Abstract
Obesity induces accumulation of adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs), which contribute to both local and systemic inflammation and modulate insulin sensitivity. Adipocyte lipolysis during fasting and weight loss also leads to ATM accumulation, but without proinflammatory activation suggesting distinct mechanisms of ATM recruitment. We examined the possibility that specific lipid mediators with anti-inflammatory properties are released from adipocytes undergoing lipolysis to induce macrophage migration. In the present study, we showed that conditioned medium (CM) from adipocytes treated with forskolin to stimulate lipolysis can induce migration of RAW 264.7 macrophages. In addition to FFAs, lipolytic stimulation increased release of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), reflecting cytosolic phospholipase A2 α activation and enhanced cyclooxygenase (COX) 2 expression. Reconstituted medium with the anti-inflammatory PGE2 potently induced macrophage migration while different FFAs and PGD2 had modest effects. The ability of CM to induce macrophage migration was abolished by treating adipocytes with the COX2 inhibitor sc236 or by treating macrophages with the prostaglandin E receptor 4 antagonist AH23848. In fasted mice, macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue coincided with increases of PGE2 levels and COX1 expression. Collectively, our data show that adipocyte-originated PGE2 with inflammation suppressive properties plays a significant role in mediating ATM accumulation during lipolysis.
Keywords: adipose tissue, cyclooxygenase, eicosanoids, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, fatty acid, inflammation, lipase
Adipose tissue is the major repository of excess energy stored in the form of triacylglycerol (TAG). During energy need, adipocyte lipolysis involving the hydrolysis of TAG releases FFAs for energy production by different tissues (1, 2). Adipose tissue also secretes various adipokines, which influence energy homeostasis and insulin sensitivity of distant tissues (3, 4). In addition to its important role in metabolic regulation, adipose tissue modulates the immune system by recruiting and activating lymphoid and myeloid cells when adipocyte fat storage is exaggerated as occurs in obesity (5). In obese individuals, there is a strong positive correlation between adipocyte size and the accumulation of proinflammatory adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs) (6, 7).
However, ATM recruitment also occurs in mice after fasting or with calorie restriction (8) and in obese patients maintained on low-calorie diets during early weight loss (9), but under these conditions, it does not associate with inflammation. The above findings suggest that the mechanisms that operate in ATM recruitment in obesity or calorie restriction are not identical. Both fasting and pharmaceutically induced lipolysis increase macrophage content in adipose tissue, and lipolysis measures correlate with increased ATM content independent of adiposity (10). This suggests that lipid turnover and not lipid accumulation per se is important for ATM recruitment. Moreover, the recruited ATMs play an adaptive role during lipid flux conditions such as with weight loss and fasting by buffering the local concentration of FFAs through their ability to accumulate TAG in lipid droplets (8). Whether adipocyte release of FFAs or FA-derived molecules might signal for ATM recruitment in addition to driving ATM lipid accumulation is not known.
FFAs, especially the saturated type, usually activate classical inflammatory responses in macrophages through engagement of pattern recognition receptors, including Toll-like receptors (11). However, they are unlikely to explain the calorie-restriction-associated ATM recruitment, which normally does not associate with inflammation. Although multiple lines of evidence support the concept that FFAs released upon lipolytic stimulation play an important role in ATM recruitment and accumulation (12), the differential effects of individual FFAs and potential involvement of FA metabolites are not well known. In the present study, we compared the effects of a series of lipid species released by adipocytes, aiming to determine the major molecules that trigger macrophage recruitment. Our results suggest that adipocyte-originated prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) plays a significant role in mediating the lipolysis-induced macrophage recruitment and influences the inflammatory response.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Calf serum, FBS, and DMEM were purchased from Invitrogen (Grand Island, NY). Antibodies for phospho-ERK1/2, total ERK1/2, phospho-cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) α (p-cPLA2α), and tubulin were ordered from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). SuperScript VILO cDNA synthesis kit, TRIzol®, and SYBRGreen reagents were ordered from Life Technologies (Foster City, CA). Antibody for calnexin was from Enzo Life Sciences (Farmingdale, NY), and antibody for Ran from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Cyclooxygenase (COX) 2 antibody was purchased from R and D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). CD11b, CD64, F4/80, NOS2, CD301, and CD206 antibodies were purchased from eBioscience (San Diego, CA). Sc236 and AH23848 were ordered from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI). Other reagents were from Sigma (St. Louis, MO).
Cell culture
The 3T3-L1 cells (from American Type Culture Collection) were cultured to confluence in DMEM with 4.5 mg/ml glucose containing 20% calf serum, as described previously (13). Two days after confluence, differentiation was initiated by incubation with DMEM containing 10% FBS, 500 µM isobutylmethylxanthine (IBMX), 0.25 µM dexamethasone, and 4 µg/ml insulin for 2 days. IBMX and dexamethasone were then removed, and insulin maintained for another 2 days. Thereafter, cells were grown in DMEM containing 10% FBS. RAW 264.7 macrophages (from American Type Culture Collection) were cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS.
Treatment of adipocytes and collection of conditioned medium
Adipocytes were serum starved for 4 h prior to different treatments in 0.4% BSA/DMEM. Cells were then washed with PBS and incubated in fresh BSA/DMEM overnight. The culture media were centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 min, and the supernatants collected as conditioned medium (CM) for the assays.
