Abstract
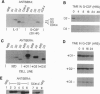
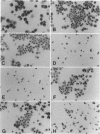
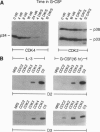
Growth factor-induced signals govern the expression of three D-type cyclins, which, in turn, function as regulatory subunits of cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) to control cell cycle transitions during the late G1 interval. 32D myeloid cells, which self-renew as uncommitted precursors in interleukin 3 (IL-3), express cyclins D2 and D3 (but not D1) in complexes with cdk4 and cdk2. When transferred to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), 32D cells stop dividing and terminally differentiate to mature neutrophils. Cyclin D and cdk4 expression ceased as cells underwent growth arrest in G-CSF, but cdk2 levels were sustained. 32D cells engineered to ectopically express D-type cyclins exhibited contracted G1 intervals with a compensatory lengthening of S phase but remained IL-3 dependent for cell growth; those overexpressing cyclins D2 and D3 (but not D1) were unable to differentiate and died in G-CSF. Cyclin D2 mutants, which cannot efficiently bind to, or functionally interact with, the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) or its relatives (p107) did not block differentiation. Conversely, the introduction of a catalytically inactive cdk4 mutant into cells overexpressing cyclin D2 restored their G-CSF response. The persistence of cdk2 and its predilection to functionally interact with cyclins D2 and D3 rather than D1 might explain the specificity of the differentiation blockade.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. J., Gonda M. A., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J. Subcellular localization of glycoproteins encoded by the viral oncogene v-fms. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):730–741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.730-741.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Maandag E. R., van Roon M., van der Lugt N. M., van der Valk M., Hooper M. L., Berns A., te Riele H. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):328–330. doi: 10.1038/359328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy S. F., Hinds P. W., Louie K., Reed S. I., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Physical interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with human D cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):499–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90137-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J. Ligand-induced tyrosine kinase activity of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor in a murine macrophage cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1795–1799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Schneider J. W., Condorelli G., Kaushal S., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Interaction of myogenic factors and the retinoblastoma protein mediates muscle cell commitment and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Sherr C. J. Human colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) receptor confers CSF-1 responsiveness to interleukin-3-dependent 32DC13 mouse myeloid cells and abrogates differentiation in response to granulocyte CSF. Blood. 1990 May 1;75(9):1780–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger A., Anderson S. M. The v-src oncogene blocks the differentiation of a murine myeloid progenitor cell line and induces a tumorigenic phenotype. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammie G. A., Fantl V., Smith R., Schuuring E., Brookes S., Michalides R., Dickson C., Arnold A., Peters G. D11S287, a putative oncogene on chromosome 11q13, is amplified and expressed in squamous cell and mammary carcinomas and linked to BCL-1. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Chang C. Y., Hu N., Wang Y. C., Lai C. C., Herrup K., Lee W. H., Bradley A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):288–294. doi: 10.1038/359288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Novel mammalian cyclins (CYL genes) expressed during G1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:69–74. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Kreider B. L., Valtieri M., Naso G., Shirsat N., Venturelli D., Reddy E. P., Rovera G. Alteration of growth and differentiation factors response by Kirsten and Harvey sarcoma viruses in the IL-3-dependent murine hematopoietic cell line 32D C13(G). Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parganas E., Matsugi T., Ihle J. N. Expression of the Evi-1 zinc finger gene in 32Dc13 myeloid cells blocks granulocytic differentiation in response to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Roberts J. M. Cyclin-dependent regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1908–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.8384376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel G., Kreider B., Rovera G., Reddy E. P. v-myb blocks granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced myeloid cell differentiation but not proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2269–2276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C. L., Wong E., Petty E. M., Bale A. E., Tsujimoto Y., Harris N. L., Arnold A. PRAD1, a candidate BCL1 oncogene: mapping and expression in centrocytic lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9638–9642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Valtieri M., Mavilio F., Reddy E. P. Effect of Abelson murine leukemia virus on granulocytic differentiation and interleukin-3 dependence of a murine progenitor cell line. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtieri M., Tweardy D. J., Caracciolo D., Johnson K., Mavilio F., Altmann S., Santoli D., Rovera G. Cytokine-dependent granulocytic differentiation. Regulation of proliferative and differentiative responses in a murine progenitor cell line. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers D. A., Harvey R. C., Faust J. B., Melnyk O., Carey K., Meeker T. C. Characterization of a candidate bcl-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4846–4853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]