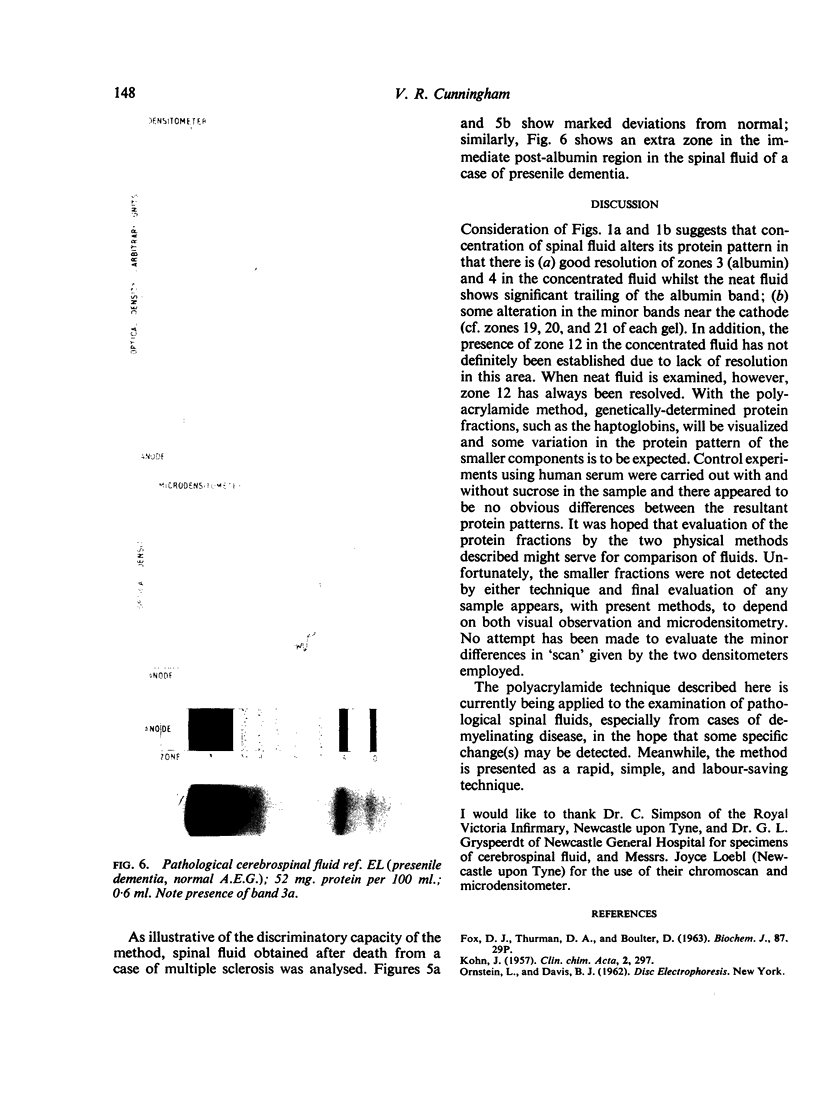
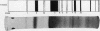Abstract
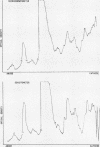
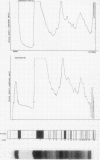
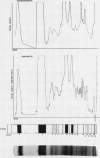
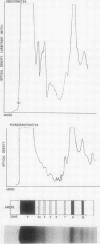
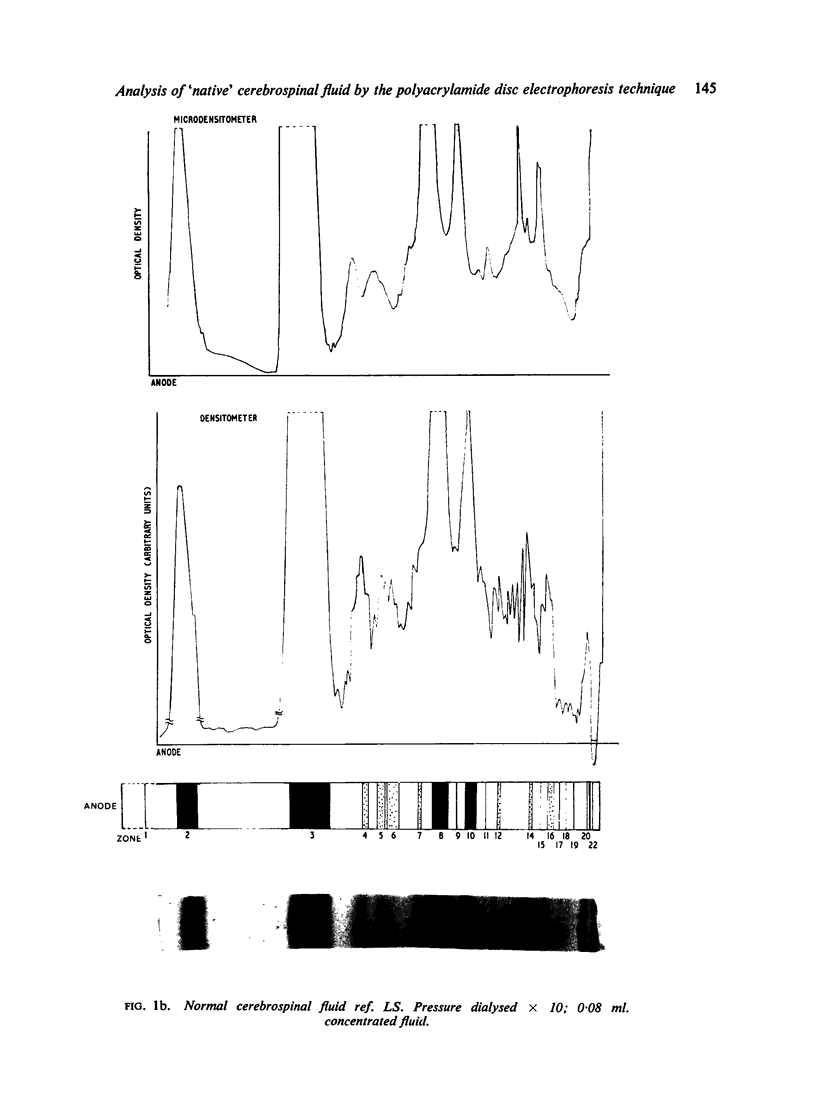
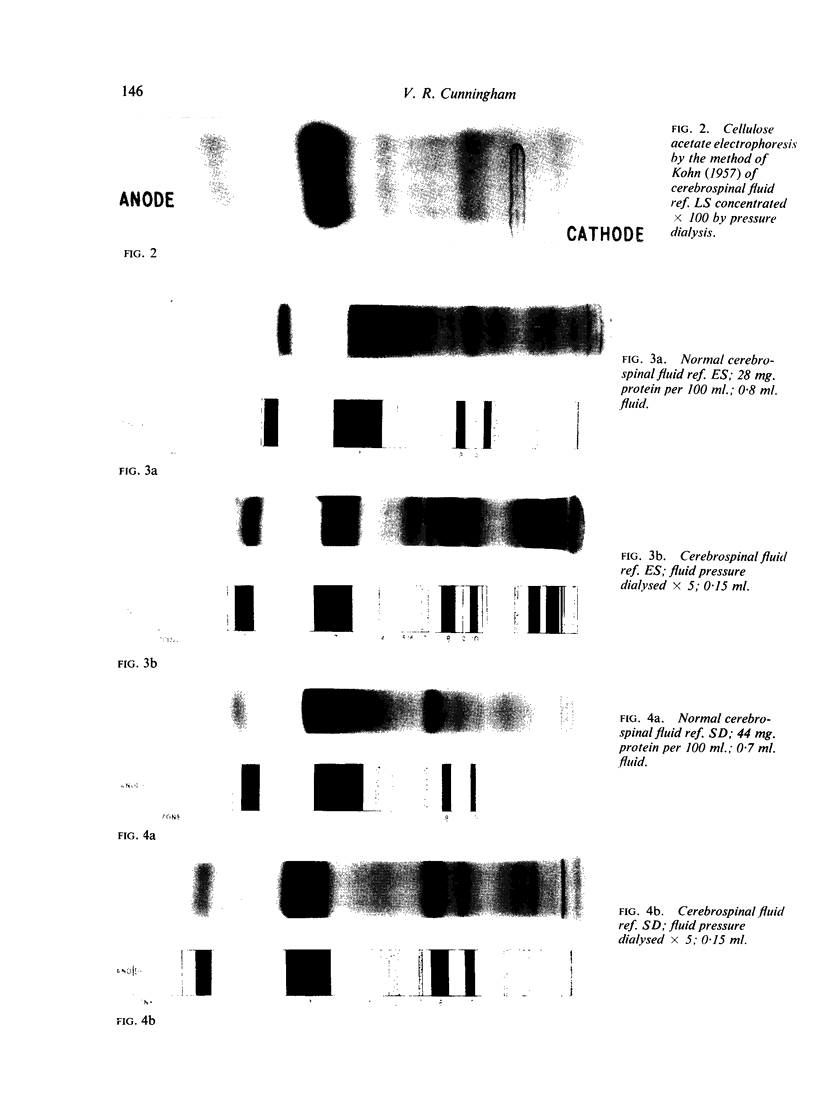
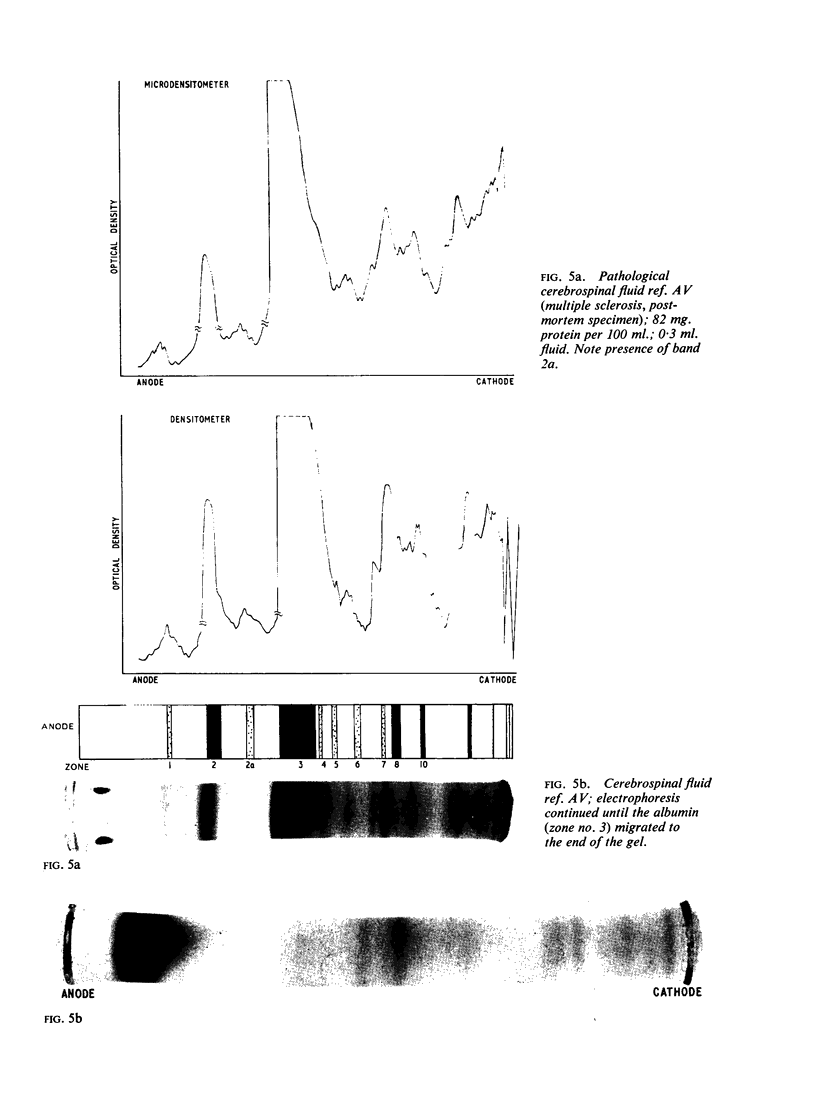
The polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis technique has been applied to the fractionation of `native' cerebrospinal fluid. Evidence is presented to show that there is an alteration in the protein profile if the fluid is subjected to a concentration stage. A minimum of 22 distinct protein zones have been detected in fluids from patients without structural changes in the nervous system. The method has also been applied to pathological fluids and the differences are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- KOHN J. A cellulose acetate supporting medium for zone electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1957 Aug;2(4):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(57)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]