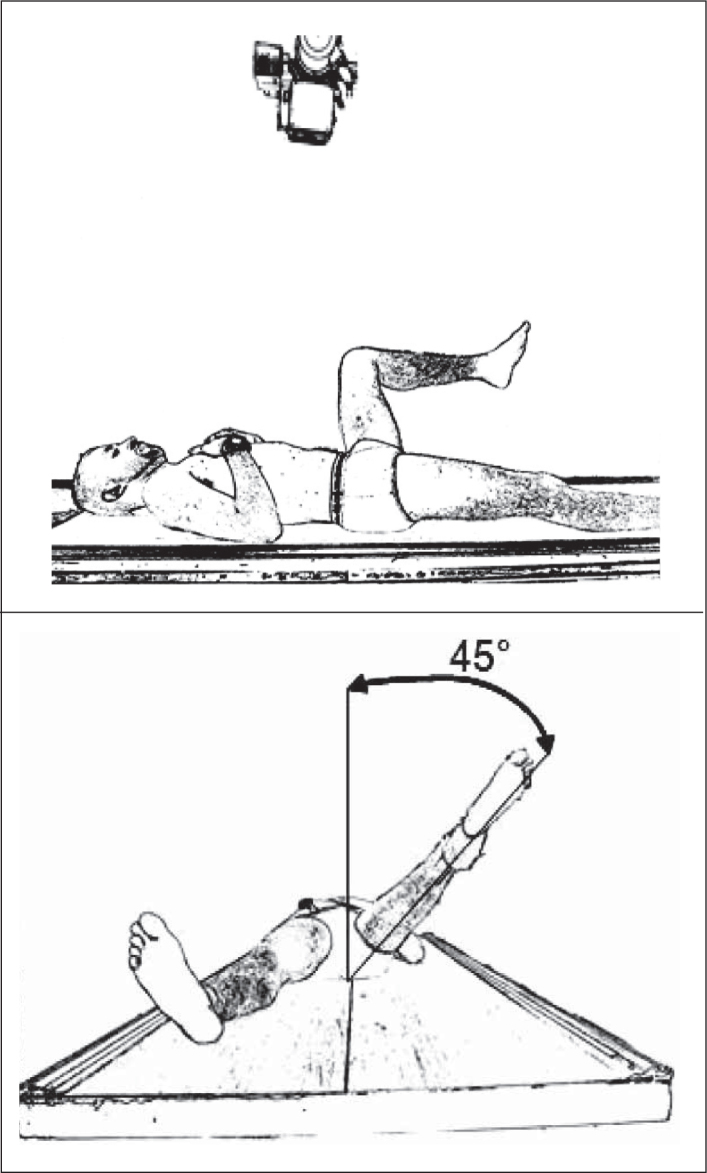
Ducroquet profile view. Patient in supine position, affected hip with flexion of 90° and abduction of 45°. Beam centered vertically on the coxofemoral joint.
Figure 8.
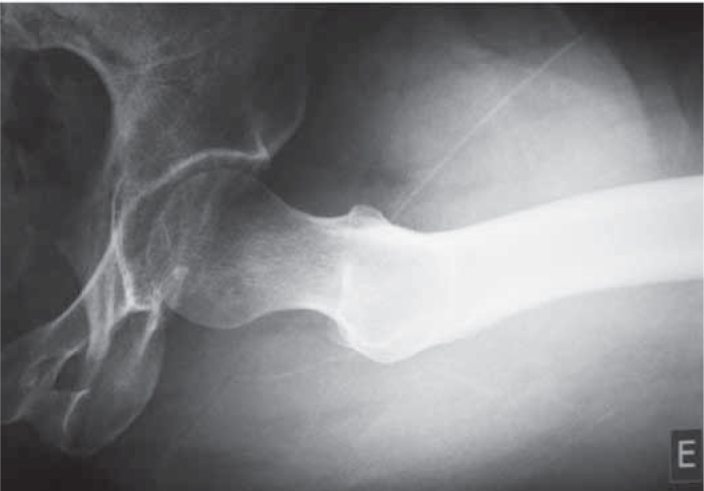
Radiograph in Ducroquet profile view.
Figure 9.
