Abstract
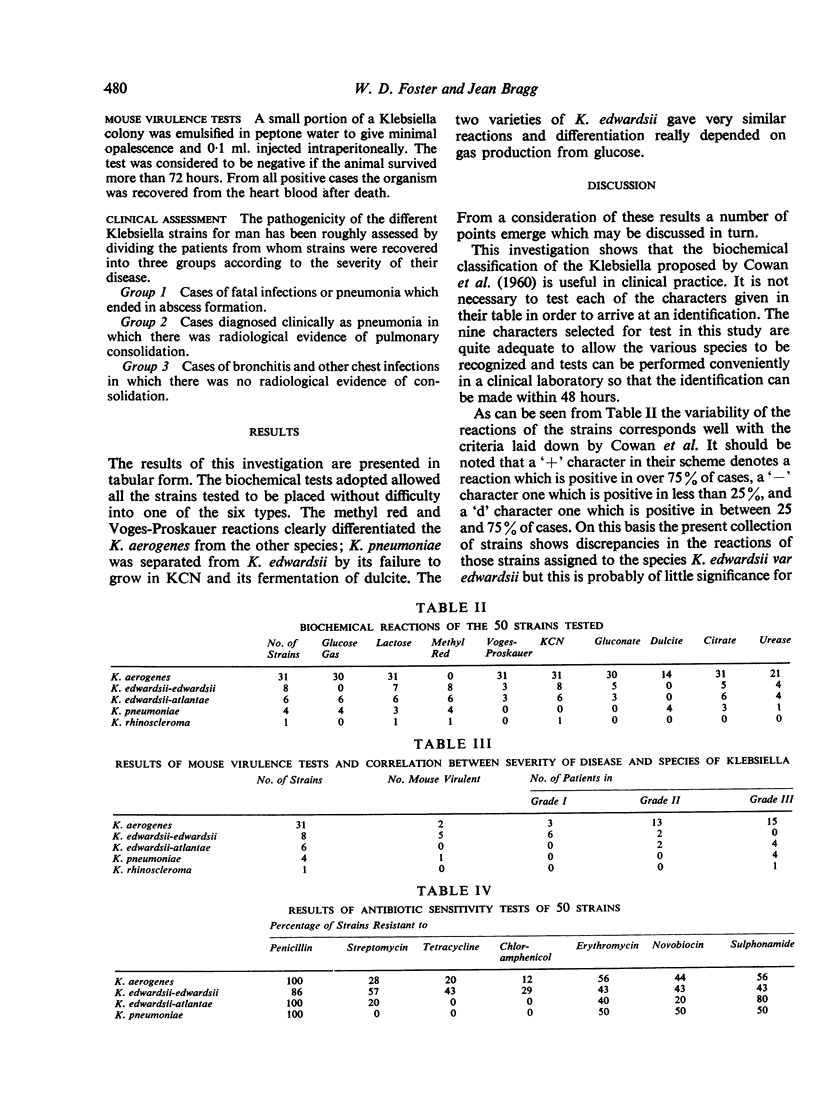
The biochemical classification of the Klebsiella proposed by Cowan, Steel, Shaw, and Duguid (1960) has been applied to 50 strains isolated as the pure or predominant growth from sputum, and Klebsiella species have been correlated with the severity of the chest infection in the patient. A modification in nomenclature is suggested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COWAN S. T., STEEL K. J., SHAW C., DUGUID J. P. A classification of the Klebsiella group. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:601–612. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. R. RELATIONSHIPS OF THE ENCAPSULATED BACILLI WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO BACT. AEROGENES. J Bacteriol. 1929 May;17(5):339–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.17.5.339-353.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAWLINS G. A. A method of liquefying sputum for the culture of organisms other than M. tuberculosis. J Med Lab Technol. 1955 Jul;13(3):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW C., CLARKE P. H. Biochemical classification of Proteus and Providence cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Aug;13(1):155–161. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS W., EISENBERG G. M., ALEXANDER J. D., Jr, FLIPPIN H. F. [Klebsiella pulmonary disease]. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Aug;228(2):148–155. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195408000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



