Abstract
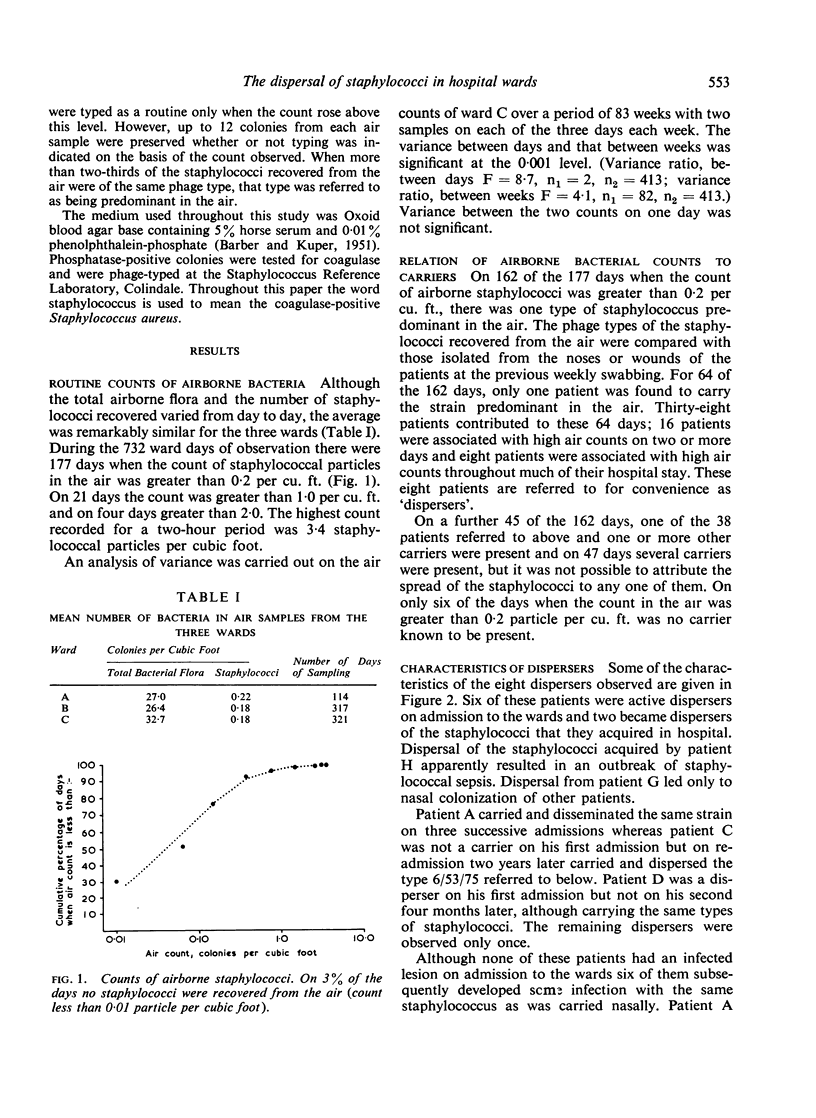
The air of three hospital wards was examined frequently for staphylococci for a period of nearly four years using slit samplers. `Broadcasts' of staphylococci into the air were observed with the air count rising well above the mean of 0·2 staphylococcal particle per cubic foot and these broadcasts often appeared to be due to single patients.
