Abstract
The technique devised by Moore (1960) for determining the sensitivity of staphylococci to mercuric chloride was investigated and the effect of variations in the medium determined. An alternative technique, in which paper discs impregnated with phenyl mercuric nitrate are used, was found to give identical results.
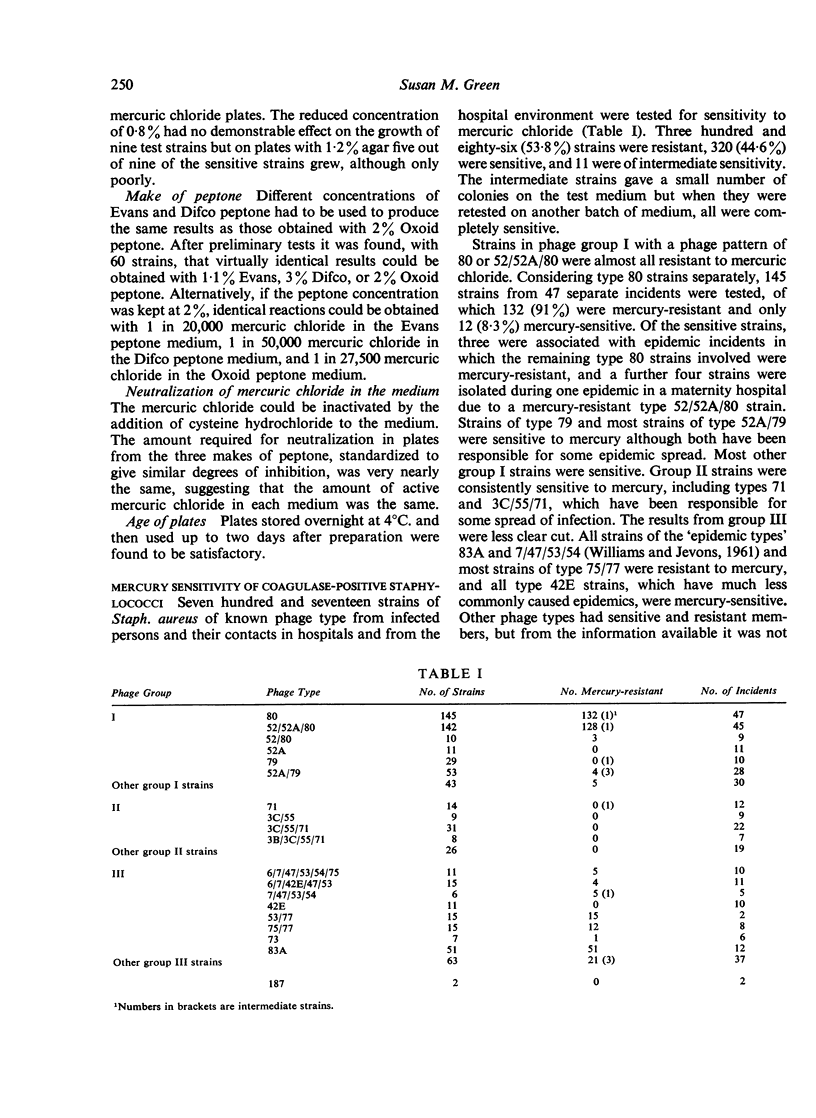
Three hundred and eighty-six out of 717 staphylococci from various sources in hospital were resistant to mercuric chloride, most of the strains belonging to phage types that have commonly produced epidemics.
Only five of 73 strains from septic lesions in R.A.F. recruits and only three of 380 strains from healthy nasal carriers among R.A.F. recruits were resistant to mercury.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MOORE B. A new screen test and selective medium for the rapid detection of epidemic strains of Staph. aureus. Lancet. 1960 Aug 27;2(7148):453–458. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91591-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