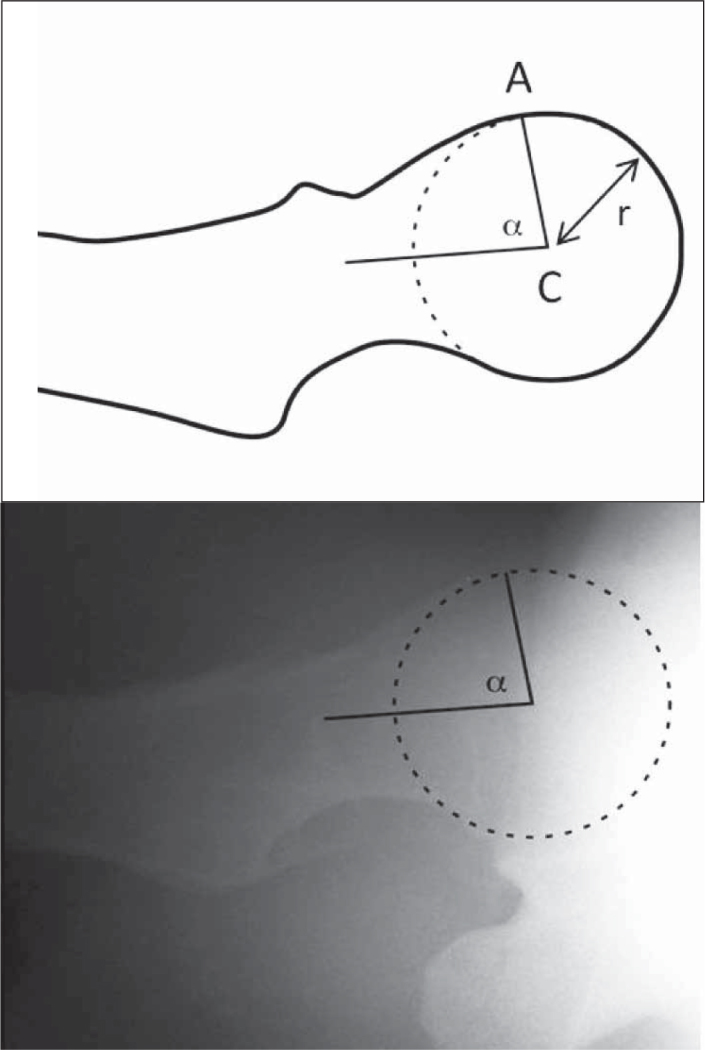
Measurement of the alpha angle (in the Ducroquet profile view: angle formed by the longitudinal axis of the femoral neck and line AC (A – point of loss of sphericity of the head-neck junction, C – center of the head, r – radius of the femoral head).
Figure 10.
A) Surgical profile view. Patient supine, the X-ray tube should be angled 45° cranially in the horizontal plane, towards the thigh root. B) Radiograph in surgical profile view.
Figure 11.
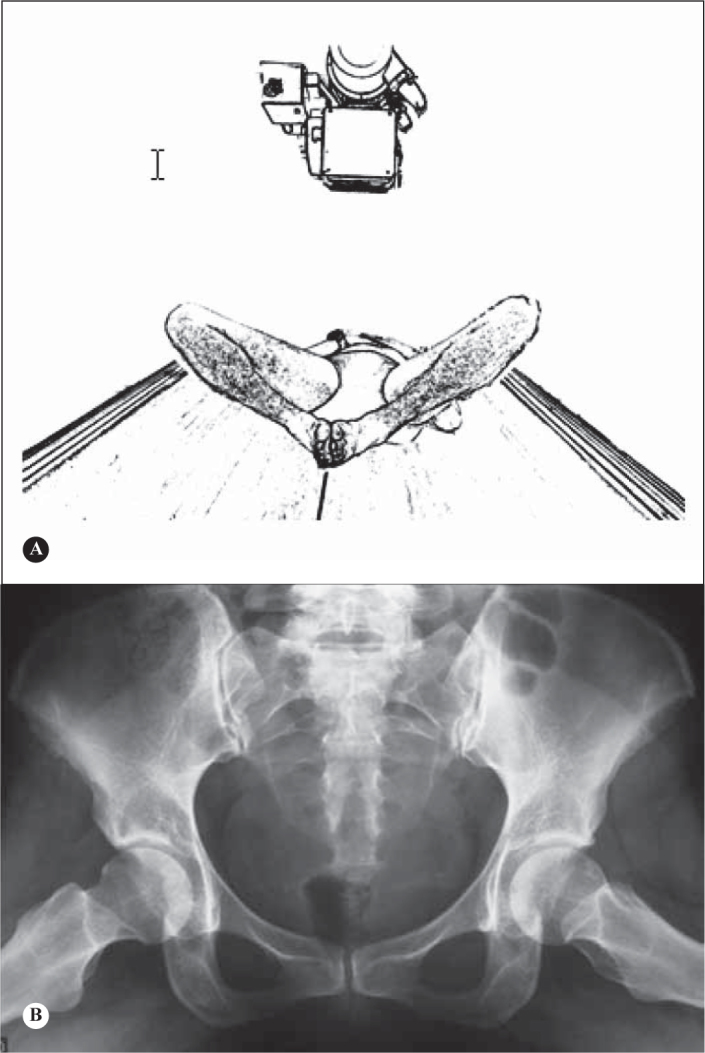
A) Lauenstein pelvic radiograph. Patient in supine position with double abduction of the lower limbs; beam incident on the median line, just below the pubic symphysis, oriented vertically. B) Lauenstein pelvic radiograph.
