Portable blood physiology meters exist that enable researchers to measure various parameters in field settings rather than having to store and transport samples. Although there is need for more thorough calibrations of these devices, they have much promise for conservation physiology of vertebrates.
Keywords: Biomarkers, field physiology, hand-held blood analyser, non-domestic, validation
Abstract
Non-human vertebrate blood is commonly collected and assayed for a variety of applications, including veterinary diagnostics and physiological research. Small, often non-lethal samples enable the assessment and monitoring of the physiological state and health of the individual. Traditionally, studies that rely on blood physiology have focused on captive animals or, in studies conducted in remote settings, have required the preservation and transport of samples for later analysis. In either situation, large, laboratory-bound equipment and traditional assays and analytical protocols are required. The use of point-of-care (POC) devices to measure various secondary blood physiological parameters, such as metabolites, blood gases and ions, has become increasingly popular recently, due to immediate results and their portability, which allows the freedom to study organisms in the wild. Here, we review the current uses of POC devices and their applicability to basic and applied studies on a variety of non-domesticated species. We located 79 individual studies that focused on non-domesticated vertebrates, including validation and application of POC tools. Studies focused on a wide spectrum of taxa, including mammals, birds and herptiles, although the majority of studies focused on fish, and typical variables measured included blood glucose, lactate and pH. We found that calibrations for species-specific blood physiology values are necessary, because ranges can vary within and among taxa and are sometimes outside the measurable range of the devices. In addition, although POC devices are portable and robust, most require durable cases, they are seldom waterproof/water-resistant, and factors such as humidity and temperature can affect the performance of the device. Overall, most studies concluded that POC devices are suitable alternatives to traditional laboratory devices and eliminate the need for transport of samples; however, there is a need for greater emphasis on rigorous calibration and validation of these units and appreciation of their limitations.
Introduction
Blood has been collected from non-human vertebrates for decades to obtain information about organismal physiology, health and condition. Blood is an essential and specialized bodily fluid that delivers necessary nutrients and transports metabolic waste products away from the tissues (Ku, 1997). As a result of its multi-faceted role in supporting organismal life, measurements of the chemical and haematological structure of blood can yield important information, often from a relatively small, non-lethal sample (Rogers and Booth, 2004; Cooke et al., 2005; Wimsatt et al., 2005). Veterinarians and animal health specialists routinely collect blood to evaluate the condition and health of animals (Schalm et al., 1975; Archer and Jeffcott, 1977; Thrall et al., 2012). Today, reference values for a range of species, including domestic and exotic vertebrates, are available to inform veterinary practice and enable health monitoring (see Thrall et al., 2012). Comparative physiologists (see Prosser, 1973) collect and study blood from a variety of model vertebrates in an attempt to understand organismal functions, such as osmoregulation (Beadle, 1957), cardiorespiratory capacity (White, 1978) and the evolutionary basis for, and ecological consequences of, intra- and inter-specific variation (Garland and Adolph, 1991; Garland and Carter, 1994; Spicer and Gaston, 1999). Likewise, much work has been devoted to understanding animal–environment interactions, such as effects of thermal extremes (di Prisco, 1997), living at high altitude (Hall et al., 1936) and seasonal influences on blood physiology (Erickson and Youatt, 1961).
Animal physiologists interested in understanding the consequences of a variety of stressors, such as climate change (Helmuth, 2009) and human disturbance (Busch and Hayward, 2009), also rely on markers in vertebrate blood to identify mechanisms of action, detect thresholds and predict consequences in the growing field of conservation physiology (Wikelski and Cooke, 2006; Cooke and O'Connor, 2010; Cooke et al., 2013). Traditionally, these applications required holding animals in captivity; however, a movement of veterinary practices towards conservation and wildlife surveillance (see Meffe, 1999; Deem et al., 2001) has led to the reinvigoration of comparative physiology, with a focus on the ecological and evolutionary processes in a diversity of non-domesticated taxa (Feder and Block, 1991; Mangum and Hochachka, 1998; Denver et al., 2009; Romero and Wikelski, 2010). This progression has led to the application of physiological approaches needed to understand and solve conservation problems (Cooke and O'Connor, 2010). Fortunately, the ‘field physiology toolbox’ has been expanding rapidly, enabling researchers to study physiological attributes, including blood physiology, outside of the laboratory and even in remote locations (Costa and Sinervo, 2004).
The ability to measure blood physiology repeatedly and accurately has relied historically on large, laboratory-bound equipment and/or complicated and time-consuming assays. While many of these traditional methods are widely accepted and still employed in laboratory/captive settings, they require field biologists to preserve and transport samples for later analysis or to focus on other observable measures, such as behaviour, instead of using physiological measures (St-Louis, 2000). Moreover, certain measurements, such as blood acid–base properties, require immediate reading for maximal accuracy, which is not possible in instances where remotely collected blood is transported back to a laboratory setting. Modern advancements in portable metering or point-of-care (POC) devices have the potential to allow biologists to move towards direct field analysis rather than laboratory-based analysis of samples. Originating in human medicine and later progressing into veterinary science, these devices have shown potential in field biology for a variety of taxa (e.g. Cooke et al., 2008; Atkins et al., 2010; Gallagher et al., 2010; Peiró et al., 2010; Gubala et al., 2012; Sampson et al., 2012).
For field biologists, the usefulness of POC devices is largely tied to their portability, allowing the device to be transported in situ with the researcher and study organism for nearly immediate sampling and results (Morgan and Iwama, 1997; Cooke et al., 2008). This early insight provided by POC devices has a range of advantages, including the option to modify a protocol on site, which is useful because pilot testing is often not possible in field studies. In addition, immediate analysis of samples can minimize the potential loss of samples by breakage, transportation and/or degradation (Clark et al., 2011). However, issues may arise when POC devices are applied more broadly, both in terms of environmental conditions and taxonomic group (Costa and Sinervo, 2004). To be functional broadly in field environments, POC devices must compensate for fluctuations in background humidity and temperature as well as account for the physiological differences between relatively stable homeotherms (for which most POC devices are initially calibrated) and heterothermic models that vary along with their external conditions (Costa and Sinervo, 2004; Gallagher et al., 2010; Mecozzi et al., 2010). Physiological conditions and species-specific differences may further complicate the reliability of POC devices, leading to inaccurate and/or imprecise results; as such, the development of species-specific blood physiology ranges may be necessary. Although there are obvious drawbacks to the use of POC devices in the field on non-domesticated and less studied organisms, the ease of use and portability of these devices may largely outweigh the disadvantages. In addition, owing to the affordability of POC devices, the growing number of validation studies on non-domesticated species and the continuing technological advances (e.g. more parameters, greater portability), these devices are likely to play an integral role in modern biology for basic and applied studies.
In this review, we have collected and synthesized information from a number of studies that have used portable POC devices to measure blood physiology parameters from non-domesticated vertebrate animals. Although POC devices vary in size, our review was limited to ‘easily portable’ POC devices due to their increased applicability to field biology. We defined ‘easily portable’ as any device <5 kg that was powered by a self-contained battery and did not require external electricity or compressed gas canisters. We assumed, based on those criteria, that devices could be carried easily by backpack, horseback, small aeroplane, canoe, etc. to remote areas. The objectives of this review were as follows: (i) to examine the current uses of POC devices in medical and veterinary science; (ii) to summarize the calibration and application of POC devices for use on non-domesticated vertebrate taxa (fish, reptiles, birds and mammals); (iii) to identify the limitations of such devices; and (iv) to consider potential future uses of POC devices.
History of point-of-care device development
In the past two decades, POC devices have revolutionized at-home patient care and emergency diagnostic capability by enabling paramedics, healthcare professionals and even patients to measure biochemical markers rapidly and accurately. The use of POC devices in humans was first recorded in 1994, and by 2009 25% of tests were being performed at the site of care (Plebani, 2009). Based on their success and convenience, the use of POC devices has been projected to increase by 12% per year (Plebani, 2009).
These devices can and have been used in various settings, including management and treatment of disease symptoms in the home and in paramedic care (i.e. ambulance), as well as use in field diagnostics (Plebani, 2009; Cima, 2011). Perhaps the most widespread application of such POC devices is for diabetic monitoring of blood glucose, with many variants available for purchase from pharmacies, which have been integrated into day-to-day management of insulin levels by millions of people around the world (Klonoff, 2005). Furthermore, POC devices have been integrated into emergency departments; for example, some units can measure biochemical markers for patients with acute chest pains suggestive of myocardial injury to provide a rapid, whole-blood analysis in 20 min (Apple et al., 2000). Ideally, these devices should help to reduce turnover time for patients in hospitals and, by doing so, enable better utilization of resources, reduce time to discharge and ensure better patient management (Altinier et al., 2001). Not only will the technology of POC devices reduce healthcare costs in North America but, owing to the portability of these devices, it also has the potential to allow the distribution of this healthcare across the world and into less developed regions (Cima, 2011). Human uses have been expanded further to include the monitoring of performance athletes (e.g. lactate levels) and, indeed, some POC devices have been developed for that explicit purpose (e.g. Lactate Pro; Pyne et al., 2000).
Since the introduction of POC devices in the medical field, veterinary science has adopted their use in clinics to monitor the health of animals (Allen and Holm, 2008). As a result of their origins in human medicine (Acierno et al., 2007), quality control is necessary because of the many physiological and biochemical differences across taxa (Allen and Holm, 2008); however, there are a growing number of such devices designed specifically for domesticated animals (e.g. Gluco Pet). Testing the precision of a POC device, or validation, is done by comparing animal- and parameter-specific values with those obtained from a ‘gold standard’ bench-top analyser or laboratory assays (e.g. Clark et al., 2008). The process of validation of POC devices is ongoing, as new devices and biomarkers used to assess animal health are constantly emerging. This task has proved to be even more complex because a specific range of measured values for a particular parameter may vary in its concordance with a bench-top analyser (e.g. POC values may agree better with laboratory-based values inside but not outside of a specific range; Hollis et al., 2008).
Once validated for a certain animal-specific physiological parameter, POC devices have been shown to improve the efficiency of establishing both a diagnosis and a prognosis for that animal (Acierno et al., 2007). Point-of-care devices allow for easy and early identification of sick animals and do not require specialized laboratory personnel (Steinmetz et al., 2007). For example, blood lactate as a measure of tissue hypoxia in sick animals can be measured quickly and accurately with a POC device using a small volume of blood (Mizock and Falk, 1992). Due to the low cost associated with the use of POC testing, many private animal owners, in particular horse owners, use these devices for establishing treatment action, because this early information can be used to determine whether additional, more expensive testing or treatment is necessary (Delesalle et al., 2007). In addition, as new biomarkers are discovered, the hope is that new POC devices will also emerge, benefitting not only veterinary medicine, but also other fields, such as conservation and field physiology.
