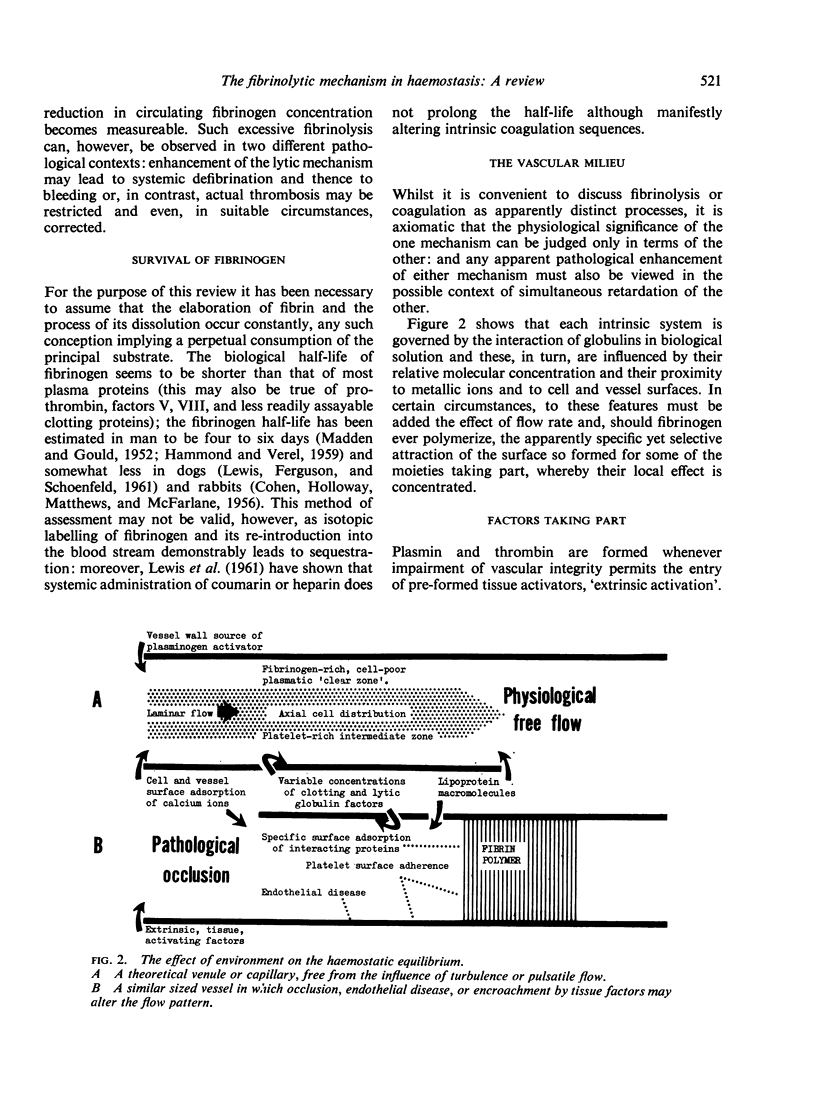
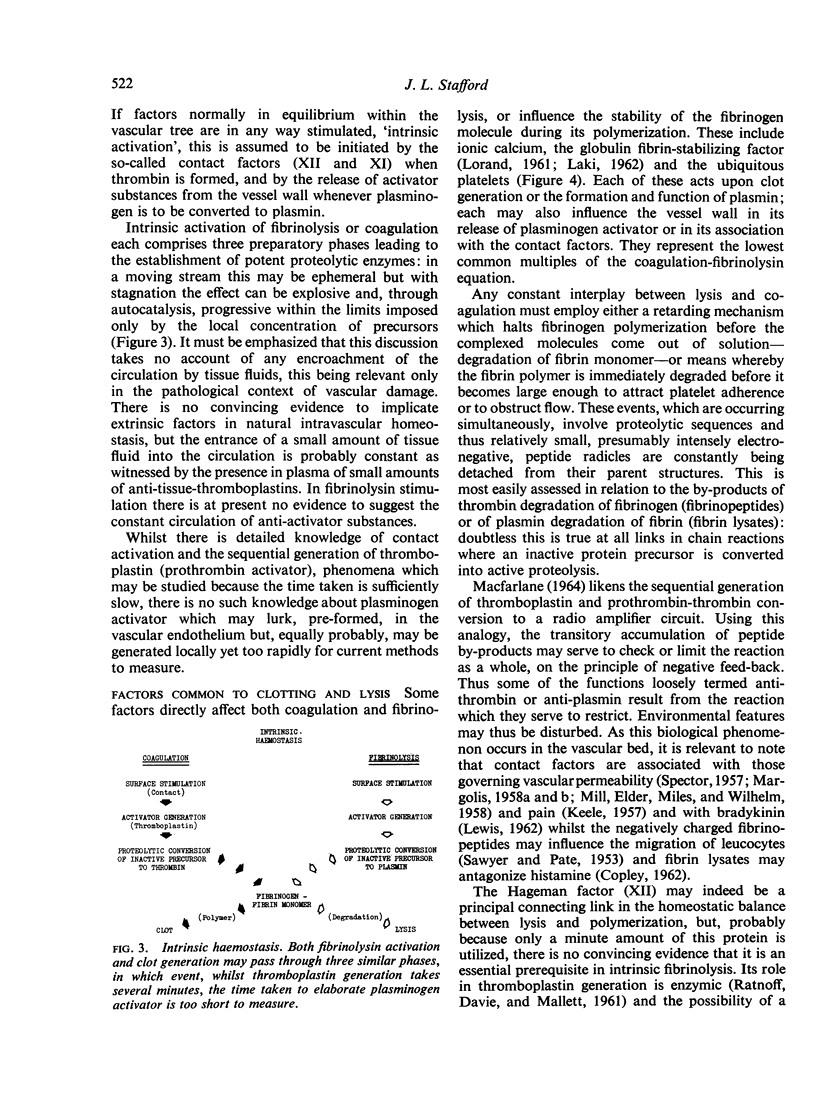
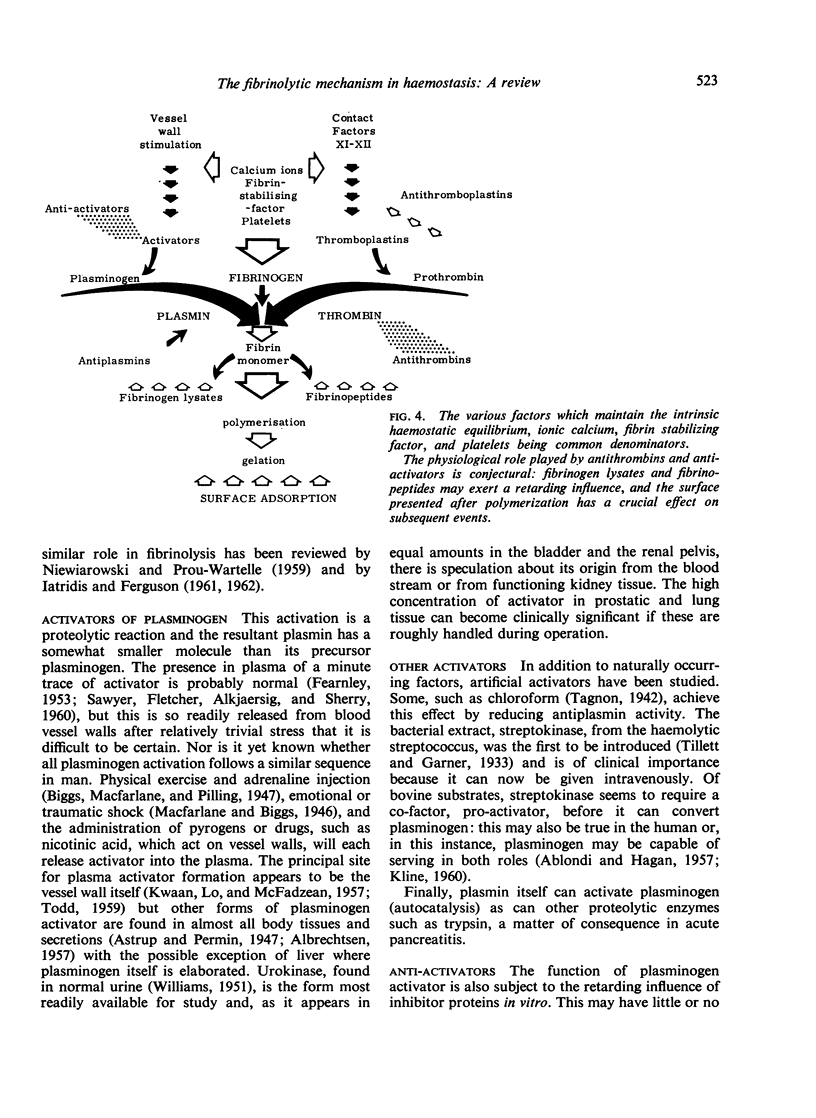
Full text
PDF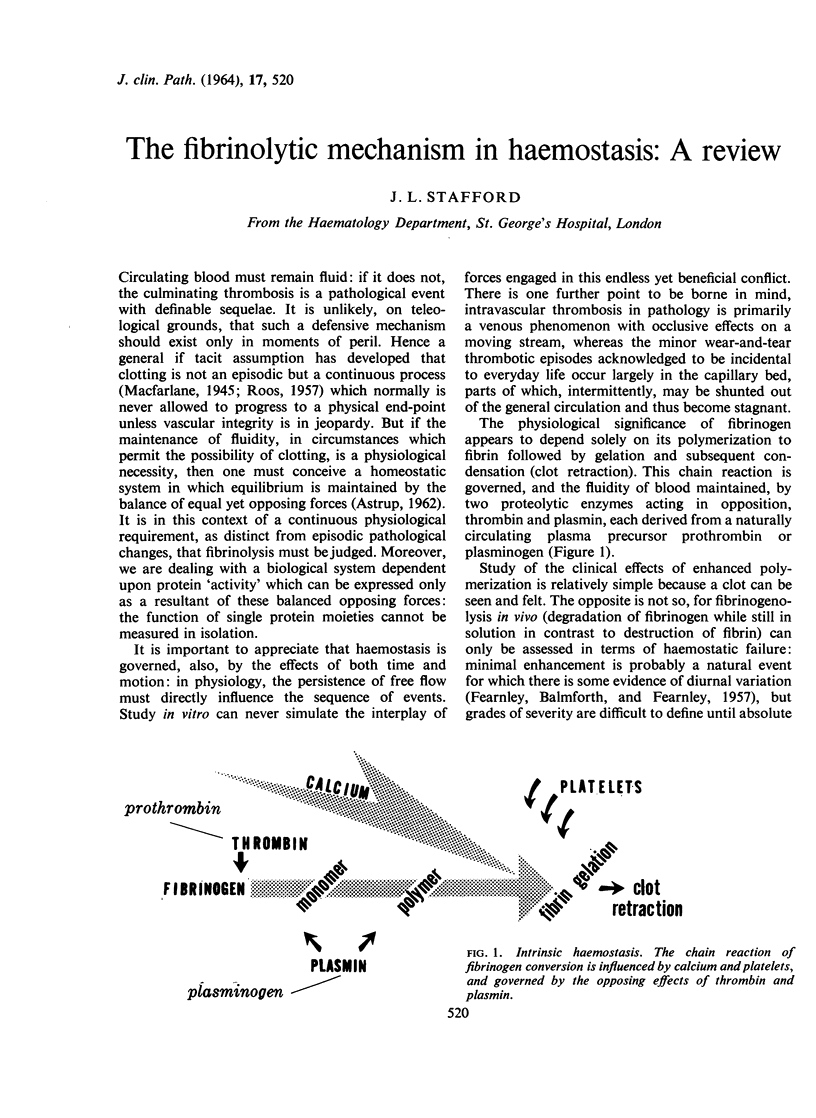






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABLONDI F. B., HAGAN J. J. Comparison of certain properties of human plasminogen and proactivator. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jun;95(2):195–200. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALBRECHTSEN O. K., THAYSEN J. H. Fibrinolytic activity in human saliva. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Dec 31;35(2):138–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALBRECHTSEN O. K. The fibrinolytic activity of human tissues. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jul;3(3):284–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. Pathogenesis of the coagulation defect developing during pathological plasma proteolytic ("fibrinolytic") states. II. The significance, mechanism and consequences of defective fibrin polymerization. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:917–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI104547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The activation of human plasminogen. II. A kinetic study of activation with trypsin, urokinase, and streptokinase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMBRUS C. M., MARKUS G. Plasmin-antiplasmin complex as a reservoir of fibrinolytic enzyme. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:491–494. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG D., JEPSON J. B., KEELE C. A., STEWART J. W. Pain-producing substance in human inflammatory exudates and plasma. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):350–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., STERNDORFF I. A fibrinolytic system in human milk. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):605–608. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANG N. U., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. Pathogenesis of the coagulation defect developing during pathological plasma proteolytic ("fibrinolytic") states. III. Demonstration of abnormal clot structure by electron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:935–948. doi: 10.1172/JCI104548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLIMORIA J. D., DRYSDALE J., JAMES D. C., MACLAGAN N. F. Determination of fibrinolytic activity of whole blood. With special reference to the effects of exercise and fat feeding. Lancet. 1959 Oct 3;2(7101):471–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90602-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM A. L. The release of thrombin from fibrin by fibrinolysin. Br J Haematol. 1962 Apr;8:129–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPARY E. A., KEKWICK R. A. Some physicochemical properties of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1957 Sep;67(1):41–48. doi: 10.1042/bj0670041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CELANDER D. R., GUEST M. M. Factors influencing susceptibility of fibrin and fibrinogen to proteolysis by fibrinolysin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Nov;72(1):176–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAKRABARTI R., FEARNLEY G. R. The 'fibrinolytic potential' as a simple measure of spontaneous fibrinolysis. J Clin Pathol. 1962 May;15:228–230. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMENT W. E., McNICOL G. P. The preparation and use of 131 I-tagged fibrinogen to demonstrate fibrinolysis. