Abstract
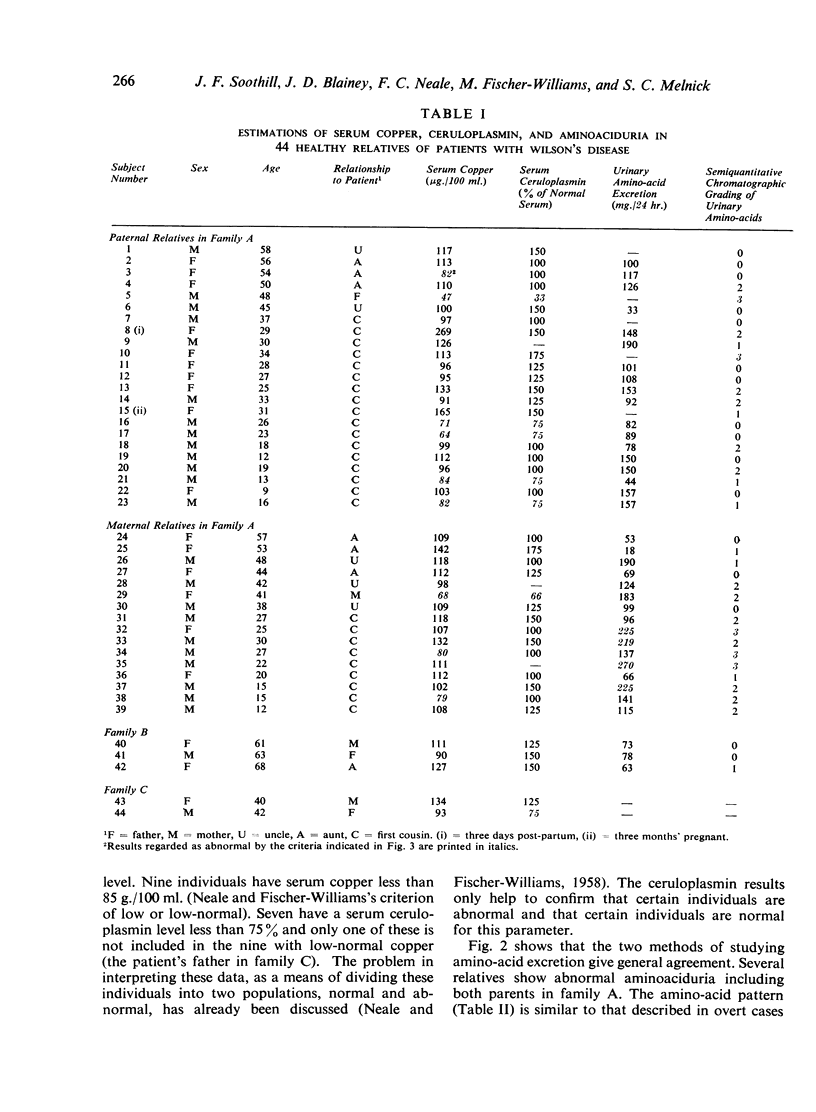
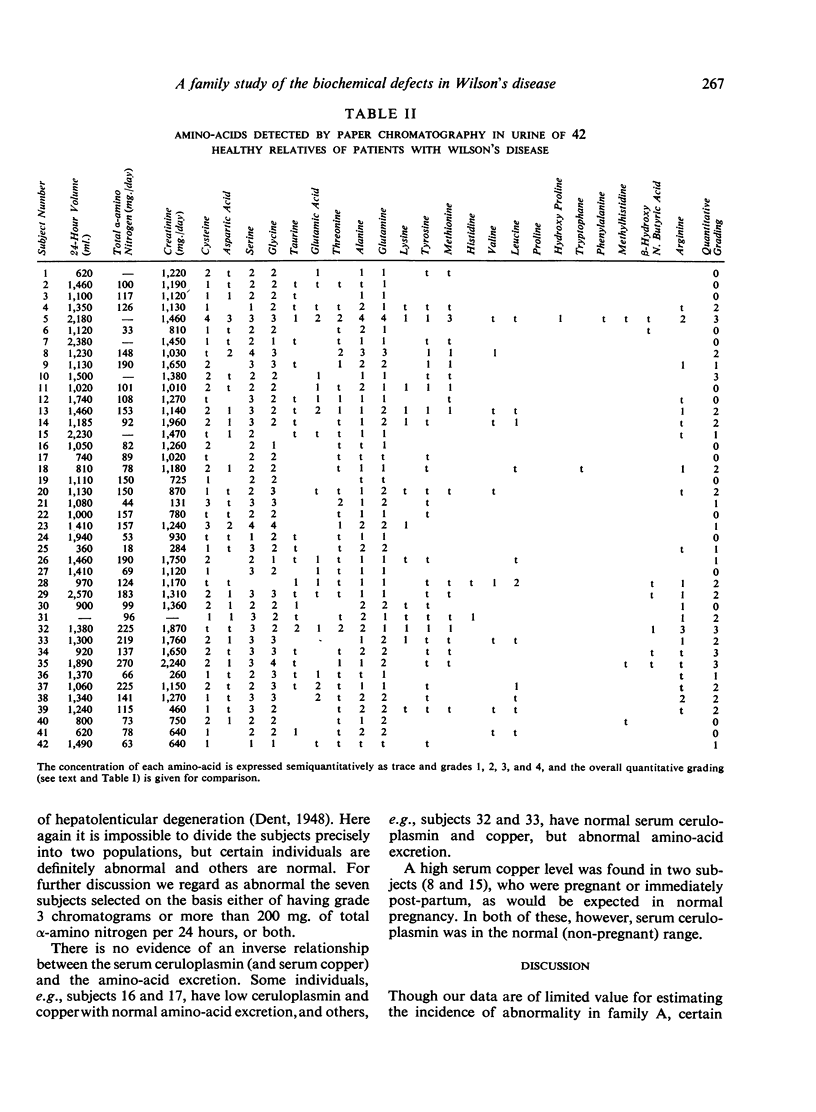
Estimations of serum copper, serum ceruloplasmin (immunochemical), and urinary amino-acids excretion (quantitative and chromatographic) in 44 healthy relatives of patients with Wilson's disease (39 from one family) are reported. Each technique revealed some abnormal individuals. Good agreement was obtained between the serum copper and serum ceruloplasmin estimations and between the quantitative and chromatographic estimations of amino-acid excretion. Some individuals were abnormal to one or other of the pairs of tests only.
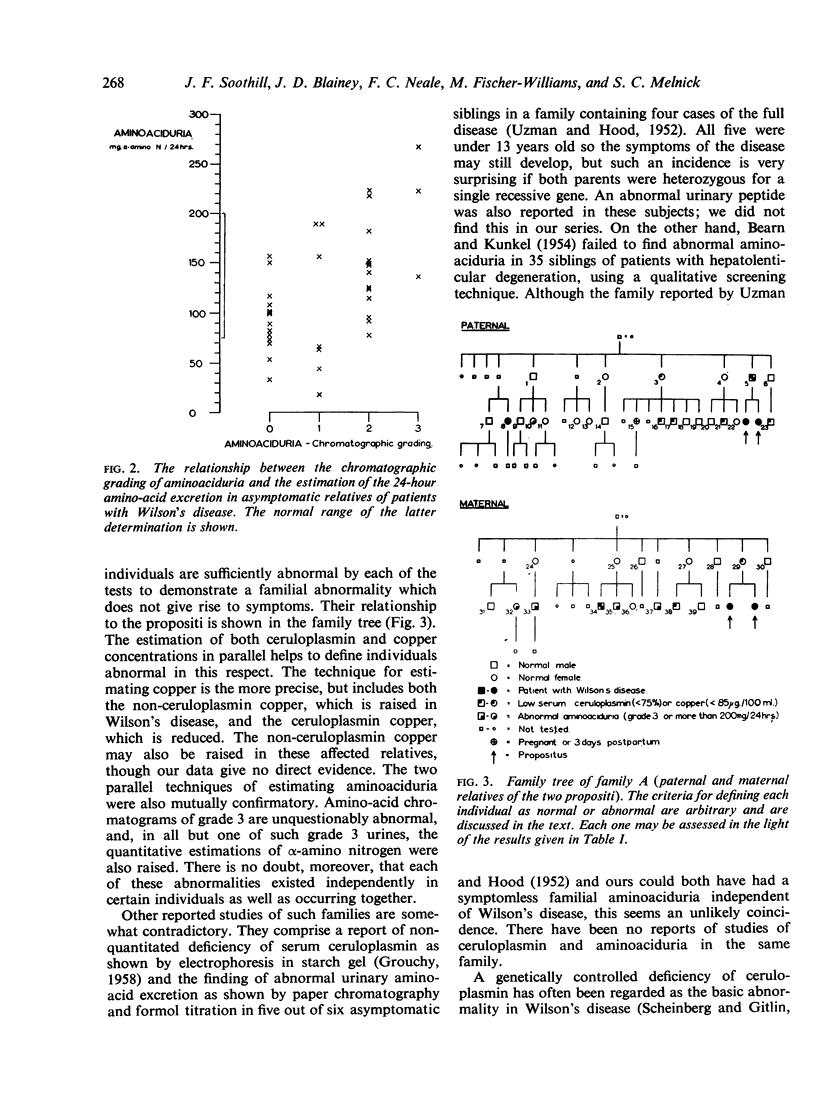
These results cast doubt on the hypothesis that the symptoms of Wilson's disease are secondary to a quantitative (or qualitative) abnormality of ceruloplasmin. They also suggest that the mode of inheritance of the biochemical defects may be more complicated than that of a simple recessive mutant gene.
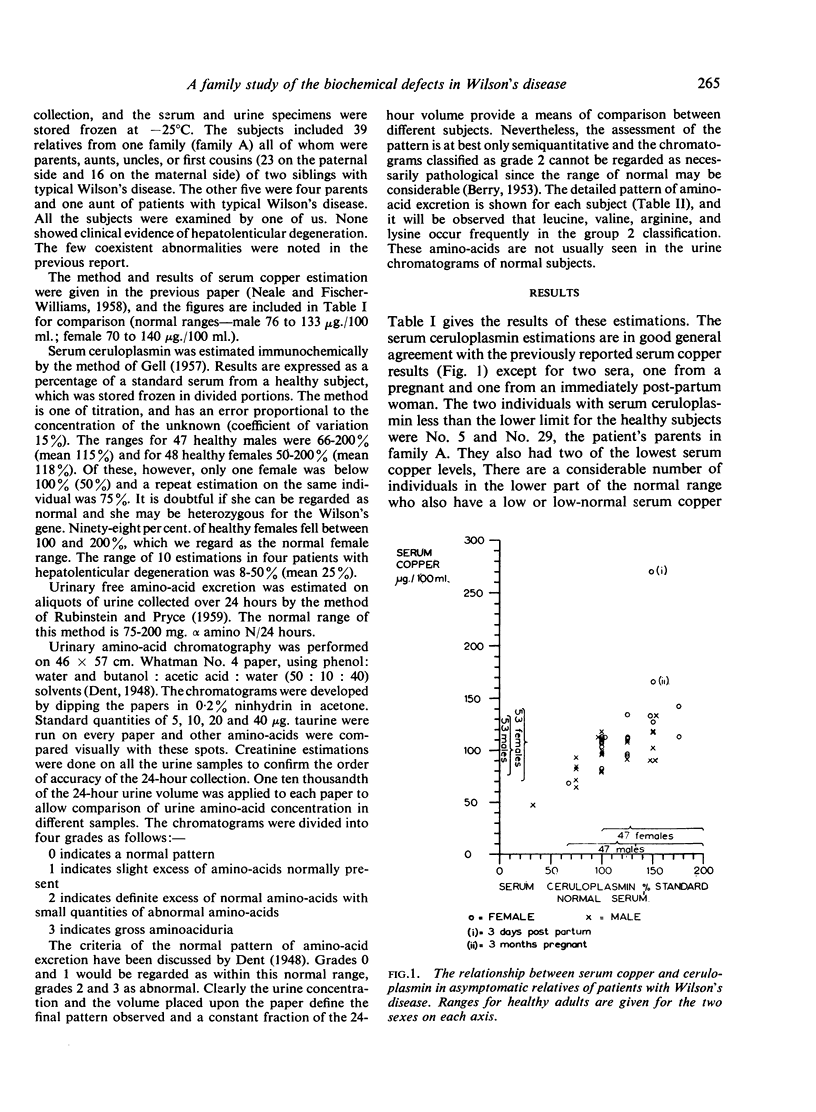
Two of the relatives (one pregnant and one immediately post-partum) had a high serum copper level, as is expected in pregnancy, but normal serum ceruloplasmin. This suggests that the mechanism of control of the serum ceruloplasmin concentration may, normally, depend on the serum copper concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARN A. G. Genetic and biochemical aspects of Wilson's disease. Am J Med. 1953 Oct;15(4):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARN A. G., KUNKEL H. G. Abnormalities of copper metabolism in Wilson's disease and their relationship to the aminoaciduria. J Clin Invest. 