Given the superimposition of images on the femoral side and on the acetabular side, it is the same as a frontal pelvic radiograph, and its usefulness in adults is questionable.
B) Traumatic series
-
1)Alar(14):
-
2)Protrusive or foraminal view(14):
-
3)Pelvic inlet(17);
-
-Patient in horizontal supine position, with beam incident in the craniocaudal direction with angulation of 60° (Figure 16);
-
-When properly executed, observe the promontory overlapping the anterior cortex of the S1 vertebral body(17);
-
-Indicated mainly for physical trauma (pelvic fracture); and
-
-It allows us to evaluate the integrity of the pelvic ring, as well as anteroposterior and rotational deviations.
-
-
-
4)Pelvic outlet(17):
-
-Patient in horizontal supine position, with beam incident in the caudocranial direction with angulation of 45° (Figure 17);
-
-Technique properly executed when the upper part of the pubic symphysis is at the same level as the second sacral body;
-
-Indicated mainly for physical trauma (pelvic fracture);
-
-It allows us to evaluate sacral fractures (to observe the wedge format when intact and to evaluate the outline of the foramens), as well as fractures of the posterior portion of the iliac wing and of the pubic ramus, sacroiliac disjunction and vertical deviations(17).
-
-
Figure 12.
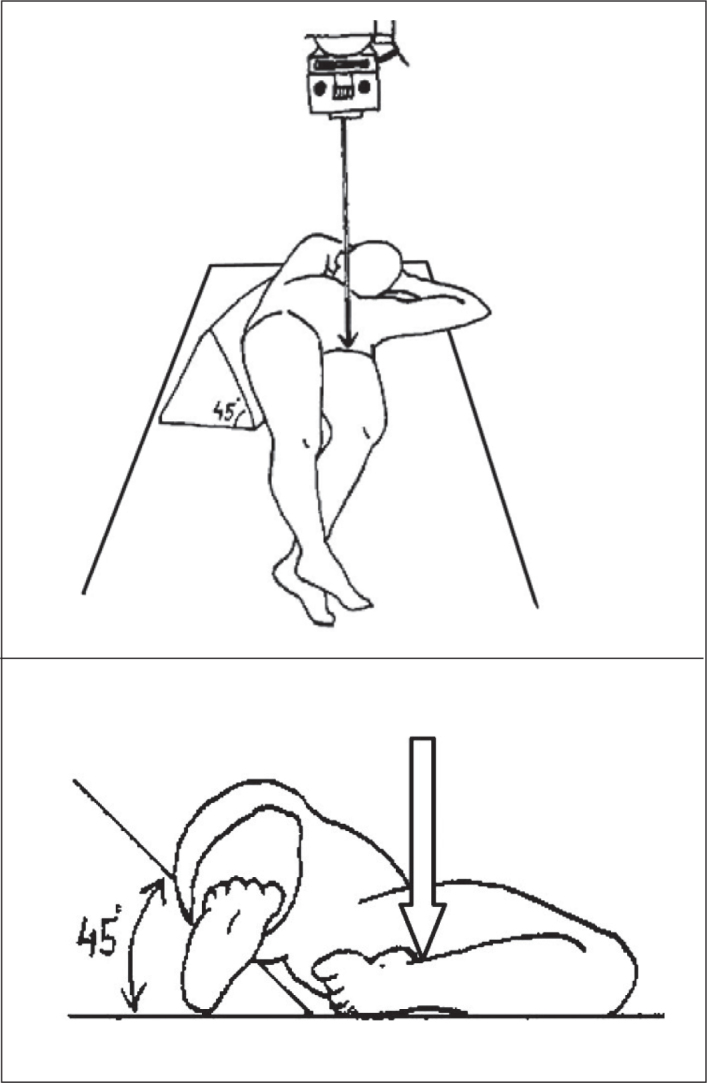
Alar oblique view of pelvis. Patient in supine position with rotation of 45° over the affected side; beam centered vertically on the thigh root.
