Abstract
Commercially supplied radioiodinated triolein has been shown by thin-layer chromatography and silicic acid column chromatography to contain impurities, consisting mainly of diglycerides and monoglycerides, but also a small amount of free fatty acid. The effect of these impurities on the radioiodinated triolein absorption test requires further investigation.
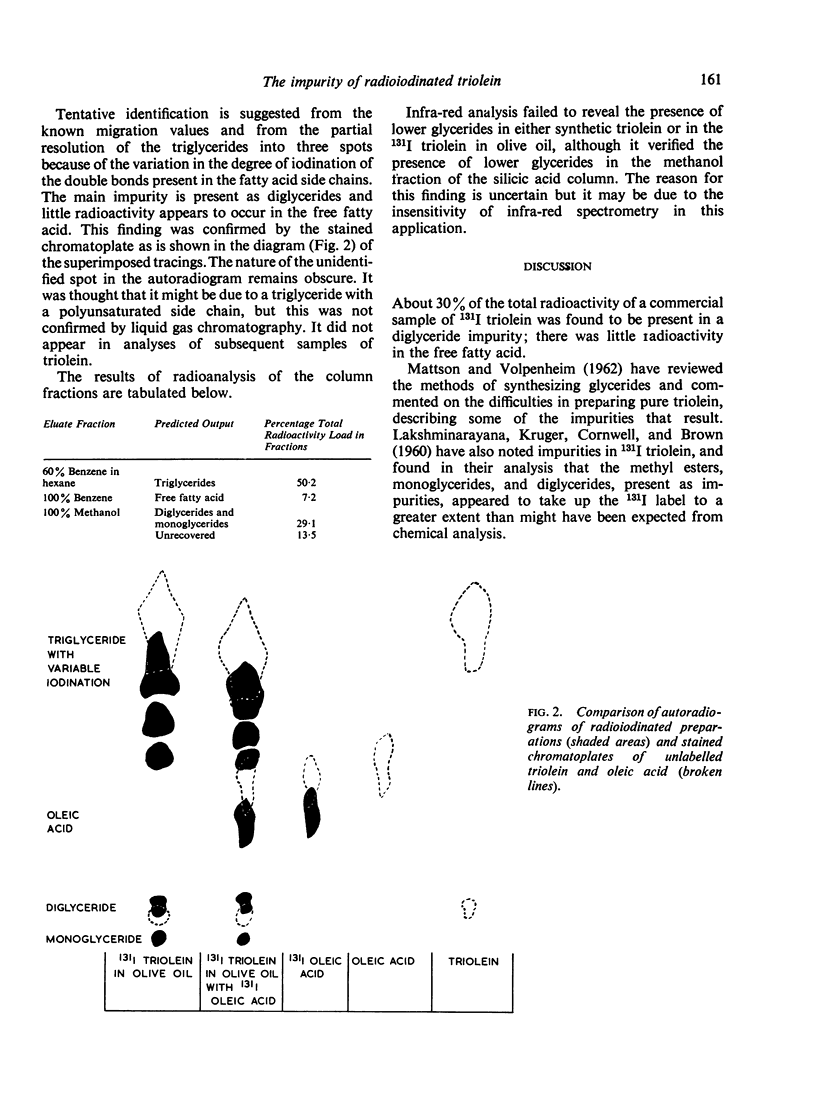
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COX A. G. Assessment of the radiotriolein test in steatorrhoea. Br Med J. 1961 Oct 7;2(5257):933–938. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5257.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNING M. G., WILLIAMS E. A., HORNING E. C. Separation of tissue cholesterol esters and triglycerides by silicic acid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1960 Oct;1:482–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKSHMINARAYANA G., KRUGER F. A., CORNWELL D. G., BROWN J. B. Chromatographic studies on the composition of commercial samples of triolein-I131 and oleic acid-I131, and the distribution of the label in human serum lipids following oral administration of these lipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Jun;88:318–327. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBRAN M., PEARSON J. D. A screening test for steatorrhoea using 131I-labelled triolein. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Mar;11(2):165–169. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



