Abstract
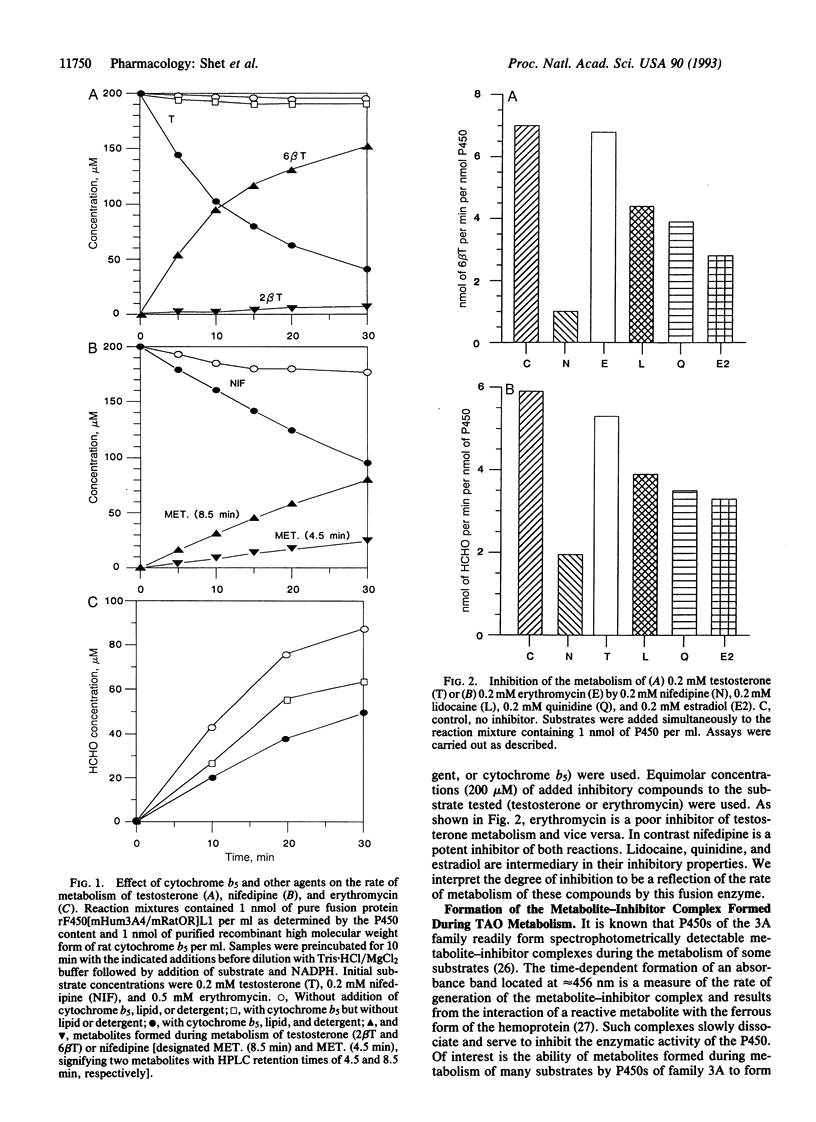
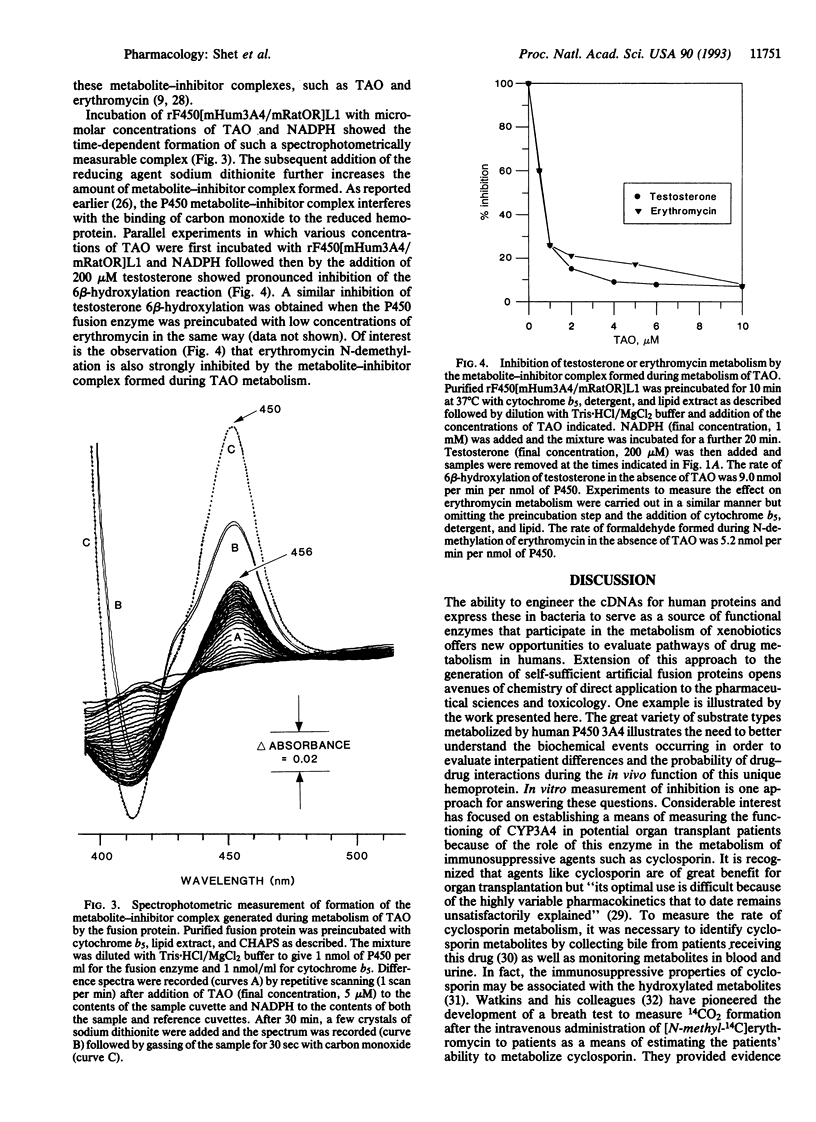
Human cytochrome P450 3A4 is recognized as the catalyst for the oxygen-dependent metabolism of a diverse group of medically important chemicals, including the immunosuppressive agent cyclosporin; macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin; drugs such as benzphetamine, nifedipine, and cocaine; and steroids; such as cortisol and testosterone to name but a few. We have engineered the cDNA for human cytochrome P450 3A4 by linkage to the cDNA for the rat or human flavoprotein, NADPH-P450 reductase (NADPH:ferrihemoprotein oxidoreductase, EC 1.6.2.4). An enzymatically active fusion protein (rF450[mHum3A4/mRatOR]L1) has been expressed at high levels in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity. Enzymatic studies show a requirement for lipid, detergent, and cytochrome b5 for the 6 beta-hydroxylation of steroids and the N-oxidation of nifedipine. In contrast, these additions are not required for the N-demethylation of erythromycin or benzphetamine. A spectrophotometrically detectable metabolite complex of P450 3A4 is formed during the metabolism of triacetyloleandomycin, and this has a pronounced inhibitory effect on the metabolism of both testosterone and erythromycin. These results relate to the interpretation of current methods used to assess the in vivo activity of P450 3A4.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlotto M. P., Trant J. M., Estabrook R. W. Measurement of steroid hydroxylation reactions by high-performance liquid chromatography as indicator of P450 identity and function. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:454–462. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)06114-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes H. J., Arlotto M. P., Waterman M. R. Expression and enzymatic activity of recombinant cytochrome P450 17 alpha-hydroxylase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5597–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian W. R., Sari M. A., Iwasaki M., Shimada T., Kaminsky L. S., Guengerich F. P. Catalytic activities of human liver cytochrome P-450 IIIA4 expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 25;29(51):11280–11292. doi: 10.1021/bi00503a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi C. L., Penman B. W., Steimel D. T., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. The development of a human cell line stably expressing human CYP3A4: role in the metabolic activation of aflatoxin B1 and comparison to CYP1A2 and CYP2A3. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Feb;12(2):355–359. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.2.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart D. C., Parkinson A. Cytochrome P450 IIIA1 (P450p) requires cytochrome b5 and phospholipid with unsaturated fatty acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Dec;291(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Guzelian P. S. Separation, purification, and characterization of a novel form of hepatic cytochrome P-450 from rats treated with pregnenolone-16 alpha-carbonitrile. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1279–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. W., Caudle D. L., Martin-Wixtrom C., Quattrochi L. C., Tukey R. H., Waterman M. R., Estabrook R. W. High-level expression of functional human cytochrome P450 1A2 in Escherichia coli. FASEB J. 1992 Jan 6;6(2):759–764. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.2.1537466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. W., Shet M. S., Caudle D. L., Martin-Wixtrom C. A., Estabrook R. W. High-level expression in Escherichia coli of enzymatically active fusion proteins containing the domains of mammalian cytochromes P450 and NADPH-P450 reductase flavoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10817–10821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam E. M., Baba T., Kim B. R., Ohmori S., Guengerich F. P. Expression of modified human cytochrome P450 3A4 in Escherichia coli and purification and reconstitution of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Aug 15;305(1):123–131. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Characterization of human cytochrome P450 enzymes. FASEB J. 1992 Jan 6;6(2):745–748. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.2.1537465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler K. A., Wrighton S. A., Kremers P., Guzelian P. S. Immunochemical evidence for multiple steroid-inducible hepatic cytochromes P-450 in the rat. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):27–33. doi: 10.1042/bj2450027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka S., Imai Y., Shimada T., Funae Y. Role of phospholipids in reconstituted cytochrome P450 3A form and mechanism of their activation of catalytic activity. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 7;31(26):6063–6069. doi: 10.1021/bi00141a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronbach T., Fischer V., Meyer U. A. Cyclosporine metabolism in human liver: identification of a cytochrome P-450III gene family as the major cyclosporine-metabolizing enzyme explains interactions of cyclosporine with other drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Jun;43(6):630–635. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronbach T., Mathys D., Umeno M., Gonzalez F. J., Meyer U. A. Oxidation of midazolam and triazolam by human liver cytochrome P450IIIA4. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunzendorf U., Brockmöller J., Jochimsen F., Roots I., Offermann G. Activity of cyclosporin metabolites M17 and M1. Transplant Proc. 1990 Aug;22(4):1697–1699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown K., Kolars J., Turgeon K., Merion R., Wrighton S. A., Watkins P. B. The erythromycin breath test selectively measures P450IIIA in patients with severe liver disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Mar;51(3):229–238. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olkkola K. T., Aranko K., Luurila H., Hiller A., Saarnivaara L., Himberg J. J., Neuvonen P. J. A potentially hazardous interaction between erythromycin and midazolam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Mar;53(3):298–305. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1993.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pershing L. K., Franklin M. R. Cytochrome P-450 metabolic-intermediate complex formation and induction by macrolide antibiotics; a new class of agents. Xenobiotica. 