Measurement of glycerol, FFA, and prostaglandins
Glycerol content in the culture media was determined by using free glycerol reagent (Sigma). For the FFA measurement, lipids from culture media were extracted in the presence of an internal control (C19:0 FA), and separated on silica gel 60 Å plates as previously described (13). The FFA fraction was scrapped from the TLC plates and collected in glass tubes after visualization with 0.01% rhodamine 6G. Fatty acid methyl esters were prepared by reaction with methanol-acetyl chloride (4:1) at 70°C for 1 h, and quantitative GC/MS analysis was conducted (Hewlett-Packard 5890GC, Palo Alto, CA) as described (14). Release of PGE2 and prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) was measured using EIA kits (Cayman Chemical Co.).
Migration assay of RAW 264.7 cells
Migration of RAW 264.7 cells was measured by a modified Boyden chamber migration assay using transwell inserts with an 8.0 μm polycarbonate membrane (Corning, NY), as previously described (15). The RAW 264.7 cells suspended in 0.4% BSA/DMEM were placed in the upper chamber, whereas adipocyte CM or media containing different lipids was placed in the lower chamber and 0.4% BSA/DMEM was used as a control. After allowing cell migration for 4–5 h, cells were fixed in formalin and stained with hematoxylin. Cells that had not migrated and remained in the upper chamber were removed by gently swiping the filters with wet cotton tips. Raw264.7 cells that migrated onto the filter were counted with a microscope (Nikon E800) and quantified (ImageJ) from four fields per condition.
Isolation of membrane and cytosol fractions
Membrane fraction was prepared as described previously (16), with minor modifications. Briefly, cells were lysed in 0.25 M sucrose buffer, containing 1 mM deoxycholate with both protease and phosphatase inhibitors, and then homogenized. Cell nuclei were removed through centrifugation (1,000 g, 4°C, 10 min). The supernatant was separated from the pellet and fat layers, and centrifuged at 100,000 g (4°C, 1 h) using a TLS-55 rotor. The resulting membrane-enriched pellet and cytosol-containing supernatant were then analyzed using Western blotting.
Gel electrophoresis and Western blotting
Whole cell lysates of mouse adipose tissue or 3T3-L1 adipocytes were prepared with lysis buffer containing a protease inhibitor cocktail and a phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Roche Pharmaceuticals). Proteins were separated on 4–12% gradient SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes after blocking were probed with primary antibodies. After incubating with infrared fluorophore-coupled secondary antibodies, the proteins were visualized on a direct infrared fluorescence detection system (Odyssey Imaging System; LI-COR, Lincoln, NE).
RNA isolation and real-time PCR
Total RNA was isolated from 3T3-L1 adipocytes and adipose tissues using TRIzol® reagent and concentration measured (Nanodrop). Reverse transcription was performed with a SuperScript VILO cDNA synthesis kit and gene expression determined with real-time quantitative PCR using SYBRGreen reagent as previously described (14). Primer sequences are listed in supplementary Table 1.
Fluorescent microscopy
The 3T3-L1 adipocytes were electroporated with enhanced green fluorescent protein-tagged cPLA2α (EGFP-cPLA2α) plasmid and seeded on cover slides. Forty-eight hours later, the cells were treated with 10 μM forskolin (FSK) for 0, 2, and 5 min and fixed and counterstained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; nuclei, blue). Images were acquired on a Nikon Eclipse TE2000-U microscope operated by MetaMorph software.
Flow cytometry of macrophages in adipose tissues
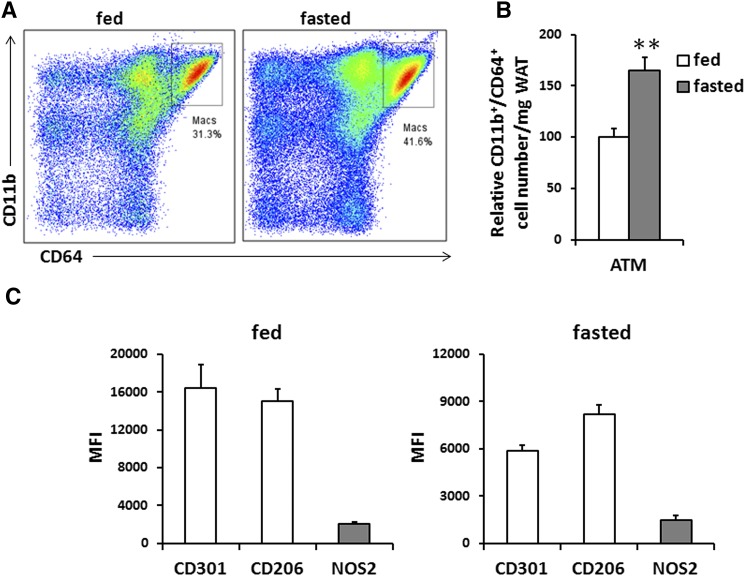
Age-matched C57BL/6 WT mice were fed ad libitum or fasted overnight. After CO2 asphyxiation, the epididymal fat pads were excised, rinsed in PBS, minced into fine pieces, and digested with collagenase. The digested samples were passed through mesh and subjected to a brief centrifugation. The pellets or stromal-vascular fraction (SVF) was collected for flow cytometry (FC). Cells in the SVF were incubated in red blood cell lysis buffer (BD Biosciences) for 5 min at 4°C to remove red cells and then with FC blocking buffer for 10 min before staining with fluorescent-labeled antibodies for 30 min at 4°C. Cells were washed and suspended before analysis. M1 and M2 macrophages were identified as CD64+/CD11b+/NOS2+ or CD64+/CD11b+/CD206+/CD301+ cells, respectively. Macrophage number was calculated by multiplying the number of total cells after digestion by the percentage of cells gated as DAPI− CD45+CD64+CD11b+ for each treatment condition. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Studies Committee of Washington University School of Medicine.
