Abstract
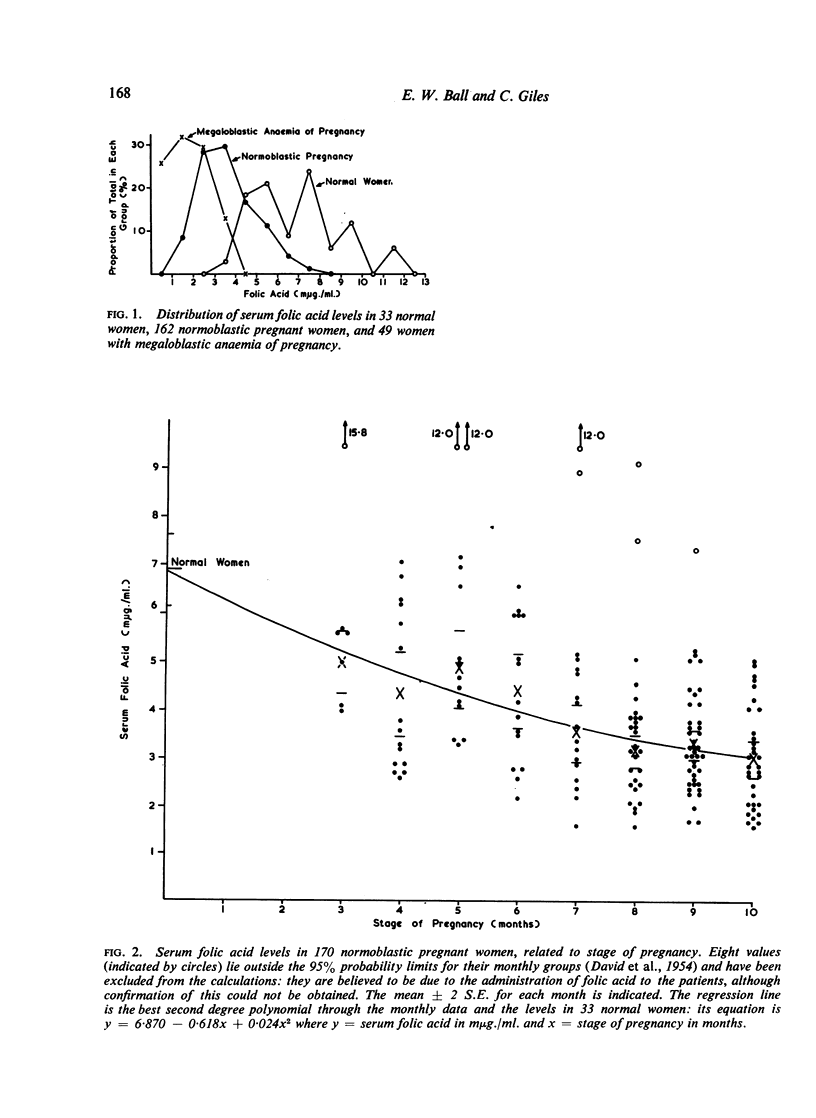
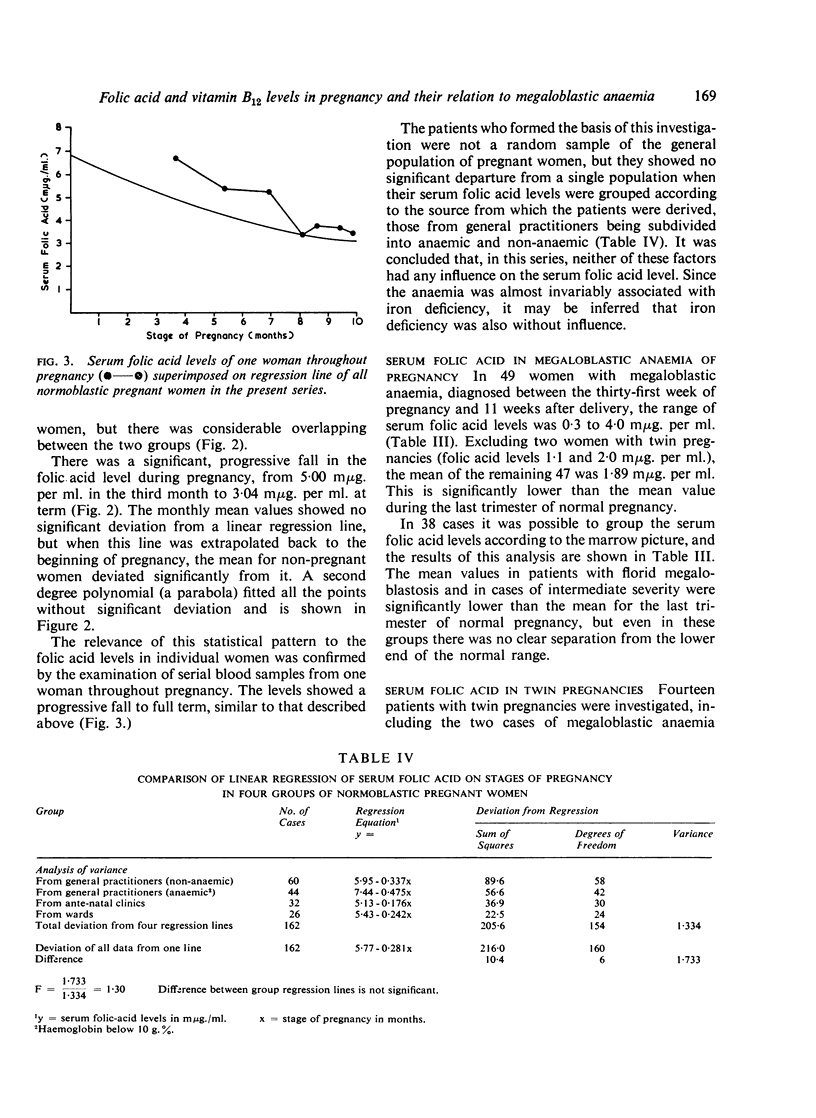
There is a significant fall in the serum folic acid level during pregnancy, reaching its lowest level at term. This is most pronounced in twin pregnancies. A similar but less spectacular fall occurs in the vitamin B12 concentration.
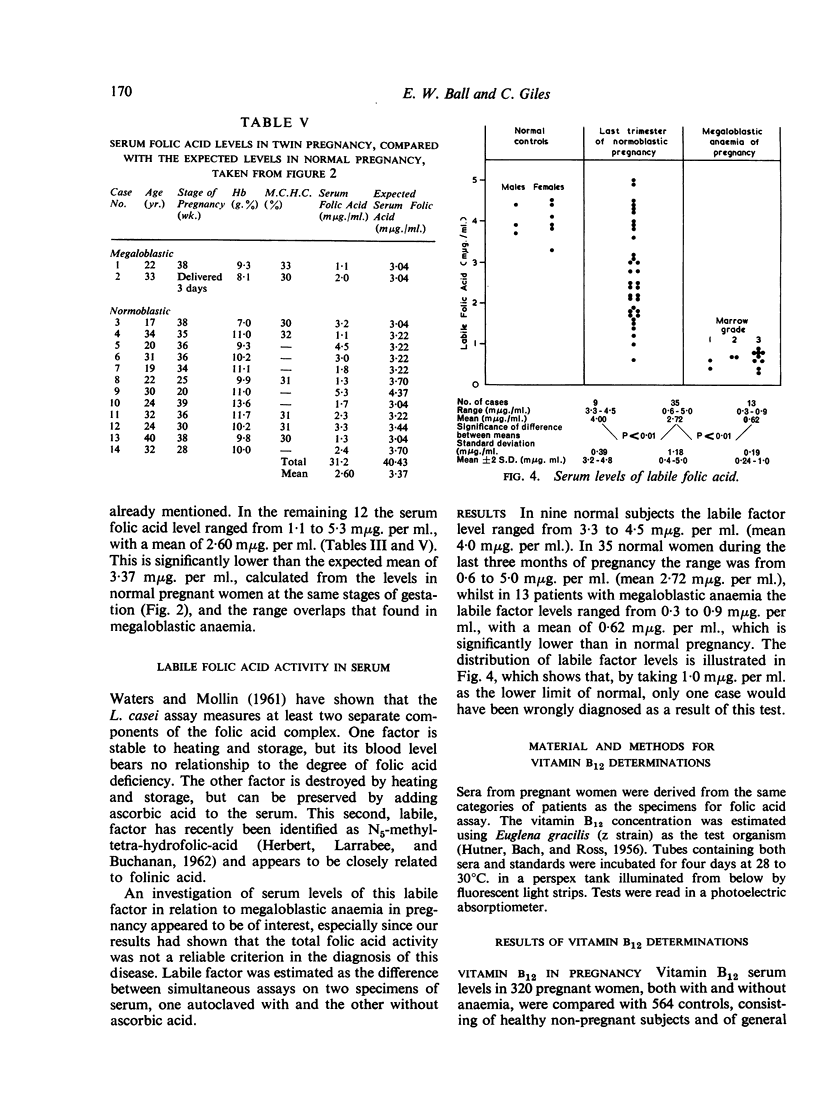
In megaloblastic anaemia both folic acid and vitamin B12 levels are lower than in other pregnant women. The degree of megaloblastic change in the bone marrow, as measured by the type and number of megaloblasts, is reflected in the vitamin levels, cases with florid megaloblastosis showing the most marked depression of vitamin B12 and folic acid activity.
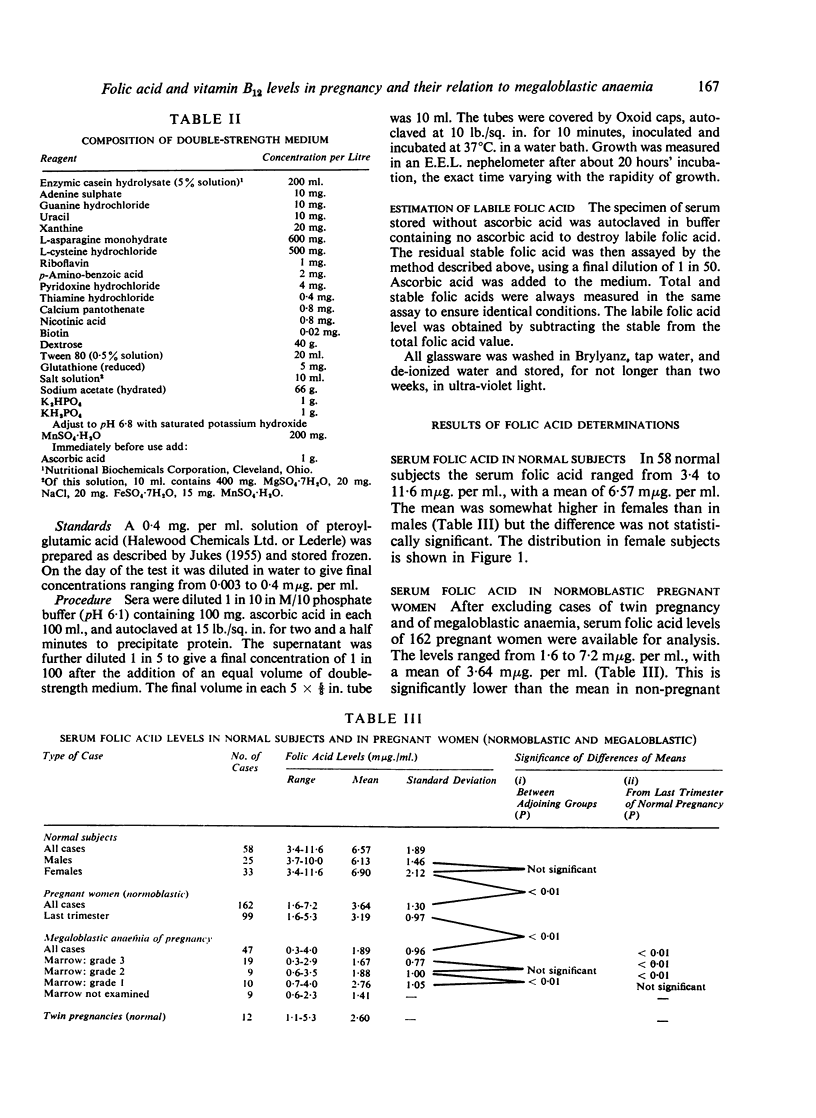
Although there is a significant difference in the mean folic acid levels between megaloblastic and normoblastic pregnant women, a considerable overlap exists between individual values in the two groups. When the labile folic-acid factor is determined separately the test becomes much more specific. In the present series, all cases of megaloblastic anaemia yielded labile-factor levels below 1·0 mμg. per ml., while a similar value was encountered in only one of 35 normal pregnancies.
