Abstract
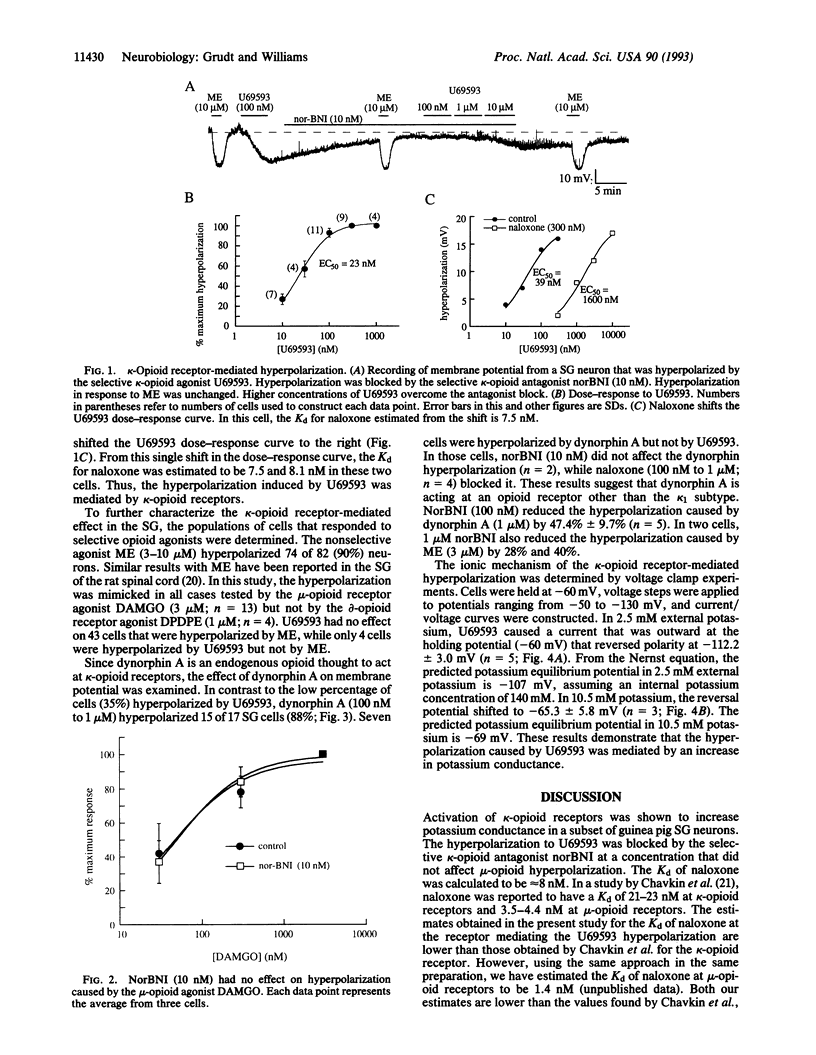
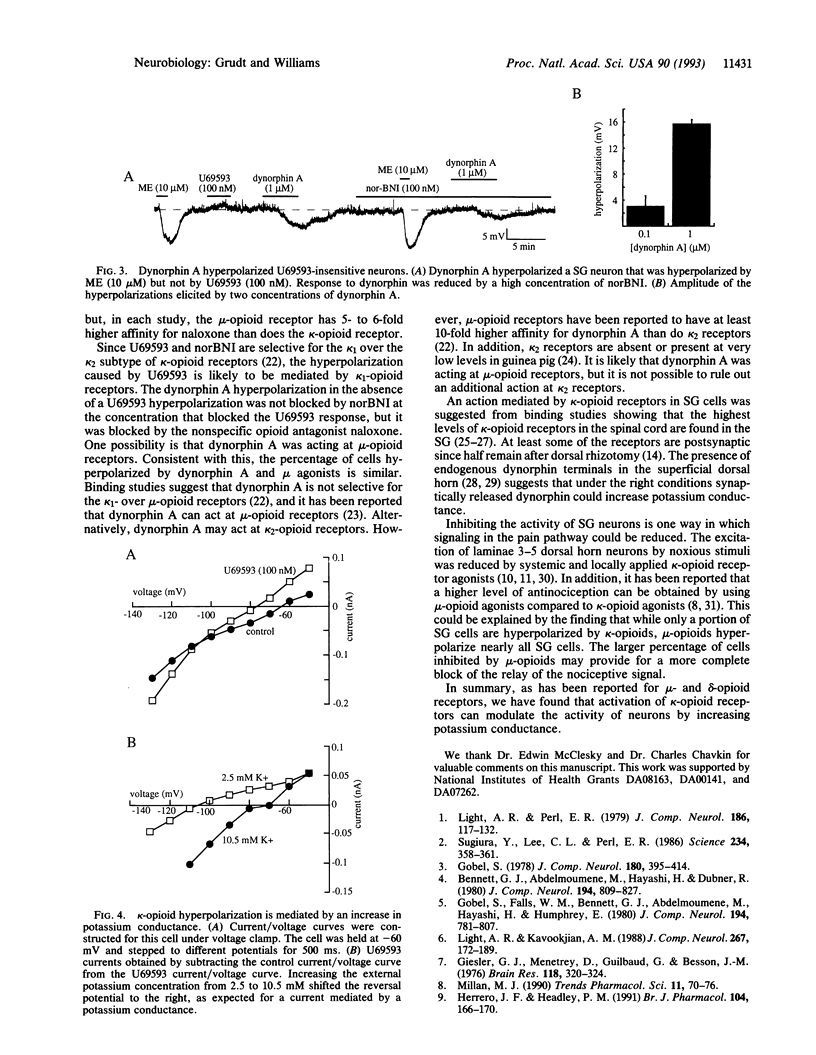
Decrease of calcium conductance induced by opioid agonists has been reported by others for mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. On the other hand, only mu- and delta-opioid receptors have been reported to increase potassium conductance. Intracellular recordings were made from guinea pig substantia gelatinosa neurons in a brain slice. A subset of cells (29 of 83) were hyperpolarized by the kappa-opioid receptor agonist U69593 with an EC50 of 23 nM. The kappa-opioid receptor antagonist norbinaltorphimine (10 nM) blocked the hyperpolarization by U69593 but had no effect on the mu-opioid hyperpolarization present in these cells. Naloxone (300 nM) shifted the U69593 dose-response curve to the right, giving an estimated Kd for naloxone of 7.5 and 8.1 nM measured in two cells. The hyperpolarization caused by U69593 was mediated by a potassium conductance as determined with voltage clamp experiments. This demonstrates, depending on the cell type, that all three major opioid receptors (mu, delta, and kappa) can increase potassium conductance as well as decrease calcium conductance.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett G. J., Abdelmoumene M., Hayashi H., Dubner R. Physiology and morphology of substantia gelatinosa neurons intracellularly stained with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Dec 15;194(4):809–827. doi: 10.1002/cne.901940407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besse D., Lombard M. C., Zajac J. M., Roques B. P., Besson J. M. Pre- and postsynaptic distribution of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in the superficial layers of the cervical dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 25;521(1-2):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91519-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., Henriksen S. J., Siggins G. R., Bloom F. E. Selective inactivation of opioid receptors in rat hippocampus demonstrates that dynorphin-A and -B may act on mu-receptors in the CA1 region. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 8;331(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91565-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L., Basbaum A. I. Multiple opioid peptides and the modulation of pain: immunohistochemical analysis of dynorphin and enkephalin in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis and spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 22;240(4):331–348. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. W., Parsons C. G., Headley P. M. Effects of intravenous mu and kappa opioid receptor agonists on sensory responses of convergent neurones in the dorsal horn of spinalized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1230–1236. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleetwood-Walker S. M., Hope P. J., Mitchell R., el-Yassir N., Molony V. The influence of opioid receptor subtypes on the processing of nociceptive inputs in the spinal dorsal horn of the cat. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90766-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesler G. J., Menétrey D., Guilbaud G., Besson J. M. Lumbar cord neurons at the origin of the spinothalamic tract in the rat. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 17;118(2):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90718-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobel S., Falls W. M., Bennett G. J., Abdelmoumene M., Hayashi H., Humphrey E. An EM analysis of the synaptic connections of horseradish peroxidase-filled stalked cells and islet cells in the substantia gelatinosa of adult cat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Dec 15;194(4):781–807. doi: 10.1002/cne.901940406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L. Dynorphin A selectively reduces a large transient (N-type) calcium current of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero J. F., Headley P. M. The effects of sham and full spinalization on the systemic potency of mu- and kappa-opioids on spinal nociceptive reflexes in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):166–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope P. J., Fleetwood-Walker S. M., Mitchell