Statistical analyses
The data are presented as means ± SE. Statistical significance was analyzed with GraphPad Prism 6.0 software. One-way ANOVA or Student’s t-test was performed with Tukey’s post hoc analysis depending on the experimental design. The correlation between COX1 and F4/80 expression was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation analysis. P < 0.05 was considered to be significant.
RESULTS
Adipocyte lipolysis induces RAW 264.7 macrophage chemotaxis
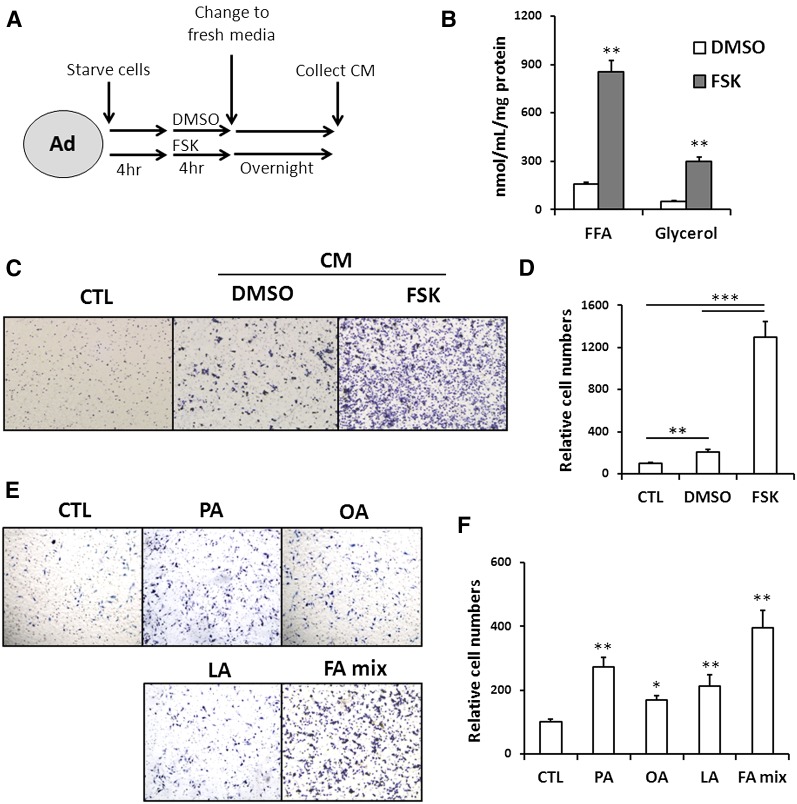
The 3T3-L1 adipocytes with or without pretreatment with 10 μM FSK were washed and then switched to fresh medium without the stimulant for an overnight incubation to procure CM (Fig. 1A). Levels of FFA and glycerol in CM from cells pretreated with FSK were markedly increased as expected (Fig. 1B). The total concentration of all major FFAs together in CM from FSK-treated (FSK-CM) adipocytes is 91 µM with the concentration of palmitic acid (PA) being the highest at ∼31 µM (supplementary Table 2). To begin to examine the effect of adipocyte lipolysis on macrophage migration, we first compared the effect of FSK-CM with that of control medium not incubated with adipocytes or CM from untreated adipocytes with only vehicle included in the preincubation medium (DMSO-CM). More migrated cells were counted in FSK-CM as compared with DMSO-CM (5.6-fold; P < 0.001) or control medium (12.8-fold; P < 0.001) (Fig. 1C, D) consistent with the effect of lipolysis to induce macrophage migration. We then examined whether the enhanced macrophage migration is due to the FFA released from the lipolytically active adipocytes. Macrophage chemotaxis was examined in response to media containing 100 μM individual FFAs: PA, oleic acid (OA), linoleic acid (LA), or 100 μM of a FFA mixture (PA, OA, and LA) all added complexed to BSA at a ratio of 4:1 (FA:BSA). As shown in Fig. 1E, PA, OA, and LA enhanced macrophage migration by 2.7-, 1.7-, and 2.1-fold, respectively, and the FA mixture was more effective, increasing migration by 4.0-fold, suggesting a potentially small cooperative regulation. The FA:BSA ratio in the FSK-CM is much lower than that in the reconstituted media because we had to include high BSA as an FA acceptor to drive lipolysis. Thus, unbound FFAs in the reconstituted media are at concentrations higher than those in FSK-CM but had only modest effects as compared with FSK-CM. Collectively, these results indicate that FFA release during lipolysis is one of the factors mediating macrophage accumulation but that FFAs alone are unlikely to account for the whole effect.
Fig. 1.
Adipocyte lipolysis induces macrophage chemotaxis. A: Schematic diagram of protocol used for preparing CM: 3T3-L1 adipocytes (Ad) were first serum-starved, then incubated in 0.4% BSA/DMEM plus DMSO or 10 μM FSK for 4 h, and finally switched to fresh medium (0.4% BSA/DMEM) for an overnight incubation. The following day, the medium was collected as CM and kept frozen at −80°C until use. B: Glycerol and FFA levels in the CM collected from adipocytes with or without 10 μM FSK pretreatment. Data are means of triplicates from three separate experiments. ** P < 0.01. C, D: Macrophage (RAW264.7) chemotaxis: Macrophages suspended in DMEM with 0.4% BSA were placed in the upper chamber of a transwell. The lower chamber contained either DMEM with 0.4% BSA (CTL) or CM from vehicle-treated (DMSO-CM) or FSK-treated (FSK-CM) adipocytes. After 5 h, the macrophages that adhered to the transwell were fixed, stained with hematoxylin, imaged using software Olympus DP controller (C), and quantified using ImageJ (D). Data are means of duplicates from three separate assays. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. E, F: Effect of different FAs (100 μM, FA:BSA = 4:1) on macrophage (RAW264.7) chemotaxis: The lower chamber contained DMEM with 0.4% BSA (CTL) or supplemented with PA(100 μM), OA (100 μM), LA (100 μM), or an FA mixture containing equal amounts of PA, OA, and LA (FA mix, total concentration of 100 μM). Data shown are means of duplicates from two experiments. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, compared with CTL group.