In five women with megaloblastic anaemia the vitamin B12 concentration was less than 100 μμg. per ml. but rose to normal levels on folic acid therapy alone.
Full text
PDF

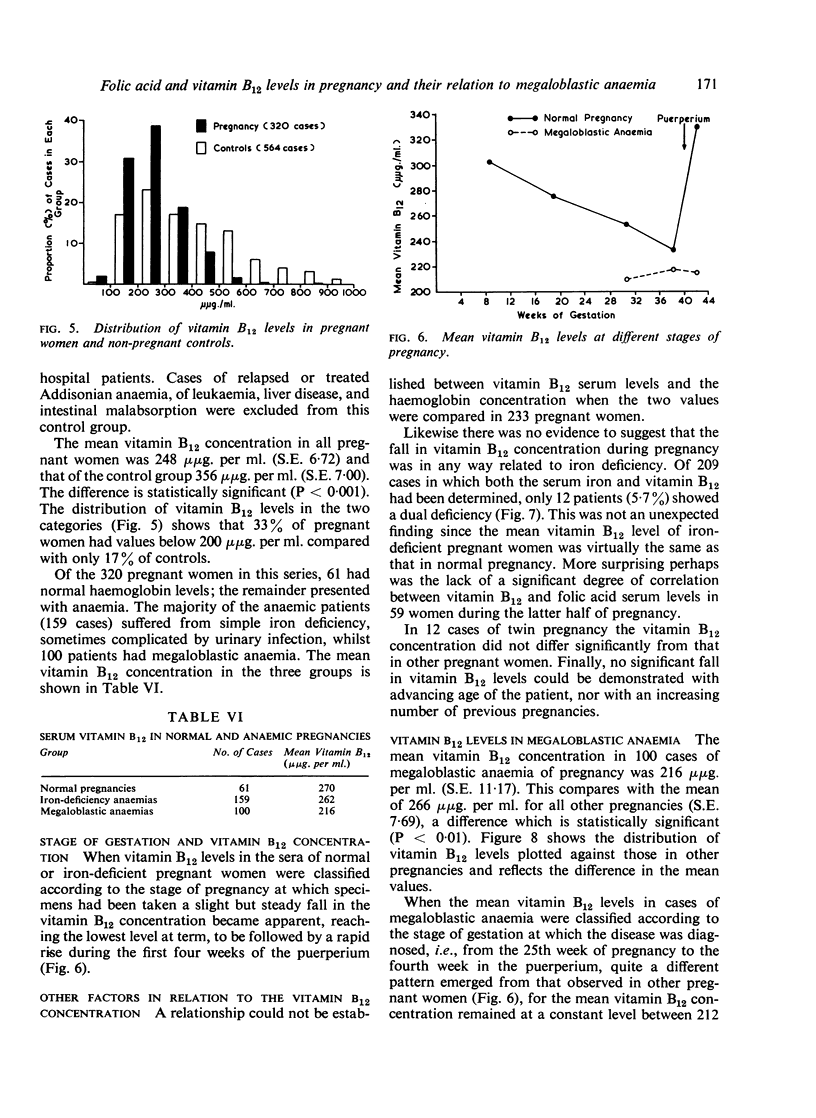
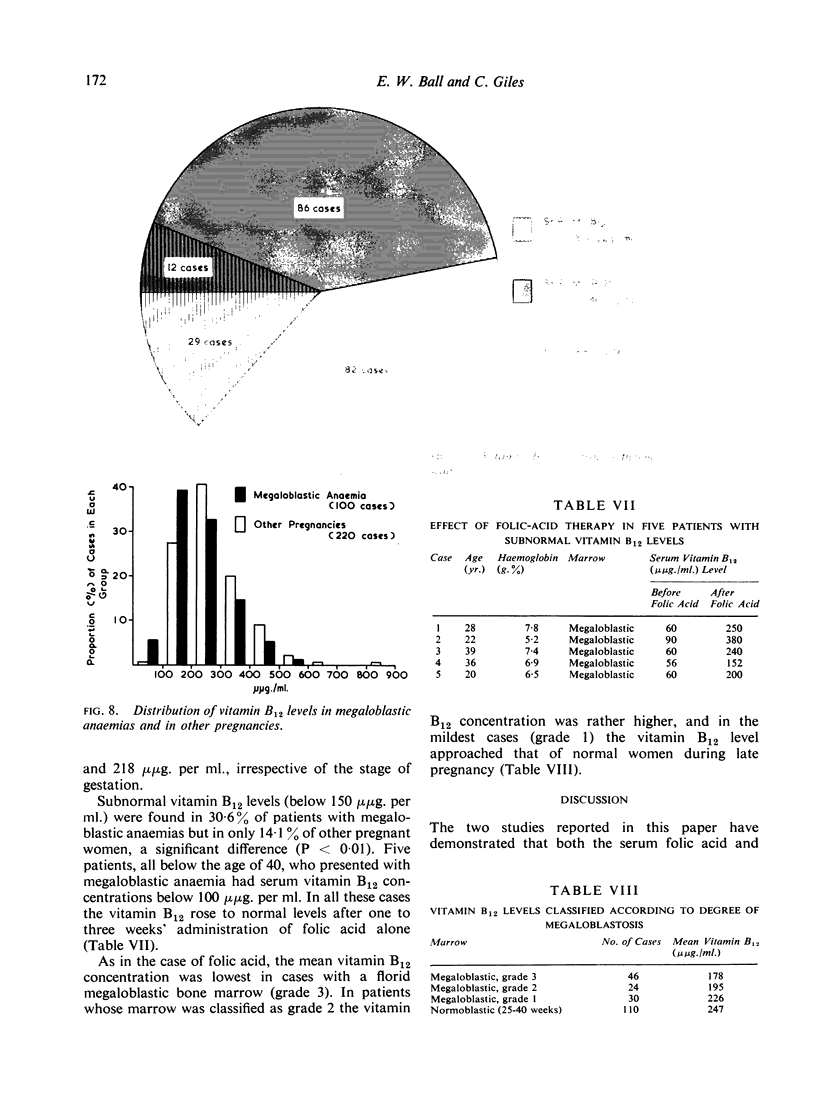


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AINLEY N. J. Megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy and the puerperium. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961 Apr;68:254–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1961.tb02718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADENOCH J., CALLENDER S. T., EVANS J. R., TURNBULL A. L., WITTS L. J. Megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy and the puerperium. Br Med J. 1955 May 21;1(4924):1245–1247. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4924.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER H., HERBERT V., FRANK O., PASHER I., HUTNER S. H., WASSERMAN L. R., SOBOTKA H. A microbiologic method for detecting folic acid deficiency in man. Clin Chem. 1959 Aug;5(4):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER S. J., JACOB E., RAJAN K. T., SWAMINATHAN S. P. Vitamin-B12 deficiency in pregnancy and the puerperium. Br Med J. 1962 Jun 16;1(5293):1658–1661. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5293.1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANARIN I., MACGIBBON B. M., O'SULLIVAN W. J., MOLLIN D. L. Folic-acid deficiency in pregnancy. The pathogenesis of megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy. Lancet. 1959 Oct 24;2(7104):634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWAN B. Observations on the incidence of megaloblastic anaemia in pregnancy and the puerperium. Scott Med J. 1957 Nov;2(11):433–434. doi: 10.1177/003693305700201105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX E. V., MEYNELL M. J., GADDIE R., COOKE W. T. Interrelation of vitamin B12 and iron. Lancet. 1959 Dec 5;2(7110):998–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON D. W., MORE J. R., AIRD D. C. Prevention of megalo-blastic anaemia in pregnancy by folic acid. Lancet. 1962 Nov 17;2(7264):1015–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92702-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON D. W. The bone marrow picture of folic acid deficiency in pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1962 Feb;69:38–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1962.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacie J. V., White J. C. Erythropoiesis with Particular Reference to its Study by Biopsy of Human Bone Marrow: A Review. J Clin Pathol. 1949 Feb;2(1):1–32. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSHAW J. W., JONES A. T., CHISHOLM W. N., MCGINLEY W. K. Megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy and the puerperium. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1957 Apr;64(2):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1957.tb02631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES C., BURTON H. Observations on prevention and diagnosis of anaemia in pregnancy. Br Med J. 1960 Aug 27;2(5199):636–640. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5199.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES C. Blood-group distribution in megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy. Lancet. 1960 Nov 12;2(7159):1063–1064. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES C., SHUTTLEWORTH E. M. Megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy and the puerperium. Lancet. 