General approach
We examined various studies that used POC devices on a range of non-domesticated vertebrate taxa. Despite the prominent use and origins of POC devices in emergency patient care and veterinary medicine of domesticated animals (e.g. horses, dogs, cats, mice), we excluded all such studies herein, given our focus on wild, traditionally non-domesticated animals. In some cases, it was unclear whether animals (mostly fish; e.g. Gomes et al., 2006a, b; Trushenski et al., 2010) in captivity were wild or captive bred, so we relied on our best judgement. We did encounter several studies that used POC devices with invertebrates (e.g. Allender et al., 2010; Butcher et al., 2012), but focused solely on vertebrates, given that invertebrate blood physiology is less well studied. As noted above, we included only studies that used devices considered to be ‘easily portable’. In addition, we excluded all portable devices that were not electronic (e.g. refractometers for plasma protein) or that simply separated blood constituents [e.g. manual or electronic centrifuges for quantifying haematocrit (Hct)].
Primary literature searches were conducted between 15 September and 18 November 2012. Relevant papers were found by searching a variety of academic journal databases (e.g. Web of Science, Scopus) and Internet search engines (e.g. Google Scholar) with relevant search terms (e.g. ‘point-of-care analyser’, ‘portable clinical analyser’, ‘glucose meter’), as well as identifying citations by other papers. To identify papers that fitted our criteria, we reviewed the study design to determine whether a POC device was used. We then extracted key information and populated a database with predetermined headings, such as species, parameters tested, POC device used, type of study and limits. Studies were classified either as validations, which compared the POC devices with traditional laboratory analysis, or as applications, which used POC devices to measure blood chemistry for either basic or applied research. In some studies, POC devices were used for both validation and application purposes, and such studies were therefore classified accordingly as both.
Characteristics and trends in point-of-care device literature
General characteristics
The literature search yielded 79 studies involving the use of POC devices in a variety of non-domesticated vertebrate species. The use of POC devices in ecology and conservation is a relatively novel concept, because the majority of published articles have appeared within the last decade and range from 1995 to the present. We collected articles from various journals (n = 42), which included a wide variety of themes, such as veterinary medicine, disease, toxicology, conservation, physiology and food science. Of the 79 peer-reviewed studies, 8.9% (n = 7) of articles were published in Fisheries Research, while 7.6% (n = 6) of articles were published in Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A. Validation studies comprised 17.7% (n = 14) of papers, from which applications studies accounted for 78.5% (n = 62) of the total. Only 3.8% (n = 3) of studies combined both validation and application.
Taxonomic patterns
We retrieved papers from four different taxonomic vertebrate groups, namely fish, birds, reptiles and mammals. Due to the large number of fish studies and the associated physiological differences between teleost and cartilaginous fishes, we separated all Chondrichthyes-based studies into a separate group. Teleost fish were the most-studied taxa, accounting for more than half of the total number of articles (n = 48; 60.8%). Studies focusing on Chondrichthyes accounted for 15.2% (n = 12) of all studies, while mammals, reptiles and birds accounted for 11.4% (n = 9), 8.9% (n = 7) and 3.8% (n = 3), respectively. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) was the most-studied species (8.9%; n = 7), while studies focused on smallmouth bass (Micropterus dolomieu) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) were the second and third most-studied organisms, with 7.6% (n = 6) and 6.3% (n = 5), respectively.
Point-of-care device tools and parameters tested
In total, studies used 20 different POC devices that fit the ‘easily portable’ definition (see Introduction). Although we found several studies using the VetScan analyser, which is considered a POC device by the authors of those papers, it did not fit our definition of ‘easily portable’ and was therefore excluded. The i-STAT hand-held blood analyser was the device most used (53.2%; n = 42), followed by the Lactate Pro lactate meter and Accu-chek glucometer, which were used in 27.8% (n = 22) and 24.1% (n = 19) of assessed studies, respectively (Table 1). In addition, glucometers were the most diverse POC device, with nine different models being used. The majority of devices used (85%; n = 17) measured only one parameter, such as the Lactate Pro, while the i-STAT analyser was the most used device that was capable of analysing more than one blood parameter. Finally, the majority of studies used whole blood, rather than plasma, when using the POC devices (94.9%; n = 75).
Table 1:
List of most common point-of-care devices used in studies analysed (note that not all data are available due to products being discontinued)
| Device | Company | Parameters tested | Additional cartridges/strips | Type of blood required | Amount of blood required (μl) | Battery required | Range (mmol/l unless otherwise stated) | Dimensions (length × width × height; mm) | Weight (g) | Current validations | Temperature range (°C) | Humidity range (relative humidity unless stated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accu-chek Advantage | Roche Diagnostics/Boehringer Mannheim | Glucose | Yes; Accu-chuk strips | Whole | 0.6 | One 3 V lithium battery | 0.6–33.3 | 84 × 53 × 21 | 60 | No | 10–40 | 10–90% |
| IQ Prestige | Home Diagnostics Inc. | Glucose | Yes; Prestige IQ strips | Whole | 4 | One AAA 1.5 V alkaline battery | 1.4–33.3 | 70 × 102 × 20 | 102 | Burdick et al. (2012), mammal | 15–37 | Any non-condensing atmosphere |
| Ascensia Elite | Bayer Corporation | Glucose | Yes; Ascensia Elite Test strips | Whole | 2 | One 3 V lithium battery | 1.1–33.3 | 81 × 51 × 14 | 50 | No | 10–40 | 20–80% |
| ExacTech | Abbott Point of Care | Glucose | Yes; ExacTech strips | Whole | 10 | Not available | Not available | 93 × 55 × 10 | 43 | No | Not available | Not available |
| Freestyle Freedom Lite | Abbott Point of Care | Glucose | Yes; Freestyle Freedom Lite strips | Whole | 0.3 | One 3 V lithium battery | 1.1–27.9 | 8.38 × 5.08 × 1.3 | 42.35 | Wells and Pankhurst (1999), fish | 4–40 | 5–90% non-condensing |
| Glucometer Elite | Bayer Corporation | Glucose | Yes; Glucometer Elite strips | Whole | 2 | Two 3 V lithium batteries | 1.1–33.3 | 97.8 × 56 × 14.5 | 60 | No | 10–40 | 20–80% |
| Sure Step | Life Scan/Johnson and Johnson | Glucose | Yes; Sure Step strips | Whole | 5 | Three AA 1.5 V alkaline batteries | 0–500 mg/dl | 89 × 61 × 20 | 107.7 | Lieske et al. (2002), birds | 10–35 | 10–90% |
| One Touch Ultra | Life Scan/Johnson and Johnson | Glucose | Yes; One Touch Ultra strips | Whole | 1 | One 3 V lithium battery | 1.1–33.3 | 79 × 57 × 23 | 42 | No | 6–44 | 10–90% |
| Precision QID | Medisense | Glucose | Yes; MicroFlo Plus strips | Whole | 3.5 | Non-replaceable | 1.1–33.3 | 97 × 48 × 15 | 39 | No | 4–30 | Not available |
| Accusport Analyser | Boehringer Mannheim | Lactate | Yes; Lactate Test strips | Whole | 10–20 | Three 1.5 V AAA batteries | 0.8–22 | 115 × 62 × 18.5 | 100 | Wells and Pankhurst (1999), fish | 5–35 | 10–90% |
| Accutrend | Roche Diagnostics | Lactate | Yes; Lactate Test strips | Whole | 20–25 | Three 1.5 V AAA batteries | 0.8–22 | 115 × 62 × 18.5 | 100 | No | 5–35 | 10–90% |
| Lactate Pro | Arkray KDK | Lactate | Yes; Lactate Pro Strips | Whole | 5 | Two 3 V lithium batteries | 0.8–23.3 | 83.8 × 55 × 14.5 | 50 | No | 10–40 | 20–80% |
| HemoCue | Hemocue 201+ | Haemoglobin | Yes; meseauring cuvette | Non-specific | Non-specific | Four AA batteries | 0–256 g/l | 160 × 85 × 43 | 350 | Clark et al. (2008) | Not available | Not available |
| BMS Hemoglo-binometer | BMS | Haemoglobin | Yes | Non-specific | Non specific | Two size ‘C’ batteries | 4–20 g/dl | 170 × 70 × 40 | Not available | Iwama et al. (1995) | 10–40 | Not available |
| IQ128 Elite | IQ Scientific Instruments Inc. | pH | No | Non-specific | Non-specific | Two 3 V lithium batteries | pH 2–12 | 152.4 × 78.57 × 16.38 | 450 | Brown et al. (2008), fish | 5–40 | Not available |
| WTW pH Meter pH330 | Hoskin Scientific Ltd | pH | No | Non-specific | Non-specific | Four AA batteries | −2.00 to 19.99 pH units | 172 × 80 × 37 | 300 | No | −5 to 105 | Not available |
| SevenGo Pro | Mettler Toledo | pH and ion | No | Non-specific | Non-specific | Four AA batteries | −2.00 to 19.99 pH units | 220 × 90 × 45 | 325 | No | 0–40 | 0–85% |
| IRMA True Point | International Technidyne Corporation | Various; lactate, glucose, pH, variety of ions | Yes; various cartridges depending on parameters to be tested | Whole blood or plasma | 125–500 | One 7.2 V battery | Various ranges depending on parameters | 292.1 × 211.3 × 127 | 2381 | No | 12–30 | 0–80% non-condensing |
| i-STAT | Abbott Point of Care | Various; lactate, glucose, pH, variety of ions | Yes; various cartridges depending on parameters to be tested | Non-specific | Non-specific | Two 9 V lithium batteries | Various ranges depending on parameters | 209 × 64 × 52 | 520 | No | 16–30 | 0–90% |
| Ames Mini-lab | Miles Canada Inc. | Various | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | Iwama et al. (1995) | Not available | Not available |
Summary of taxon-specific validation and application studies
Chondrichthyes
Validation studies
Only two studies were found that assessed the accuracy of POC devices with Chondrichthyes species. Both validation studies compared laboratory-based equipment with POC devices using linear regressions (Table 2). Gallagher et al. (2010) used the i-STAT analyser to measure acid–base parameters and/or a lone metabolite (lactate) in the whole blood of three different Chondrichthyes species. The i-STAT analyser was determined to be acceptable for the measurement of pH, partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) and carbon dioxide (pCO2) with temperature correction, as well as lactate, but given that derived correction factors varied by species and only a lone temperature point was examined, the authors cautioned against broad applicability across taxa and temperatures without further testing (Gallagher et al., 2010). Awruch et al. (2011) determined that the use of the Lactate Pro was acceptable for measuring lactate, using a single species (i.e. Galeorhinus galeus), despite the fact that the device consistently overestimated lactate concentrations in whole blood relative to plasma. Further research is suggested into this lack of consistency between blood and plasma lactate values (Awruch et al., 2011). While not a validation relative to traditional instrumentation, a third study found compatibility in side-by-side acid–base values between two POC instruments (i-STAT analyser vs. IRMA TruPoint analyser) when reading whole blood from minimally stressed chondrichthyans (Mandelman and Skomal, 2009). While more work is needed in parameters beyond acid–base, initial studies signify that POC devices can be acceptable tools for blood parameter readings in Chondrichthyes.