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Nov;12:544–550. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.6.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., HOLLOWAY R. C., MATTHEWS C., MCFARLANE A. S. Distribution and elimination of 131 I- and 14C-labelled plasma proteins in the rabbit. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):143–154. doi: 10.1042/bj0620143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTTON L. T., FLUTE P. T., TSAPOGAS M. J. Popliteal artery thrombosis treated with streptokinase. Lancet. 1962 Nov 24;2(7265):1081–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90786-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen L. R. METHODS FOR MEASURING THE ACTIVITY OF COMPONENTS OF THE STREPTOCOCCAL FIBRINOLYTIC SYSTEM, AND STREPTOCOCCAL DESOXYRIBONUCLEASE. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):163–172. doi: 10.1172/JCI102045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES M. C., ENGLERT M. E. Physical properties of highly purified human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:1011–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWAR H. A., STEPHENSON P., HORLER A. R., CASSELLS-SMITH A. J., ELLIS P. A. Fibrinolytic therapy of coronary thrombosis. Controlled trial of 75 cases. Br Med J. 1963 Apr 6;1(5335):915–920. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5335.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON V. H. Effect of plasmin in vitro on clotting factors in plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Oct;56:644–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Discussion on the Factors concerned in Blood Coagulation and their Clinical Significance. Proc R Soc Med. 1945 Jun;38(8):399–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Observations on intrinsic kinin-forming factors in human plasma: the effect of acid, acetone, chloroform, heat and euglobulin separation on kinin formation. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(3):496–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEARNLEY G. R., BALMFORTH G., FEARNLEY E. Evidence of a diurnal fibrinolytic rhythm; with a simple method of measuring natural fibrinolysis. Clin Sci. 1957 Nov;16(4):645–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEARNLEY G. R., CHAKRABARTI R. Increase of blood fibrinolytic activity by testosterone. Lancet. 1962 Jul 21;2(7247):128–132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEARNLEY G. R. Fibrinolysis by adsorption. Nature. 1953 Sep 19;172(4377):544–545. doi: 10.1038/172544b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. The maintenance of a sustained thrombolytic state in man. I. Induction and effects. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1096–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI103886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLUTE P. T. The clinical assessment of fibrinolysis. Proc R Soc Med. 1963 May;56:411–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANS H. FIBRINOLYTIC PROPERTIES OF PROTEASES DERIVED FROM HUMAN, DOG AND RABBIT LEUKOCYTES. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jan 1;10:379–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREIG H. B. Inhibition of fibrinolysis by alimentary lipaemia. Lancet. 1956 Jul 7;271(6932):16–18. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. E., SLAYTER H. S. The fibrinogen molecule: its size, shape, and mode of polymerization. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):11–16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMOND J. D., VEREL D. Observations on the distribution and biological half-life of human fibrinogen. Br J Haematol. 1959 Oct;5:431–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1959.tb04053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKEY C. M., STAFFORD J. L. A STANDARD CLOT METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATORS, ANTI-ACTIVATORS, AND PLASMIN. J Clin Pathol. 1964 Mar;17:175–181. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKEY C., HOWELL M. THE LABORATORY CONTROL OF THROMBOLYTIC THERAPY. J Clin Pathol. 1964 May;17:287–291. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLEMANS R., GROSS R. Influence of blood platelets on fibrinolysis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1961 Sep 1;6:196–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLEMANS R. ORIGIN OF BLOOD FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY. Lancet. 1963 Aug 17;2(7303):364–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)93047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL M. A method for the comparison of the antiplasmin activity of two groups of blood sera. J Clin Pathol. 1963 May;16:289–290. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IATRIDIS S. G., FERGUSON J. H. Effect of surface and Hageman factor on the endogenous or spontaneous activation of the fibrinolytic system. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1961 Dec 15;6:411–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON S. A., McKENNA J. L. An investigation of the possible role of platelet fibrinogen in thrombi formation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Apr 15;9:102–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON S. A., SCHNEIDER C. L. The existence of antifibrinolysin activity in platelets. Science. 1953 Feb 27;117(3035):229–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON S. A., SMATHERS W. M., SCHNEIDER C. L. Platelets and their plasma cofactor activity in the activation of purified prothrombin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Sep;170(3):631–635. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.170.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEELE C. A. Chemical causes of pain & itch. Proc R Soc Med. 1957 Jul;50(7):477–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., MACKAY M. E., NANCE M. H., RECORD B. R. The purification of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):671–683. doi: 10.1042/bj0600671b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOWALSKI E., KOPEC M., NIEWIAROWSKI An evaluation of the euglobulin method for the determination of fibrinolysis. J Clin Pathol. 1959 May;12(3):215–218. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KWAAN H. C., LO R., MCFADZEAN A. J. On the production of plasma fibrinolytic activity within veins. Clin Sci. 1957 May;16(2):241–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K. The polymerization of proteins; the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENDRUM A. C., FRASER D. S., SLIDDERS W., HENDERSON R. Studies on the character and staining of fibrin. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Sep;15:401–413. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.5.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS J. H., FERGUSON E. E., SCHOENFELD C. Studies concerning the turnover of fibrinogen I-131 in the dog. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Aug;58:247–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY M., MAYCOCK W. D., COMBRIDGE B. S. Activation of endogenous plasma proteolytic enzymes with the consequent production of pharmacologically active polypeptides. Nature. 1962 Sep 22;195:1206–1207. doi: 10.1038/1951206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. Activation of a permeability factor in plasma by contact with glass. Nature. 1958 Mar 1;181(4609):635–636. doi: 10.1038/181635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNICOL G. P., DOUGLAS A. S., BAYLEY C. Experience with streptokinase infusions. Lancet. 1962 Dec 22;2(7269):1297–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90850-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNICOL G. P., GALE S. B., DOUGLAS A. S. In-vitro and in-vivo studies of a preparation of urokinase. Br Med J. 1963 Apr 6;1(5335):909–915. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5335.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNICOL G. P., REID W., BAIN W. H., DOUGLAS A. S. Treatment of peripheral arterial occlusion by streptokinase perfusion. Br Med J. 1963 Jun 8;1(5344):1508–1512. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5344.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNICOL G. P. Thrombolytic therapy. Proc R Soc Med. 1963 May;56:414–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILL P. J., ELDER J. M., MILES A. A., WILHELM D. L. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. VI. Isolation and properties of permeability factor and its inhibitor in human plasma. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Aug;39(4):343–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., MORE R. H. The nature and origin of fibrinoid. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Oct;28(4):331–353. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/28.4.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Gordon H., Lackner H., Schrire V., Kaplan B. J., Sougin-Mibashan R., Nossel H. L., Moodie A. Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Relation to Coronary Heart Disease. Br Med J. 1960 Jan 23;1(5168):219–227. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5168.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEWIAROWSKI S., PROU-WARTELLE O. [Role of the contact factor (Hageman factor) in fibrinolysis]. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1959 Sep 1;3:593–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON I. M., OLOW B. Determination of fibrinogen and fibrinogenolytic activity. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 Nov 15;8:297–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN P. S. Studies of the plasmin system. II. Inhibition of plasmin by serum or plasma. J Exp Med. 1958 Jul 1;108(1):53–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGSTON D., FULLERTON H. W. Effect of alimentary lipaemia on plasma fibrinolytic activity. Br Med J. 1962 Nov 17;2(5315):1288–1290. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5315.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONCLEY J. L., MELIN M. The separation of the antibodies, isoagglutinins, prothrombin, plasminogen and beta1-lipoprotein into subfractions of human plasma. J Am Chem Soc. 1949 Feb;71(2):541–550. doi: 10.1021/ja01170a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. Blood capillaries of the heart and other organs. Circulation. 