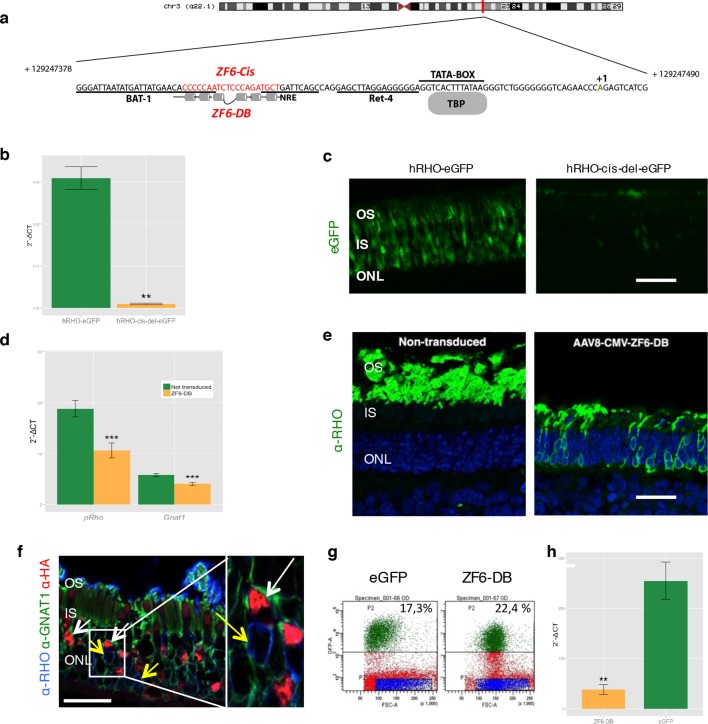
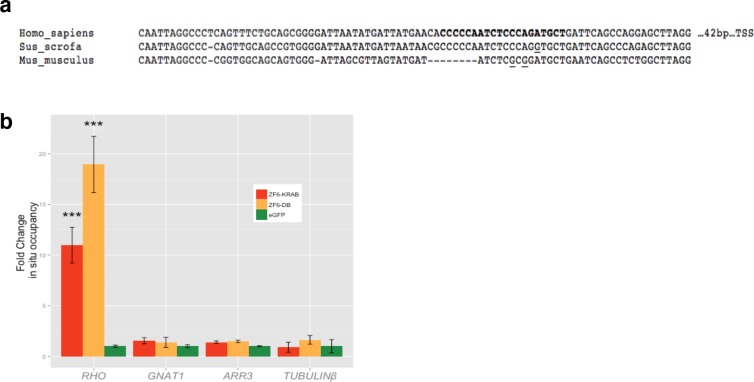
Figure 1. Delivery of ZF6-DB DNA-binding synthetic trans-acting factor targeted to a 20 bp of RHO cis-acting regulatory element (CRE) dramatically reduces Rho expression in photoreceptors.
(a) Schematic representation of the chromosomal location of the RHO locus and its proximal promoter elements indicating the transcription start site (in green, +1) and the location of ZF6-DB binding site (in red, ZF6-Cis) and ZF6-DB (based on Mitton et Al., 12); BAT1, Bovine A/T-rich sequence1; NRE, NRL response element; TBP, TATA box binding protein. (b) qReal Time PCR of mRNA levels (2^-ΔCT) on the adult porcine retina 15 days after vector delivery of either AAV8-hRHO-eGFP (n=2) or AAV8-hRHO-cis-del-eGFP (n=2) subretinally administered at a dose of 1x1010, showed that AAV8-hRHO-cis-del-eGFP resulted in decreased transduction (about fifty fold) compared with hRHO. (c) Histology confirmed the decrease of eGFP expression in hRHO-cis-del-eGFP injected retina compared with the retina injected with hRHO-eGFP. Scale bar, 50 µm. (d) qReal Time PCR of mRNA levels (2^-ΔCT) of adult porcine retina injected subretinally with AAV8-CMV-ZF6-DB (n=6) at a vector dose of 1x1010 genomes copies (gc) compared with non-transduced area (n=7) of the same eye 15 days after vector delivery, resulted in robust transcriptional repression of the Rho transcript. pRHO, porcine Rhodopsin; Gnat1, Guanine Nucleotide Binding Protein1. (e) Rho Immunofluorescence (green) histological confocal analysis of AAV8-CMV-ZF6-DB treated porcine retina compared with non-transduced area. Scale bar, 100 um. The treatment with ZF6-DB determined collapse of the outer-segment (OS) with apparent retention of nuclei (stained with DAPI) in the outer nuclear layer (ONL). (f) Immunofluorescence triple co-localization staining of porcine retina shown in (b) with Rho (blue), rod specific protein Gnat1 (green) and HA (ZF6-DB, red) antibodies. White arrows indicate co-localization of both HA-tag-ZF6-DB and Gnat1 rods depleted of Rho, whereas yellow arrows showed residual Rho and Gnat1 positive cells lacking ZF6-DB. A magnification of the triple staining (box) is highlighted. Scale bar, 100 µm. OS, outer segment; IS, inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer. (g) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of porcine retina 15 days after injections of either AAV8-GNAT1-eGFP (dose 1x1012 gc) or co-injection with both AAV8-GNAT1-eGFP and AAV8-CMV-ZF6-DB (dose of eGFP, 1x1012 gc; ZF6-DB dose 5x1010 gc). eGFP positive sorted cells (AAV8-GNAT1-eGFP) corresponded to 17,3% of the analysed population (left panel; P2 area, green dots), whereas, 22,4% of eGFP positive cells in the retina that received both vectors (AAV8-GNAT1-eGFP and AAV8-CMV-ZF6-DB; right panel; P2 area, green dots). (h) qReal Time PCR on sorted rods treated with AAV8-GNAT1-eGFP (n=3) and AAV8-CMV-ZF6-DB (n=3) showed a repression of about 85% of total rhodopsin when compared with rods treated with eGFP (mRNA levels: 2^-ΔCT). Error bars, means +/- s.e.m. n =; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; two-tailed Student’s t test.