Table 2:
The point-of-care (POC) device validation studies used in this study, grouped by class
| Citation | Species | Temperature (°C) | POC device used | Standard method | Analyte measured | Comparison with POC reading | Acceptable comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Awruch et al. (2011) | Shark (Galeorhinus galeus) | Not available | Lactate Pro | Enzymatic kit/spectrophotometer | Lactate | Similar | Yes |
| Gallagher et al. (2010) | Sharks (Carcharhinus plumbeus, Mustelus canis) | 25 | i-STAT (CG4+) | Blood gas analyser (thermostatted) | pH | Similar | Yes |
| Blood gas analyser (thermostatted) | pO2 | Similar | Yes | ||||
| Blood gas analyser (thermostatted) | pCO2 | Similar | Yes | ||||
| Laboratory lactate and glucose analyser | Lactate | Similar | Yes | ||||
| Brown et al. (2008) | Bony fish (Gadus morhua) | Not available | Lactate Pro | Enzymatic kit/spectrophotometer | Lactate | Similar | Yes |
| Clark et al. (2008) | Bony fish (Oncorhynchus nerka, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha, Thunnus orientalis, Scomber japonicus) | Not available | HemoCue | Drabkin method | Haemoglobin | Higher | Somewhat |
| Cooke et al. (2008) | Bony fish (Albula vulpes) | 21–25 | i-STAT (E3+) | Laboratory chemistry analyser | Na+ | Higher | Yes |
| K+ | Lower | Yes | |||||
| Cl− | Lower | Somewhat | |||||
| Centrifuge | Haematocrit | Variable | Yes | ||||
| Accu-Chek Advantage | Laboratory chemistry analyser | Glucose | Similar | Yes | |||
| DiMaggio et al. (2010) | Bony fish (Fundulus seminolis) | Not available | i-STAT (E3+) | Centrifuge | Haematocrit | Lower | No |
| Flame photometer | Na+ | Lower | No | ||||
| Flame photometer | K+ | Lower | No | ||||
| Chloridometer | Cl− | Higher | No | ||||
| Evans et al. (2003) | Bony fish (Oreochromis niloticus) | 25–28 | One Touch Ultra | Laboratory colorimetric method | Glucose | Lower | Yes |
| Harrenstien et al. (2005) | Bony fish (Sebastes melanops, Sebastes mystinus) | 11.5 | i-STAT (EC8+) | Laboratory chemistry analyser | Na+ | Lower | Somewhat |
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | K+ | Similar | No | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Cl− | Variable | No | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | BUN | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Glucose | Similar | No | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Haemoglobin | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Blood gas analyser | pH | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Blood gas analyser | pCO2 | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Blood gas analyser | TCO2 | Lower | No | ||||
| Blood gas analyser | HCO3− | Lower | No | ||||
| Blood gas analyser | Base excess | Lower | No | ||||
| Iwama et al. (1995) | Bony fish (Salmo salar) | Not available | ExacTech | Laboratory assay kit | Glucose | Similar | Yes |
| BMS Hemoglobinometer | Laboratory assay kit | Haemoglobin | Similar | Yes | |||
| Ames minilab | Laboratory assay kit | Glucose, haemoglobin | Similar | Yes | |||
| Serra-Llinares et al. (2012) | Bony fish (Gadus morhua) | 4 | Lactate Pro | Reference values | Lactate | Similar | Yes |
| Wells and Pankhurst (1999) | Bony fish (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | 14–40 | Accuchek Advantage | Hexokinase method | Glucose | Lower | Somewhat |
| Accusport | Enzymatic kit/spectrophotometer | Lactate | Lower | Somewhat | |||
| McCain et al. (2010) | Reptiles (Pogona vitticeps, Tiliqua gigas, Geochelone platynota, Geochelone elegans, Boa constrictor, Pituophis melanoleucus) | Not available | i-STAT (6+) | Laboratory chemistry analyser | Na+ | Similar | Somewhat |
| K+ | Similar | Somewhat | |||||
| Cl− | Similar | Somewhat | |||||
| Glucose | Similar | Somewhat | |||||
| Wolf et al. (2008) | Reptile (Caretta caretta, Chelonia mydas, Lepidochelys kempii) | 18.9–27.2 | i-STAT (EC8+) | Centrifuge | Haematocrit | Lower | Somewhat |
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Na+ | Similar | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | K+ | Similar | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Cl− | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Glucose | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | BUN | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Lieske et al. (2002) | Bird (Cerorhinca monocerata) | Not available | Accu-Chek Advantage | Reagent strips | Glucose | Similar | Yes |
| Precision QID | Reagent strips | Glucose | Similar | Yes | |||
| Glucometer Elite | Reagent strips | Glucose | Similar | Yes | |||
| Sure Step | Reagent strips | Glucose | Similar | Yes | |||
| Burdick et al. (2012) | Mammal (Odocoileus virginianus) | Not available | IQ Prestige Smart | Laboratory/portable chemistry analyser | Glucose | Variable | No |
| Prestige Smart | Laboratory/portable chemistry analyser | Glucose | Variable | No | |||
| Hopper and Cray (2007) | Mammal (Macaca fasicularis) | Not available | i-STAT (EC8+) | Centrifuge | Haematocrit | Lower | Somewhat |
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Na+ | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | K+ | Similar | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Cl− | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | BUN | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Glucose | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Haemoglobin | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | TCO2 | Higher | Yes | ||||
| Larsen et al. (2002) | Mammal (Mirounga angustirostris) | Not available | i-STAT (6+) | Laboratory chemistry analyser | Na+ | Lower | No |
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | K+ | Similar | Yes | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Cl− | Higher | Somewhat | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | BUN | Similar | Yes | ||||
| Laboratory chemistry analyser | Glucose | Lower | Somewhat | ||||
| Centrifuge | Haematocrit | Similar | Yes |
Na+, sodium; K+, potassium; Cl−, chloride; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; TCO2, total carbon dioxide; pCO2, partial pressure of carbon dioxide; HCO3, bicarbonate; pO2, oxygen partial pressure. For each species and analyte, the POC and standard (control) device are presented together with the relative comparison between the two. Where possible, the relevant body/experimental temperatures are presented. The distilled opinions presented by the authors of each study are also presented, but case-by-case caveats are not reported here. Many papers with ‘acceptable’ comparisons argue the need for corrective calculations or find these devices acceptable for relative rather than absolute measurement of an analyte.
Application studies
As a result of their frequency of capture in commercial fisheries as bycatch and target species, many application studies of chondrichthyans have focused on the physiological consequences related to acute capture stress. The physiological effects of otter trawl capture in spiny dogfish was a reoccurring topic, presented by Mandelman and Farrington (2007a, b) as a duo of papers, which assessed pH, pO2 and pCO2 values in relationship to various aspects of capture (e.g. transport, captivity; Mandelman and Farrington, 2007b). Researchers have compared pH values generated with POC devices for Chondrichthyes captured by long-line (Mandelman and Skomal, 2009; Brooks et al., 2011; Hyatt et al., 2012), rod and reel (Brill et al., 2008) and gillnet (Frick et al., 2012; Hyatt et al., 2012). Additional physiological parameters associated with aerial exposure and seasonality (Cicia et al., 2012), tonic immobility (Brooks et al., 2011) and reference ranges of wild and captive individuals (Naples et al., 2012) have been studied. Most of these studies were conducted in the field, although four studies (Brill et al., 2008; Brooks et al., 2011; Cicia et al., 2012; Naples et al., 2012) were conducted fully or partly in a laboratory setting. A total of four POC devices were used to assess blood physiology in various Chondrichthyes species. The i-STAT analyser, a multi-parameter POC device, was the most commonly used device, while two single-parameter devices (Accu-chek glucometer and Lactate Pro lactate meter) were both used in more than one study. Numerous blood parameters were measured, with pH, lactate and pCO2 being the most commonly studied variables as indicators of acute stress.
Teleost fish
Validation studies
Point-of-care devices have been used widely in teleost fishes. The accuracy of these devices has been validated by nine studies in teleosts, where POC devices were statistically compared with laboratory-based equipment (Table 2). The i-STAT analyser has been validated for use in bonefish (Albula vulpes; Cooke et al., 2008) and Seminole killifish (Fundulus seminoles; DiMaggio et al., 2010) as well as two species of rockfish (Sebastes melanops and Sebastes mystinus; Harrenstien et al., 2005). Cooke et al. (2008) validated the i-STAT analyser for chloride (Cl−), sodium (Na+), potassium (K+) and haematocrit (Hct), and although the POC device and laboratory reference results deviated slightly, they concluded that relative differences could be determined accurately for bonefish. This differed from a study by DiMaggio et al. (2010), where the same blood parameters were assessed by the i-STAT, but the device was determined to be unsuitable for assessment in Seminole killifish, largely due to issues with blood clotting. In a third study on two species of rockfish by Harrenstien et al. (2005), the i-STAT was validated for pH, pCO2, Na+, urea nitrogen, Hct and haemoglobin (Hb); however, it was found to be unsuitable for glucose (due to a wide reference range), total CO2, bicarbonate (HCO3−) and K+ (due to unknown factors or device inconsistency), as well as Cl− (and therefore anion gap; as these values were outside the measurable range of the device). The Ames Minilab and ExacTech glucose meter has also been validated for use in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Atlantic salmon for analysis of glucose and Hb but not erythrocyte number (Iwama et al., 1995). Minilab erythrocyte number measurements were thought to have varied from laboratory reference values due to physiological differences in human and teleost red blood cells, because this device was originally calibrated for use on human samples (Iwama et al., 1995). Generally, these studies suggest that the i-STAT, Minilab analyser and ExacTech glucose meter are useful in the measurement of blood parameters in teleost fish; however, species-specific validation is necessary for these devices because they were originally designed for use on mammals.
Glucose has also been validated for measurement by multiple versions of the Accu-chek, Freestyle Freedom Lite and the OneTouch Ultra glucose meter. Two other studies determined that glucose could be measured by the Accu-chek glucose meter in bonefish (Cooke et al., 2008) and rainbow trout (Wells and Pankhurst, 1999). One further study validated the use of the OneTouch Ultra glucose meter in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus; Evans et al., 2003). Overall, these studies suggested that relative rather than absolute values should be represented, because these devices tended to underestimate glucose values compared with laboratory reference values.
Two lactate POC devices, the Accusport and Lactate Pro lactate analysers, have been validated for use in teleost fishes. The Accusport (Wells and Pankhurst, 1999) lactate meter underestimated lactate levels compared with laboratory reference values in rainbow trout; similar to glucose, it was suggested that relative rather than absolute values should be represented. Alternatively, Brown et al. (2008) found that the Lactate Pro meter provided more accurate lactate values in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua), when compared with laboratory reference values; however, resting lactate levels were below the detection limit of this meter. Serra-Llinares et al. (2012) has suggested that the Lactate Pro meter can effectively measure lactate levels from frozen plasma in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). These studies suggest that these two POC devices may provide reliable and useful lactate measurements.
