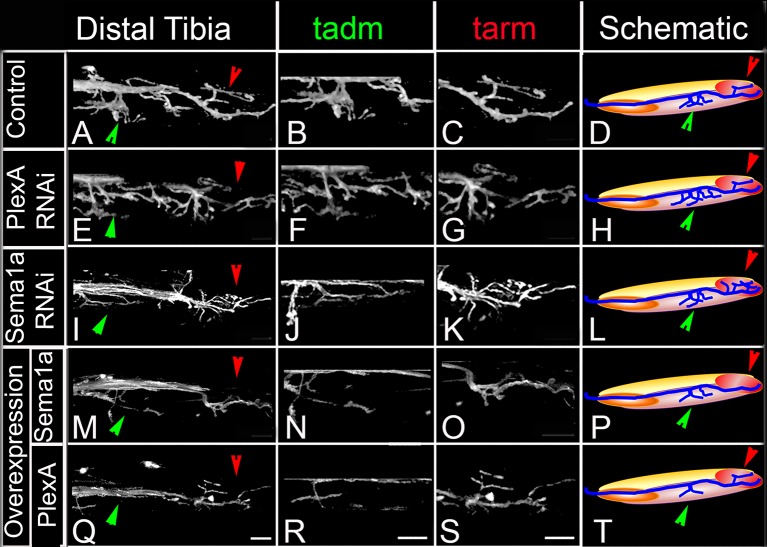
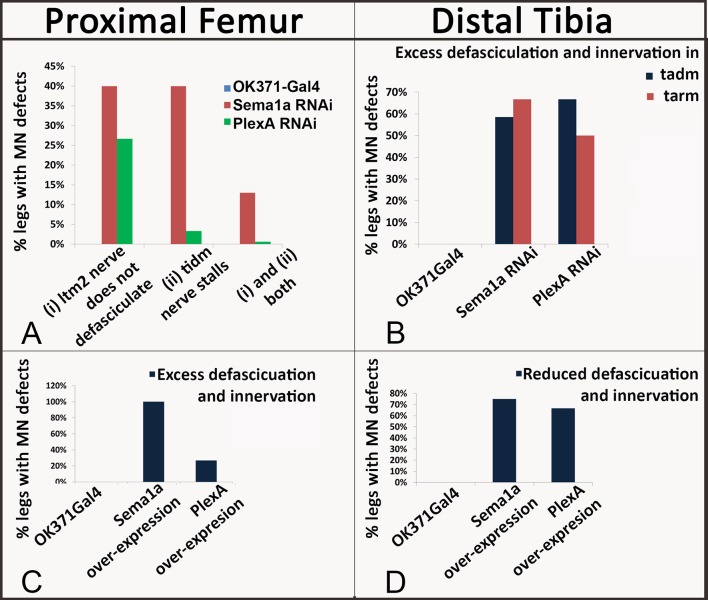
Figure 3. PlexA and Sema 1a are required for correct axonal projections of leg motoneurons in the distal tibia.
Targeted knockdown, overexpression, and labeling mediated by motoneuron-specific OK371-Gal4 driver. (A–D) Control innervation of distal tibia. Axon projection defects characterized by increased innervation observed in (E–H) PlexA RNAi knockdown and (I–L) Sema1a RNAi knockdown. Decreased defasciculation of axonal branches exiting the main motor nerve are observed in (M–P) Sema1a overexpression and (Q–T) PlexA overexpression. (A, E, I, M, Q) show overviews of distal tibia innervation. (B, F, J, N, R) show magnified views of innervation of tadm (tarsus depressor muscle). (C, G, K, O, S) show magnified views of innervation of tarm (tarsus reductor muscle). (D, H, L, P, T) show schematic summaries of tibia innervation. Green arrowheads point toward innervations in tadm and red arrowheads point toward tarm. Scale bars = 20 microns.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11572.008