Figure 13.
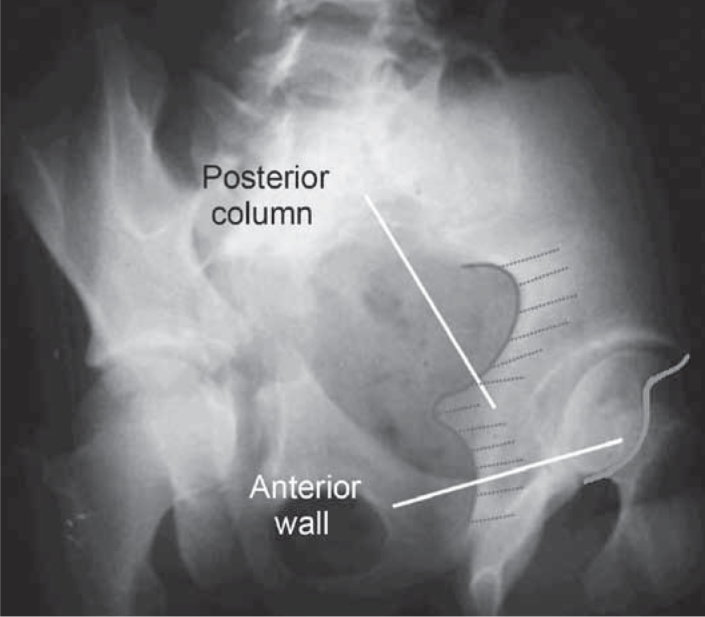
Alar pelvic radiograph of the left hip.
Figure 14.
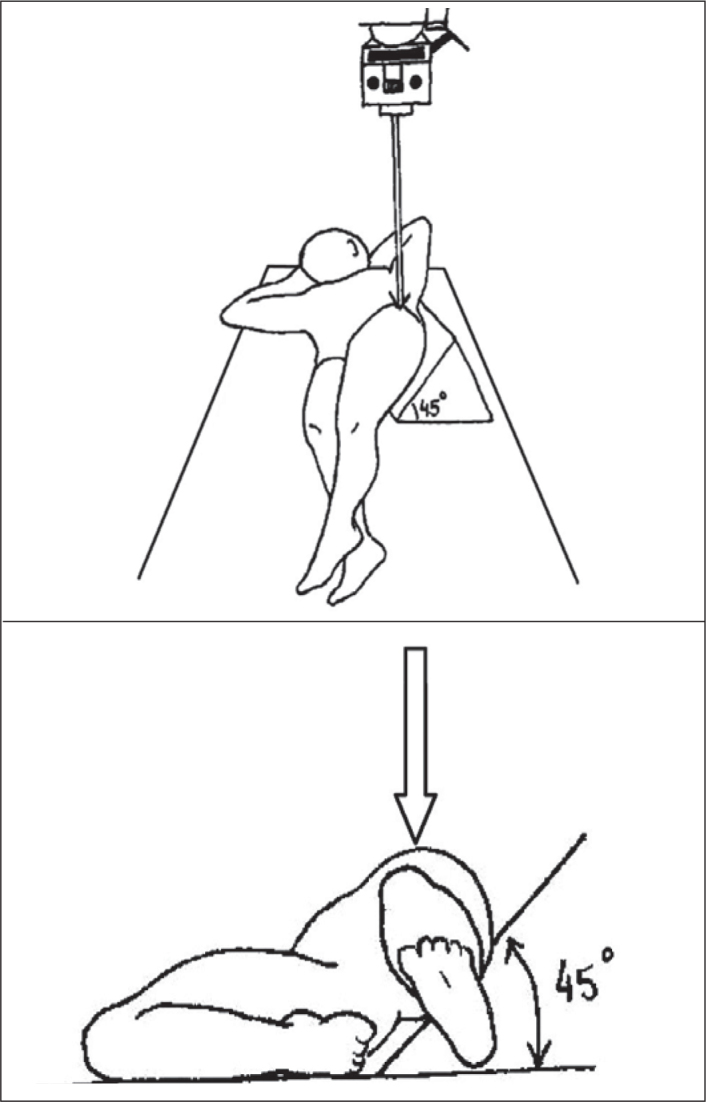
Foraminal oblique view of the pelvis. Patient in supine position with rotation of 45° over the unaffected side; beam centered vertically on the thigh root.
