Abstract
The aggregating effects of adenosine diphosphate, thrombin, 5-hydroxytryptamine, tryptamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline, and tri-ethyl tin have been carefully compared. The first three compounds in some circumstances produce remarkably similar effects although there are important differences. The kinetics of aggregation induced by adrenaline (and noradrenaline) are quite different and the tri-ethyl tin effects are different again. Anti-serotonins specifically inhibit 5-hydroxytryptamine and the anti-adrenaline drug phentolamine specifically inhibits the effects of the catecholamines.
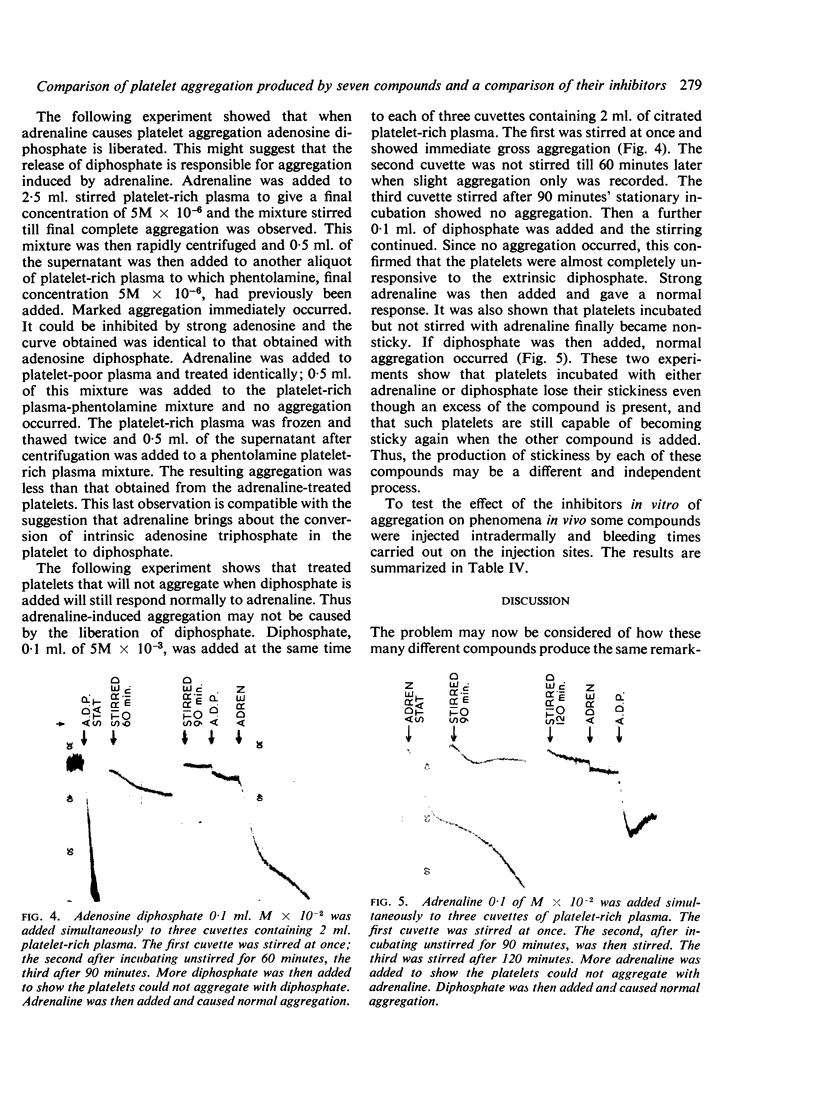
Experiments presented suggest but do not prove that aggregation produced by all these compounds is accompanied by the liberation of diphosphate from the platelets and that platelet triphosphate may be converted to diphosphate. How these different compounds all produce this effect is discussed. Either the presence of diphosphate or the action of a triphosphatase might be the immediate cause of aggregation if there is a single final common cause. The anti-adrenaline phentolamine prolongs the bleeding time, so adrenaline or noradrenaline may be involved in platelet phenomena in haemostasis.