R. Distinct antinociceptive actions mediated by different opioid receptors in the region of lamina I and laminae III-V of the dorsal horn of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light A. R., Kavookjian A. M. Morphology and ultrastructure of physiologically identified substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) neurons with axons that terminate in deeper dorsal horn laminae (III-V). J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jan 8;267(2):172–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.902670203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light A. R., Perl E. R. Reexamination of the dorsal root projection to the spinal dorsal horn including observations on the differential termination of coarse and fine fibers. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jul 15;186(2):117–131. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Werz M. A. Dynorphin A decreases voltage-dependent calcium conductance of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:237–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Khachaturian H., Lewis M. E., Akil H., Watson S. J. Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A. Opioids increase potassium conductance in submucous neurones of guinea-pig caecum by activating delta-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J. Kappa-opioid receptor-mediated antinociception in the rat. I. Comparative actions of mu- and kappa-opioids against noxious thermal, pressure and electrical stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J. Kappa-opioid receptors and analgesia. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Herz A. Distinct distribution of opioid receptor types in rat lumbar spinal cord. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;336(2):240–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00165811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nock B., Giordano A. L., Cicero T. J., O'Connor L. H. Affinity of drugs and peptides for U-69,593-sensitive and -insensitive kappa opiate binding sites: the U-69,593-insensitive site appears to be the beta endorphin-specific epsilon receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Aug;254(2):412–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif N. A., Hunter J. C., Hill R. G., Hughes J. [125I]dynorphin(1-8) produces a similar pattern of kappa-opioid receptor labelling to [3H]dynorphin(1-8) and [3H]etorphine in guinea pig brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Apr 12;86(3):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura Y., Lee C. L., Perl E. R. Central projections of identified, unmyelinated (C) afferent fibers innervating mammalian skin. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.3764416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Ho B. Y., Naeseth J. S., Portoghese P. S. Nor-binaltorphimine, a highly selective kappa-opioid antagonist in analgesic and receptor binding assays. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jul;246(1):255–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Hökfelt T., Christensson I., Terenius L. Dynorphin-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Nov 30;33(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Christie M. J., North R. A., Roques B. P. Potentiation of enkephalin action by peptidase inhibitors in rat locus ceruleus in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):397–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A. Opiate-receptor interactions on single locus coeruleus neurones. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):489–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpey T. L., Chavkin C. Opioids activate both an inward rectifier and a novel voltage-gated potassium conductance in the hippocampal formation. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., North R. A. Substantia gelatinosa neurones hyperpolarized in vitro by enkephalin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):529–530. doi: 10.1038/305529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Eghbali M., Olive D., Unterwald E. M., Tempel A. Characterization and visualization of rat and guinea pig brain kappa opioid receptors: evidence for kappa 1 and kappa 2 opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