Figure 15.
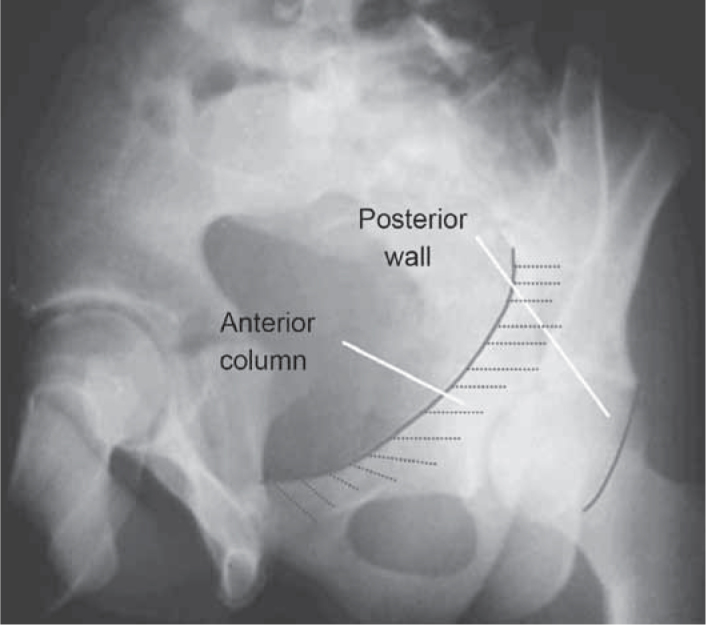
Foraminal pelvic radiograph of the left hip.
Figure 16.
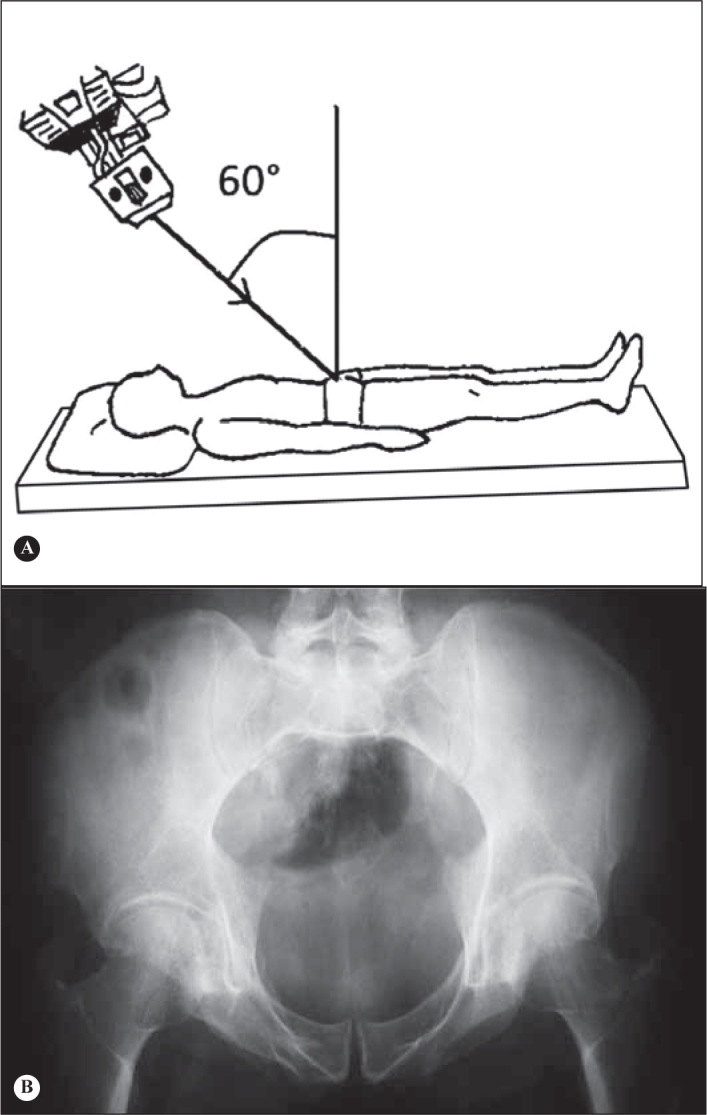
Inlet view of pelvis. A) Patient in horizontal supine position, with beam incident in the craniocaudal direction with angulation of 60°. B) Inlet pelvic radiograph executed with correct technique. Observe the promontory overlapping the anterior cortex of the S1 vertebral body.
