Abstract
A 59-year-old woman admitted to hospital in coma also showed generalized muscular rigidity and porphyria. After two days she became fully conscious but the muscular rigidity increased and persisted until death occurred 12 weeks later.
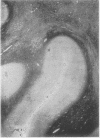
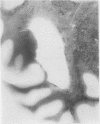
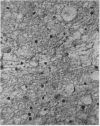
The brain showed diffuse degeneration of the white matter; symmetrical necrosis of the globus pallidus was associated with severe localized atherosclerosis.
The lesions probably resulted from the combined effects of porphyria and atherosclerosis. It is suggested that in later life unusual cerebral lesions may occur with porphyria because of associated atherosclerosis. The porphyria may be overlooked clinically.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COURVILLE C. B. The process of demyelination in the central nervous system. IV. Demyelination as a delayed residual of carbon monoxide asphyxia. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1957 Oct-Dec;125(4):534–546. doi: 10.1097/00005053-195710000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON J. B., GOLDBERG A. The neuropathology of acute porphyria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(2):495–509. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG A. Acute intermittent porphyria: a study of 50 cases. Q J Med. 1959 Apr;28(110):183–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIERONS R. Changes in the nervous system in acute porphyria. Brain. 1957 Jun;80(2):176–192. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.2.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLUM F., POSNER J. B., HAIN R. F. Delayed neurological deterioration after anoxia. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Jul;110:18–25. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620190020003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON E. P., Jr Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1961 Oct 26;265:815–823. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196110262651701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARZ G. A., MOULTON J. A. Porphyria; a clinical and neuropathologic report. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1954 Aug;94(2):221–247. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1954.00250020055004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRICH S. J. Diffuse degeneration of the cerebral white matter in severe dementia following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 Aug;19(3):163–185. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER S. R., WHITEHEAD T. P. Acute and latent porphyria. Lancet. 1956 Apr 28;270(6922):547–551. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]