Figure 1.
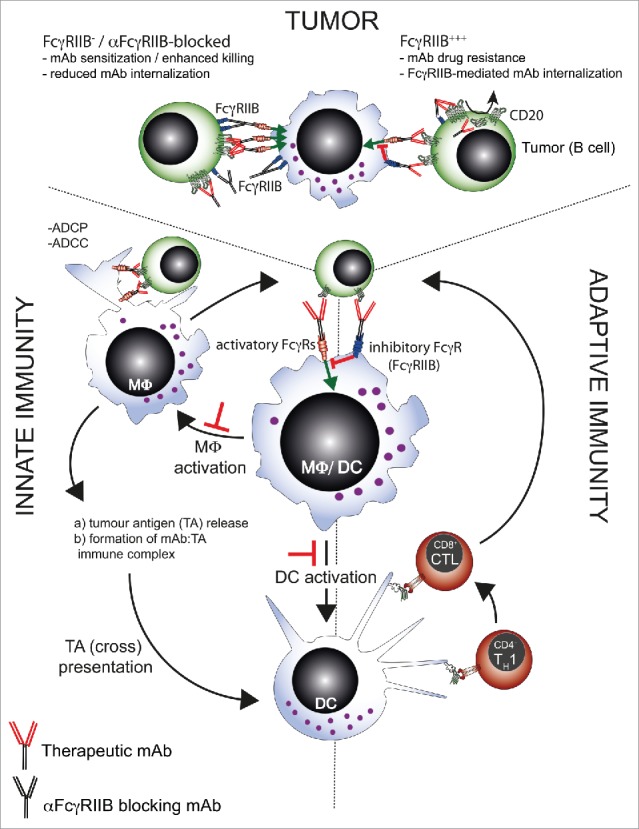
Schematic diagram demonstrating how FcγRIIB can regulate innate and adaptive immunity to influence immunotherapy. FcγRIIB can regulate mAb-mediated immunotherapy at multiple points indicated by the red ┴ symbol. Within the tumor, FcγRIIB can accelerate the internalization of direct targeting mAbs such as rituximab, leading to drug resistance. FcγRIIB can also transmit negative signals to the innate immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, reducing tumor destruction, antigen release and uptake, presentation and activation of adaptive immunity. Targeting of FcγRIIB using anti-FcγRIIB mAbs may therefore potentially intersect at several points o boost mAb-mediated immunotherapy.
