Abstract
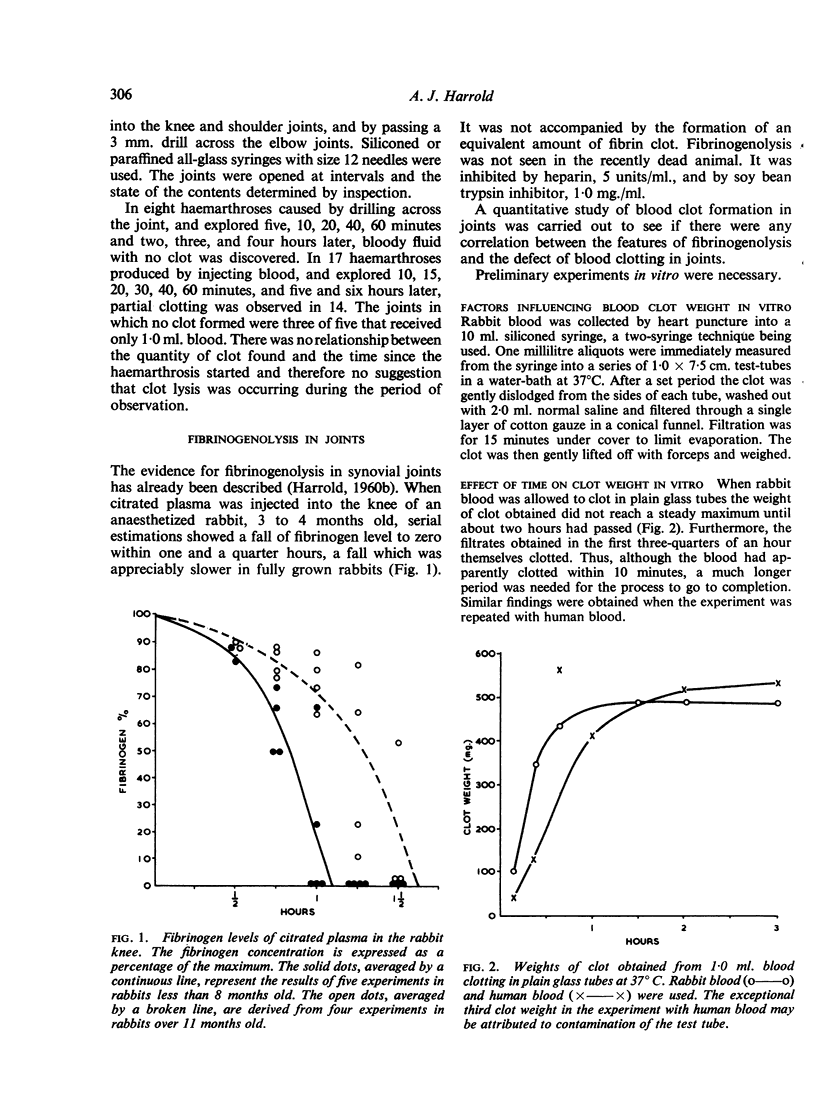
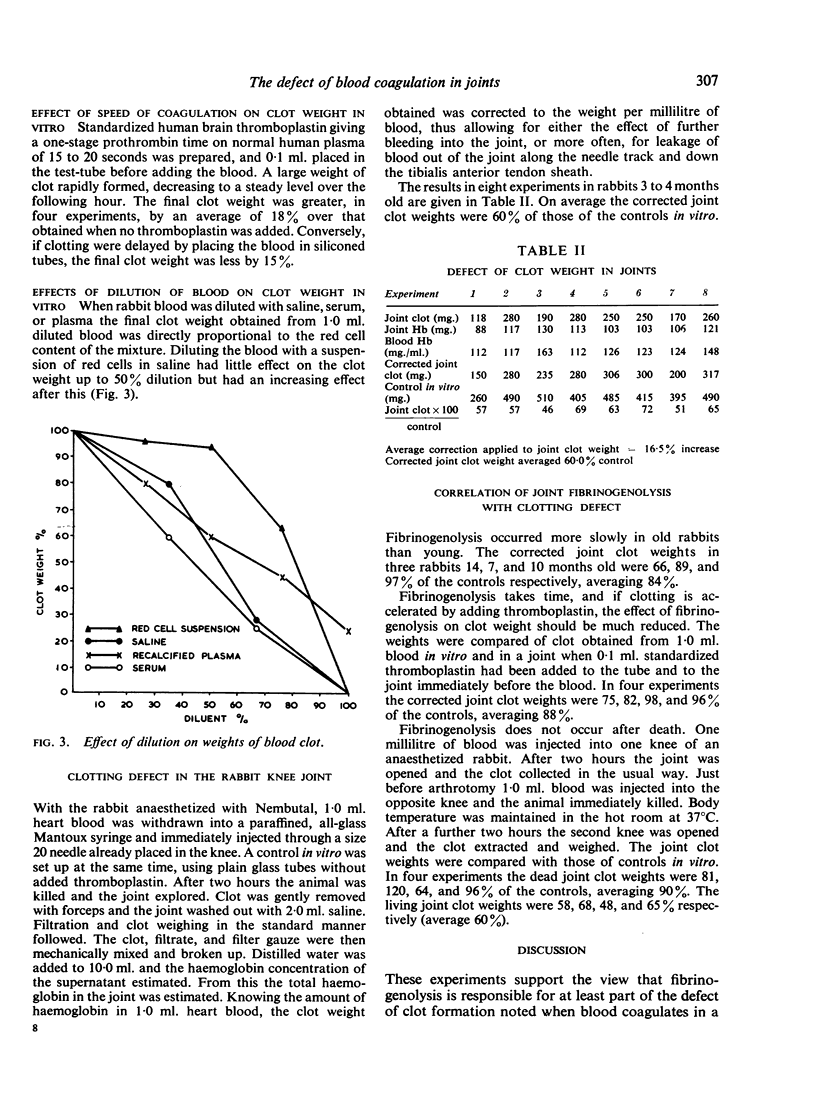
Clinical and experimental observations are described that indicate that intra-articular fibrinogenolysis is a cause of the defect of coagulation seen when blood is extravasated into a synovial joint.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK C. H. Chondrolysis in arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959 May;41-B(2):384–387. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.41B2.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEWIAROWSKI S., LATALLO Z., STACHURSKA J. Apparition d'un inhibiteur de la thromboplastinoformation au cours de la protéolyse du fibrinogène. Rev Hematol. 1959 Apr-Jun;14(2):118–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORMORKEN H. Reactivity of stored plasma to thrombin, with reference to the fibrinogen conversion accelerator and heparinoid activity. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jul;3(3):299–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIANTAPHYLLOPOULOS D. C. Anticoagulant effect of incubated fibrinogen. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Mar;36(3):249–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