1961 Aug;24:368–388. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.24.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHAGEN A. R., KOPPEL J. L., OLWIN J. H. Observations on the in vitro effects of chylomicra, low-density lipoproteins and phospholipids on human plasma euglobulin lysis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Apr 15;9:164–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOLE J. C. A study of artificial thrombi produced by a modification of Chandler's method. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Oct;44:377–384. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOLE J. C., FRENCH J. E., CLIFF W. J. THE EARLY STAGES OF THROMBOSIS. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Nov;16:523–528. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.6.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagel W. Polyarteritis Nodosa and the "Rheumatic" Diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1951 May;4(2):137–157. doi: 10.1136/jcp.4.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., COLOPY J. E. A familial hemorrhagic trait associated with a deficiency of a clot-promoting fraction of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI103109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., DAVIE E. W., MALLETT D. L. Studies on the action of Hageman factor: evidence that activated Hageman factor in turn activates plasma thromboplastin antecedent. J Clin Invest. 1961 May;40:803–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI104314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., ROSENBLUM J. M. Role of Hageman factor in the initiation of clotting by glass; evidence that glass frees Hageman factor from inhibition. Am J Med. 1958 Aug;25(2):160–168. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D. Studies on a proteolytic enzyme in human plasma. IX. Fibrinogen and fibrin as substrates for the proteolytic enzyme of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1953 Jun;32(6):473–479. doi: 10.1172/JCI102762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN N. F., Jr, MASON R. G., BRINKHOUS K. M. SOME PATHOGENETIC MECHANISMS OF WHITE THROMBUS FORMATION: AGGLUTINATION AND SELF-DESTRUCTION OF THE PLATELET. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1356–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROOS J. Blood coagulation as a continuous process. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1957 Dec 15;1(3-4):471–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAAMELI K., ESKES T. K. Bradykinin and cardiovascular system: estimation of half-life. Am J Physiol. 1962 Aug;203:261–265. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER P. N., PATE J. W., WELDON C. S. Relations of abnormal and injury electric potential differences to intravascular thrombosis. Am J Physiol. 1953 Oct;175(1):108–112. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.175.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER W. D., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIN N., SHERRY S. Studies on the thrombolytic activity of human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1960 Feb;39:426–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI104054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERAGA H. A. Thrombin and its interaction with fibrinogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SGOURIS J. T., INMAN J. K., McCALL K. B., HYNDMAN L. A., ANDERSON H. D. The preparation of human fibrinolysin (plasmin). Vox Sang. 1960 Jul;5:357–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1960.