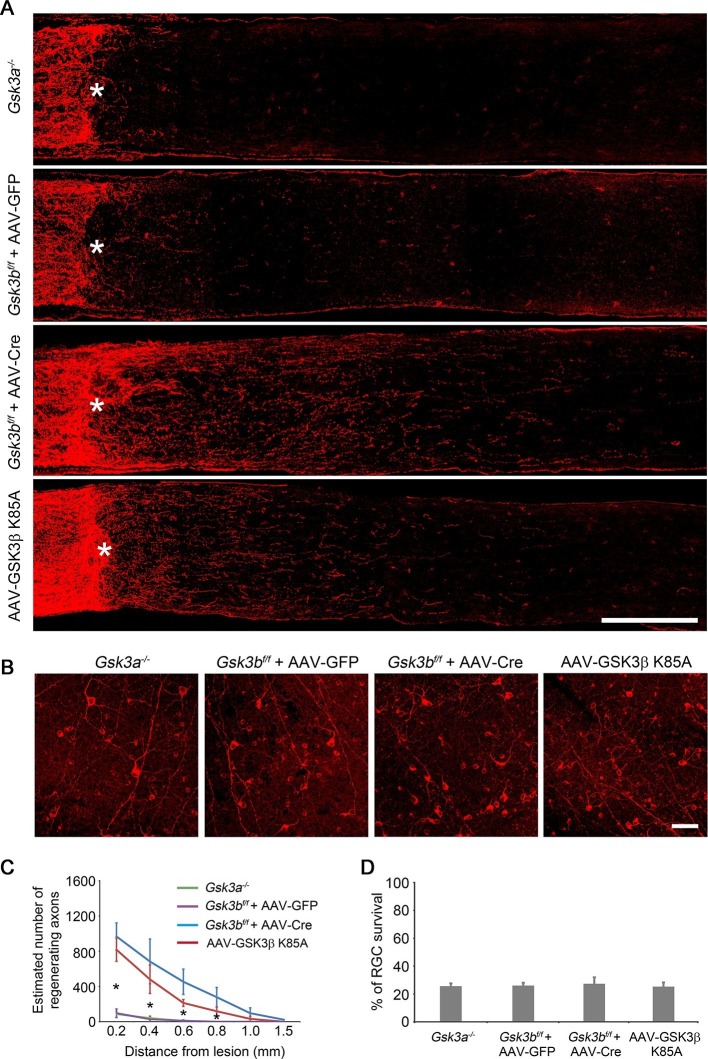
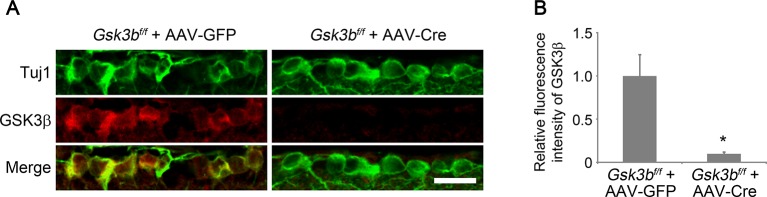
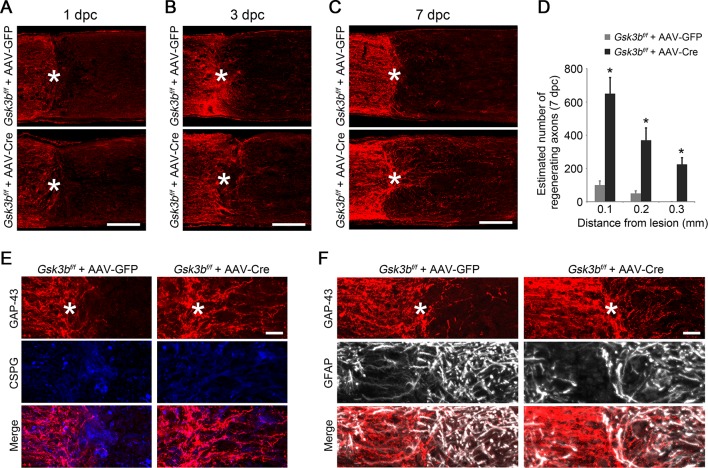
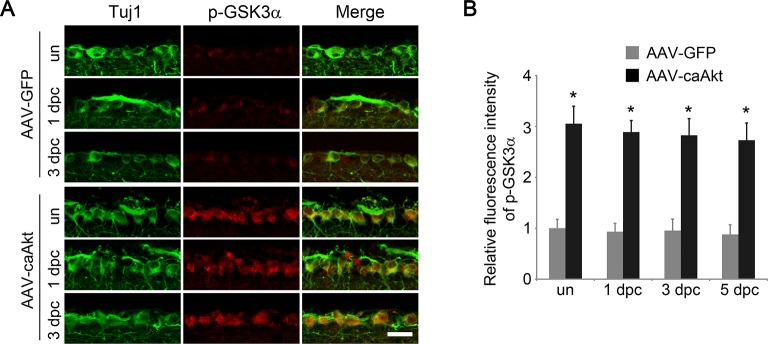
Figure 3. Deletion or inactivation of GSK3β promotes axon regeneration.
(A) Confocal images of optic nerve sections showing regenerating axons labeled by anti-GAP43 immunohistochemistry at 2 weeks after optic nerve crush from Gsk3a−/− mice, Gsk3bf/f mice injected with AAV-GFP or AAV-Cre, or AAV-GSK3β K85A injected wild-type mice. *, crush site. Scale bar, 200 µm. (B) Confocal images of retinal whole-mounts showing surviving Tuj1+ RGCs at 2 weeks after optic nerve injury. Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Quantification of regenerating axons at different distances distal to the lesion site. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n=5 per group. *p<0.01, Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (D) Quantification of RGC survival at 2 weeks after injury, expressed as a percentage of total Tuj1+ RGCs in the uninjured retina. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n=5 per group.