Abstract
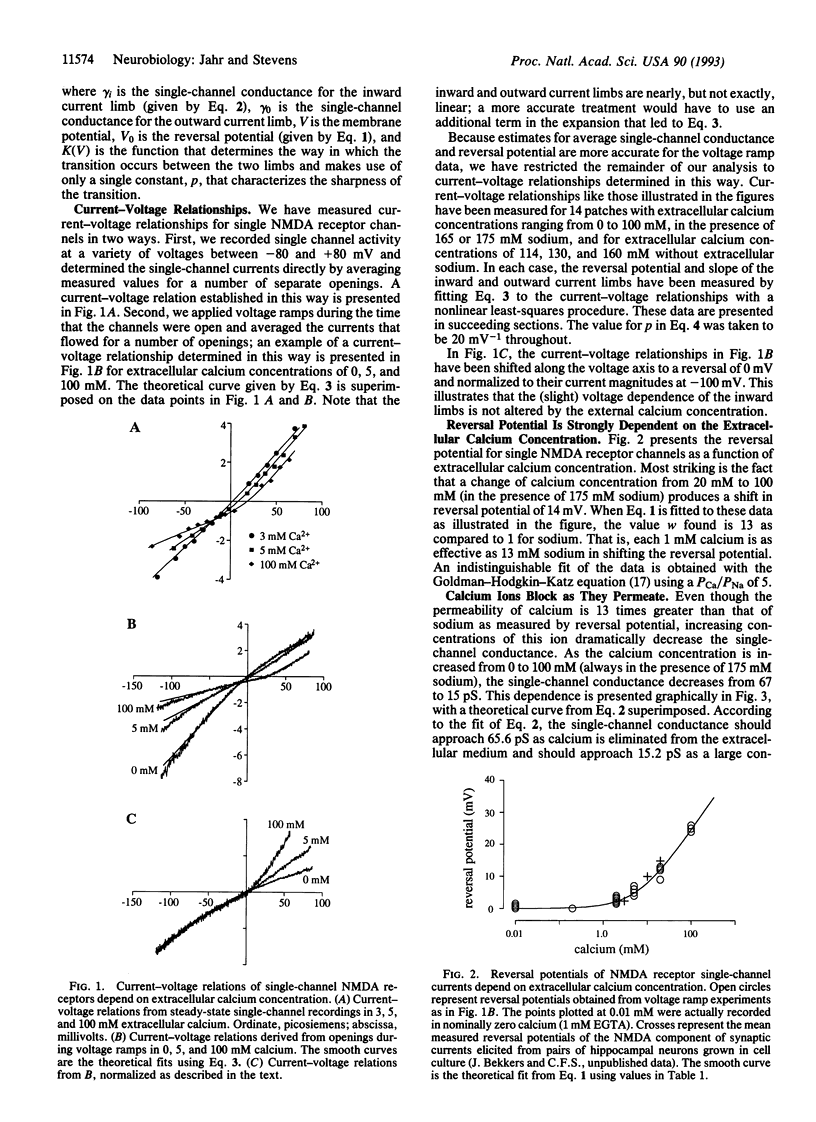
We have developed a quantitative description for calcium permeability of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel to permit predictions of the reversal potential and calcium influx at different voltages for different extracellular calcium concentrations. Increasing the external calcium concentration markedly shifted the reversal potential to positive values and simultaneously decreased the single-channel conductance at potentials negative to the reversal potential. Very simple quantitative descriptions of calcium permeation and channel block by calcium ions accurately characterize our data and permit the prediction of reversal potentials and magnitudes of calcium influx for a wide range of conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregestovski P. D., Miledi R., Parker I. Calcium conductance of acetylcholine-induced endplate channels. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):638–639. doi: 10.1038/279638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Ruppersberg J. P., Günther W., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1415–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1382314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmignoto G., Vicini S. Activity-dependent decrease in NMDA receptor responses during development of the visual cortex. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):1007–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.1279803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Ionic dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):369–379. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00369.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Rothman S. M. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:171–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Ozawa S., Tsuzuki K. Permeation of calcium through excitatory amino acid receptor channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:151–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Tong G., Jahr C. E. Interactions between the glycine and glutamate binding sites of the NMDA receptor. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):1088–1096. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-01088.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G., Larson J., Kelso S., Barrionuevo G., Schottler F. Intracellular injections of EGTA block induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):719–721. doi: 10.1038/305719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A., Zucker R. S., Nicoll R. A. Postsynaptic calcium is sufficient for potentiation of hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2845577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Masaki H., Yamakura T., Mishina M. Identification by mutagenesis of a Mg(2+)-block site of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):673–675. doi: 10.1038/358673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozhayeva G. N., Naumov A. P. The permeability of sodium channels to hydrogen ions in nerve fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Feb;396(2):163–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00615521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Noise analysis of drug induced voltage clamp currents in denervated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):705–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Alteration of Ca2+ permeability and sensitivity to Mg2+ and channel blockers by a single amino acid substitution in the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):410–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze S. M., Role L. W. Developmental regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:403–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