Lipolytic stimulation increased arachidonic acid release by activation of cPLA2α
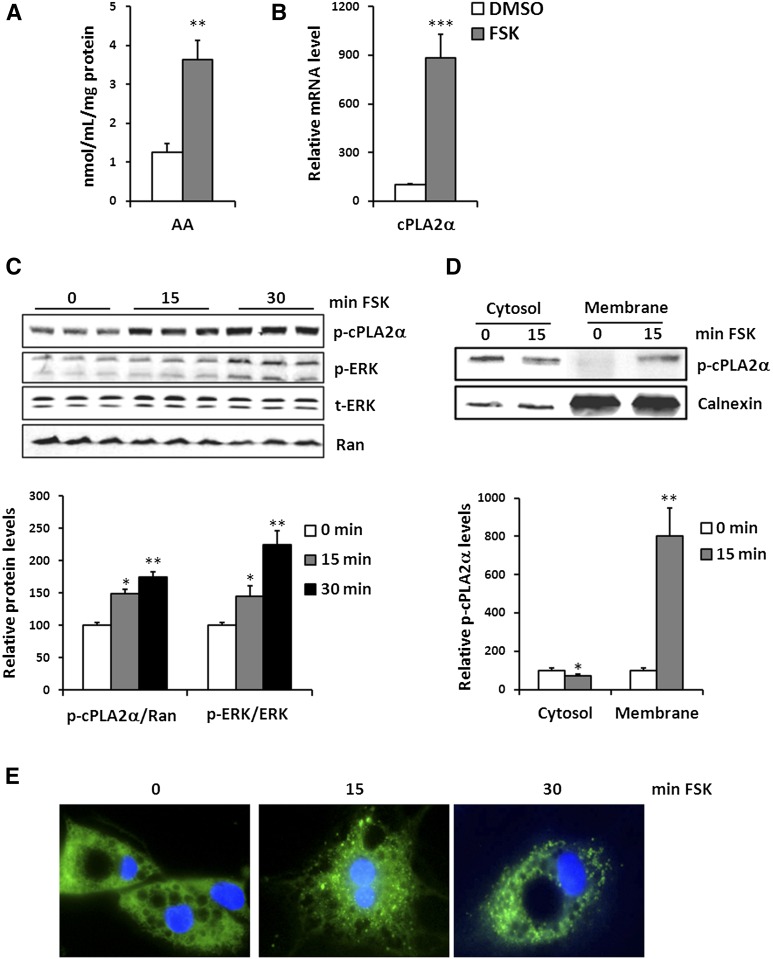
Because FSK-CM has a greater effect in inducing macrophage migration than what is observed with FFAs (Fig. 1D vs. Fig. 1E), we explored potential involvement of additional lipid mediators. Arachidonic acid (AA) is the primary source of prostaglandins that mediate inflammatory responses and play a role in macrophage migration. Cellular AA is primarily esterified into phospholipids, and free AA is kept very low. AA release is controlled by activation of cPLA2 and adipocyte phospholipase A2 (adPLA2) (17, 18). Interestingly, FSK-treated adipocytes were found to produce more AA than vehicle-treated cells (Fig. 2A). We explored the potential involvement of different PLA2 in adipocyte AA release following FSK. We first examined the expression levels of cPLA2α, cPLA2γ, and adPLA2 and observed a dramatic increase of cPLA2α expression after exposure to FSK (Fig. 2B). However, FSK treatment did not alter cPLA2γ expression and significantly decreased adPLA2 level (supplementary Fig. 1). It has been reported that cPLA2α is activated by phosphorylation at serine-505 by ERK (19, 20). We determined that phosphorylation of cPLA2α and ERK occurred rapidly at 15 min, and further increased at 30 min following FSK treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes (Fig. 2C). Similarly, adrenergic activation by isoproterenol also increased phosphorylation of both cPLA2α and ERK (supplementary Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Adipocyte lipolysis releases AA by activating cPLA2α. A: AA levels in the CM collected from vehicle-treated (DMSO) or FSK-treated (FSK) adipocytes. Data are means of triplicates from three experiments. ** P < 0.01. B: mRNA levels of cPLA2α in vehicle-treated (DMSO) or FSK-treated (FSK) adipocytes. Data shown are means of triplicates from two separate experiments. *** P < 0.001. C: Whole-cell lysates of adipocytes treated with FSK for 0, 15, and 30 min were prepared and analyzed by Western blot for p-cPLA2α (S505), phospho-ERK1/2 (T202, Y204) (p-ERK), total ERK1/2 (t-ERK), and Ran. Protein levels were quantified using LI-COR technology. Data are from two experiments conducted in triplicates. p-cPLA2 adjusted to the control Ran and p-ERK to t-ERK are presented relative to vehicle-treated cells and are plotted as means ± SE. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, compared with 0 min. D: cPLA2 translocation in response to FSK treatment in adipocytes. The 3T3-L1 adipocytes were starved and treated with FSK for 15 min. Cells were lysed, separated into cytosol and membrane fractions, and probed for p-cPLA2 and calnexin. Signal intensity was analyzed by LI-COR technology and is plotted as means ± SE. Data in the graph are from two separate experiments conducted in duplicates. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. E: 3T3-L1 adipocytes transfected with EGFP-cPLA2α plasmid were treated with 10 μM FSK for 0, 2, or 5 min, and then fixed and counterstained with DAPI (nuclei, blue) before imaging with MetaMorph. The data are representative of three experiments.