Figure 17.
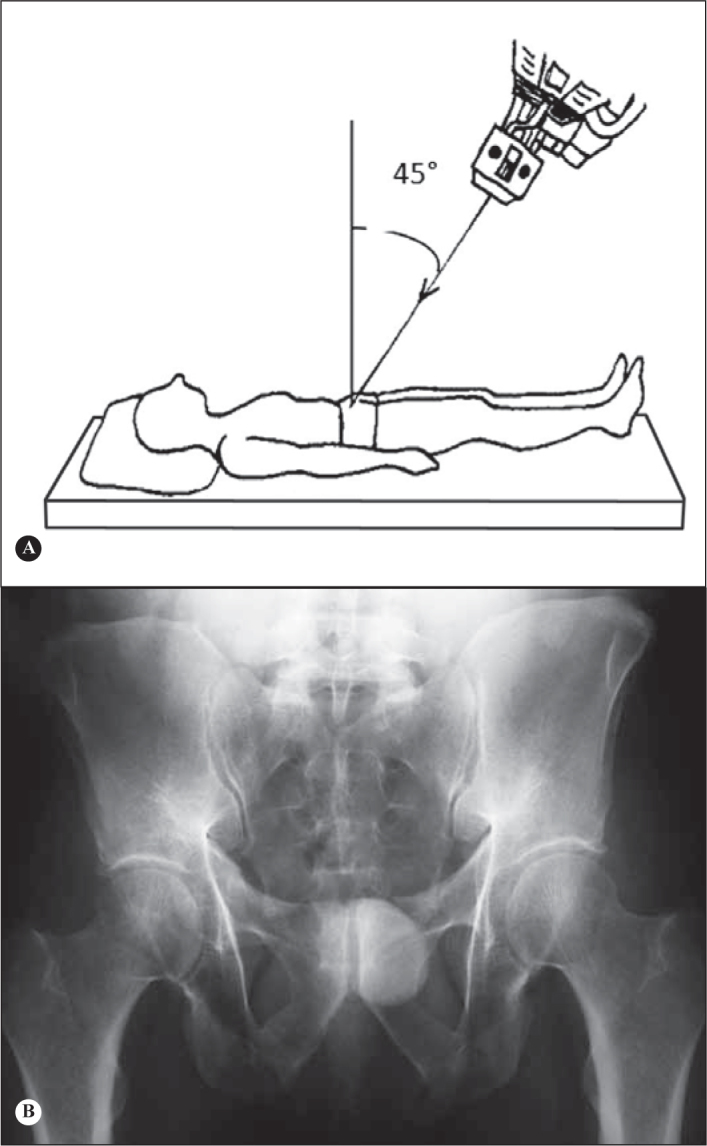
Outlet view of the pelvis. A) Patient in horizontal supine position, with beam incident in the caudocranial direction with angulation of 45°. B) Outlet pelvic radiograph.
C) Suggestions of views by condition
-
1)
Coxarthrosis:
The AP pelvic radiograph is still the main examination, where it is possible to classify the degree of arthrosis.
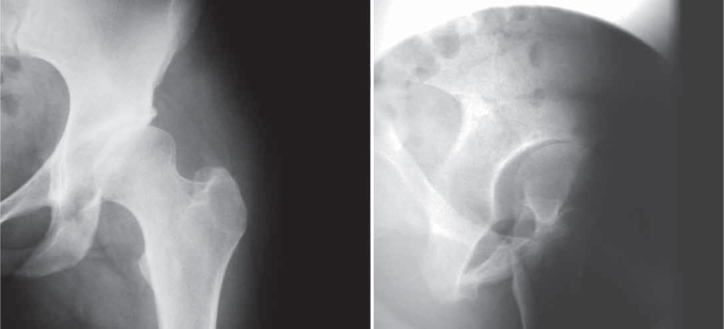
Another very useful view, particularly for initial cases of arthrosis, is Lequesne's false profile, as it evidences anterosuperior and medial impingement, often not clearly observed in the AP view (Figure 18), which can lead to inappropriate indications and surgeries.
-
2)
Alterations in the acetabular morphology and depth:
The AP pelvic radiograph allows us to visualize alterations in the acetabular version, dysplasia, acetabular protrusion and coxa profunda.
Alterations in the acetabular depth should be based on the ilioischial line, and are called coxa profunda when the floor of the acetabulum touches the line and acetabular protrusion when the femoral head surpasses such line (Figure 19).