Haemoglobin measurements by POC devices have been validated for the BMS Hemoglobinometer and the HemoCue haemoglobin analyser in four Salmonid and two Perciformes species. Iwama et al. (1995) found that the BMS Hemoglobinometer accurately measured Hb levels in two salmonid species; however, readings below 4 g/dl were not possible. Haemoglobin levels were generally overestimated by the HemoCue haemoglobin analyser in comparison to laboratory analysis (Drabkin's method) in two Salmonid and two Perciformes species; however, it was suggested that calibration equations could be applied to the data due to the systematic nature of the overestimation (Clark et al., 2008). Overall, both POC devices may provide valuable Hb measurements, provided they are validated in the species of interest prior to application.
Application studies
Teleosts represent an important group of vertebrates in fisheries and aquaculture; as such, there is a demand for understanding the physiological impacts of these practices on fish. Point-of-care devices provide a convenient method to assess the effects of commercial and recreational fishing on a number of fish species. The effects of catch-and-release angling and barotrauma have been assessed mainly using glucose and lactate levels as indicators of stress, as well as Hct and Hb in smallmouth and largemouth bass (Micropterus salmonides; Gravel and Cooke, 2008; Hanson et al., 2008; White et al., 2008; Nguyen et al., 2009; Thompson et al., 2012), muskellunge (Esox masquinongy; Landsman et al., 2011), northern pike (Esox lucius; Arlinghaus et al., 2009), great barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda; O'Toole et al., 2010), snapper (Pagrus auratus; Wells and Dunphy, 2009) and bonefish (Suski et al., 2007). Henry et al. (2009) quantified the effects of fishing lure retention on smallmouth bass (glucose and lactate), while Roth and Rotabakk (2012) assessed the consequences of commercial and recreational fisheries in saithe (Pollachius virens; multiple parameters).
Field and laboratory-based experiments as well as aquaculture facility practices generally require fish handling. As such, the physiological effects of fish manipulation have been assessed in a number of studies using POC devices. Fish capture, transportation, holding and sedation are some of the common practices involved when researching teleosts. Using bonefish, Murchie et al. (2009) assessed the effect of capture, transport and long-term holding, while Cooke et al. (2008) evaluated the effect of different capture techniques to assess post-capture stress on a number of blood physiology parameters. Moran et al. (2008) assessed the effect of hypercapnic conditions associated with transportation on glucose and lactate levels in yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Further studies investigated the physiological effects of sedation on fish. The effects of electrosedation on glucose and lactate levels were examined in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella; Bowzer et al., 2012), hybrid striped bass (Morone chrysops × Morone saxatilis; Trushenski and Bowker, 2012; Trushenski et al., 2012a) and largemouth bass (Trushenski et al., 2012b). Anaesthetics used prior to harvest in channel catfish (Bosworth et al., 2007) have been assessed for various parameters; in addition, the effects of the overall anaesthetic efficiency and how this affects the quality of RNA extracted (Olsvik et al., 2007) have been studied. The post-mortem effects of carbon monoxide (Bjørlykke et al., 2011) and pre-slaughter live-chilling sedation effects (Foss et al., 2012) have been examined in Atlantic salmon. Point-of-care devices have also been used to measure glucose, potassium and sodium in Atlantic salmon fillets to determine retention of the synthetic antioxidant, butylated hydroxyanisole (Petri et al., 2008).
In addition to capture and handling, teleosts are often exposed to a number of other abiotic and biotic stressors. For example, using glucose and/or lactate levels, Bjørn et al. (2001) studied infection of brown trout (Salmo trutta) by salmon lice, Evans et al. (2003) studied sub-lethal dissolved oxygen stress and susceptibility to Streptococcus algalactiae in Nile tilapia, and Breau et al. (2011) studied the effects of increased water temperature on Atlantic salmon. Effects of captive rearing have been studied by looking at the effects of water reuse and stock density on growth rate in juvenile cod (Gadus morhua; Foss et al., 2006) and the interactive effects of ammonia and oxygen on the growth and physiology of juvenile Atlantic cod (Remen et al., 2008). Several additional studies have examined effects of anthropogenically induced stressors, mainly on glucose and lactate levels, but also other blood parameters, including blood gas and ion levels, Hct and Hb levels. The effects of confinement in rainbow trout (Wells and Pankhurst, 1999), as well as pre-slaughter stress and stress assessment in aquaculture facilities in Atlantic cod (Hultmann et al., 2012), have been examined. Surgical techniques and recovery have been examined, specifically focusing on hepatic portal vein cannulation technique in Atlantic salmon (Eliason et al., 2007). In addition, the effect of squeezing to simulate gill net damage in rainbow trout (Kojima et al., 2004) and stress associated with dam-related changes in river flow in mountain whitefish (Prosopium williamsoni; Taylor et al., 2012) have been assessed. Finally, the effects of various toxicants and pollutants on blood parameters have been examined in a cichlid species (Cichlasoma dimerus; Da Cuña et al., 2011), two salmonid species (Meland et al., 2010; Olsvik et al., 2010) and the round goby (Neogobius melanostomus; Marenetette et al., 2012).
The manipulation of teleost physiology is also of particular relevance to investigators interested in understanding the intrinsic principles of physiological processes, as well as the result of these manipulations on physiological processes. Point-of-care devices provide a means to examine such physiological end-points easily. Dey et al. (2010) examined the effect of altering cortisol and androgen levels on glucose levels during the parental care period of smallmouth bass. In addition, Herbert et al. (2002) measured glucose and lactate levels during strenuous exercise in 14 species of tropical reef fish. Laporte and Trushenski (2012) studied the effect of manipulating the composition of aquafeeds on glucose and/or lactate levels in hybrid striped bass. Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) were used to determine the interaction effects of oxygen saturation on growth and blood physiology (Foss et al., 2007).
Overall, 10 POC devices have been used in applied studies to assess blood physiology parameters in teleost fish; however, not all devices have been validated for use in teleosts. The Accu-chek glucose meter and Lactate Pro were the most widely used POC devices, followed by the i-STAT, Freestyle blood glucose meter, Accutrend and Accusport lactate meters. The use of these POC devices in teleost fish across a wide range of applied studies demonstrates not only their usefulness in field and laboratory-based physiology, but also the need for further species-specific validation of these tools.
Reptiles
Validation studies
Two studies were conducted to validate the use of the i-STAT analyser for various blood parameters on reptiles (Table 2). McCain et al. (2010) concluded that whole-blood readings for Cl−, glucose, K+ and Na+ using the i-STAT analyser in various reptiles were not accurate compared with laboratory measurements. Despite its variation from laboratory-based results, McCain et al. (2010) suggested that as a result of consistently biased values, the i-STAT could provide clinical utility if analyser-specific reference intervals were set. Wolf et al. (2008) compared the i-STAT analyser with four other analysers (two laboratory diagnostic methods and two table-top analysers) using whole blood from various sea turtle species [loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta), green turtles (Chelonia mydas) and Kemp's ridley turtles (Lepidochelys kempii)] for Na+, K+, Cl−, glucose, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and Hct. In most cases, i-STAT readings disagreed with other analysers, except for BUN, which the authors proposed was a result of differences in the mechanisms used to measure the analytes. Given that the use of POC analysers has generated mixed results in reptiles in general, additional research to validate various POC devices in this group is warranted.
Application studies
Five studies have used POC devices to measure blood parameters, such as acid–base properties, in reptiles. The i-STAT analyser was the most frequently used device, with three studies using this tool to assess the health and wellbeing of various sea turtle species. Sea turtles are frequently encountered as bycatch in marine fisheries, and two studies assessed the physiological effects of different capture and handling techniques. Harms et al. (2003) examined the differential effects of trawl vs. pound net in loggerhead sea turtles and Innis et al. (2010) evaluated the physiological status and health of leatherback sea turtles directly captured by hoop net or incidentally entangled in fixed (i.e. stationary) fishing gears. Anderson et al. (2011) also measured blood parameters in green turtles that were cold stunned or hypothermic. In addition, bycatch-related blood physiology was assessed in freshwater fisheries using the Lactate Pro and IQ128 Elite pH meter to evaluate the physiological response to various types of bycatch-reduction devices, using painted turtles (Chrysemys picta; Larocque et al., 2012) as well as eastern musk (Sternotherus odoratus) and northern map turtles (Graptemys geographica; Stoot et al., 2013). Given the recent increase in research effort, the use of POC analysers is becoming a more common mode to evaluate stress and health in both marine and freshwater reptiles.
Birds
Validation studies
Based on our search criteria, only one study has validated the use of POC devices for avian species (Table 2). Lieske et al. (2002) used adult rhinoceros auklets (Cerorhinca monocerata) to assess the accuracy of four POC devices (Accu-chek Advantage, Bayer Glucometer Elite, Precision QID and Sure Step). Based on mean difference and regression models, all devices were deemed reliable and potentially useful for screening in the field, although the four hand-held devices underestimated blood glucose of rhinoceros auklets by an average of 33% compared with reference values (Lieske et al., 2002). Based on ease of use, comparative accuracy, test time, cost and blood volume requirement, the Accu-chek Advantage and Precision QID monitors were the most appropriate POC devices for this avian model, and future research is suggested with known hypoglycaemic avian blood as well as blood from different species to assess overall utility of the devices (Lieske et al., 2002).
Application
Two POC devices have been used in practical applications to measure glucose and numerous other physiological parameters in avian species. Researchers have used the Bayer Glucometer Elite device in the field and laboratory to assess the possible effect of nectar consumption on plasma glucose in various passerine species, including warblers (Cecere et al., 2011), and to determine whether plasma glucose levels were based on circadian rhythm or temperature (Downs et al., 2010). Although not validated for avian species, the i-STAT analyser has been used to analyse blood acid–base, ionic and haematological properties to provide reference data for non-anaesthetized Amazon parrots (Amazona aestiva; Paula et al., 2008).
Mammals
Validation
Our search discovered three studies that have assessed the accuracy of POC devices for use in non-domesticated mammals (Table 2). All but one validation study compared the i-STAT analyser with laboratory-based equipment to measure various blood parameters in three different mammalian species. The i-STAT analyser was determined to be acceptable for the measurement of glucose, BUN, Na+, K+ and total CO2 in cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fasicularis; Hopper and Cray, 2007) and glucose, BUN, Na+, K+, Cl− and Hct in elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris; Larsen et al., 2002). In addition, Burdick et al. (2012) compared laboratory-based equipment (Hitachi 917 chemistry analyser) with the IQ Prestige Smart System Handheld Glucometer and the Prestige Smart System Glucometer for measurement of blood glucose levels in juvenile white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Agreement between laboratory-based equipment and the two POC glucometers was poor, thus driving the conclusion that these two POC devices were not appropriate for measurement of blood glucose concentrations in this species.
Applications
Two POC devices, the i-STAT analyser and Accutrend lactate meter, were used to assess blood physiology in various non-domesticated mammal species. Of the six application studies completed to date, all six used the i-STAT, with pH and blood gases being the most commonly measured variables. Application studies examined the physiological effects related to invasive capture techniques in white-tailed deer (Boesch et al., 2011), anaesthetics in polar bears (Ursus maritimus; Cattet et al., 2003), immobilization in Baird's tapirs (Tapirus bairdii; Feorster et al., 2000) and manual restraint as opposed to anaesthetic in the Arabian oryx (Oryx leucoryx; Kilgallon et al., 2008). Application studies also examined the physiological effects related to sleep apnoea in Northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris; Stockard et al., 2007), as well as an assessment and post-release monitoring of mass-stranded dolphins (Sampson et al., 2012).
