Abstract
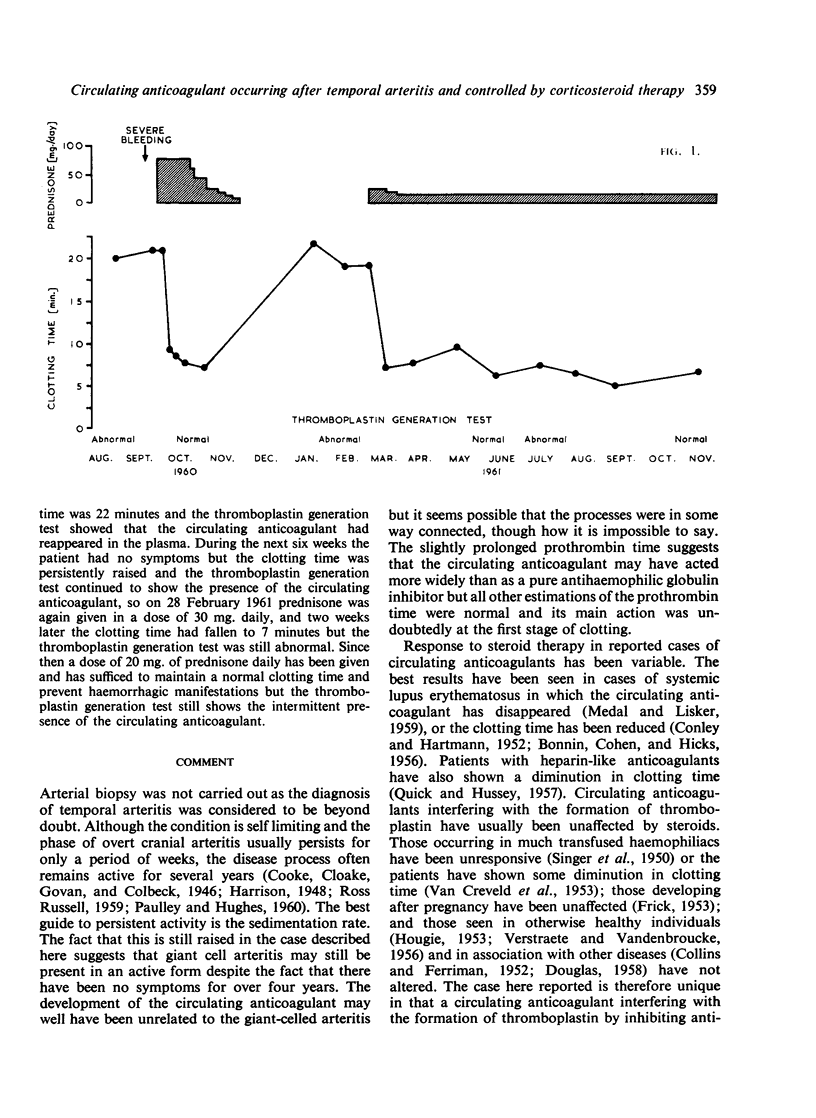
A case is described in which a circulating anticoagulant, inhibiting antihaemophilic globulin, developed following temporal arteritis. The circulating anticoagulant disappeared with steroid therapy, reappearing when steroids were withdrawn. Permanent maintenance therapy appears necessary in this case to prevent haemorrhagic manifestations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRE R., DREYFUS B., JACOB S., LEY G. Sur les formes hémorragiques des myélomes. Rev Hematol. 1952;7(2):296–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Association of Clinical Pathologists: 51st General Meeting. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Nov;6(4):326–331. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.4.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL W. N. A coagulation defect due to an anticoagulant possessing antithromboplastic and antithrombic properties, probably heparin. Blood. 1951 Nov;6(11):1199–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNARD J., INCEMAN S., ZARA M., CHRISTOL D. La dysglobulinémie maligne hémorragipare. Rev Hematol. 1952;7(2):264–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIGGS R., BIDWELL E. A method for the study of antihaemophilic globulin inhibitors with reference to six cases. Br J Haematol. 1959 Oct;5:379–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1959.tb04049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONNIN J. A., COHEN A. K., HICKS N. D. Coagulation defects in a case of systemic lupus erythematosus with thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 1956 Apr;2(2):168–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1956.tb06825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CETINGIL A. I., ULUTIN O. N., KARACA M. Heparin-like anticoagulant occurring in association with chronic nephritis. Br Med J. 1959 Jul 11;2(5140):38–39. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5140.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS I. S., FERRIMAN D. G. Haemophilia-like syndrome from anticoagulants affecting the production of thromboplastin. Lancet. 1952 Oct 11;2(6737):712–714. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLNEY C. L., RATNOFF O. D., ELLICOTT C. E., HARTMANN R. C. Studies on the initiation of blood coagulation. II. An anticoagulant inhibiting the activation of a plasma thromboplastic factor. J Clin Invest. 1950 Sep;29(9):1182–1188. doi: 10.1172/JCI102356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS A. S. An atypical circulating thromboplastin inhibitor. Br J Haematol. 1958 Jul;4(3):302–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1958.tb06033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRICK P. G. Hemophilia-like disease following pregnancy with transplacental transfer of an acquired circulating anticoagulant. Blood. 1953 Jul;8(7):598–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M. Acquired haemophilia-like disease; report of a case with studies on the mode of action of the circulating anticoagulant. J Clin Pathol. 1954 Feb;7(1):26–28. doi: 10.1136/jcp.7.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGIE C. Pseudo-haemophilia: an acquired haemorrhagic diathesis due to a circulating anticoagulant. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Feb;6(1):30–33. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. V. Giant-Cell or Temporal Arteritis: a Review. J Clin Pathol. 1948 Aug;1(4):197–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE S. L., SANDERS M. A disorder of blood coagulation in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1955 Dec;34(12):1814–1822. doi: 10.1172/JCI103237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER J. F., RATNOFF O., HEINLE R. W. Observations on the characteristics of an unusual circulating anticoagulant. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Aug;38(2):254–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro F. L., Munro M. P. ELECTROPHORETIC ISOLATION OF A CIRCULATING ANTICOAGULANT. J Clin Invest. 1946 Nov;25(6):814–815. doi: 10.1172/JCI101768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro F. L. PROPERTIES OF AN ANTICOAGULANT FOUND IN THE BLOOD OF A HEMOPHILIAC. J Clin Invest. 1946 May;25(3):422–427. doi: 10.1172/JCI101724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOUR-ELDIN F., WILKINSON J. F. Bridge anticoagulant; a hitherto unrecognized blood clotting inhibitor in haemophilic and Christmas-disease plasma; a simple method for its demonstration. Br J Haematol. 1958 Jan;4(1):38–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1958.tb03832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSEY A. M., DAWSON D. W. Haemophilia-like disease due to an auto-antibody. Br Med J. 1957 Nov 9;2(5053):1077–1079. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5053.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULLEY J. W., HUGHES J. P. Giant-cell arteritis, or arteritis of the aged. Br Med J. 1960 Nov 26;2(5212):1562–1567. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5212.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONS E. R., Jr, DE TORREGROSA M. V. Hemorrhagic diathesis due to a circulating anticoagulant. Report of case with laboratory observations. Blood. 1952 Jan;7(1):20–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUICK A. J., HUSSEY C. V. Hyperheparinemia: report of a case. Am J Med Sci. 1957 Sep;234(3):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANCHEZ MEDAL L., LISKER R. Circulating anticoagulants in disseminated lupus erythematosus. Br J Haematol. 1959 Jul;5:284–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1959.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER K., MOND E., HYMAN J., LEVY R. C. Circulating anticoagulants in hemophilia and in hemophilia-like disease. Blood. 1950 Dec;5(12):1135–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEER R. J., HILL J. M., MALONEY M., ROBERTS A. Hemorrhagic diathesis associated with hyperheparinemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 May;45(5):730–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TZANCK A., SOULIER J. P., BLATRIX C. Deux nouvelles observations de syndromes hémorragiques avec présence d'un anticoagulant circulant; étude électrophorétique et thérapeutique. Rev Hematol. 1949;4(3):502–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van CREVELD S., HOORWEG P. G., PAULSSEN M. M. P. Researches on a circulating anticoagulant in a hemophiliac. Blood. 1951 Mar;6(3):233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]