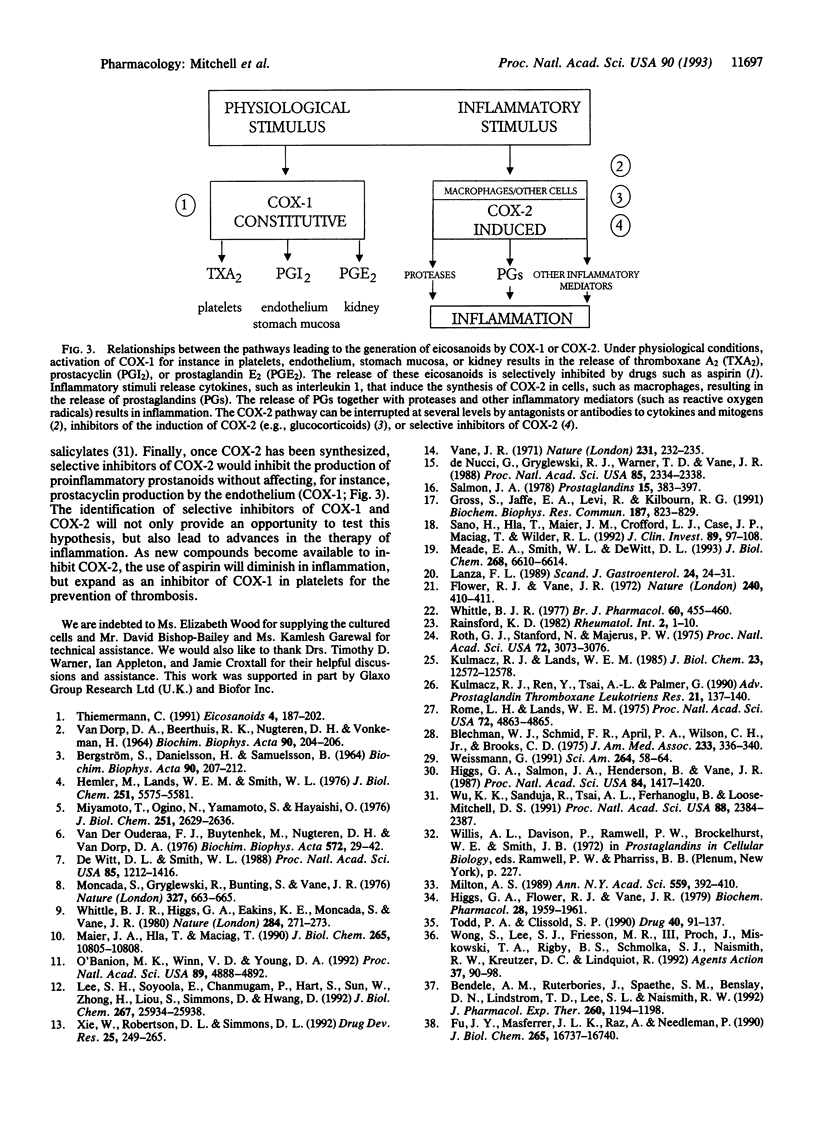
Abstract
Constitutive cyclooxygenase (COX-1; prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase, EC 1.14.99.1) is present in cells under physiological conditions, whereas COX-2 is induced by some cytokines, mitogens, and endotoxin presumably in pathological conditions, such as inflammation. Therefore, we have assessed the relative inhibitory effects of some nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs on the activities of COX-1 (in bovine aortic endothelial cells) and COX-2 (in endotoxin-activated J774.2 macrophages) in intact cells, broken cells, and purified enzyme preparations (COX-1 in sheep seminal vesicles; COX-2 in sheep placenta). Similar potencies of aspirin, indomethacin, and ibuprofen against the broken cell and purified enzyme preparations indicated no influence of species. Aspirin, indomethacin, and ibuprofen were more potent inhibitors of COX-1 than COX-2 in all models used. The relative potencies of aspirin and indomethacin varied only slightly between models, although the IC50 values were different. Ibuprofen was more potent as an inhibitor of COX-2 in intact cells than in either broken cells or purified enzymes. Sodium salicylate was a weak inhibitor of both COX isoforms in intact cells and was inactive against COX in either broken cells or purified enzyme preparations. Diclofenac, BW 755C, acetaminophen, and naproxen were approximately equipotent inhibitors of COX-1 and COX-2 in intact cells. BF 389, an experimental drug currently being tested in humans, was the most potent and most selective inhibitor of COX-2 in intact cells. Thus, there are clear pharmacological differences between the two enzymes. The use of such models of COX-1 and COX-2 activity will lead to the identification of selective inhibitors of COX-2 with presumably less side effects than present therapies. Some inhibitors had higher activity in intact cells than against purified enzymes, suggesting that pure enzyme preparations may not be predictive of therapeutic action.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGSTROEM S., DANIELSSON H., SAMUELSSON B. THE ENZYMATIC FORMATION OF PROSTAGLANDIN E2 FROM ARACHIDONIC ACID PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS 32. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:207–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendele A. M., Ruterbories K. J., Spaethe S. M., Benslay D. N., Lindstrom T. D., Lee S. J., Naismith R. W. Correlation of anti-inflammatory activity with peak tissue rather than peak plasma levels of BF389. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1194–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blechman W. J., Schmid F. R., April P. A., Wilson C. H., Jr, Brooks C. D. Ibuprofen or aspirin in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. JAMA. 1975 Jul 28;233(4):336–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein. Sci Am. 1991 Jun;264(6):58–65. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0691-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase in brain explains the anti-pyretic activity of paracetamol (4-acetamidophenol). Nature. 1972 Dec 15;240(5381):410–411. doi: 10.1038/240410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. Y., Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Raz A., Needleman P. The induction and suppression of prostaglandin H2 synthase (cyclooxygenase) in human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16737–16740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Kilbourn R. G. Cytokine-activated endothelial cells express an isotype of nitric oxide synthase which is tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent, calmodulin-independent and inhibited by arginine analogs with a rank-order of potency characteristic of activated macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90965-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M., Lands W. E. Purification of the cyclooxygenase that forms prostaglandins. Demonstration of two forms of iron in the holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5575–5579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Salmon J. A., Henderson B., Vane J. R. Pharmacokinetics of aspirin and salicylate in relation to inhibition of arachidonate cyclooxygenase and antiinflammatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1417–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulmacz R. J., Lands W. E. Stoichiometry and kinetics of the interaction of prostaglandin H synthase with anti-inflammatory agents. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12572–12578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F. L. A review of gastric ulcer and gastroduodenal injury in normal volunteers receiving aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;163:24–31. