Abstract
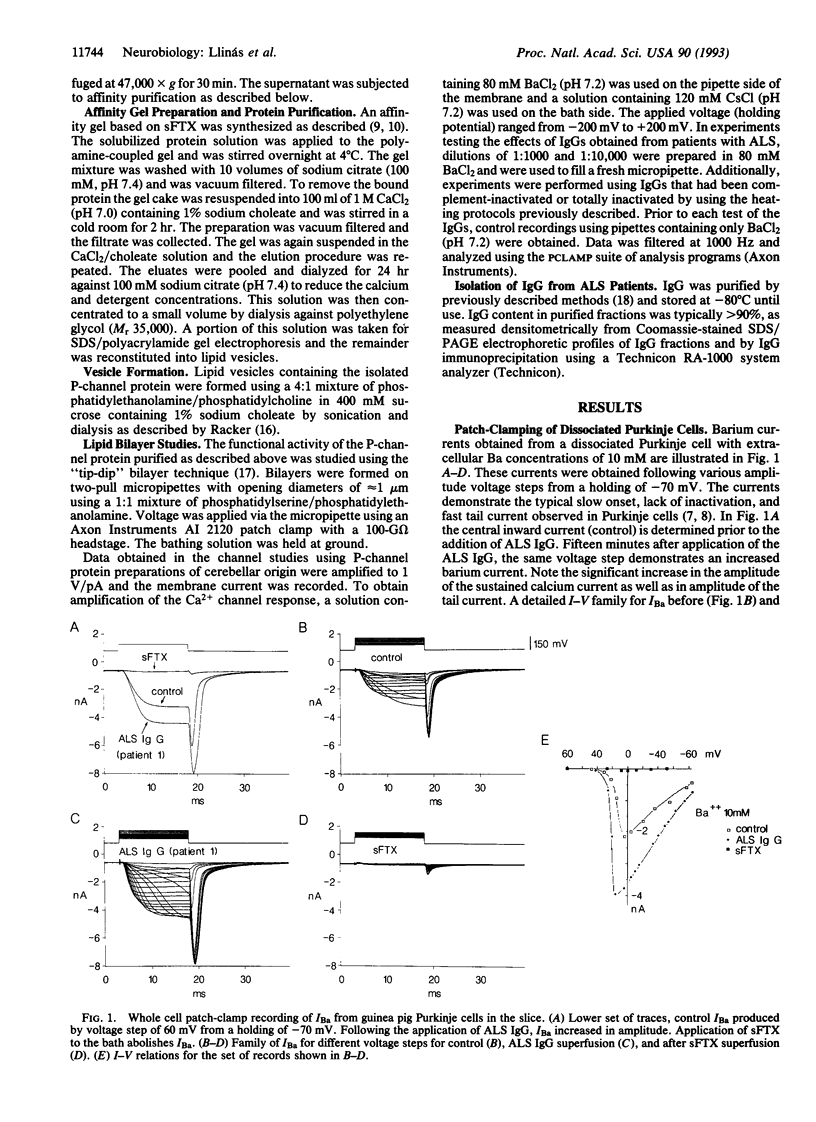
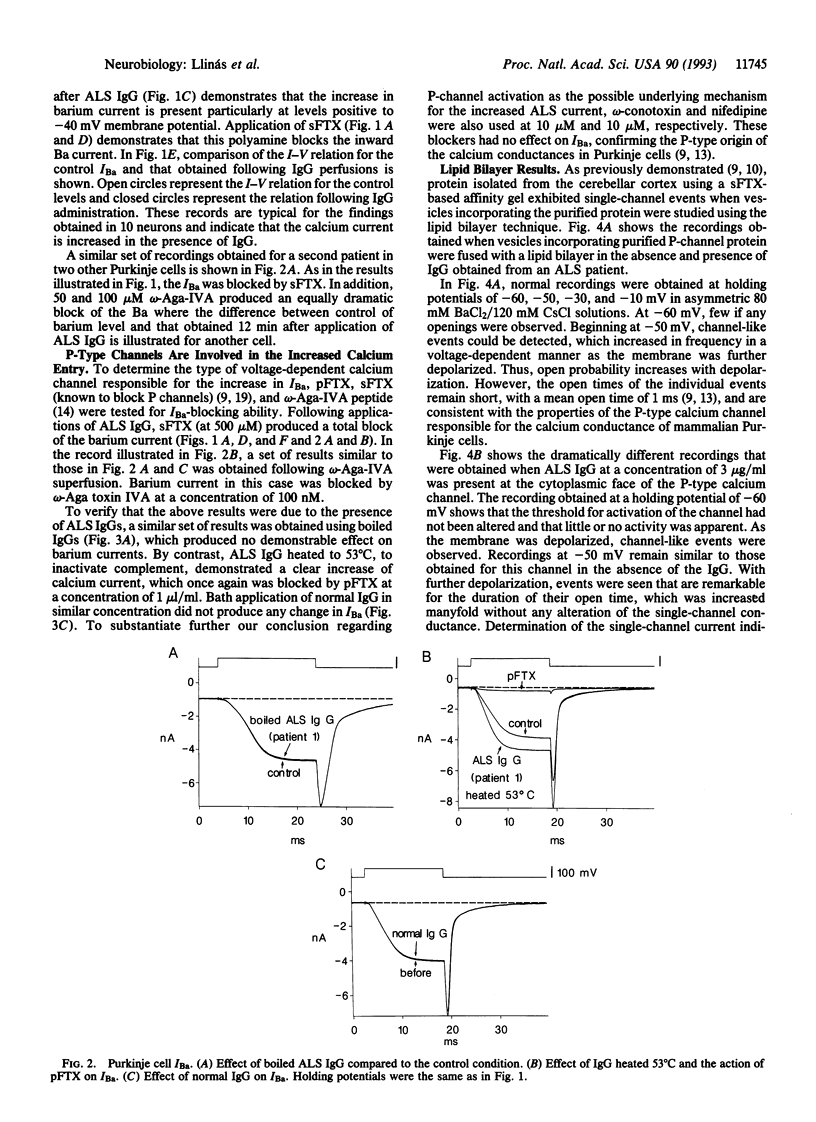
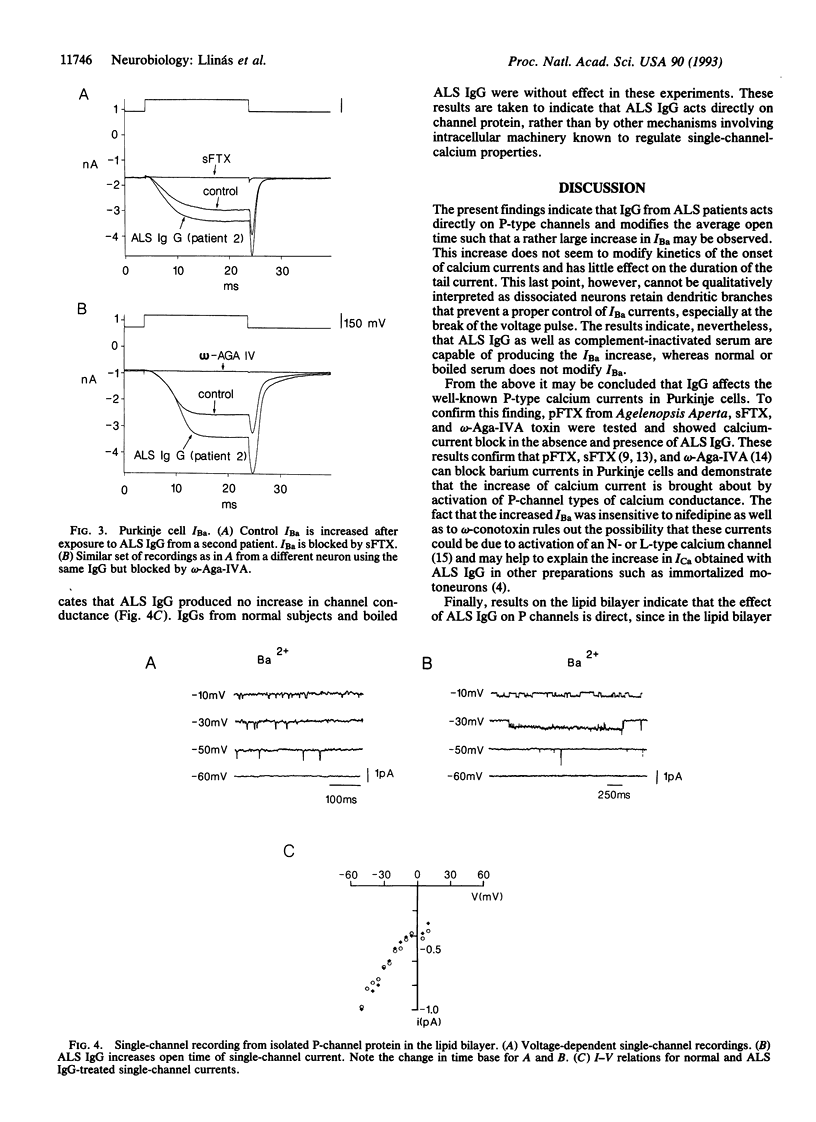
The effect of the IgG from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients was tested on the voltage-dependent barium currents (IBa) in mammalian dissociated Purkinje cells and in isolated P-type calcium channels in lipid bilayers. Whole cell clamp of Purkinje cells demonstrates that ALS IgG increases the amplitude of IBa without modifying their voltage kinetics. This increased IBa could be blocked by a purified nonpeptide toxin from Agelenopsis aperta venom (purified funnel-web spider toxin) or by a synthetic polyamine analog (synthetic funnel-web spider toxin) and by a peptide toxin from the same spider venom, omega-Aga-IVA. Similar results were obtained on single-channel recordings from purified P channel protein. The addition of ALS IgG increased single-channel IBa open time without affecting slope conductance. The results described above were not seen with normal human IgG nor with boiled ALS IgG. It is concluded that ALS IgG enhances inward current through P-type calcium channels. Since P-type Ca2+ channels are present in motoneuron axon terminals, we propose that the enhanced calcium current triggered by ALS IgG may contribute to neuronal damage in ALS.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel S. H., Engelhardt J. I., García J., Stefani E. Immunoglobulins from animal models of motor neuron disease and from human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients passively transfer physiological abnormalities to the neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):647–651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherksey B. D., Sugimori M., Llinás R. R. Properties of calcium channels isolated with spider toxin, FTX. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:80–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Latorre R. Phospholipid bilayers made from monolayers on patch-clamp pipettes. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84343-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbono O., García J., Appel S. H., Stefani E. IgG from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis affects tubular calcium channels of skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):C1347–C1351. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.6.C1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman D., Chen S., Aung T. T., Cherksey B., Sugimori M., Llinás R. R. Localization of P-type calcium channels in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7076–7080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Isolation of neurons suitable for patch-clamping from adult mammalian central nervous systems. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 May;16(3):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. W., Rudy B., Llinás R. Funnel-web spider venom and a toxin fraction block calcium current expressed from rat brain mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R., Sugimori M., Cherksey B. Voltage-dependent calcium conductances in mammalian neurons. The P channel. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Hillman D. E., Cherksey B. Distribution and functional significance of the P-type, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the mammalian central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90053-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnelli V., Sawada T., Delbono O., Smith R. G., Appel S. H., Stefani E. The action of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis immunoglobulins on mammalian single skeletal muscle Ca2+ channels. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:103–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Knowles A. F., Eytan E. Resolution and reconstitution of ion-transport systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:17–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan L. J., Sah D. W., Bean B. P. Ca2+ channels in rat central and peripheral neurons: high-threshold current resistant to dihydropyridine blockers and omega-conotoxin. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Hamilton S., Hofmann F., Schneider T., Nastainczyk W., Birnbaumer L., Stefani E., Appel S. H. Serum antibodies to L-type calcium channels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 10;327(24):1721–1728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212103272405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchitel O. D., Protti D. A., Sanchez V., Cherksey B. D., Sugimori M., Llinás R. P-type voltage-dependent calcium channel mediates presynaptic calcium influx and transmitter release in mammalian synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3330–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Sugimori M., Cherksey B., Llinás R. P-type calcium channels in the somata and dendrites of adult cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1185–1199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90076-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