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRY S., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N. Fibrinolysis and fibrinolytic activity in man. Physiol Rev. 1959 Apr;39(2):343–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRY S., LINDEMEYER R. I., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N. Studies on enhanced fibrinolytic activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):810–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI103863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R., TAGNON H. J. Proteolytic activity determined with a substrate tagged with radioactive iodine. J Biol Chem. 1950 Sep;186(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN S., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. Physicochemical studies on human plasminogen (profibrinolysin) and plasmin (fibrinolysin). J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):91–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., TOZER B. T., GALLOP R. C., SCANES F. S. Separation of antigens by immunological specificity. 1. Method for separating individual antigen-antibody complexes from mixed antigens and antibodies. Biochem J. 1962 Jul;84:74–80. doi: 10.1042/bj0840074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNES R. D. Estimation of plasminogen in biological fluids by agar/fibrinogen gel diffusion. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jan;16:87–88. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. The histological localisation of fibrinolysin activator. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:281–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., SHERRY S., WACHMAN J. The action of plasmin on synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSAPOGAS M. J., COTTON L. T., FLUTE P. T., MURRAY J. G. The effects of chlorpropamide on intermittent claudication and fibrinolysis. Lancet. 1962 Jun 9;1(7241):1213–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSAPOGAS M. J., FLUTE P. T., COTTON L. T., MILROY S. D. Lysis of experimental thrombi by streptokinase. Br J Surg. 1962 Nov;50:334–337. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18005022118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillett W. S., Garner R. L. THE FIBRINOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1933 Sep 30;58(4):485–502. doi: 10.1084/jem.58.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERSTRAETE M., AMERY A., VERMYLEN J. Feasibility of adequate thrombolytic therapy with streptokinase in peripheral arterial occlusions. I. Clinical and arteriographic results. Br Med J. 1963 Jun 8;1(5344):1499–1504. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5344.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON KAULLA K. N., SHETTLES L. B. Relationship between human seminal fluid and the fibrinolytic system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Aug-Sep;83(4):692–694. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN B. A. FIBRINOLYTIC PROPERTIES OF VASCULAR ENDOTHELIUM. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:365–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. R. B. The fibrinolytic activity of urine. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Dec;32(6):530–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