In addition to phosphorylation, cPLA2 activity is also enhanced by its translocation from cytosol to membrane to access AA-containing phospholipid substrates. FSK decreased p-cPLA2α in the cytosolic fraction, while increasing in the membrane fraction (Fig. 2D). We further examined subcellular localization of EGFP-cPLA2α in adipoctyes by fluorescent microscopy. Under basal condition, cPLA2α displayed diffused cytoplasmic distribution in adipocytes. However, FSK treatment triggered the formation of numerous fluorescent puncta (Fig. 2E), confirming its translocation from cytosol to membrane.
PGE2 released from adipocytes mediated macrophage migration
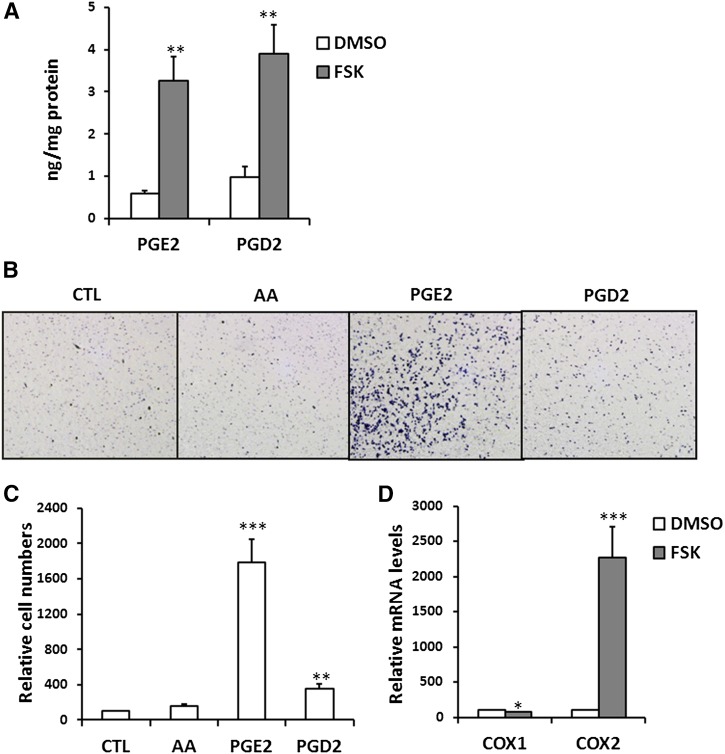
In addition to increase of AA release (Fig. 2A), FSK pretreatment also resulted in higher levels of both PGE2 and PGD2 in the FSK-CM (Fig. 3A). Accordingly, we compared the effects of AA, PGE2, and PGD2 on macrophage chemotaxis. AA did not show a stimulatory effect on RAW macrophages, while macrophage chemotaxis was strongly activated by PGE2 (17.8-fold) while PGD2 had a much weaker impact (3.5-fold) (Fig. 3B, C). The effect of PGE2 on macrophage migration was also more potent than that of FFA (Figs. 1E and 3B), suggesting that PGE2 could be the most important mediator linking adipocyte lipolysis and macrophage migration. We further examined COX gene expression and found that COX2 expression was strongly stimulated by FSK treatment while COX1 level was not significantly changed (Fig. 3D).
Fig. 3.
PGE2 produced by adipocytes during lipolysis induces macrophage migration. A: PGE2 and PGD2 levels in CM from vehicle-treated (DMSO) or FSK-treated (FSK) adipocytes. Data are from duplicates of two experiments, ** P < 0.01. B, C: Macrophage (RAW264.7) chemotaxis: Macrophages suspended in DMEM with 0.4% BSA were placed in the upper chamber of the transwell and the lower chamber was filled with DMEM plus 0.4% BSA (CTL), 100 μM AA complexed to BSA (FA:BSA = 2:1), and 5 μM PGE2 or PGD2. Migrated cells were quantified with ImageJ (C). Data are means of duplicates from three independent assays. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, compared with CTL group. D: mRNA levels of COX enzymes in adipocytes treated with 10 μM FSK. All data are means of triplicates from two separate experiments. * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001.
