Abstract
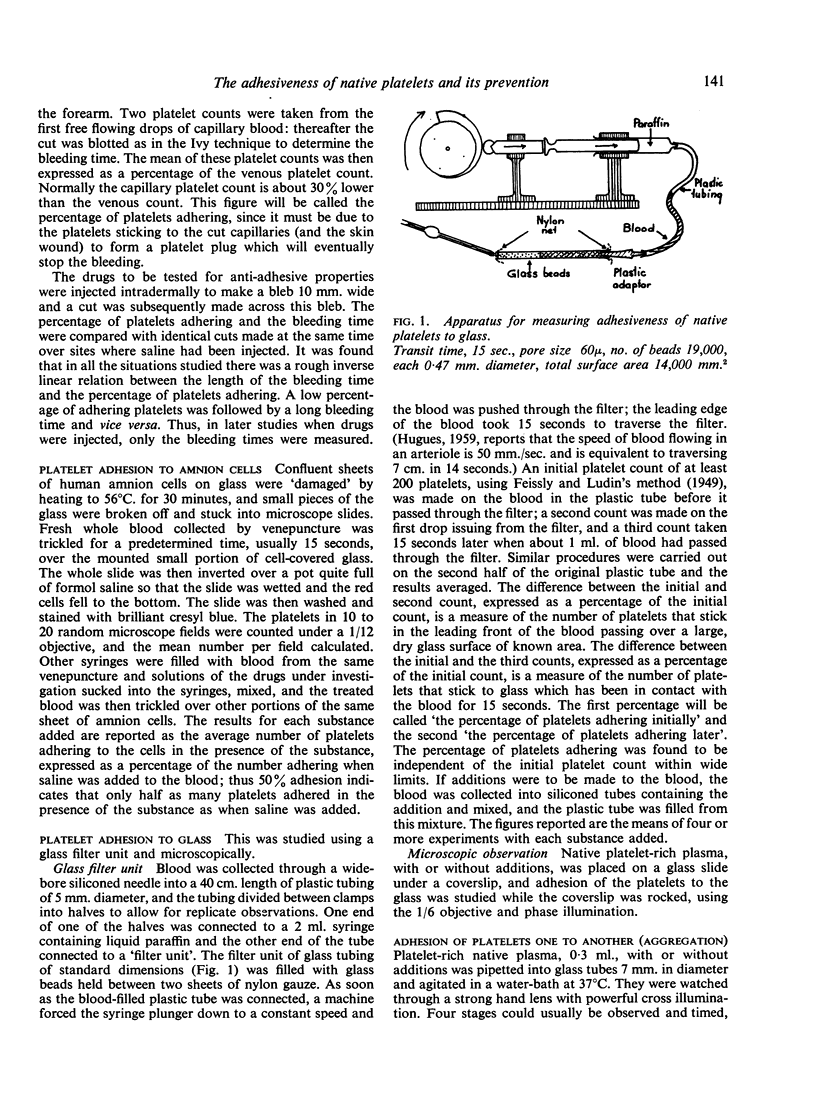
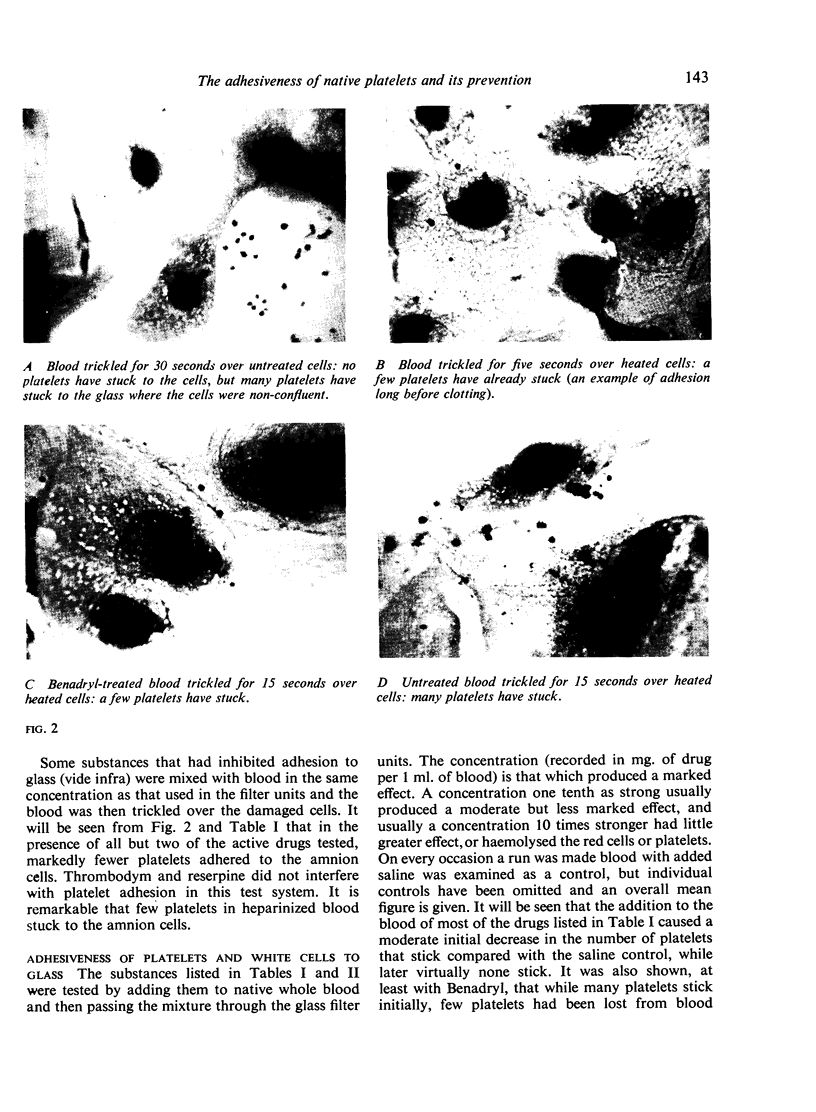
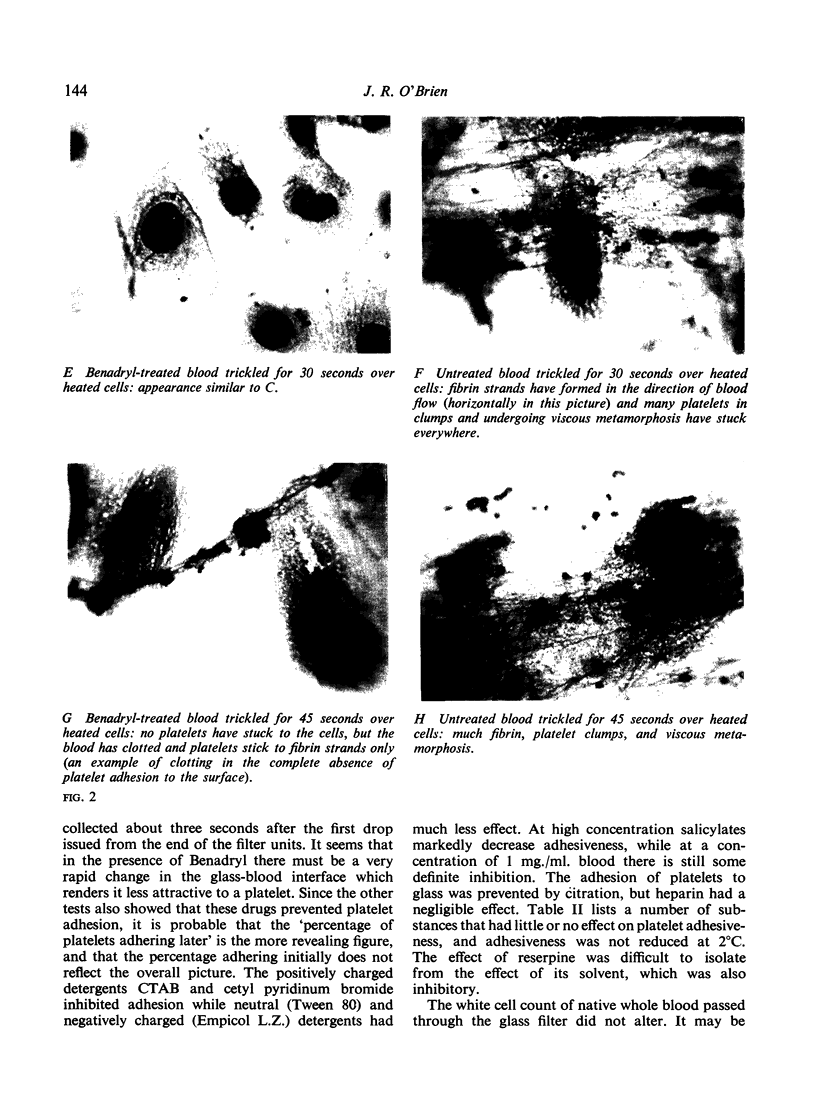
The following methods were used to measure the adhesion to various surfaces of platelets in whole blood or plasma: 1, two measurements gave an estimate in vivo of platelet adhesion to cut human capillaries; 2, platelets adhering to damaged cells in vitro were counted directly; 3, a highly reproducible method for estimating platelet adhesion to glass was devised; 4, the manner in which platelets adhere to each other (aggregation) was also studied.
