Abstract
Three cases of exertional haemoglobinuria are described. So far, the cause of the underlying haemolysis in this condition has not been satisfactorily explained, but in the cases described, the haemoglobinuric episodes appeared to be related to traumatic damage to the soles of the feet. Experimental studies support the hypothesis that the intravascular haemolysis results from mechanical damage to red cells in the soles of the feet. Furthermore, since adopting remedial measures, haemoglobinuria has not recurred in any of the patients, although they have continued to pursue their strenuous athletic activities.
Full text
PDF

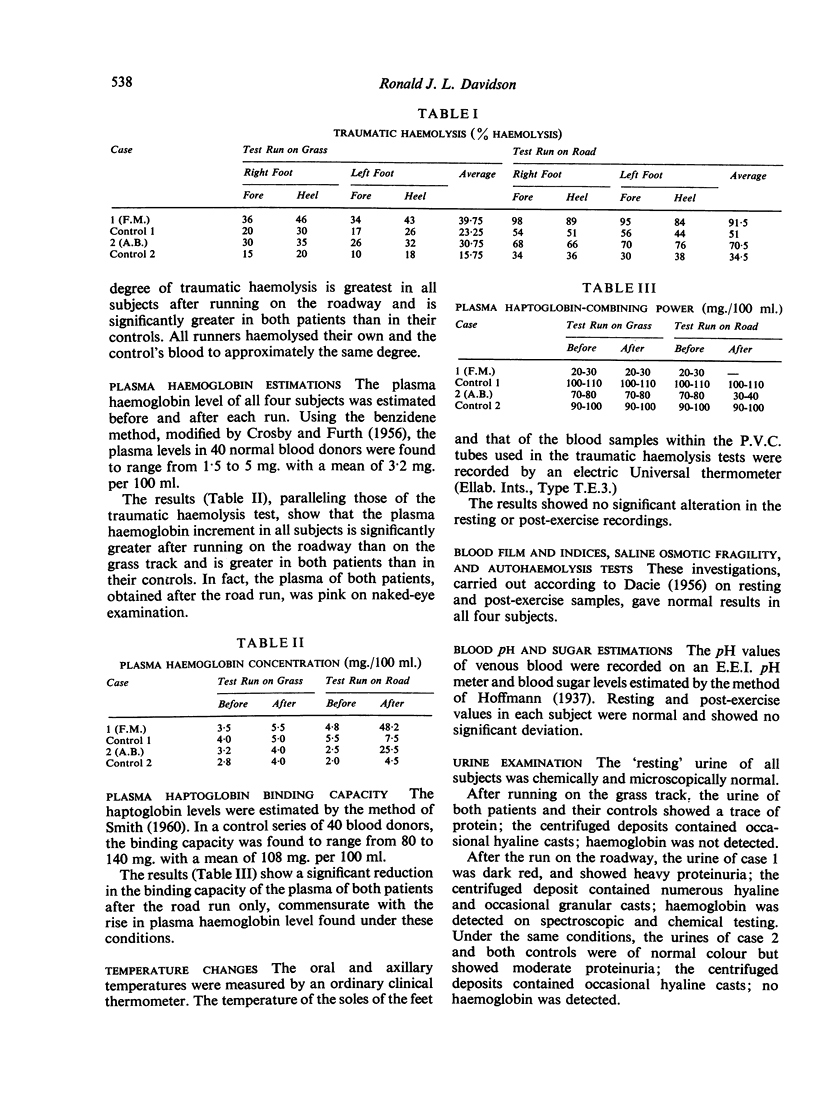


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C., REES W. A. The binding of haemoglobin by plasma proteins (haptoglobins); its bearing on the renal threshold for haemoglobin and the aetiology of haemoglobinuria. Br Med J. 1957 Nov 16;2(5054):1137–1143. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5054.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLONDHEIM S. H., MARGOLIASH E., SHAFRIR E. A simple test for myohemoglobinuria (myoglobinuria). J Am Med Assoc. 1958 May 24;167(4):453–454. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.72990210001009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H., FURTH F. W. A modification of the benzidine method for measurement of hemoglobin in plasma and urine. Blood. 1956 Apr;11(4):380–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLATMARK T. Studies on the hemolytic mechanism in March hemoglobinuria. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Mar;173:307–313. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1963.tb17410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIGAN D. R., ALTSCHULE M. D. March hemoglobinuria in a woman. N Engl J Med. 1950 Dec 14;243(24):944–948. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195012142432402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan D. R., Altschule M. D., Katersky E. M. PHYSIOLOGICAL INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS OF EXERCISE. HEMOGLOBINEMIA AND HEMOGLOBINURIA FOLLOWING CROSS-COUNTRY RUNS. J Clin Invest. 1943 Nov;22(6):859–869. doi: 10.1172/JCI101460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATHEM W. The renal excretion of hemoglobin: regulatory mechanisms and the differential excretion of free and protein-bound hemoglobin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Apr;38(4):652–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI103843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B., NYMAN M. Studies on the serum haptoglobin level in hemoglobinemia and its influence on renal excretion of hemoglobin. Blood. 1957 Jun;12(6):493–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN H., KILIAN P. [March hemoglobinuria (Studies on the mechanism of hemolysis and review of the literature)]. Folia Haematol (Frankf) 1959 Jul;4:92–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. H., McDONALD R. K. The effect of hemoglobin on renal function in the human. J Clin Invest. 1951 Oct;30(10):1033–1040. doi: 10.1172/JCI102522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARE C. M., SANDLER M. Amino-aciduria in March haemoglobinuria. Lancet. 1954 Apr 3;266(6814):702–704. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)92109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. A., Mitchell H. S. March Haemoglobinuria. Can Med Assoc J. 1943 Dec;49(6):465–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]