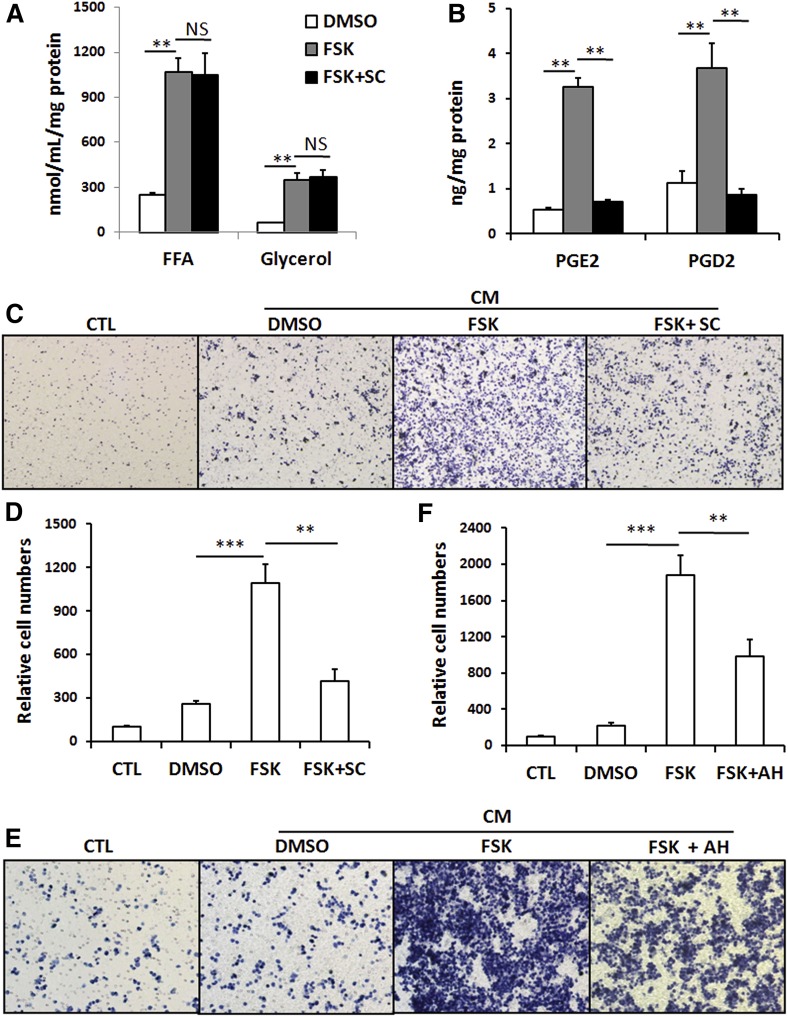
To evaluate the relative contribution of COX-generated eicosanoids in the FSK-CM to the induction of macrophage recruitment, we examined the effect of a specific COX2 inhibitor, sc236 (21). Adipocytes were incubated with FSK in the presence or absence of sc236 prior to collection of CM. Sc236 did not affect FSK-induced release of glycerol and FFA (Fig. 4A), but significantly inhibited PGE2 and PGD2 production as would be expected (Fig. 4B). In the presence of the COX2 inhibitor, CM derived from FSK-treated adipocytes lost most of its ability to stimulate macrophage migration (Fig. 4C, D). These results indicate that prostaglandins (mostly likely PGE2) and not FFAs play a major role in inducing macrophage recruitment during adipocyte lipolysis.
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of PGE2 production suppresses macrophage migration induced by adipocytes lipolysis. A: Levels of glycerol and FFA in CM collected from vehicle-treated (DMSO) or FSK-treated (FSK) adipocytes or cells pretreated with FSK and sc236 (FSK+ SC). Data are means of triplicates from two independent assays. ** P < 0.01. B: PGD2 and PGE2 content in CM. Data are means of triplicates from one assay. C, D: Macrophage (RAW264.7) chemotaxis: Macrophages suspended in DMEM with 0.4% BSA were placed in the upper chamber of a transwell. The lower chamber contained either DMEM with 0.4% BSA (CTL) or CM from vehicle-treated (DMSO), FSK-treated (FSK) adipocytes or cells pretreated with FSK and sc236 (FSK+SC). After 5 h, the macrophages that adhered to the transwell were fixed, stained with hematoxillin, imaged using software Olympus DP controller (C), and quantified using ImageJ (D). Data are means of duplicates from three separate assays. ** P < 0.01. E, F: Macrophage (RAW264.7) chemotaxis: Cells were preincubated with 3 μM of AH23848, a prostaglandin E receptor (EP) 4 antagonist before the migration assay using FSK-CM (FSK+AH). Data are means of duplicates from two independent experiments. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.
PGE2 regulates various pathways by binding to multiple EPs, including EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4. Recently, the EP4 receptor was shown most important for PGE2-mediated macrophage migration (22). Pretreatment of macrophages with the EP4 antagonist, AH23848, significantly inhibited FSK-CM-induced macrophage migration (Fig. 4E), suggesting that CM PGE2 is acting via the macrophage EP4 receptor. Interestingly, virtual elimination of PGE2 in adipocytes or inhibition of EP4 on the macrophages blunts most but not all of the FSK effect on cell migration, suggesting contribution from FFAs or other unidentified factors in FSK-CM.
Increased macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue during fasting
ATM recruitment occurs in mice after fasting, which does not associate with inflammation (8). Based on the results that macrophage migration was stimulated by adipocyte lipolysis in vitro, we aimed to examine whether PGE2 could play a role in ATM recruitment in fasting mice. We first confirmed ATM accumulation in white adipose tissue (WAT) from fed and fasted mice by measuring expression levels of macrophage/myeloid cell-specific markers F4/80 and CD11b. Significant increases in the expression of these markers were observed after overnight fasting, and immunohistochemistry of adipose tissue with the F4/80 antibody also showed that ATM numbers were markedly increased (data not shown). ATMs were further analyzed by FC with a broad mononuclear gate consisting of CD64+/CD11b+ cells (Fig. 5A), and this confirmed the effect of overnight fasting to enhance macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue (Fig. 5B). ATMs are broadly divided into the proinflammatory M1 and the anti-inflammatory M2 subclasses. We analyzed the different populations by FC. As shown in Fig. 5C, under both fed and fasted conditions, expression of the CD206 and CD301, markers of M2 macrophages, were much higher than those of the M1 marker NOS2. Fasting did not significantly alter the M1/M2 ratio, and the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype remained dominant over the proinflammatory M1. This confirmed that adipocyte lipolysis induces ATM recruitment without inducing inflammation in WAT.
Fig. 5.
