Abstract
Protein kinases play essential roles in the development of eukaryotic cells. These enzymes display various degrees of sequence similarity in their catalytic domains. This conservation has allowed the identification of protein kinases in a variety of organisms, including the Gram-negative bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. In this study, sequences related to those encoding eukaryotic protein kinases were amplified by PCR from DNA of Anabaena PCC 7120, a filamentous cyanobacterium that differentiates cells specifically for nitrogen fixation, called heterocysts, under conditions of combined nitrogen limitation. Results from Southern hybridization and sequencing of PCR products suggest the presence of a family of similar protein kinases in this strain. One of the corresponding genes (pknA) was isolated from a gene library. The N-terminal region of its amino acid sequence shows significant similarity to the catalytic domains of eukaryotic-type protein kinases. Expression of this gene was found to be developmentally regulated. Inactivation of pknA led to colonies that appeared light green and rough in the absence of combined nitrogen. Mutant filaments produce fewer heterocysts than wild-type ones. These results suggest that pknA is required for both normal cellular growth and differentiation of Anabaena PCC 7120.
Full text
PDF

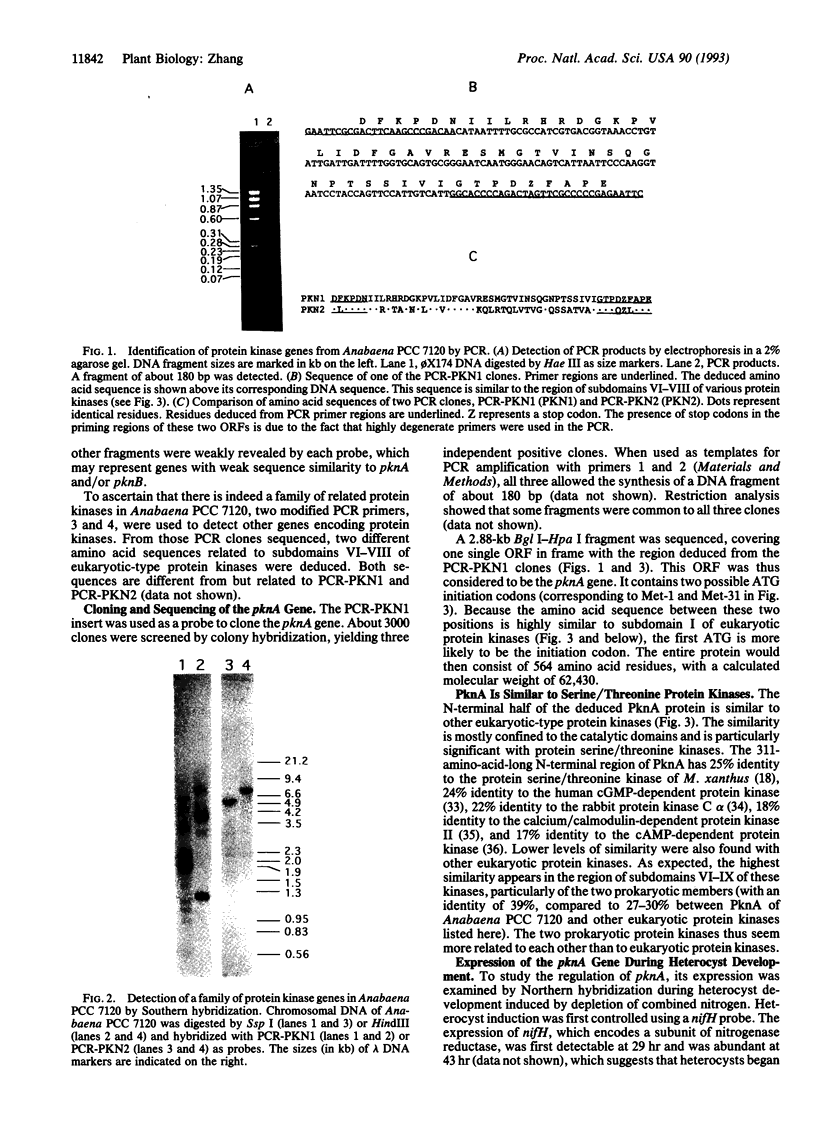


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Haselkorn R. Characterization of a gene controlling heterocyst differentiation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):321–330. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Haselkorn R. Isolation and complementation of nitrogen fixation mutants of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1879–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1879-1885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Y. P., Wolk C. P. Use of a conditionally lethal gene in Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 to select for double recombinants and to entrap insertion sequences. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3138–3145. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3138-3145.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang G. G., Schaefer M. R., Grossman A. R. Complementation of a red-light-indifferent cyanobacterial mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9415–9419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai J., Wolk C. P. Conjugal transfer of DNA to cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1988;167:747–754. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)67086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Robinson S. J., Haselkorn R. Rearrangement of nitrogen fixation genes during heterocyst differentiation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):419–423. doi: 10.1038/314419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland D., Wolk C. P. Identification and characterization of hetA, a gene that acts early in the process of morphological differentiation of heterocysts. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3131–3137. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3131-3137.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J., Scappino L., Haselkorn R. The patA gene product, which contains a region similar to CheY of Escherichia coli, controls heterocyst pattern formation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J., Scappino L., Haselkorn R. The patB gene product, required for growth of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 under nitrogen-limiting conditions, contains ferredoxin and helix-turn-helix domains. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1697-1704.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison G. J., Wilcox M. Alteration in heterocyst pattern of Anabaena produced by 7-azatryptophan. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):229–233. doi: 10.1038/newbio246229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Buikema W. J., Haselkorn R. Bacterial-type ferredoxin genes in the nitrogen fixation regions of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 and Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4406–4410. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4406-4410.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Dorado J., Inouye S., Inouye M. A gene encoding a protein serine/threonine kinase is required for normal development of M. xanthus, a gram-negative bacterium. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):995–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Suzuki K., Inagaki M., Yokokura H., Sakoh T., Hidaka H. Tissue-specific expression of three distinct types of rabbit protein kinase C. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):161–166. doi: 10.1038/325161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Natarajan V., Ronander I., Kalderon D., Walter U., Lohmann S. M., Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning and predicted full-length amino acid sequence of the type I beta isozyme of cGMP-dependent protein kinase from human placenta. Tissue distribution and developmental changes in rat. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 25;255(2):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Notch and the choice of cell fate in Drosophila neuroepithelium. Trends Genet. 1990 Nov;6(11):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90260-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobimatsu T., Fujisawa H. Tissue-specific expression of four types of rat calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17907–17912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Mitchison G. J., Smith R. J. Mutants of Anabaena cylindrica altered in heterocyst spacing. Arch Microbiol. 1975 May 5;103(3):219–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00436353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Mitchison G. J., Smith R. J. Pattern formation in the blue-green alga Anabaena. II. Controlled proheterocyst regression. J Cell Sci. 1973 Nov;13(3):637–649. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Mitchison G. J., Smith R. J. Pattern formation in the blue-green alga, Anabaena. I. Basic mechanisms. J Cell Sci. 1973 May;12(3):707–723. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.3.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. One-dimensional pattern found in blue-green algae. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):686–687. doi: 10.1038/228686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolk C. P., Quine M. P. Formation of one-dimensional patterns by stochastic processes and by filamentous blue-green algae. Dev Biol. 1975 Oct;46(2):370–382. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C. C., Durand M. C., Jeanjean R., Joset F. Molecular and genetical analysis of the fructose-glucose transport system in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1221–1229. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Munoz-Dorado J., Inouye M., Inouye S. Identification of a putative eukaryotic-like protein kinase family in the developmental bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5450–5453. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5450-5453.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]