Lequesne's view is also useful in the evaluation of acetabular dysplasia, measuring the angle of anterior coverage of the femoral head, whose normal value is 25° or higher(2) (Figure 20).
-
3)
Femoroacetabular impingement:
With the AP radiograph we can evaluate the presence of deformity in the proximal portion of the femur, alterations in the acetabular version and dysplasia.
The Lequesne, Ducroquet and Dunn views are used to evaluate the sphericity of the cervicocephalic junction, mainly in the anterolateral portion, as well as the acetabular coverage of the femoral head. Through Lequesne's false profile view we can visualize potential excessive acetabular coverage (Pincer impingement)(18).
As described previously, the Dunn and Ducroquet views are useful to measure the alpha angle, important in the study of CAME impingement.
-
4)Fractures:
-
a)Pelvis – AP, inlet and outlet;
-
b)Acetabulum – AP, alar and foraminal; and
-
c)Fractures of the proximal third of the femur – AP, AP with traction and internal rotation (aiming to predict the degree of instability, and consequently, the surgical technical difficulty), cross table (an advantage in traumatized patients, since the affected hip is not mobilized).
-
a)
Figure 18.
AP view of left hip with slight anterosuperior impingement. Lequesne's false profileview of the same patient with more evident anterosuperior impingement.
Figure 19.
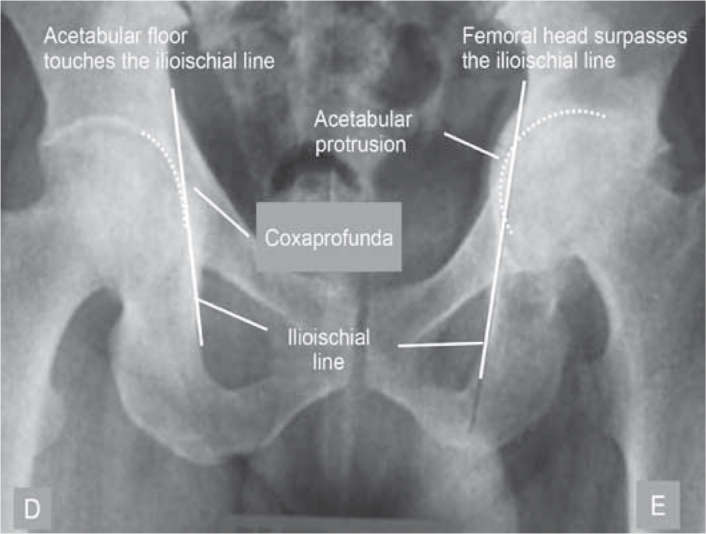
AP pelvic radiograph with coxaprofunda of the right hip and protrusion of the left hip.
Figure 20.
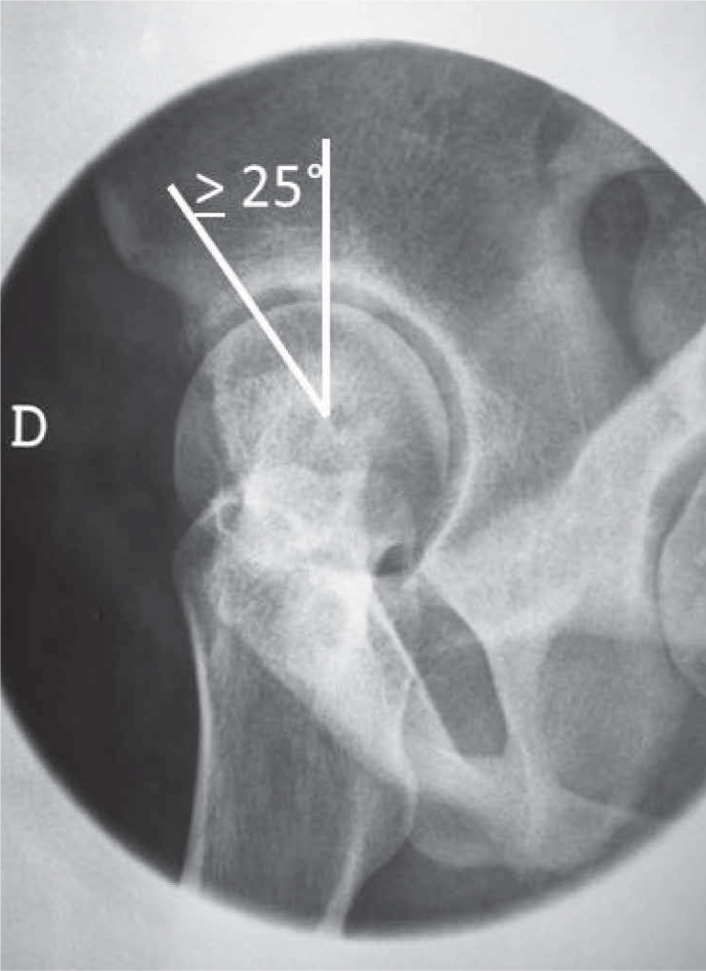
Lequesne's false profile radiograph. Visibility of the angle of anterior coverage of the femoral head. The lines are drawn passing through the center of rotation of the femoral head, with one vertical and the other passing across the more ossified edge of the acetabular portion.