Macrophage content in adipose tissues of mice in fed or fasted states. A: Representative FC plots of CD11b+/CD64+ cells in adipose tissue; n = 2, 3 mice pooled each experiment. B: ATM numbers are shown as CD11b+/CD64+ cells; data are means ± SE; n = 2, 3 mice pooled each experiment. **P < 0.01. C: Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of markers for M1 (NOS2, gray fill) and M2 (CD301 and CD206, no fill) macrophages in adipose tissue; data are means ± SE; n = 2, 3 mice pooled in each experiment.
ATM content correlates with COX expression in WAT
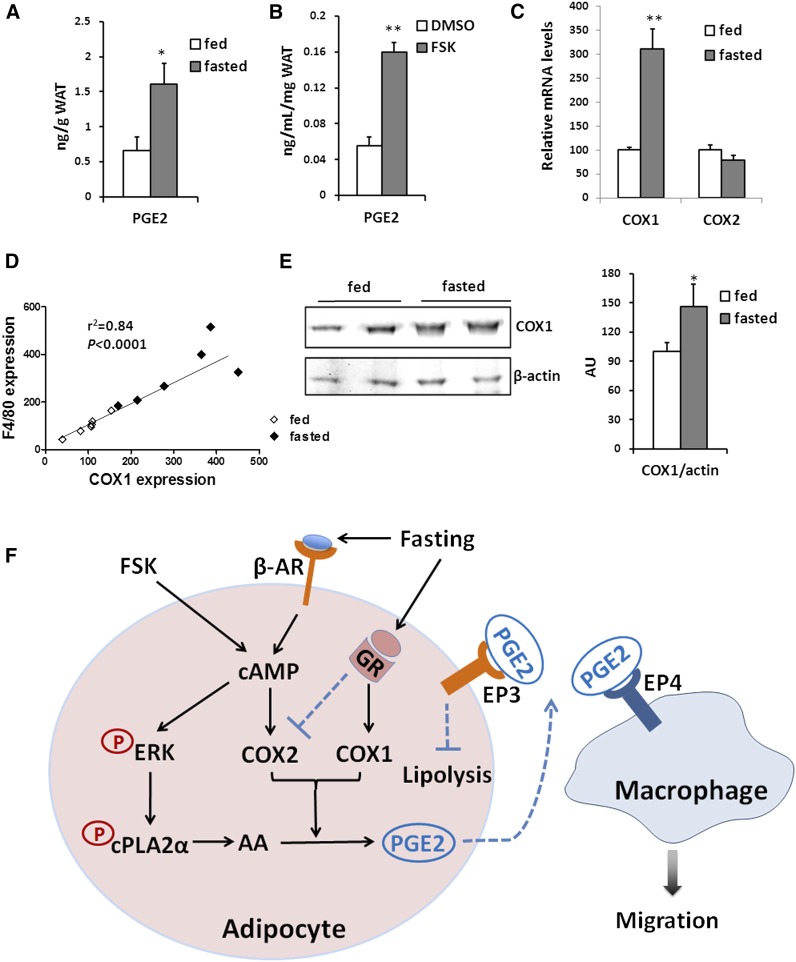
We examined if the increased ATM accumulation in fasted WAT in mice might also associate with PGE2 production. Indeed, overnight fasting increased PGE2 levels in WAT almost threefold (Fig. 6A). In vitro PGE2 levels in explants of WAT were also increased by FSK treatment (Fig. 6B). We examined COX1 and COX2 expression in WAT and found that COX1 expression in WAT was increased 3-fold after an overnight fast while COX2 expression was not stimulated (Fig. 6C). Notably, COX1 mRNA expression highly correlated (r2 = 0.84, P < 0.0001) with tissue f4/80 expression levels (Fig. 6D). In agreement with the fasting-induced upregulation of COX1 mRNA level in WAT, COX1 protein level also increased after fasting (Fig. 6E). Collectively, our results suggest that adipocyte lipolysis enhances AA release from membrane phospholipids and PGE2 production by activating cPLA2α and upregulating COX level. The net result is promotion of macrophage recruitment in the absence of inflammation.
Fig. 6.
Macrophage markers correlate with COX1 expression. A: PGE2 levels in adipose tissue of 6 mice/group. B: PGE2 levels in medium from adipose tissue explants treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 10 μM of FSK; n = 3 explants. C: mRNA levels of COX enzymes of adipose tissues from fed and fasted mice. Fed, n = 6 mice/group; fasted, n = 6 mice/group. D: Correlation between COX1 mRNA and F4/80 mRNA in adipose tissues. Pearson’s correlation coefficient is shown. The points represent data from individual fed (black diamond) and fasted (white diamond) mice. E: Total lysates of epididymal adipose tissue from fasted mice were probed for COX1 and β-actin. Signal intensity was analyzed by LI-COR technology and is plotted as means ± SE. n = 3 mice/group. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. F: Model of how adipocyte lipolysis induces macrophage recruitment in adipose tissue. Fasting or FSK treatment increases cAMP levels in adipocytes, which induces lipolysis of stored triglycerides. At the same time cAMP activates the ERK1/2, which phosphorylates cPLA2α enhancing its activity. Translocation of cPLA2α to membranes releases AA from phospholipids, a step that is essential for production of the prostaglandin PGE2. COX2 expression in adipocytes is upregulated by FSK via cAMP-dependent signaling. In WAT, it is likely that COX1 was induced after fasting by GR activation, while COX2 induction by cAMP is neutralized. The PGE2 produced by adipocytes acting via its receptor EP4 promotes recruitment of M2 macrophages. In addition, PGE2 feedbacks to prevent excess lipolysis by adipocytes. PGE2 release during lipolysis would help to limit the increase of local lipid concentration and lipotoxicity, unlike the chronic stimulation of ATM recruitment in obese WAT, which leads to inflammation. β-AR, β adrenergic receptor; GR, glucocorticoid receptor.
