Abstract
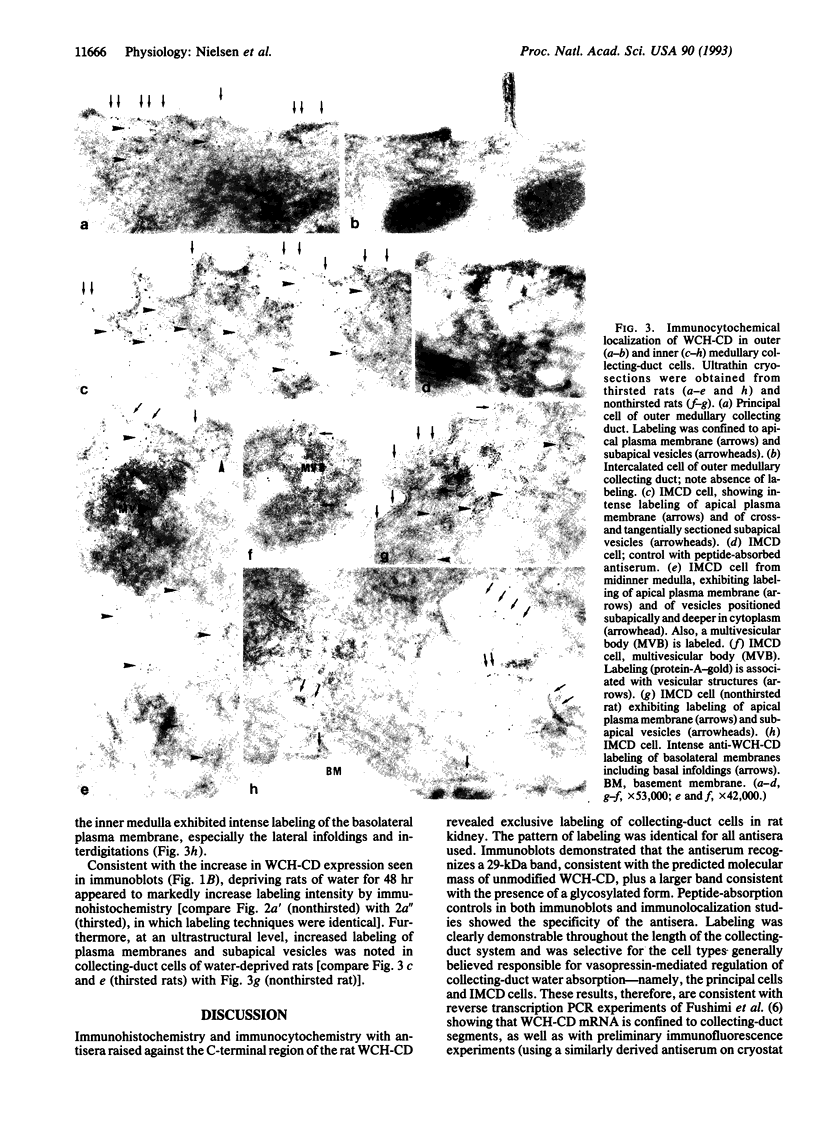
Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) regulates body water balance by controlling water permeability of the renal collecting ducts. The control mechanisms may involve alterations in the number or unit conductance of water channels in the apical plasma membrane of collecting-duct cells. How this occurs is unknown, but indirect evidence exists for the "shuttle" hypothesis, which states that vasopressin causes exocytic insertion of water channel-laden vesicles from the apical cytosol. To test key aspects of the shuttle hypothesis, we have prepared polyclonal antisera against the recently cloned collecting-duct water channel protein and used the antisera in immunolocalization studies (light and electron microscopic levels) in thin and ultrathin cryosections from rat kidney. Labeling was seen exclusively in collecting-duct principal cells and inner medullary collecting-duct cells. Apical membrane labeling was intense. There was heavy labeling of abundant small subapical vesicles and of membrane structures within multivesicular bodies. In addition, labeling of basolateral plasma membranes in inner medullary collecting ducts was present. Depriving rats of water for 24 or 48 hr markedly increased collecting-duct water-channel protein expression determined by immunoblotting and immunolabeling. These results are compatible with at least two complementary modes of water-channel regulation in collecting-duct cells: (i) control of channel distribution between the apical membrane and a reservoir in subapical vesicles (shuttle hypothesis) and (ii) regulation of the absolute level of expression of water-channel protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Preston G. M., Smith B. L., Jung J. S., Raina S., Moon C., Guggino W. B., Nielsen S. Aquaporin CHIP: the archetypal molecular water channel. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 2):F463–F476. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.4.F463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. Membrane recycling and epithelial cell function. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F1–12. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., Bennett V. Brain ankyrin. Purification of a 72,000 Mr spectrin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1874–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker B. M., Smith B. L., Kuhajda F. P., Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15634–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echevarria M., Frindt G., Preston G. M., Milovanovic S., Agre P., Fischbarg J., Windhager E. E. Expression of multiple water channel activities in Xenopus oocytes injected with mRNA from rat kidney. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jun;101(6):827–841. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.6.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamion B., Spring K. R. Water permeability of apical and basolateral cell membranes of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F986–F999. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Jr, Strange K., Zeidel M. L. Current understanding of the cellular biology and molecular structure of the antidiuretic hormone-stimulated water transport pathway. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):1–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI115263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankford S. P., Chou C. L., Terada Y., Wall S. M., Wade J. B., Knepper M. A. Regulation of collecting duct water permeability independent of cAMP-mediated AVP response. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):F554–F566. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hir M., Kaissling B. Distribution and regulation of renal ecto-5'-nucleotidase: implications for physiological functions of adenosine. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):F377–F387. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.3.F377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Muller J., Knepper M. A. Vasopressin- and cAMP-induced changes in ultrastructure of isolated perfused inner medullary collecting ducts. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 2):F225–F238. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.2.F225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Agre P. Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7275–7279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange K., Spring K. R. Cell membrane water permeability of rabbit cortical collecting duct. J Membr Biol. 1987;96(1):27–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01869332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc. 1986 Aug;143(Pt 2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Silverman M. Interaction of phlorizin and sodium with the renal brush-border membrane D-glucose transporter: stoichiometry and order of binding. J Membr Biol. 1981 Jan 30;58(1):43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01871033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Stetson D. L., Lewis S. A. ADH action: evidence for a membrane shuttle mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:106–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]