Limitations across taxonomic groups
General limitations
Of the devices used in this data set, two broad categories of POC devices can be designated: the widely applicable multi-analyte devices (e.g. i-STAT analyser) and the specialized single-analyte devices (e.g. Lactate Pro). The i-STAT analyser is beneficial in that it can be used to test a variety of analytes, but it requires a certain amount of user knowledge and training in order to operate the machine settings, to dispense the sample into the cartridge appropriately and to avoid cartridge errors. These devices require a working knowledge of the device as well as the physiology of the organism but are ideal for obtaining multiple physiological measures from a single sample. Conversely, single-analyte devices, such as the Lactate Pro, are more specialized in scope, function on a limited number of analytes and operate on the submitted blood sample without further input or setting configuration. These devices are typically small, easy to use, relatively inexpensive and ideal if only one blood variable measurement is required.
Physiological limitations
As a result of their origins in medical sciences, POC devices were designed to measure blood parameters of homeothermic mammals, particularly humans. These devices rely on individuals with a body temperature of ∼37°C and non-nucleated blood cells, thus the ability of POC devices to be applied to a broader variety of taxa will have challenges. Consequently, body temperature was a reoccurring caveat across studies of ectotherms using these devices, especially in relationship to temperature-sensitive blood acid–base measurements (Harrenstien et al., 2005; Gallagher et al., 2010; Sampson et al., 2012). Indeed, several studies concluded that there is a need for species-specific temperature corrections for these parameters and emphasized that extrapolation of published temperature corrections from one species to another should be done with caution [e.g. Chondrichthyes (Mandelman and Skomal, 2009; Cicia et al., 2012), teleost fish (Olsvik et al., 2010; Foss et al., 2012), reptiles (Harms et al., 2003; Anderson et al., 2011) and birds (Paula et al., 2008)].
Inaccurate readings can be the result of incorrect measurements. Many devices rely on pre-set ratios to calculate parameters and have species-specific correction values, which differ among species and taxa. For example, the i-STAT analyser was not used to measure base excess and saturated arterial oxygen in sea turtles due to its use of human-specific conversion factors (Harms et al., 2003). Along the same lines, the internal temperature calibration capability for pH and blood gases on the i-STAT analyser is based on mammalian conversion factors, and may thus compromise accuracy of values of those parameters when the conversion tool is employed for ectotherms, such as fish (Mandelman and Skomal, 2009). Glucose monitors have similar issues, because they are designed to measure whole-blood samples but use a correction factor to convert results to plasma glucose concentrations (Kuwa et al., 2001). These devices use human plasma-to-whole-blood corrective values, which can underestimate glucose values in birds (Lieske et al., 2002; Acierno et al., 2008). In addition, this trend for underestimation is also seen in POC lactate measurements in teleost fish (e.g. Wells and Pankhurst, 1999; Venn Beecham et al., 2006).
Whole blood vs. plasma and point-of-care value range restrictions
The input medium is important to consider when using POC devices, where whole blood and plasma are the two most prevalent media used. Whole blood is unmodified (with the potential exception of the addition of an anticoagulant) and is therefore ideal for field studies where processing and storage may be difficult or impossible. Plasma is extracellular fluid retrieved by spinning down whole blood by centrifugation to remove haematocytes. Plasma is often the preferred medium for laboratory studies owing to its higher stability for storage compared with whole blood (Thrall et al., 2012); however, the need for centrifugation can limit feasibility in the field. Although urine may be analysed by POC devices for some analytes, it is not as widely used. For example, urine cannot be tested reliably using the i-STAT analyser (Erickson and Wilding, 1993). Serum can also be used as an input medium, but it has certain advantages and disadvantages similar to plasma (Thrall et al., 2012).
In the studies investigated here, the vast majority assessed whole blood when using a POC device, while some used plasma, particularly those in controlled environments where plasma was often stored and analysed at a later date. Validation studies that measured the difference between whole blood and plasma analyte levels found that the analyte value differed significantly but in a predictable manner, with plasma values typically being higher (Iwama et al., 1995). The persistent differences between plasma- and whole-blood-derived values allow for relative but not direct comparisons, which limits inference across studies (Larsen et al., 2002; Cooke et al., 2008).
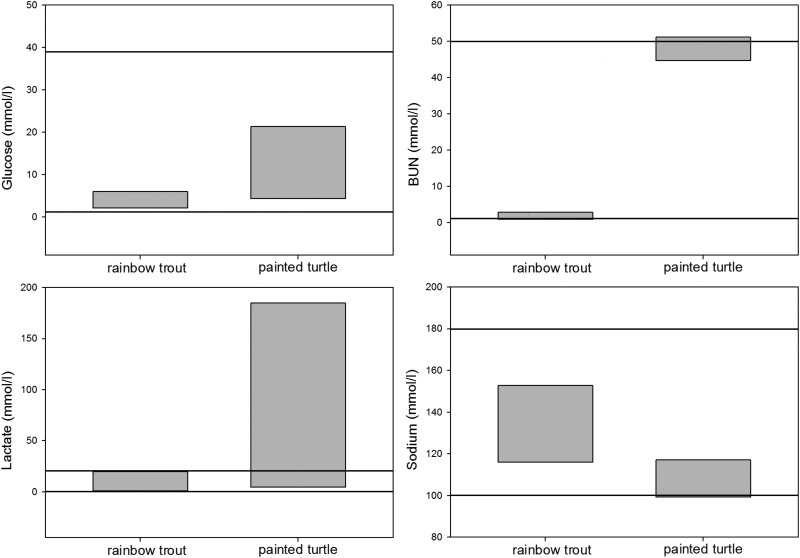
As these devices are designed for human blood parameter ranges, their tolerances can often be too restrictive for other taxa and result in error readings [e.g. Chondrichthyes (Awruch et al., 2011; Hyatt et al., 2012; Naples et al., 2012), teleost fish (Harrenstien et al., 2005; Brown et al., 2008), reptiles (Larocque et al., 2012) and birds (Lieske et al., 2002); Fig. 1). For example, many studies that used the i-STAT analyser to assess blood physiology in teleost fish and Chondrichthyes have reported out-of-range readings for various parameters, including Na+ (Olsvik et al., 2007; Suski et al., 2007; Brill et al., 2008) and Cl− (Harrenstien et al., 2005; Brill et al., 2008; DiMaggio et al., 2010). In situations when limits are too narrow, dilutions can be used to obtain measurable readings (Suski et al., 2007; Brill et al., 2008); however, this can only be achieved with plasma, creating a problem for any cartridge type (e.g. the EC8+ on the i-STAT) on a multi-analyte device that includes both out-of-range analytes as well as those specific to whole blood for a given species (e.g. certain acid–base and haemotogical parameters). In such instances, the user is unable to obtain value readings for all analytes for that cartridge and must prioritize whether to run the cartridge on whole blood or on extracted and diluted plasma, depending on which analyte(s) is less valuable to lose.
Figure 1:
Whole blood values for select analytes on representative commonly studied species, the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and the painted turtle (Chrysemys picta). Box plots represent the maximal ranges from the literature and horizontal lines represent the maximal reportable range of the most commonly used point-of-care device in the present study, the i-STAT analyser.
Field and environmental limitations
When conducting fieldwork, researchers may encounter several different environmental conditions that have the potential to interfere with POC device use (Fig. 2). Waterproofing becomes necessary when working with species in aquatic settings to protect devices from potential water damage. Small amounts of water (especially saltwater) within cartridge ports and battery compartments of POC devices can compromise the condition of the unit and damage it. Waterproof cases protect devices from water and general damage during transport, although depending on case size, portability can be reduced. In addition, these cases protect the device only while in transit, and care must be taken during device use to avoid potential submersion. Future steps to develop POC devices that are waterproof and more durable would reduce the need for bulky cases.
Figure 2:
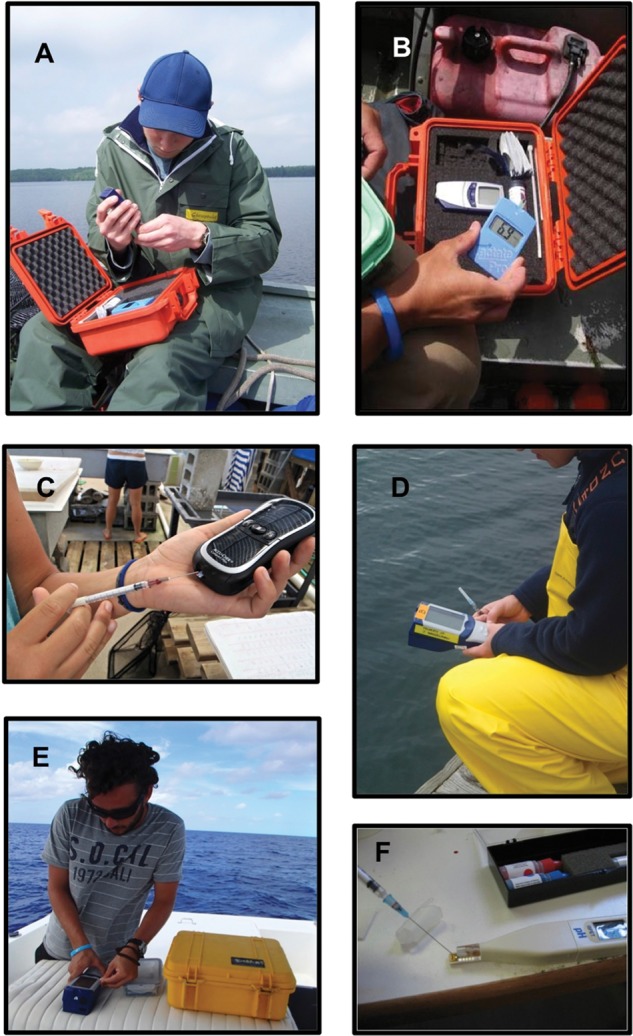

Point-of-care (POC) devices can be used in the field in a variety of situations. (A) Point-of-care glucose meter being set up on a boat (photograph by Lisa Thompson). (B) Protective cases, similar to the one shown, are useful for ensuring that POC devices are not damaged by the elements (photograph by Lisa Thompson). (C) Point-of-care devices, such as this glucose meter, can be used in laboratory trials to obtain immediate results on the condition of the individual (photograph by Petra Szekeres). (D) Some POC devices, such as the i-STAT, can obtain multiple blood parameters to be measured from one sample (photograph by John Mandelman). (E) Point-of-care i-STAT device in use on a boat (photograph by John Mandelman). (F) Point-of-care pH meter in use to examine blood pH in freshwater turtles (photograph by Sarah Larocque).