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Soyoola E., Chanmugam P., Hart S., Sun W., Zhong H., Liou S., Simmons D., Hwang D. Selective expression of mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25934–25938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Cyclooxygenase is an immediate-early gene induced by interleukin-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10805–10808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade E. A., Smith W. L., DeWitt D. L. Differential inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) isozymes by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6610–6614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S. Thermoregulatory actions of eicosanoids in the central nervous system with particular regard to the pathogenesis of fever. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;559:392–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Ogino N., Yamamoto S., Hayaishi O. Purification of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase from bovine vesicular gland microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2629–2636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Banion M. K., Winn V. D., Young D. A. cDNA cloning and functional activity of a glucocorticoid-regulated inflammatory cyclooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4888–4892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainsford K. D. An analysis of the gastro-intestinal side-effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, with particular reference to comparative studies in man and laboratory species. Rheumatol Int. 1982;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00541263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome L. H., Lands W. E. Structural requirements for time-dependent inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis by anti-inflammatory drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4863–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Acetylation of prostaglandin synthase by aspirin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3073–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A. A radioimmunoassay for 6-keto-prostaglandin F1alpha. Prostaglandins. 1978 Mar;15(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Hla T., Maier J. A., Crofford L. J., Case J. P., Maciag T., Wilder R. L. In vivo cyclooxygenase expression in synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis and rats with adjuvant and streptococcal cell wall arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):97–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI115591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C. Biosynthesis and interaction of endothelium-derived vasoactive mediators. Eicosanoids. 1991;4(4):187–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P. A., Clissold S. P. Naproxen. A reappraisal of its pharmacology, and therapeutic use in rheumatic diseases and pain states. Drugs. 1990 Jul;40(1):91–137. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199040010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DORPD, BEERTHUIS R. K., NUGTEREN D. H., VONKEMAN H. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF PROSTAGLANDINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:204–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Higgs G. A., Eakins K. E., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Selective inhibition of prostaglandin production in inflammatory exudates and gastric mucosa. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):271–273. doi: 10.1038/284271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Mechanisms underlying gastric mucosal damage induced by indomethacin and bile-salts, and the actions of prostaglandins. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;60(3):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S., Lee S. J., Frierson M. R., 3rd, Proch J., Miskowski T. A., Rigby B. S., Schmolka S. J., Naismith R. W., Kreutzer D. C., Lindquist R. Antiarthritic profile of BF-389--a novel anti-inflammatory agent with low ulcerogenic liability. Agents Actions. 1992 Sep;37(1-2):90–98. doi: 10.1007/BF01987895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K., Sanduja R., Tsai A. L., Ferhanoglu B., Loose-Mitchell D. S. Aspirin inhibits interleukin 1-induced prostaglandin H synthase expression in cultured endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2384–2387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Gryglewski R. J., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Receptor-mediated release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and prostacyclin from bovine aortic endothelial cells is coupled. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ouderaa F. J., Buytenhek M., Slikkerveer F. J., van Dorp D. A. On the haemoprotein character of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 29;572(1):29–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




