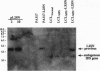
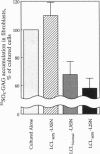
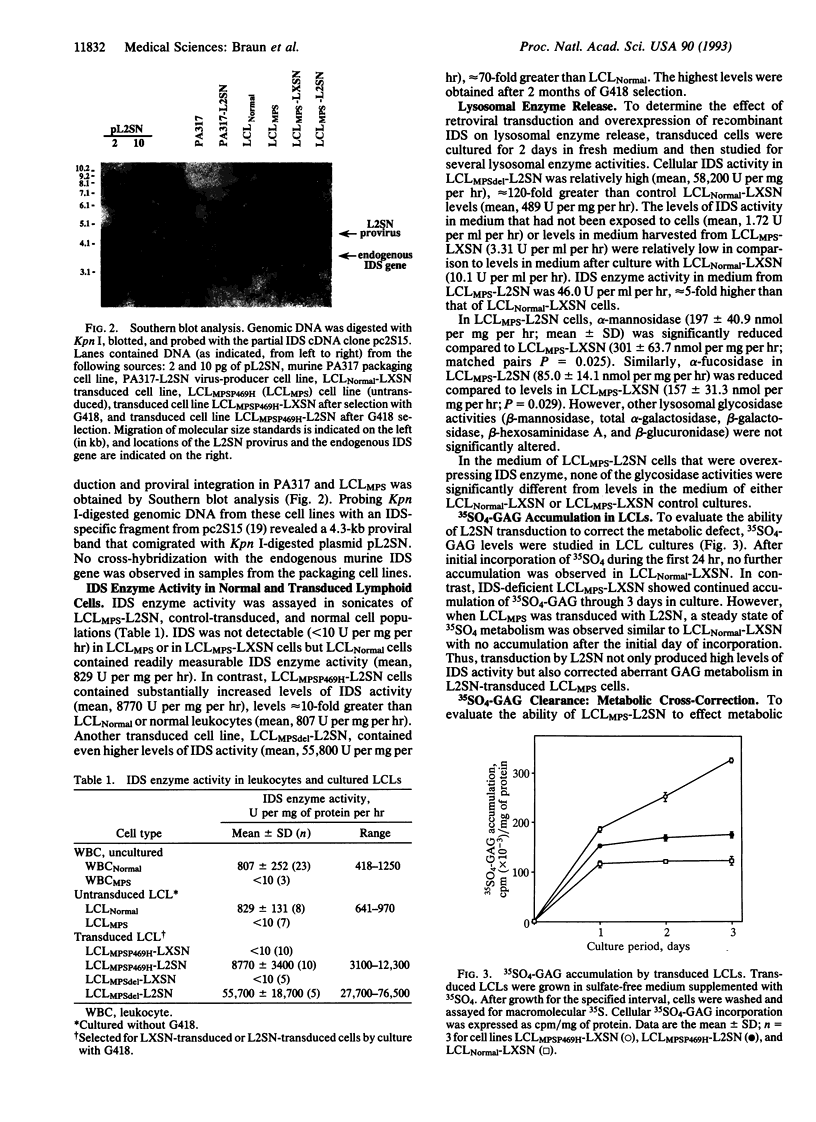
Abstract
To explore the possibility of using gene transfer to provide iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS; EC 3.1.6.13) enzyme activity for treatment of Hunter syndrome, an amphotropic retroviral vector, L2SN, containing the human IDS coding sequence was constructed and studied for gene expression in vitro. Lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from patients with Hunter syndrome were transduced with L2SN and expressed high levels of IDS enzyme activity, 10- to 70-fold higher than normal human peripheral blood leukocytes or LCLs. Such L2SN-transduced LCLs failed to show accumulation of 35SO4 into glycosaminoglycan (35SO4-GAG), indicating that recombinant IDS enzyme participated in GAG metabolism. Coculture of L2SN-transduced LCLs with fibroblasts from patients with Hunter syndrome reduced the accumulation of 35SO4-GAG. These results demonstrated retroviral-mediated IDS gene transfer into lymphoid cells and the ability of such cells to provide recombinant enzyme for intercellular metabolic cross-correction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. French, Blaese R. Michael, Culver Kenneth. The ADA human gene therapy clinical protocol: Points to Consider response with clinical protocol, July 6, 1990. Hum Gene Ther. 1990 Fall;1(3):331–362. doi: 10.1089/hum.1990.1.3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anson D. S., Bielicki J., Hopwood J. J. Correction of mucopolysaccharidosis type I fibroblasts by retroviral-mediated transfer of the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Aug;3(4):371–379. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.4-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielicki J., Hopwood J. J., Wilson P. J., Anson D. S. Recombinant human iduronate-2-sulphatase: correction of mucopolysaccharidosis-type II fibroblasts and characterization of the purified enzyme. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):241–246. doi: 10.1042/bj2890241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Barker J. E., Vogler C. A., Kyle J. W., Sly W. S., Gwynn B., Levy B., Pegors C. Increased life span and correction of metabolic defects in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII after syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1991 Dec 1;78(11):3081–3092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazar B. R., Whitley C. B., Desnick R. J., Pierpont M. E., Filipovich A. H., Ramsay N. K., Kersey J. H., Orr H. T., Yasmineh W. G., Tsai M. Y. Comparison of enzymatic activity with evidence of engraftment in patients with inborn errors of metabolism receiving allogeneic marrow transplantation. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1986;22(1):135–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Willard H. F., Teshima I., Chang P. L., Skomorowski M. A. Hunter disease (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) in a karyotypically normal girl. Clin Genet. 1990 May;37(5):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Partial enzyme deficiencies: residual activities and the development of neurological disorders. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(1):58–71. doi: 10.1159/000112332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotty P. L., Braun S. E., Anderson R. A., Whitley C. B. Mutation R468W of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in mild Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) confirmed by in vitro mutagenesis and expression. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):755–757. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotty P. L., Whitley C. B. Assessment of iduronate-2-sulfatase mRNA expression in Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II). Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):285–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00220080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M. F., McNamara A., Jenne B. M. Direct transfer of beta-glucuronidase from mouse macrophages to other types of cell. J Cell Sci. 1985 Nov;79:137–149. doi: 10.1242/jcs.79.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Ferrante N., Nichols B. L., Donnelly P. V., Neri G., Hrgovcic R., Berglund R. K. Induced degradation of glycosaminoglycans in Hurler's and Hunter's syndromes by plasma infusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):303–307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Natale P., Annella T., Daniele A., Negri R., Nitsch L. Cell-to-cell contact between normal fibroblasts and lymphoblasts deficient in lysosomal enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 14;1138(2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(92)90054-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. K., Correll P. H., Perry L. K., Brady R. O., Karlsson S. Correction of glucocerebrosidase deficiency after retroviral-mediated gene transfer into hematopoietic progenitor cells from patients with Gaucher disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratantoni J. C., Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. The defect in Hurler's and Hunter's syndromes: faulty degradation of mucopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):699–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Hugh-Jones K., Barrett A. J., Byrom N., Chambers D., Henry K., James D. C., Lucas C. F., Rogers T. R., Benson P. F. Reversal of clinical features of Hurler's disease and biochemical improvement after treatment by bone-marrow transplantation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 3;2(8249):709–712. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. The mucopolysaccharidoses. Diagnosis, molecular genetics and treatment. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Oct;7(5):381–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou Y. A., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J. Overexpression of human alpha-galactosidase A results in its intracellular aggregation, crystallization in lysosomes, and selective secretion. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1137–1150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr, Di Ferrante N., Curtis J. E. Effect of leukocyte transfusion in a child with type II mucopolysaccharidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1738–1741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivit W., Pierpont M. E., Ayaz K., Tsai M., Ramsay N. K., Kersey J. H., Weisdorf S., Sibley R., Snover D., McGovern M. M. Bone-marrow transplantation in the Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type VI). Biochemical and clinical status 24 months after transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 20;311(25):1606–1611. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412203112504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinekugel P., Michel S., Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Quantitative correlation between the residual activity of beta-hexosaminidase A and arylsulfatase A and the severity of the resulting lysosomal storage disease. Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;88(5):513–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00219337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. A safe packaging line for gene transfer: separating viral genes on two different plasmids. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1120-1124.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIvor R. S., Johnson M. J., Miller A. D., Pitts S., Williams S. R., Valerio D., Martin D. W., Jr, Verma I. M. Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase: gene transfer into cultured cells and murine hematopoietic stem cells by using recombinant amphotropic retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):838–846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Occhiodoro T., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P., Anson D. S. Correction of alpha-L-fucosidase deficiency in fucosidosis fibroblasts by retroviral vector-mediated gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Aug;3(4):365–369. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.4-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen I., Dean M. F., Harris G., Muir H. Direct transfer of a lysosomal enzyme from lymphoid cells to deficient fibroblasts. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):244–247. doi: 10.1038/291244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen I., Dean M. F., Muir H., Harris G. Acquisition of beta-glucuronidase activity by deficient fibroblasts during direct contact with lymphoid cells. J Cell Sci. 1982 Jun;55:211–231. doi: 10.1242/jcs.55.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R. The application of bone marrow transplantation to the treatment of genetic diseases. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1373–1378. doi: 10.1126/science.3520819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C., Rommerskirch W., Modaressi S., von Figura K. Restoration of arylsulphatase B activity in human mucopolysaccharidosis-type-VI fibroblasts by retroviral-vector-mediated gene transfer. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):499–504. doi: 10.1042/bj2760499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommerskirch W., Fluharty A. L., Peters C., von Figura K., Gieselmann V. Restoration of arylsulphatase A activity in human-metachromatic-leucodystrophy fibroblasts via retroviral-vector-mediated gene transfer. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):459–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2800459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. M., Hastings N. E., Selcer R. R., Jones J. B., Smith J. R., Cullen W. C., Constantopoulos G. Bone marrow transplantation in canine mucopolysaccharidosis I. Effects within the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):435–443. doi: 10.1172/JCI112830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchi M., Dinur T., Desnick R. J., Gatt S., Pereira L., Gilboa E., Schuchman E. H. Retroviral-mediated transfer of the human acid sphingomyelinase cDNA: correction of the metabolic defect in cultured Niemann-Pick disease cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3227–3231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warkentin P. I., Dixon M. S., Jr, Schafer I., Strandjord S. E., Coccia P. F. Bone marrow transplantation in Hunter syndrome: a preliminary report. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1986;22(1):31–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Neufeld E. F. Iduronate sulfatase from human plasma. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:573–578. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley C. B., Belani K. G., Chang P. N., Summers C. G., Blazar B. R., Tsai M. Y., Latchaw R. E., Ramsay N. K., Kersey J. H. Long-term outcome of Hurler syndrome following bone marrow transplantation. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Apr 15;46(2):209–218. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley C. B., Ramsay N. K., Kersey J. H., Krivit W. Bone marrow transplantation for Hurler syndrome: assessment of metabolic correction. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1986;22(1):7–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J., Morris C. P., Anson D. S., Occhiodoro T., Bielicki J., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8531–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. H., Sands M. S., Barker J. E., Gwynn B., Rowe L. B., Vogler C. A., Birkenmeier E. H. Reversal of pathology in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII by somatic cell gene transfer. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):749–753. doi: 10.1038/360749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]