1982 Nov;12(11):687–699. doi: 10.3109/00498258209038944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessayre D., Descatoire V., Konstantinova-Mitcheva M., Wandscheer J. C., Cobert B., Level R., Benhamou P. J., Jaouen M., Mansuy D. Self-induction by triacetyloleandomycin of its own transformation into a metabolite forming a stable 456 nm-absorbing complex with cytochrome P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 15;30(6):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets J. J., Mason J. I. Ketoconazole: a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P-450-dependent drug metabolism in rat liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984 Sep-Oct;12(5):603–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. K., Trull A. K., Hue K. L., Best N. G., Wallwork J., Higenbottam T. W. Pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in heart and lung transplant candidates and recipients with cystic fibrosis and Eisenmenger's syndrome. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993 May;53(5):544–554. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1993.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. P., Hartman N. R., Venkataramanan R., Jardine I., Lin F. T., Knapp J. E., Starzl T. E., Burckart G. J. Isolation of 10 cyclosporine metabolites from human bile. Drug Metab Dispos. 1989 May-Jun;17(3):292–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Murray S. A., Winkelman L. G., Heuman D. M., Wrighton S. A., Guzelian P. S. Erythromycin breath test as an assay of glucocorticoid-inducible liver cytochromes P-450. Studies in rats and patients. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):688–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI113933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Turgeon D. K., Saenger P., Lown K. S., Kolars J. C., Hamilton T., Fishman K., Guzelian P. S., Voorhees J. J. Comparison of urinary 6-beta-cortisol and the erythromycin breath test as measures of hepatic P450IIIA (CYP3A) activity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Sep;52(3):265–273. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Attisano C., Guengerich F. P., Lapenson D. P. Human liver microsomal steroid metabolism: identification of the major microsomal steroid hormone 6 beta-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jun;263(2):424–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90655-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werringloer J. Assay of formaldehyde generated during microsomal oxidation reactions. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:297–302. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werringloer J., Estabrook R. W. Evidence for an inhibitory product-cytochrome P-450 complex generated during benzphetamine metabolism by liver microsomes. Life Sci. 1973 Nov 16;13(10):1319–1330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Maurel P., Schuetz E. G., Watkins P. B., Young B., Guzelian P. S. Identification of the cytochrome P-450 induced by macrolide antibiotics in rat liver as the glucocorticoid responsive cytochrome P-450p. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2171–2178. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Stevens J. C. The human hepatic cytochromes P450 involved in drug metabolism. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1992;22(1):1–21. doi: 10.3109/10408449209145319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukochi Y., Okita R. T., Masters B. S. Comparison of the properties of detergent-solubilized NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductases from pig liver and kidney. Immunochemical, kinetic, and reconstitutive properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):491–498. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