Full text
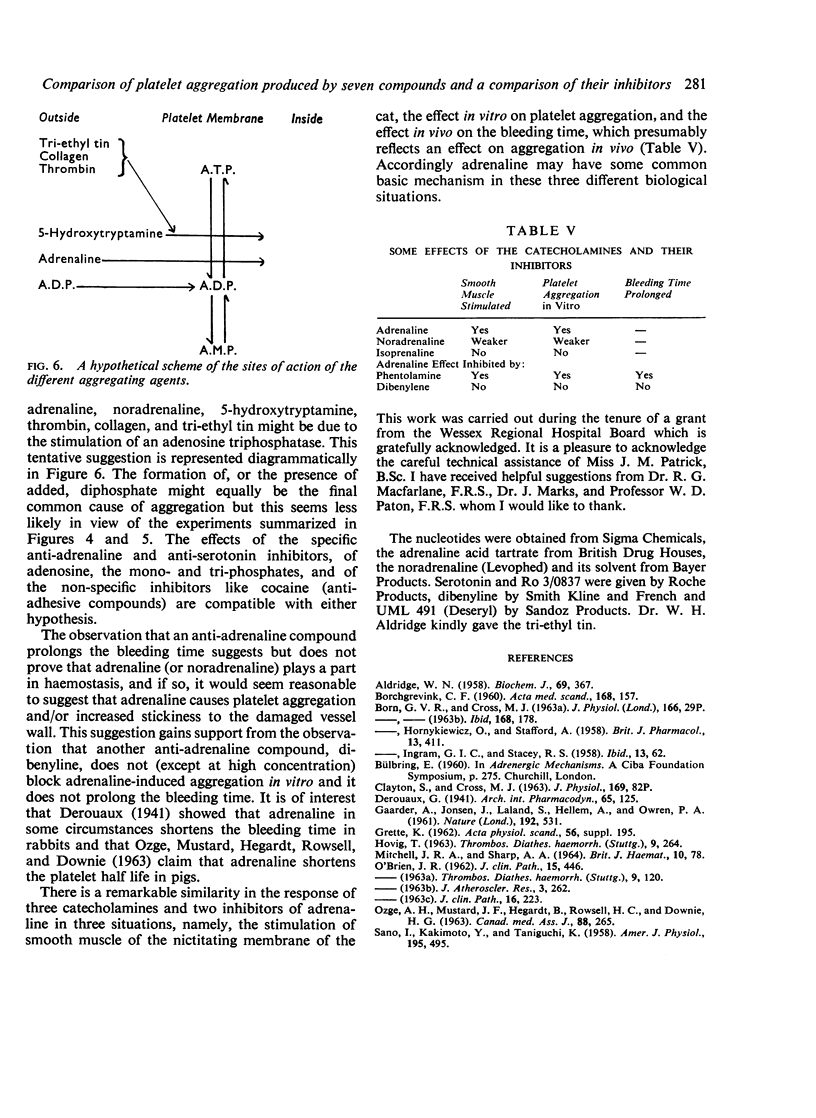
PDF

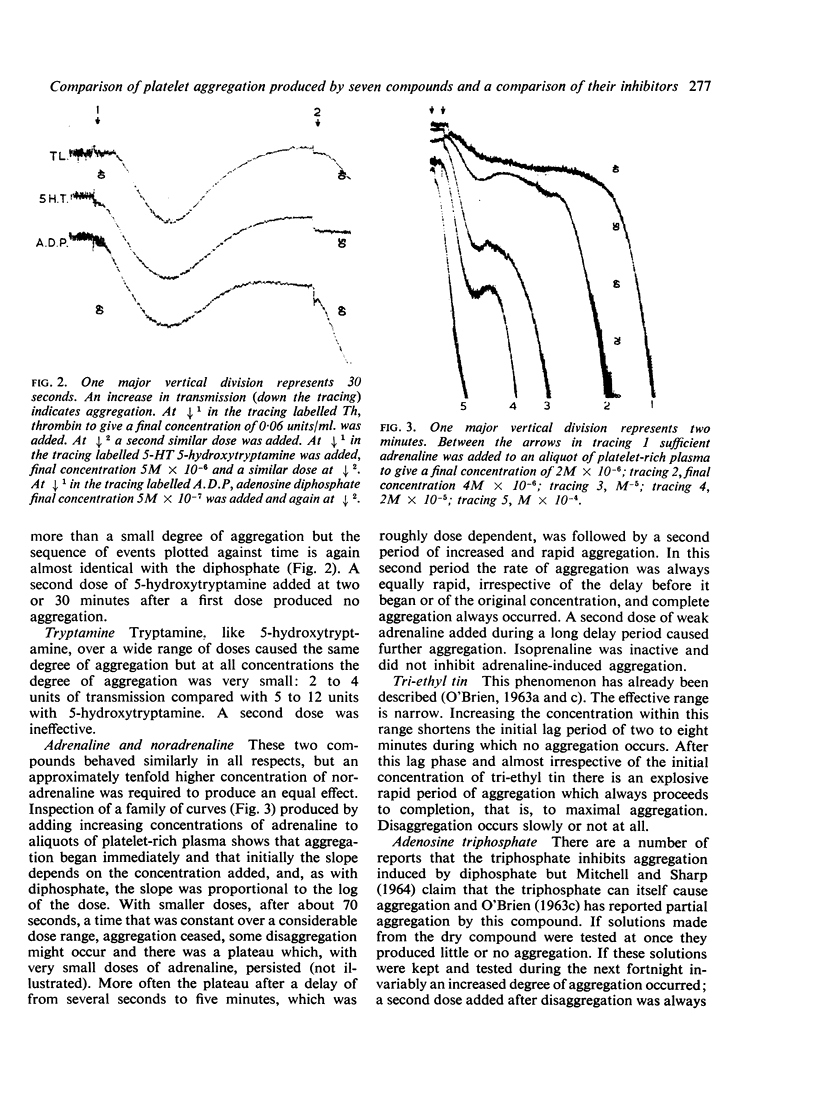
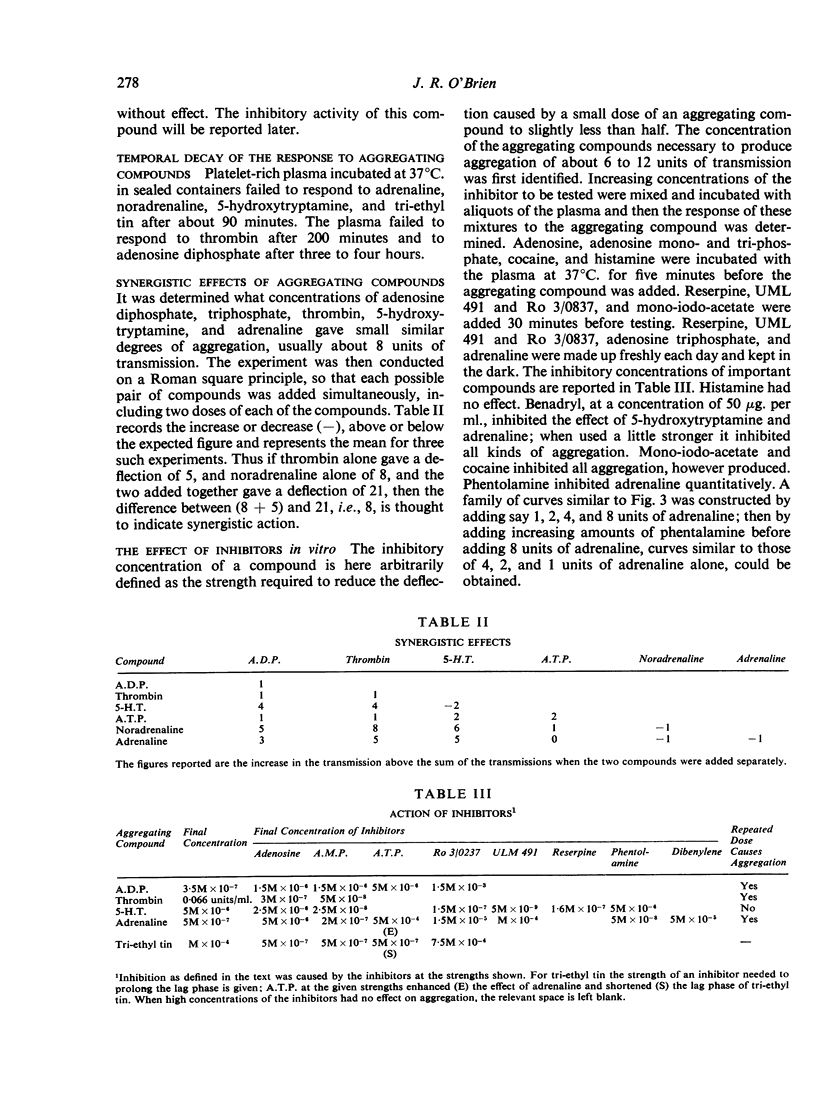
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. The biochemistry of organotin compounds: trialkyltins and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):367–376. doi: 10.1042/bj0690367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., HORNYKIEWICZ O., STAFFORD A. The uptake of adrenaline and noradrenaline by blood platelets of the pig. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Dec;13(4):411–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., KURIYAMA H. Effects of changes in the external sodium and calcium concentrations on spontaneous electrical activity in smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:29–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAARDER A., JONSEN J., LALAND S., HELLEM A., OWREN P. A. Adenosine diphosphate in red cells as a factor in the adhesiveness of human blood platelets. Nature. 1961 Nov 11;192:531–532. doi: 10.1038/192531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL J. R., SHARP A. A. PLATELET CLUMPING IN VITRO. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jan;10:78–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'brien J. R. Platelet aggregation: Part I Some effects of the adenosine phosphates, thrombin, and cocaine upon platelet adhesiveness. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Sep;15(5):446–452. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.5.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANO I., KAKIMOTO Y., TANIGUCHI K. Binding and transport of serotonin in rabbit blood platelets and action of reserpine. Am J Physiol. 1958 Nov;195(2):495–498. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.195.2.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]