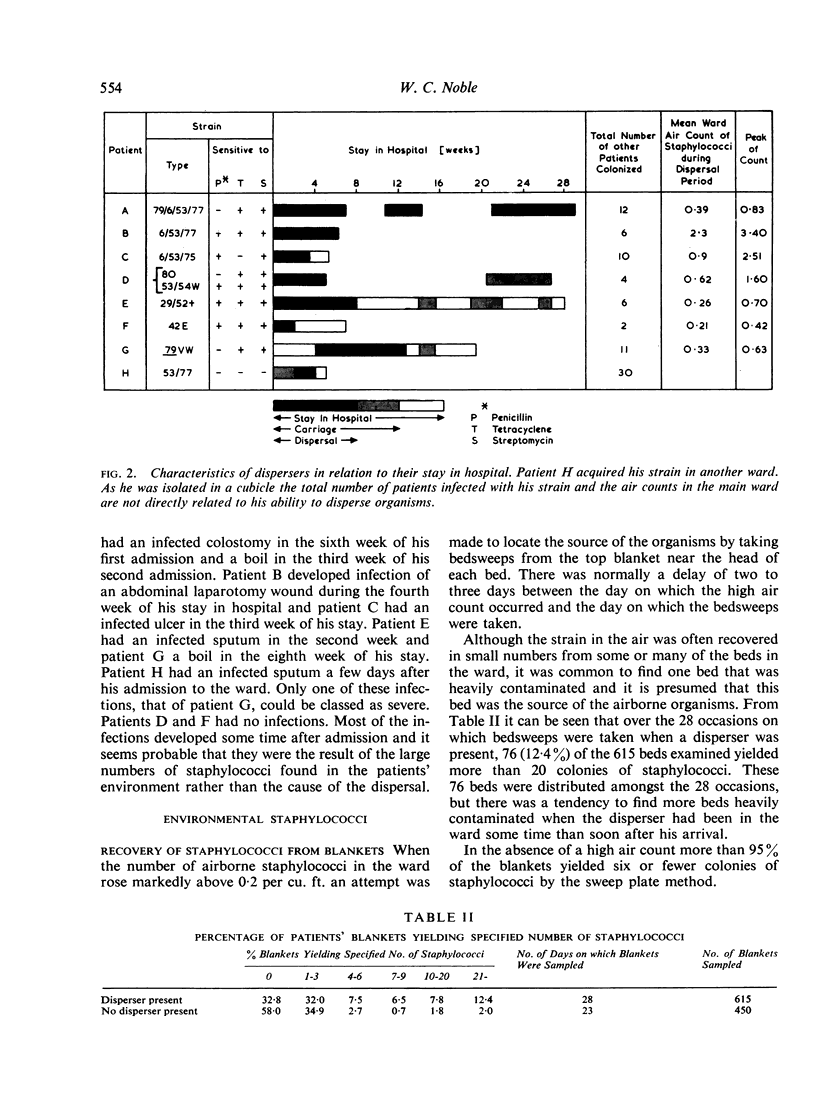
Eight of the 3,675 patients admitted to the wards possessed an ability to disperse staphylococci into the air of the wards which was markedly greater than normal.
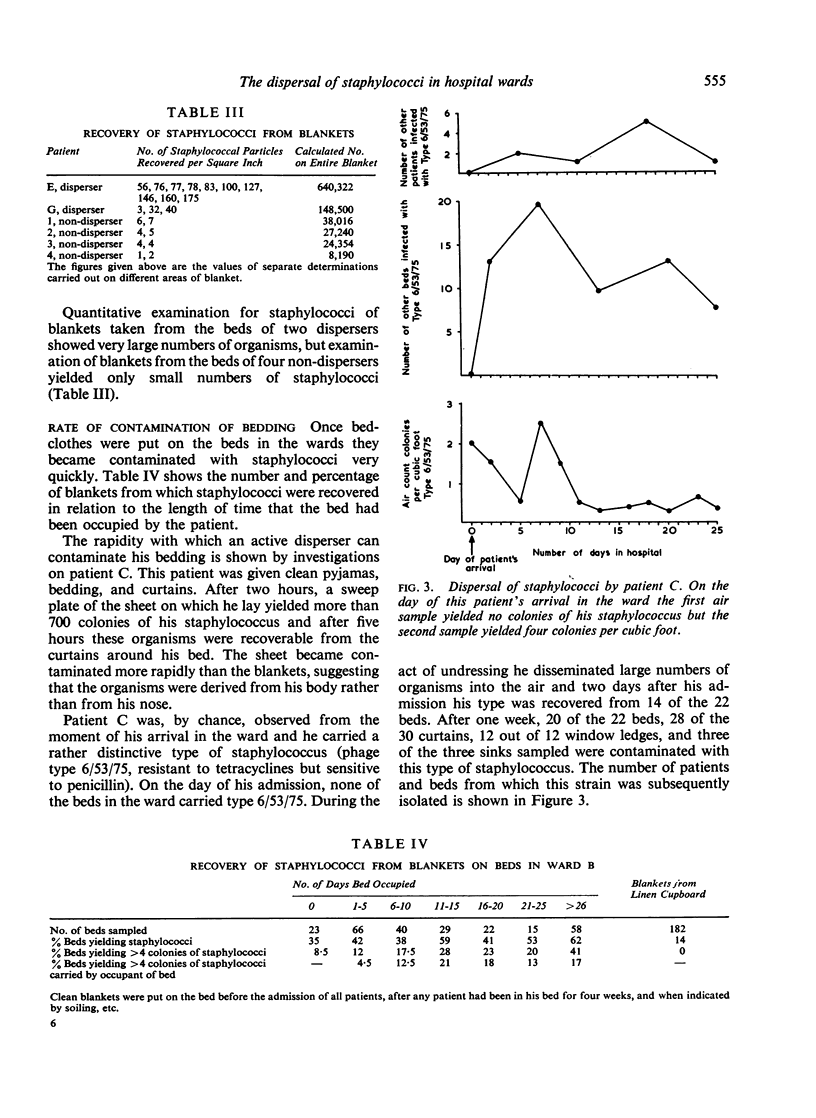
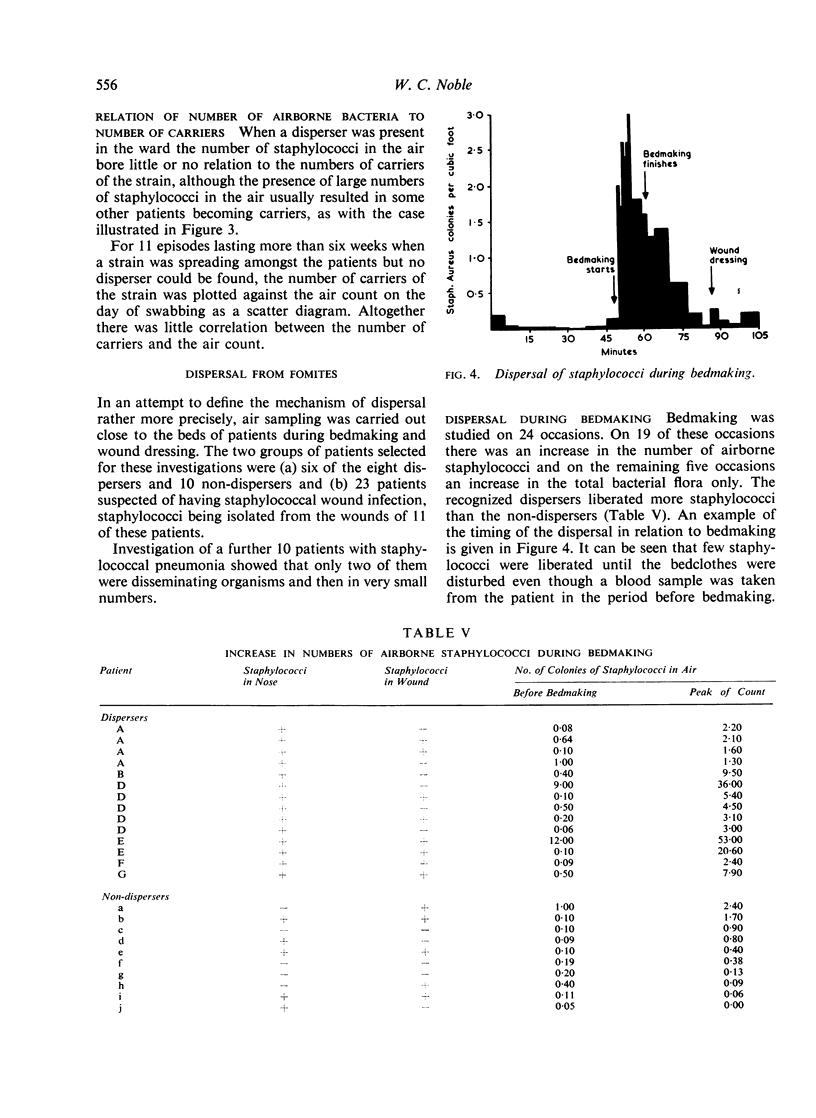
The actual dispersal about the ward appeared to be mediated by the bedclothes, for, when these were disturbed, large numbers of staphylococci were disseminated into the air.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EICHENWALD H. F., KOTSEVALOV O., FASSO L. A. The "cloud baby": an example of bacterial-viral interaction. Am J Dis Child. 1960 Aug;100:161–173. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1960.04020040163003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARE R., COOKE E. M. Self-contamination of patients with staphylococcal infections. Br Med J. 1961 Aug 5;2(5248):333–336. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5248.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOOTER R. A., SMITH M. A., GRIFFITHS J. D., BROWN M. E., WILLIAMS R. E., RIPPON J. E., JEVONS M. P. Spread of staphylococci in a surgical ward. Br Med J. 1958 Mar 15;1(5071):607–613. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5071.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE A. Relation between quantitative nasal cultures and dissemination of staphylococci. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Aug;58:273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E., JEVONS M. P., SHOOTE R. A., THOM B. T., NOBLE W. C., LIDWELL O. M., WHITE R. C., TAYLOR G. W. Isolation for the control of staphylococcal infection in surgical wards. Br Med J. 1962 Aug 4;2(5300):275–282. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5300.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