Footnotes
Study conducted at the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology of the School of Medical Sciences, Santa Casa de São Paulo – Director: Prof. Dr. Osmar Avanzi.
The authors declare that there was no conflict of interest in conducting this work
This article is available online in Portuguese and English at the websites:www.rbo.org.brandwww.scielo.br/rbort
REFERENCES
- 1.Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC, Trousdale R, Kim YJ, Beaule PE, Morgan P, Steger-May K, Schoenecker PL, Millis M. Radiographic evaluation of the hip has limited reliability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(3):666–675. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0626-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Godefroy D, Chevrot A, Morvan G, Rousselin B, Sarazin L. [Plain films of pelvis] J Radiol. 2008;89(5 Pt 2):679–690. doi: 10.1016/s0221-0363(08)71503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tannast M, Siebenrock KA, Anderson SE. Femoroacetabular impingement: radiographic diagnosis–what the radiologist should know. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(6):1540–1552. doi: 10.2214/AJR.06.0921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Armbuster TG, Guerra J, Jr, Resnick D, Goergen TG, Feingold ML, Niwayama G, Danzig LA. The adult hip: an anatomic study. Part I: the bony landmarks. Radiology. 1978;128(1):1–10. doi: 10.1148/128.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Conrozier T, Lequesne MG, Tron AM, Mathieu P, Berdah L, Vignon E. The effects of position on the radiographic joint space in osteoarthritis of the hip. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997;5(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/s1063-4584(97)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vanni GF, Stucky JM, Schwarstmann CR. Avaliação radiológica do espaço articular na artrose do quadril: estudo comparativo em decúbito e ortostatismo. Rev Bras Ortop. 2008;43(10):460–464. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Auleley GR, Duche A, Drape JL, Dougados M, Ravaud P. Measurement of joint space width in hip osteoarthritis: influence of joint positioning and radiographic procedure. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001;40(4):414–419. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.4.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vignon E, Conrozier T, Piperno M, Richard S, Carrillon Y, Fantino O. Radiographic assessment of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Recommendations: recommended guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999;7(4):434–436. doi: 10.1053/joca.1999.0235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lequesne MG, Laredo JD. The faux profil (oblique view) of the hip in the standing position. Contribution to the evaluation of osteoarthritis of the adult hip. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lequesne M, Laredo JD. The faux profil view of the hip may detect joint space narrowing when lacking on the anteroposterior radiograph in incipient osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(Suppl):145. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Conrozier T, Bochu M, Gratacos J, Piperno M, Mathieu P, Vignon E. Evaluation of the ‘Lequesne's false profile’ of the hip in patients with hip osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999;7(3):295–300. doi: 10.1053/joca.1998.0203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Meyer DC, Beck M, Ellis T, Ganz R, Leunig M. Comparison of six radiographic projections to assess femoral head/neck asphericity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;445:181–185. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000201168.72388.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Polesello GC, Queiroz MC, Ono NK, Honda EK, Guimarães RP, Ricioli W. Tratamento artroscópico do impacto femoroacetabular. Rev Bras Ortop. 2009;44(3):230–238. doi: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30073-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reilly MC. Fractures of the acetabulum. In: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, editors. Rockwood & Green's fractures in adults. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2006. pp. 1666–1714. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Judet R, Judet J, Letournel E. Fractures of the acetabulum: classification and surgical approaches for open reduction. Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46:1615–1646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Letournel E. Acetabulum fractures: classification and management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(151):81–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Starr AJ, Malekzadeh AS. Fractures of the pelvic ring. In: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, editors. Rockwood & Green's fractures in adults. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2006. pp. 1585–1664. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Crestani MV, Teloken MA, Gusmão PDF. Impacto femoroacetabular: uma das condições precursoras da osteoartrose do quadril. Rev Bras Ortop. 2006;41(8):285–293. [Google Scholar]