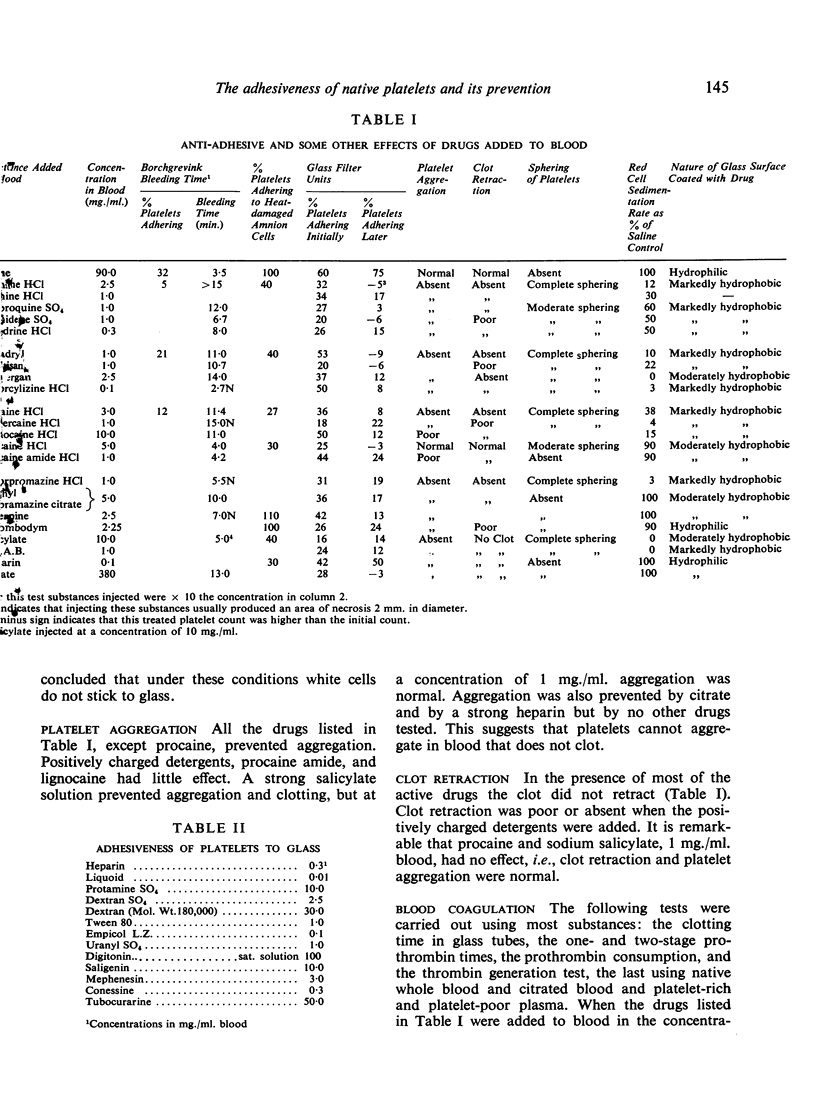
Platelet adhesion to all these surfaces was found to be dependent upon calcium and independent of all clotting factors except that platelet aggregation is probably dependent upon thrombin. A number of drugs—mostly antimalarials, antihistaminics, and local anaesthetics—in suitable concentration inhibited adhesion. They probably form a fixed, orientated layer on glass and possibly on cells and make these surfaces unattractive to a platelet. They also stick reversibly to live cells (including platelets) altering their permeability, and they may make platelets less adhesive. Consequently the possibility of using antiadhesive drugs therapeutically to inhibit thrombus formation was considered.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM A. D., PETHICA B. A., SEAMAN G. V. The charged groups at the interface of some blood cells. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):12–19. doi: 10.1042/bj0690012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOUNAMEAUX Y. Antihistaminiques de synthèse et rétraction du caillot. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1958 Aug 1;116(1-2):252–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEISSLY R., LUDIN H. Microscopie par contrastes de phases; applications à l'hématologie. Rev Hematol. 1949;4(3):481–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT P. F., BORCHGREVINK C. F., IVERSON O. H., STORMORKEN H. The effect of heparin on the bleeding time. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Jun 15;4:389–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUDAH J. D. Phosphoproteins and mitochondrial and cell water. Nature. 1960 Aug 6;187:506–507. doi: 10.1038/187506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE W. F., MARSHALL J. Experience with human amnion cell culture as a routine diagnostic method in a bacteriological laboratory. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1957 Oct;16:198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUESCHER E. F. [Biochemical properties and physiological significance of the blood platelets]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1959 Oct 3;89:1021–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN J. R. The bleeding time in normal and abnormal subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1951 Aug;4(3):272–285. doi: 10.1136/jcp.4.3.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. Local anaesthetics. VI. Relation between blocking potency and penetration of a monomolecular layer of lipoids from nerves. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1954;10(4):325–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1954.tb01349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]