The effects of temperature and atmospheric humidity on the usability and accuracy of POC devices are further potential issues when working in the field. Studies conducted on the use of POC devices in disaster-relief situations have concluded that temperature and humidity can affect glucose test strips, which alters the readings of various glucose monitors (Louie et al., 2000; Nichols, 2011). Many POC devices and their associated cartridges have environmental range limits in which they function optimally, and deviations outside of this range can produce inaccurate readings (Sampson et al., 2012). Functional minima and maxima (e.g. i-STAT analyser has a functional range of 16–30°C; Lactate Pro cannot function properly above 40°C) limit the possible field season in some climates and preclude sampling altogether in some areas (e.g. polar and desert regions). Users are often forced to carry a cooling or heating mechanism to ensure that the POC device is kept within the usable thermal range. In addition, many POC devices use a cartridge or strip that requires storage at specific temperatures (e.g. i-STAT cartridges require refrigeration before use and can be kept at room temperature for only 2 weeks following removal). Furthermore, these devices are affected by extreme humidity conditions, such that most devices operate between 10 and 90% relative humidity (e.g. Lactate Pro and i-STAT operate in the range 20–80 and 0–90% relative humidity, respectively). Overall, field settings can make storage and maintenance of POC devices in varying temperatures and humidities difficult. As such, modifications of POC devices to incorporate a broader thermal and humidity tolerance is needed before these devices can be considered fully effective for studies of species inhabiting a wide range of environments.
Conclusions and future directions
Overall, most POC devices have been found to be suitable alternatives to traditional laboratory-based devices in conservation physiology studies, although they should be used with caution. With continuing technological developments, such devices have the potential to be used more widely in field physiology studies on a variety of taxa. However, the popularity of such devices will depend on technological advances in the usability and reliability of POC devices in the field. Environmental conditions (e.g. temperature and humidity) affect the usability and accuracy of POC devices; as such, POC devices need to be functional broadly in field environments and require improvements or modifications to overcome their functional limitations (temperature range, humidity, storage requirements, maintenance etc.). Technological advances will increase the applicability of POC devices to a variety of species living in different field conditions or in wide demographic ranges. This will ensure that extreme or fluctuating environmental field conditions do not interfere with the use of POC devices by damaging the devices or affecting the accuracy of the results. Partnerships and collaborations between field biologists and manufacturing companies can help to formulate such technological improvements.
In addition to technological advancements of POC devices, there is an increased need for validation studies on non-human and non-domesticated species to confirm the accuracy and reliability of these devices, particularly given the lack of universality in the calibrations of POC devices among species evaluated to date. Therefore, precise calibration and species-specific validation of POC devices are necessary prior to application in a broader range of species (Lieske et al., 2002; DiMaggio et al., 2010; Gallagher et al., 2010). Validation studies should address taxonomic and thermal effects on device precision and accuracy (Cicia et al., 2012). In particular, efforts should be made to garner larger sample sizes to compare with current reference values (Naples et al., 2012). Optimally, a calibration can be established across the broadest possible range of values for a given analyte, in the event of a lack of equivalence or linearity across the full spectrum of readable or biologically/clinically relevant values. Furthermore, biases can occur among taxa, where validation studies tend to be carried out in species or groups that are easy to study or are of economic importance (e.g. Atlantic salmon). The diversity among taxa in terms of habitat ecology and blood physiology points to the need for further investigation into a broader range of organisms, especially non-mammalian taxa. Focusing on representative models within each taxa, validating commonly used devices and assessing blood parameters in natural, free-living animals would be a good starting point. Validations of these devices on ectothermic species should be of high importance due to their physiological differences from endothermic species. In addition, developing a standardized protocol to validate devices, within the taxon level, would be beneficial and aid with the standardization of validations.
With the growing use of POC devices in field-based conservation physiology studies, there is a push towards the streamlined approach that is provided by multi-analyte devices (e.g. i-STAT). The ability to measure multiple blood parameters from a single sample by a single device is ideal for field-based studies, where extensive sample analysis is often difficult. Currently, the majority of the POC devices (e.g. LactatePro and various glucometers) measure one parameter exclusively, which can not only increase the equipment load for field biologists but also the amount of sample required. The development of more multi-analyte devices that are able to measure multiple blood parameters efficiently and accurately across a variety of taxa will increase the use of these devices by field physiologists.
In addition to the current POC devices available, there is the potential to develop devices that could measure blood parameters beyond those that are currently possible, again allowing conservation physiologists the flexibility of on-site sample analysis. Point-of-care devices that would enable direct measurement of primary in addition to secondary stress analytes would allow remote determination of levels now attainable only via more time-consuming processes in the laboratory. The ability to obtain POC measurements of glucocorticoids or other steroids (such as reproductive hormones), among other biomarkers, would be highly valuable for field-based conservation physiology studies.
In conclusion, the use of hand-held and portable POC devices is appealing for field-based conservation physiology studies because they rapidly provide on-site results without the need for sample storage. Overall, there is great potential for the use of POC devices to advance the field of conservation physiology, but continued progress is needed in the areas discussed to increase both the utility of these devices across environments and taxonomic groups and their capacity to obtain additional information on stress levels and health of animals in remote settings. Also needed is a more thorough appreciation of the various limitations associated with POC devices and recognition that although they provide rapid information, they do not replace traditional analytical methods.
Acknowledgements
S.J.C. is supported by the Canada Research Chairs Program and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. We thank Nick Lapointe, Jon Midwood and two anonymous referees for providing comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
References
- 1.Acierno MJ, Johnson ME, Eddleman LA, Mitchell MA. (2008) Measuring statistical agreement between four point of care (POC) lactate meters and a laboratory blood analyzer in cats. J Feline Med Surg 10: 110–114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Allen SE, Holm JL. (2008) Lactate: physiology and clinical utility. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 18: 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allender MC, Schumacher J, George R, Milam J, Odoi A. (2010) The effects of short- and long-term hypoxia on hemolymph gas values in the American horseshow crab (Limulus polyphemus) using a point-of-care analyzer. J Zoo Wildl Med 41: 193–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Altinier S, Zaninotto M, Mion M, Carraro P, Rocco S, Tosato F, Plebani M. (2001) Point-of-care testing of cariac markers: results from an experience in an emergency department. Clin Chim Acta 311: 67–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Anderson ET, Harms CA, Stringer EM, Cluse WM. (2011) Evaluation of hematology and serum biochemistry of cold-stunned green sea turtles (Chelonia mydas) in North Carolina, USA. J Zoo Wildl Med 42: 247–255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Apple FS, Anderson FP, Collinson P, Jesse RL, Kontos MC, Levitt MA, Miller EA, Murakami MM. (2000) Clinical evaluation of the first medical whole blood, point-of-care testing device for detection of myocardial infarction. Clin Chem 46: 1604–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Archer RK, Jeffcott LB. (1977) Comparative Clinical Haematology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, pp 737. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Arlinghaus R, Klefoth T, Cooke SJ, Gingerich A, Suski CD. (2009) Physiological and behavioural consequences of catch-and-release angling on northern pike (Esox lucius L.). Fish Res 97: 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Atkins A, Jacobson E, Hernandez J, Bolten AB, Lu X. (2010) Use of a portable point-of-care (Vetscan Vs2) biochemical analyzer for measuring plasma biochemical levels in free-living loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta). J Zoo Wildl Med 41: 585–593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Awruch CA, Simpfendorfer C, Pankhurst NW. (2011) Evaluation and use of a portable field kit for measuring whole-blood lactate in sharks. Mar Freshwater Res 62: 694–699. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Beadle LC. (1957) Respiration in the African swamp-worm, Alma emini Mich. J Exp Biol 34: 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bjørlykke GA, Roth B, Sørheim O, Kvammeb BO, Slinde E. (2011) The effects of carbon monoxide on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Food Chem 127: 1706–1711. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bjørn PA, Finstad B, Kristoffersen R. (2001) Salmon lice infection of wild sea trout and Arctic char in marine and freshwaters: the effects of salmon farms. Aquacult Res 32: 947–962. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Boesch JM, Boulanger JR, Curtis PD, Erb HN, Ludders JW, Kraus MS, Gleed RD. (2011) Biochemical variables in free-ranging white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) after chemical immobilization in clover traps or via ground-darting. J Zoo Wildl Med 42: 18–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bosworth BG, Small BC, Gregory D, Kim J, Black S, Jerrett A. (2007) Effects of rested-harvest using the anesthetic AQUI-S™ on channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, physiology and fillet quality. J World Aquac Soc 30: 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bowzer JC, Trushenski JT, Gause BR, Bowker JD. (2012) Efficacy and physiological responses of grass carp to different sedation techniques: II. Effect of pulsed DC electricity voltage and exposure time on sedation and blood chemistry. N Am J Aquacult 74: 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Breau C, Cunjak RA, Peake SJ. (2011) Behaviour during elevated water temperature: can physiology explain movement of juvenile Atlantic salmon to cool water? J Anim Ecol 80: 844–853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brill R, Bushnell P, Schroff S, Seifert R, Galvin M. (2008) Effects of anaerobic exercise accompanying catch-and-release fishing on blood-oxygen affinity of the sandbar shark (Carcharhinus plumbeus, Nardo). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 354: 132–143. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brooks EJ, Sloman KA, Liss S, Hassan-Hassanein L, Danylchuk AJ, Cooke SJ, Mandelman JW, Skomal GB, Sims DW, Suski CD. (2011) The stress physiology of extended duration tonic immobility in the juvenile lemon shark, Negaprion brevirostris (Poey 1868). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 409: 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brown JA, Watson J, Bourhill A, Wall T. (2008) Evaluation and use of the Lactate Pro, a portable lactate meter, in monitoring the physiological well-being of farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquaculture 285: 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Burdick S, Mitchell MA, Neil J, Heggem B, Whittington J, Acierno MJ. (2012) Evaluation of two point-of-care meters and a portable chemistry analyzer for measurement of blood glucose concentrations in juvenile white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Am Vet Med Assoc 240: 596–599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Busch DS, Hayward LS. (2009) Stress in a conservation context: a discussion of glucocorticoid actions and how levels change with conservation-relevant variables. Biol Conserv 142: 2844–2853. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Butcher PA, Leland JC, Broadhurst MK, Paterson BD, Mayer DG. (2012) Giant mud crab (Scylla serrata): relative efficiencies of common baited traps and impacts on discards. ICES J Mar Sci 69: 1511–1522. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cattet MRL, Caulkett NA, Lunn NJ. (2003) Anesthesia of polar bears using xylazine-zolazepam-tiletamine or zolazepam-tiletamine. J Wildl Dis 39: 655–664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cecere JG, Spina F, Jenni-Eiermann S, Boitani L. (2011) Nectar: an energy drink used by European songbirds during spring migration. J Ornithol 152: 923–931. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cicia AM, Schlenker LS, Sulikowski JA, Mandelman JW. (2012) Seasonal variations in the physiological stress responses to discrete bouts of aerial exposure in the little skate, Leucoraja erinacea. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 162: 130–138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cima M. (2011) Microsystems technologies for medical applications. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng 2: 355–378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Clark TD, Eliason EJ, Sandblom E, Hinch SG, Farrell AP. (2008) Calibration of a hand-held haemoglobin analyser for use on fish blood. J Fish Biol 73: 2587–2595. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Clark TD, Donaldson MR, Drenner SM, Hinch SG, Patterson DA, Hills J, Ives V, Carter JJ, Cooke SJ, Farrell AP. (2011) The efficacy of field techniques for obtaining and storing blood samples from fishes. J Fish Biol 79: 1322–1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cooke SJ, O'Connor CM. (2010) Making conservation physiology relevant to policy makers and conservation practitioners. Conserv Lett 3: 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cooke SJ, Crossin GT, Patterson DA, English KK, Hinch SG, Young JL, Alexander RF, Healey MC, Van Der Kraak G, Farrell AP. (2005) Coupling non-invasive physiological assessments with telemetry to understand inter-individual variation in behaviour and survivorship of sockeye salmon: development and validation of a technique. J Fish Biol 67: 1342–1358. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cooke SJ, Suski CD, Danylchuk SE, Danylchuk AJ, Donaldson MR, Pullen C, Bulté G, O'Toole A, Murchie KJ, Koppelman JB, et al. (2008) Effects of different capture techniques on the physiological condition of bonefish Albula vulpes evaluated using field diagnostic tools. J Fish Biol 73: 1351–1375. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cooke SJ, Sack L, Franklin CE, Farrell AP, Beardall J, Wikelski M, Chown SL. (2013) Conservation physiology: perspectives on an increasingly integrated and essential science. Conserv Physiol 1: doi:10.1093/conphys/cot001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Costa DP, Sinervo B. (2004) Field physiology: physiological insights from animals in nature. Annu Rev Physiol 66: 209–238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Da Cuña RH, Rey Vázquez G, Piol MN, Guerrero NV, Maggese MC, Lo Nostro FL. (2011) Assessment of the acute toxicity of the organochloride pesticide endosulfan in Cichlasoma dimerus (Teleostei, Perciformes). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74: 1065–1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Deem SL, Karesh WB, Weisman W. (2001) Putting theory into practice: wildlife health in conservation. Conserv Biol 15: 1224–1233. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Delesalle C, Dewulf J, Lefebvre RA. (2007) Determination of Lactate concentration in blood plasma and peritoneal fluid in horses with colic by an Accusport analyzer. J Vet Intern Med 21: 293–301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Denver RJ, Hopkins PM, McCormick SD, Propper CR, Riddiford L, Sower SA, Wingfield JC. (2009) Comparative endocrinology in the 21st century. Integr Comp Biol 49: 339–348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dey CJ, O'Connor CM, Gilmour KM, Van Der Kraak G, Cooke SJ. (2010) Behavioral and physiological responses of a wild teleost fish to cortisol and androgen manipulation during parental care. Hormones Behav 58: 599–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.DiMaggio MA, Ohs CL, Petty BD. (2010) Evaluation of a point-of-care-blood analyzer for use in determination of select hematological indices in the Seminole killifish. N Am J Aquacult 72: 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- 41.di Prisco G. (1997) Physiological and biochemical adaptations in fish to a cold marine environment. In Battaglia B, Valencia J, Walton DWH, eds, Antarctic Communities: Species, Structure and Survival. 6th SCAR Biology Symposium, Venice, Italy, 1996. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Downs CT, Wellmann AE, Brown M. (2010) Diel variations in plasma glucose concentrations of Malachite Sunbirds Nectarinia famosa. J Ornithol 151: 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Eliason EJ, Kiessling A, Karlsson A, Djordjevic B, Farrell AP. (2007) Validation of the hepatic portal vein cannulation techniques using Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. J Fish Biol 71: 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Erickson AW, Youatt WG. (1961) Seasonal variations in the hematology and physiology of black bears. J Mammal 42: 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Erickson KA, Wilding P. (1993) Evaluation of a novel point-of-care system, the i-STAT portable clinical analyzer. Clin Chem 39: 283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Evans JJ, Shoemaker CA, Klesius PH. (2003) Effects of sublethal dissolved oxygen stress on blood glucose and susceptibility to Streptococcus agalactiae in Nile Tilapia. J Aquat Anim Health 15: 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Feder ME, Block BA. (1991) On the future of animal physiological ecology. Funct Ecol 5: 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Feorster SH, Bailey JE, Aguilar R, Loria DL, Foerster CR. (2000) Butorphanol/xylazine/ketamine immobilization of free-ranging Baird's tapirs in Costa Rica. J Wildl Dis 36: 335–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Foss A, Kristensen T, Åtland Å, Hustveit H, Hovland H, Øfsti A, Imsland AK. (2006) Effects of water reuse and stocking density on water quality, blood physiology and growth rate of juvenile cod (Gadus morhua). Aquaculture 256: 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Foss A, Imsland AK, Roth B, Schram E, Stefansson SO. (2007) Interactive effects of oxygen saturation and ammonia on growth and blood physiology in juvenile turbot. Aquaculture 271: 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Foss A, Grimsbø E, Vikingstad E, Nortvedt R, Slinde E, Roth B. (2012) Live chilling of Atlantic salmon: physiological response to handling and temperature decrease on welfare. Fish Physiol Biochem 38: 656–571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Frick LH, Walker TI, Reina RD. (2012) Immediate and delayed effects of gill-net capture on acid–base balance and intramuscular lactate concentration of gummy sharks, Mustelus antarcticus. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 162: 88–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gallagher AJ, Frick LH, Bushnell PG, Brill RW, Mandelman JW. (2010) Blood gas, oxygen saturation, pH, and lactate values in Elasmobranch blood measured with a commercially available portable clinical analyzer and standard laboratory instruments. J Aquat Anim Health 22: 229–234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Garland T, Jr, Adolph SC. (1991) Physiological differentiation of vertebrate populations. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 22: 193–228. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Garland T, Jr, Carter PA. (1994) Evolutionary physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 56: 579–621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gomes LC, Chagas EC, Brinn RP, Roubach R, Coppati CE, Baldisserotto B. (2006a) Use of salt during transportation of air breathing pirarucu juveniles (Arapaima gigas) in plastic bags. Aquaculture 256: 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gomes LC, Chagas EC, Martin-Junior H, Roubach R, Ono EA, Lourenço JNP. (2006b) Cage culture of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) in a central Amazon floodplain lake. Aquaculture 253: 374–384. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gravel MA, Cooke SJ. (2008) Severity of barotrauma influences the physiological stats, postrelease behaviour, and fate of tournament-caught smallmouth bass. N Am J Fish Manag 28: 607–617. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gubala V, Harris LF, Ricco AJ, Tan MX, Williams DE. (2012) Point of care diagnostics: status and future. Anal Chem 84: 487–515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hall FG, Dill DB, Guzman Barron ES. (1936) Comparative physiology in high altitudes. J Cell Comp Physiol 8: 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hanson KC, Gravel M-A, Redpath T, Cooke SJ, Seipker MJ. (2008) Latitudinal variation in physiological and behavioral responses of nest-guarding smallmouth bass to common recreational angling practices. Trans Am Fish Soc 137: 1558–1566. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Harms CA, Mallo KM, Ross PM, Segars A. (2003) Venous blood gases and lactates of wild loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caratta) following two capture techniques. J Wildl Dis 39: 366–374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Harrenstien LA, Tornquist SJ, Miller-Morgan TJ, Fodness BG, Clifford KE. (2005) Evaluation of a point-of-care blood analyzer and determination of reference ranges for blood parameters in rockfish. J Am Vet Med Assoc 226: 255–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Helmuth B. (2009) From cells to coastlines: how can we use physiology to forecast the impacts of climate change? J Exp Biol 212: 753–760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Henry NA, Cooke SJ, Hanson KC. (2009) Evaluation of a point-of-care blood analyzer and determination of reference ranges for blood parameters in rockfish. Fish Res 100: 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Herbert NA, Wells RMG, Baldwin J. (2002) Correlates of choroid rete development with the metabolic potential of various tropical reef fish and the effect of strenuous exercise on visual performance. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 275: 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hollis AR, Dallap Schaer BL, Boston RC, Wilkins PA. (2008) Comparison of the Accu-Chek Aviva point-of-care glucometer with blood gas and laboratory methods of analysis of glucose measurements in equine emergency patients. J Vet Int Med 22: 1189–1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hopper KJ, Cray C. (2007) Evaluation of a portable clinical analyzer in cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fasicularis). J Am Assoc Lab Ani Sci 46: 53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hultmann L, Phu TM, Tobiassen T, Aus-Hansen Ø, Rustad T. (2012) Effects of pre-slaughter stress on proteolytic enzyme activities and muscle quality of farmed Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Food Chem 134: 1399–1408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hyatt MW, Anderson PA, O'Donnell PM, Berzins IK. (2012) Assessment of acid–base derangements among bonnethead (Sphyrna tiburo), bull (Carcharhinus leucas), and lemon (Negaprion brevirostris) sharks from gillnets and longline capture and handling methods. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 162: 113–120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Innis C, Merigo C, Dodge K, Tlusty M, Dodge M, Sharp B, Myers A, McIntosh A, Wunn D, Perkins C, et al. (2010) Health evaluation of leatherback turtles (Dermochelys coriacea) in the northwest Atlantic during first capture and fisheries gear disentanglement. Chelonian Conserv Biol 9: 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Iwama GK, Morgan JD, Barton BA. (1995) Simple field methods for monitoring stress and general condition of fish. Aquacult Res 26: 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kilgallon C, Bailey T, Arca-Ruibal B, Misheff M, O'Donovan D. (2008) Blood-gas and acid-base parameters in nontranquilized Arabian Oryx (Oryx leucoryx) in the United Arab Erimates. J Zoo Wildl Med 39: 6–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Klonoff DC. (2005) Continuous glucose monitoring: roadmap for 21st century diabetes therapy. Diabetes Care 28: 1231–1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kojima T, Ishii M, Kobayashi M, Shimizu M. (2004) Blood parameters and electrocardiogram in squeezed fish simulating the effect of net damage and recovery. Fish Sci 70: 860–866. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ku DN. (1997) Blood flow in arteries. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 29: 399–434. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Kuwa K, Nakayama T, Hoshino T, Tominaga M. (2001) Relationships of glucose concentrations in capillary whole blood, venous whole blood and venous plasma. Clin Chim Acta 307: 187–192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Landsman SJ, Wachelkab HJ, Suski CD, Cooke SJ. (2011) Evaluation of the physiology, behaviour, and survival of adult muskellunge (Esox masquinongy) captured and released by specialized anglers. Fish Res 110: 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Laporte J, Trushenski JT. (2012) Production performance, stress tolerance and intestinal integrity of sunshine bass fed increasing levels of soybean meal. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 96: 513–526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Larocque SM, Cooke SJ, Blouin-Demers G. (2012) A breath of fresh air: avoiding anoxia and mortality of freshwater turtles in fyke nets by the use of floats. Aquat Conserv 22: 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Larsen RS, Haulena M, Grindem CB, Gulland FMD. (2002) Blood values of juvenile northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris) obtained using a portable clinical analyzer. Vet Clin Path 31: 106–110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lieske CL, Ziccardi MH, Mazet JAK, Newman SH, Gardner IA. (2002) Evaluation of 4 handheld blood glucose monitors for use in seabird rehabilitation. J Avian Med Surg 164: 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Louie RF, Tang Z, Shelby DG, Kost GJ. (2000) Point-of-care testing: millennium technology for critical care. Lab Med 31: 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- 84.McCain SL, Flatland B, Schumacher JP, Clarke EO, III, Fry MM. (2010) Comparison of chemistry between 2 portable, commercially available analyzers and a conventional laboratory analyzer in reptiles. Vet Clin Path 39: 474–479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Mandelman JW, Farrington MA. (2007a) The estimated short-term discard mortality of a trawled elasmobranch, the spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Fish Res 83: 238–245. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Mandelman JW, Farrington MA. (2007b) The physiological status and mortality associated with otter-trawl capture, transport, and captivity of an exploited elasmobranch, Squalus acanthias. ICES J Marine Sci 64: 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mandelman JW, Skomal GB. (2009) Differential sensitivity to capture stress assess by blood acid–base status in five carcharhinid sharks. J Comp Physiol B 179: 267–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Mangum CP, Hochachka PW. (1998) New directions in comparative physiology and biochemistry: mechanisms, adaptations, and evolution. Physiol Biochem Zool 71: 471–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Marenetette JR, Tong S, Balshine S. (2012) The cortisol stress response in male round goby (Neogobius melanostomus): effects of living in polluted environments. Environ Biol Fish 96: 723–733. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Mecozzi DM, Brock K, Tran NK, Hale KN, Kost GJ. (2010) Evidence-based point-of-care device design for emergency and disaster care. Point Care 9: 65–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Meffe GK. (1999) Conservation medicine. Conserv Biol 13: 953–954. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Meland S, Heier LS, Salbu B, Tollefsen KE, Farmen E, Rosseland BO. (2010) Exposure of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) to tunnel wash water runoff — chemical characterisation and biological impact. Sci Total Environ 408: 2646–2656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Mizock BA, Falk JL. (1992) Lactic acidosis in critical illness. Crit Care Med 20: 80–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Moran D, Wells RMG, Pether SJ. (2008) Low stress response exhibited by juvenile yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi Valenciennes) exposed to hypercapnic conditions associated with transportation. Aquacult Res 39: 1399–1407. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Morgan JD, Iwama GK. (1997) Measurements of stressed states in the field. In Iwama G, Pickering A, Sumpter J, Schreck C, eds, Fish Stress and Health in Aquaculture. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 247–268. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Murchie KJ, Danylchuk SE, Pullen CE, Brooks E, Shultz AD, Suski CD, Danylchuk AJ, Cooke SJ. (2009) Strategies for the capture and transport of bonefish, Albula vulpes, from tidal creeks to a marine research laboratory for long-term holding. Aquacult Res 40: 1538–1550. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Naples LM, Mylniczenko ND, Zuchariah TT, Wilborn RE, Young FA. (2012) Evaluation of critical care blood analytes assessed with a point-of-care portable blood analyzer in wild and aquarium-housed elasmobranchs and the influence of phlebotomy site on results. J Am Vet Med Assoc 241: 117–125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Nguyen V, Gravel M-A, Mapleston A, Hanson KC, Cooke SJ. (2009) The post-release behaviour and fate of tournament-caught smallmouth bass after ‘fizzing’ to alleviate distended swim bladders. Fish Res 96: 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Nichols JH. (2011) Blood glucose testing in the hospital: error sources and risk management. J Diabetes Sci Techol 5: 173–177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Olsvik PA, Lie KK, Hevrøy EM. (2007) Do anesthetics and sampling strategies affect transcription analysis of fish tissues? BMC Mol Biol 8: 48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Olsvik PA, Kroglund F, Finstad B, Kristensen T. (2010) Effects of the fungicide azoxystrobin on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) smolt. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73: 1852–1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.O'Toole AC, Danylchuk AJ, Suski CD, Cooke SJ. (2010) Consequences of catch-and-release angling on the physiological status, injury, and immediate mortality of great barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) in The Bahamas. ICES J Mar Sci 67: 1667–1675. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Paula VV, Fantoni DT, Otsuki DA, Auler JOC., Jr (2008) Blood-gas and electrolyte values for Amazon parrots (Amazona aestiva). Pesq Vet Bras 28: 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Peiró JR, Borges AS, Gonçalves RC, Mendes LCN. (2010) Evaluation of a portable clinical analyzer for the determination of blood gas partial pressures, electrolyte concentrations, and hematocrit in venous blood samples collected from cattle, horses, and sheep. Am J Vet Res 71: 515–521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Petri D, Hamre K, Lundebye AK. (2008) Retention of the synthetic antioxidant butylated hydroxyanisole in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets. Aquacult Nutr 14: 453–458. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Plebani M. (2009) Does POCT reduce the risk of error in laboratory testing? Clim Chim Acta 404: 59–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Prosser CL. (1973) Comparative Animal Physiology: Sensory, Effector and Integrative Physiology, Ed 3 Saunders, Philadelphia, USA, pp 145–147. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Pyne BP, Boston T, Martin DT, Logan A. (2000) Evaluation of the Lactate Pro blood analyser. Eur J Appl Physiol 82: 112–116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Remen M, Imsland AK, Stefansson SO, Jonassen TM, Foss A. (2008) Interactive effects of ammonia and oxygen on growth and physiological status of juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquaculture 274: 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- 110.Rogers KD, Booth DT. (2004) A method of sampling blood from Australian freshwater turtles. Wildlife Res 31: 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Romero LM, Wikelski M. (2010) Stress physiology as a predictor of survival in Galapagos marine iguanas. Proc Biol Sci 277: 3157–3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Roth B, Rotabakk BT. (2012) Stress associated with commercial longlining and recreational fishing of saithe (Pollachius virens) and the subsequent effect on blood gases and chemistry. Fish Res 115–116: 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- 113.St-Louis P. (2000) Status of point-of-care testing: promise, realities, and possibilities. Clin Biochem 33: 427–440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Sampson K, Merigo C, Lagueux K, Rice J, Cooper R, Weber ES, III, Kass P, Mandelman JW, Innis C. (2012) Clinical assessment and postrelease monitoring of 11 mass stranded dolphins on Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Mar Mammal Sci 28: 404–425. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Schalm OW, Jain NC, Carroll EJ. (1975) Veterinary Haematology, Ed 3 Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia. [Google Scholar]
- 116.Serra-Llinares RM, Tveiten H, Damsgård B, Aas-Hansen O. (2012) Evaluation of a fast and simple method for measuring plasma lactate levels in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua (L.). Intern J Fish Aquacult 4: 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Spicer JI, Gaston KJ. (1999) Physiological Diversity and its Ecological Implications. Blackwell Science, Oxford, UK. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Steinmetz HW, Vogt R, Sabine K, Riond B, Hatt J-M. (2007) Evaluation of the i-STAT portable clinical analyzer in chickens (Gallus gallus). J Vet Diagn Invest 19: 382–388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Stockard TK, Levenson DH, Berg L, Fransioli JR, Baranov EA, Pronganis PJ. (2007) Blood oxygen depletion during rest-associated apneas of northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirstris). J Exp Biol 210: 2607–2617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Stoot LJ, Cairns NA, Blouin-Demers G, Cooke SJ. (2013) Physiological disturbances and behavioural impairment associated with the incidental capture of freshwater turtles in a commercial fyke-net fishery. Endang Species Res 21: 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- 121.Suski CD, Cooke SJ, Danylchuk AJ, O'Connor CM, Gravel M-A, Redpath T, Hanson KC, Gingerich AJ, Murchie K, Danylchuk SE, et al. (2007) Physiological disturbance and recovery dynamics of bonefish (Albula vulpes), a tropical marine fish, in response to variable exercise and exposure to air. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 148: 664–673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Taylor MK, Cook KV, Hasler CT, Schmidt DC, Cooke SJ. (2012) Behaviour and physiology of mountain whitefish (Prosopium williamsoni) relative to short-term changes in river flow. Ecol Freshw Fish 21: 495–657. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Thompson LA, Cooke SJ, Donaldson MR, Hanson KC, Gingerich A, Klefoth T, Arlinghaus R. (2012) Physiology, behaviour, and survival of angled and air-exposed largemouth bass. North Am J Fish Manage 28: 1059–1068. [Google Scholar]
- 124.Thrall MA, Weiser G, Allison R, Campbell TW. (2012) Veterinary Hematology and Clinical Chemistry. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, UK. [Google Scholar]
- 125.Trushenski JT, Bowker JD. (2012) Effect of voltage and exposure time on fish response to electrosedation. J Fish Wildl Manage 3: 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 126.Trushenski JT, Schwarz M, Takeuchi R, Delbos B, Sampaio LA. (2010) Physiological responses of cobia Rachycentron canadum following exposure to low water and air exposure stress challenges. Aquaculture 307: 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- 127.Trushenski JT, Bowker JD, Gause BR, Mulligan BL. (2012a) Chemical and electrical approaches to sedation of hybrid striped bass: induction, recovery, and physiological responses to sedation. Trans Am Fish Soc 141: 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Trushenski JT, Bowker JD, Mulligan BL, Gause BR. (2012b) Induction, recovery, and hematological responses of largemouth bass to chemo- and electrosedation. N Am J Aquacult 74: 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Venn Beecham R, Small BC, Minchew CD. (2006) Using portable lactate and glucose meters for catfish research: acceptable alternatives to established laboratory methods? N Am J Aquacult 68: 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- 130.Wells RMG, Dunphy BJ. (2009) Potential impact of metabolic acidosis on the fixed-acid Bohr effect in snapper (Pagrus auratus) following angling stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 154: 56–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Wells RMG, Pankhurst NW. (1999) Evaluation of simple instruments for the instruments for the measurement of blood glucose and lactate, and plasma protein as stress indicators in fish. J World Aquacult Soc 30: 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- 132.White AJ, Schreer JF, Cooke SJ. (2008) Behavioural and physiological responses of the congeneric largemouth (Micropterus salmoides) and smallmouth bass (M. dolomieu) to various exercise and air exposure durations. Fish Res 89: 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- 133.White FN. (1978) Comparative aspects of vertebrate cardiorespiratory physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 40: 471–499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Wikelski M, Cooke SJ. (2006) Conservation physiology. Trends Ecol Evol 21: 38–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Wimsatt J, O'Shea TJ, Ellison LE, Pearce RD, Price VR. (2005) Anesthesia and blood sampling of wild big brown bats (Eptesicus fuscus) with an assessment of impacts on survival. J Wildl Dis 41: 87–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Wolf KN, Harms CA, Beasley JF. (2008) Evaluation of five clinical chemistry analyzers for use in health assessment in sea turtles. J Am Vet Med Assoc 233: 470–475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]