1954 Mar;33(3):400–409. doi: 10.1172/JCI102912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY H. K. Variations in urinary excretion patterns in a Texas population. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1953 Dec;11(4):559–575. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330110405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BICKEL H., NEALE F. C., HALL G. A clinical and biochemical study of hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson's disease). Q J Med. 1957 Oct;26(104):527–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE GROUCHY J. Electrophorèse de sérums humains à travers gel d'amidon et identification de la céruloplasmine, chez des sujets normaux ainsi que chez des sujets homozygotes et hétérozygotes pour le gène de la maladie de Wilson. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1958 Jun;3(6):621–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent C. E. A study of the behaviour of some sixty amino-acids and other ninhydrin-reacting substances on phenol-;collidine' filter-paper chromatograms, with notes as to the occurrence of some of them in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):169–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELL P. G. The estimation of the individual human serum proteins by an immunological method. J Clin Pathol. 1957 Feb;10(1):67–71. doi: 10.1136/jcp.10.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOWITZ H., GUBLER C. J., MAHONEY J. P., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Studies on copper metabolism. XIV. Copper, ceruloplasmin and oxidase activity in sera of normal human subjects, pregnant women, and patients with infection, hepatolenticular degeneration and the nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1955 Oct;34(10):1498–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI103201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEALE F. C., FISCHER-WILLIAMS M. Copper metabolism in normal adults and in clinically normal relatives of patients with Wilson's disease. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;11(5):441–447. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.5.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENOER V. M., FRANGLEN G. Caeruloplasmin in Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1959 Dec 26;2(7113):1163–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91739-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBINSTEIN H. M., PRYCE J. D. The colorimetric estimation of alpha-amino nitrogen in tissue fluids. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jan;12(1):80–84. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASS-KORTSAK A., CHERNIAK M., GEIGER D. W., SLATER R. J. Observations on ceruloplasmin in Wilson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1959 Oct;38:1672–1682. doi: 10.1172/JCI103945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEINBERG I. H., GITLIN D. Deficiency of ceruloplasmin in patients with hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson's disease). Science. 1952 Oct 31;116(3018):484–485. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3018.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEINBERG I. H., MORELL A. G. Exchange of ceruloplasmin copper with ionic Cu64 with reference to Wilson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1957 Aug;36(8):1193–1201. doi: 10.1172/JCI103515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN W. H., BEARN A. G., MOORE S. The amino acid content of the blood and urine in Wilson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1954 Mar;33(3):410–419. doi: 10.1172/JCI102913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UZMAN L. L., HOOD B. The familial nature of the amino-aciduria of Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Am J Med Sci. 1952 Apr;223(4):392–400. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195204000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSHE J. M. Treatment of Wilson's disease with penicillamine. Lancet. 1960 Jan 23;1(7117):188–192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