1958 Dec 27;2(7061):1341–1347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRDWOOD R. H., DELAMORE I. W. Observations on tests of folic acid absorption and clearance. Scott Med J. 1961 Feb;6:44–59. doi: 10.1177/003693306100600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., LARRABEE A. R., BUCHANAN J. M. Studies on the identification of a folate compound of human serum. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:1134–1138. doi: 10.1172/JCI104565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUKES T. H. Assay of compounds with folic acid activity. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:121–151. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METZ J., LEWIS S. M., KEELEY K. J., HART D. The absorption of vitamin B12 in megaloblastic anaemia associated with pregnancy. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Sep;13:394–395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAYANAN M. S., RAMASARMA G. B., SHENOY K. G. Rise of serum folic acid-levels after injection of vitamin B12 in nutritional macrocytic anaemia. Nature. 1956 Dec 15;178(4546):1347–1348. doi: 10.1038/1781347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. M. Therapy in the megaloblastic anaemias of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1954 Oct;61(5):646–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1954.tb07700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMONS E., LEE S. L., WASSERMAN M., MALKIN J. Association of anaemia in pregnancy and folic acid deficiency. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1962 Oct;69:724–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1962.tb01270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAY G. H., WITTS L. J. Results of three years' experience with microbiological assay of vitamin B12 in serum. Br Med J. 1958 Feb 8;1(5066):295–298. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5066.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERS A. H., MOLLIN D. L. Studies on the folic acid activity of human serum. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Jul;14:335–344. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.4.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIFFER H., BAKER H., PASHER I., SOBOTKA H. A comparison of maternal and foetal folic acid and vitamin B12 at parturition. Br Med J. 1958 Apr 26;1(5077):978–979. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5077.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




