Abstract
Blankets may be disinfected in steam at subatmospheric pressures by temperatures below boiling point inside a suitably adapted autoclave chamber.
The chamber and its contents are thoroughly evacuated of air so as to allow rapid heat penetration, and steam is admitted to a pressure of 10 in. Hg below atmospheric pressure, which corresponds to a temperature of 89°C. Woollen blankets treated 50 times by this process were undamaged. Vegetative organisms were destroyed but not spores.
The method is suitable for large-scale disinfection of blankets and for disinfecting various other articles which would be damaged at higher temperatures.
Full text
PDF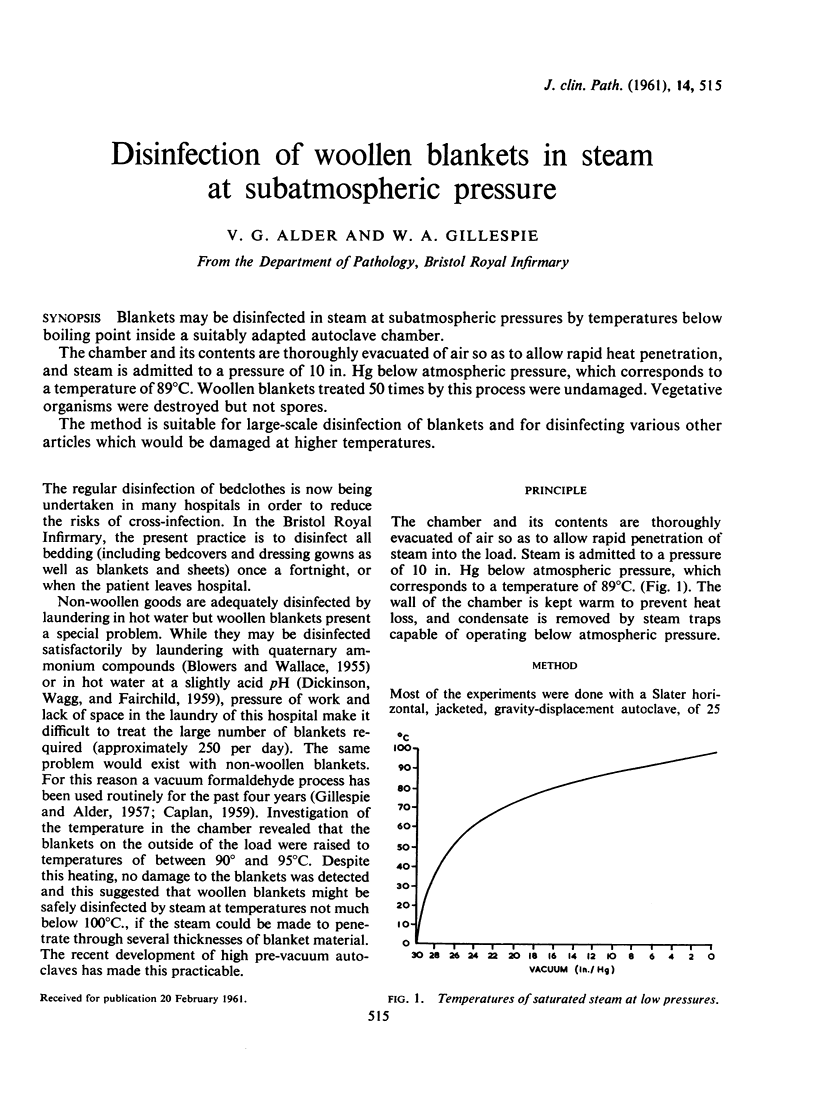
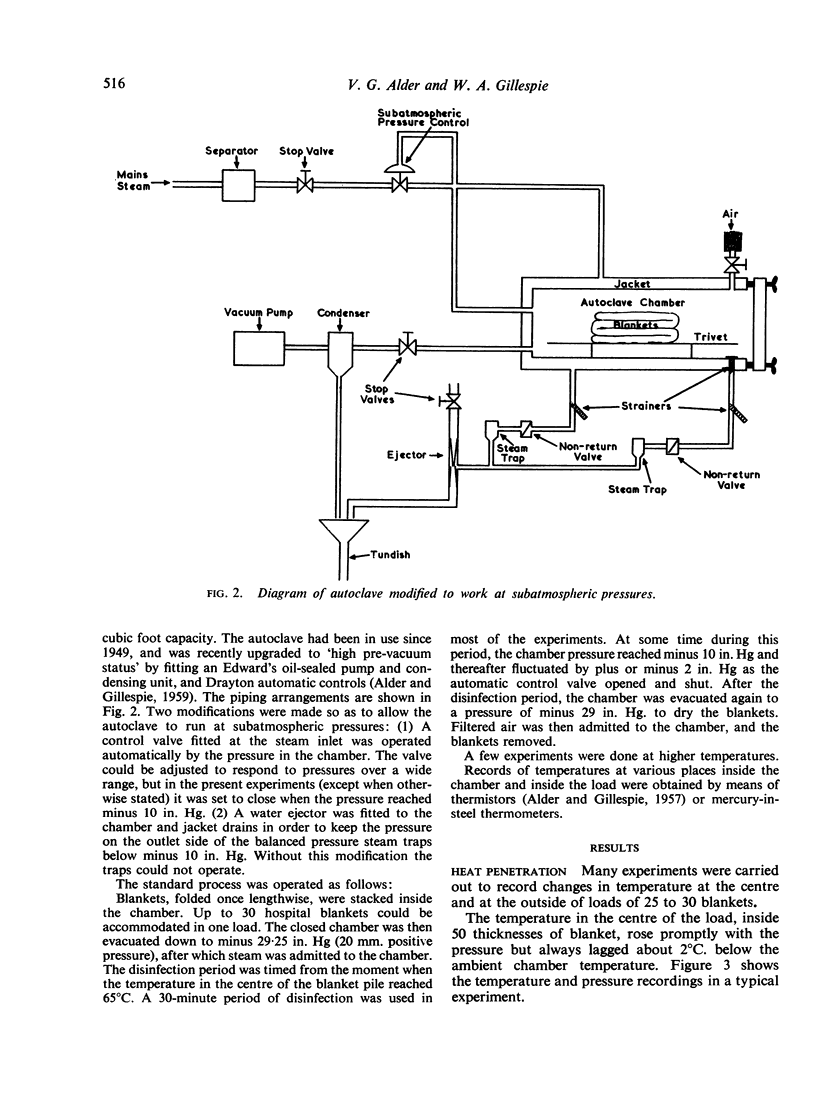
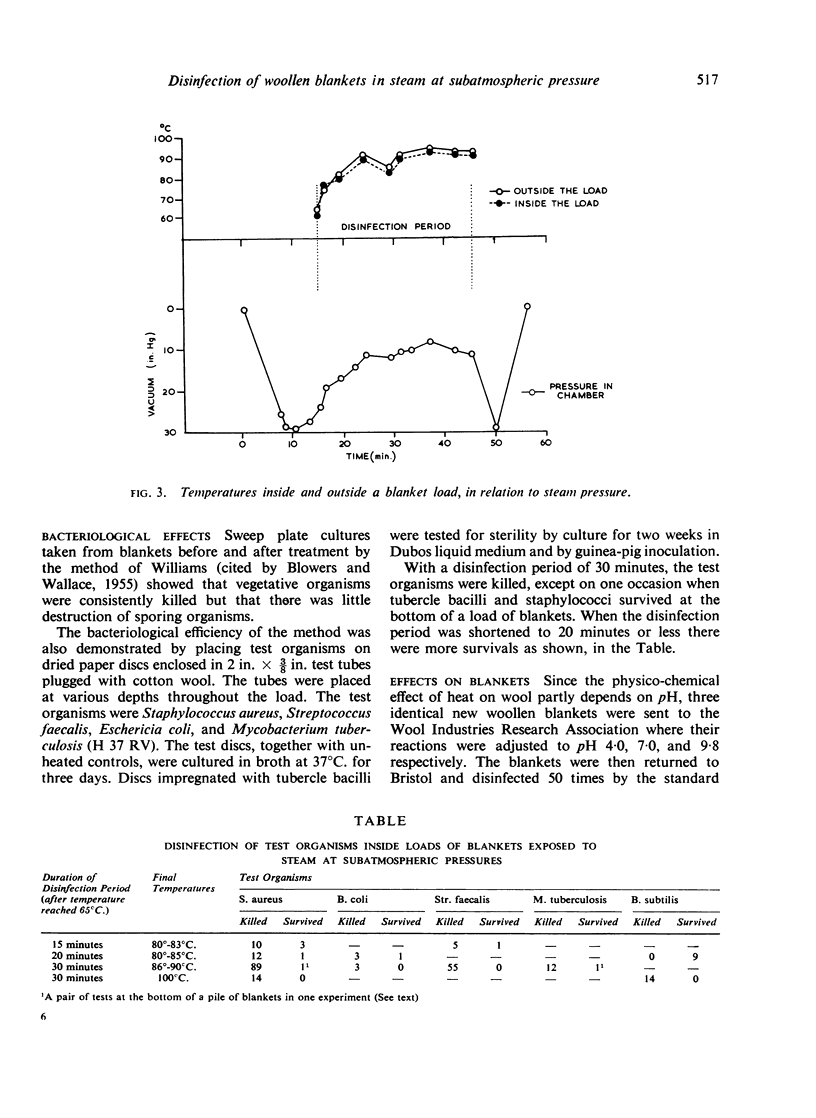

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDER V. G., GILLESPIE W. A. The sterilization of dressings. J Clin Pathol. 1957 Nov;10(4):299–306. doi: 10.1136/jcp.10.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOWERS R., WALLACE K. R. The sterilisation of blankets with cetyl trimethylamine bromide. Lancet. 1955 Jun 18;268(6877):1250–1251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)91022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPLAN H. Control of cross-infection by formaldehyde disinfection of blankets. Lancet. 1959 May 23;1(7082):1088–1089. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE W. A., ALDER V. G. Control of an outbreak of staphylococcal infection in a hospital. Lancet. 1957 Mar 23;272(6969):632–634. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