DISCUSSION
Recent studies suggested that macrophage recruitment to adipose tissue is a normal response that associates with activation of adipocyte lipolysis during the early phase of weight loss and fasting (8, 23). However, the metabolic factors that induce ATM infiltration during lipolysis are still undefined. The present study using in vitro and in vivo models identified production by adipocytes upon lipolytic stimulation of the lipid mediator PGE2, which strongly promotes macrophage migration. Our data provided multiple lines of evidence to support PGE2 as the most credible mediator of ATM recruitment and showed that its production is due to lipolysis-induced activation of cPLA2α and to upregulation of COX level (Fig. 6F).
It is likely that acute ATM recruitment induced by lipolytic stimulation of adipocytes is under distinct regulation and has different effects as compared with chronic ATM accumulation during the development of obesity. Adipose tissue during the development of obesity produces a variety of bioactive molecules that initiate infiltration of M1 macrophages and produces proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) (24, 25). Macrophages are functionally and numerically the most important type of immune cells recruited in obese WAT (26, 27). The role of WAT macrophage infiltration during the development of obesity in the etiology of local and systemic chronic inflammation and in insulin resistance has been intensively investigated (25). However, activation of adipocyte lipolysis, although strongly inducing macrophage recruitment, does not induce inflammation. The expression of CCL2 and TNFα was not enhanced in adipocytes pretreated with FSK (data not shown), and while fasting of mice increased ATM accumulation, this did not associate with a change in macrophage polarization as the M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype remained the predominant macrophage type present. It has been proposed that lipolysis and the associated increase in FFA concentration regulate macrophage accumulation without activation of the proinflammatory M1-polarized state (8). In addition to proinflammatory cytokines, some FA metabolites have been proposed as potential triggers of macrophage recruitment, especially AA and eicosanoids (28, 29). Our results show that macrophage chemotaxis was only mildly promoted by FFAs including AA but that it was strongly activated by the FA metabolite PGE2, which dramatically increased in the culture media from FSK-treated adipoctyes (Fig. 3A) or WAT explants (Fig. 6B), and in the WAT from fasted mice (Fig. 6A). Furthermore, inhibition of COX2 in adipocytes (Fig. 4C, D) or of EP4 in macrophages (Fig. 4E) diminished the ability of FSK-CM to induce macrophage migration. These findings demonstrate that PGE2 release from adipocytes directly mediates macrophage infiltration during lipolysis. Interestingly, PGE2 acting via its EP3 receptor is a documented antilipolytic action as it suppresses hormone-stimulated lipolysis in adipocytes (30). This suggests that PGE2 production by adipocytes undergoing lipolysis serves to buffer the local increase in FA concentration by recruiting M2 macrophages that can store FA in cytosolic lipid droplets and by exerting negative feedback to prevent excess lipolysis (Fig. 6F). In line with this interpretation, rapid appearance of lipid droplets in ATMs during a fast has been described (8). In addition, PGE2 can suppress production of acute inflammatory mediators and inhibit attraction of proinflammatory cells (31). Suppressing PGE2 production by deletion of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 exacerbates neutrophil-mediated inflammation (11) while activation of the PGE2 receptor EP4 inhibits inflammasome activation through EP4 receptor and intracellular cAMP in human macrophages (32). These results suggest that PGE2 normally plays a key role in regulating anti-inflammation and immune suppression during lipolysis. Synthesis of PGE2 is impaired in adipocytes isolated from obese Zucker rats (33), and high-fat feeding leads to suppression of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 in WAT (34). Accordingly, it is possible that a more limited PGE2 production during the development of obesity might play a role in the activation of inflammatory immune cells.
Release of AA from phospholipids is essential for the initiation of eicosanoid generation, and the release process is dependent on PLA2 activation (35). In the present study, FSK treatment dramatically increased expression level of cPLA2α, but not that of cPLA2γ or adPLA2 in adipocytes (Fig. 2B). The importance of cPLA2α in adipocyte AA release and PGE2 production following FSK treatment was further confirmed by the increase in its phosphorylation and membrane localization. Both calmodulin-dependent kinase II and ERK can phophorylate cPLA2α, respectively, at Ser515 and Ser505 (19). Our results show that activation of lipolysis induces cPLA2α phosphorylation at Ser505 in adipocytes (Fig. 2). Thus, the increase in cAMP that initiates lipolysis also leads to downstream activation of ERK, which phosphorylates and activates cPLA2α (36).
COX exists in two isoforms, and COX1 is generally considered to be constitutively expressed and responsible for the production of prostaglandins important for homeostatic functions. In contrast, COX2 is highly inducible in response to specific stimuli and growth factors, and its expression is usually restricted under basal conditions (37). The response of adipocyte COX2 to FSK in our study is consistent with the established role of cAMP-dependent signaling in regulating COX2 expression (38). Regulation of the COX isoforms under physiological conditions in animal tissues is more complicated. Fasting induces increases in levels of several hormones, notably glucocorticoids, in addition to norepinephrine and epinephrine, and glucocorticoids enhance COX1 gene expression (39) and selectively inhibit COX2 expression (40). Thus, it is likely that COX1 was induced after fasting in WAT by glucocorticoid, while COX2 induction by cAMP is neutralized (Fig. 6F). The selective response of adipose tissue COX1 and not COX2 during fasting may explain why WAT recruits macrophages but does not induce inflammation.
The identified ERK/cPLA2α/PGE2 pathway may also provide insight into the pathology of diseases influenced by altered cell migration. For example, cPLA2α is highly expressed in many tumors, and the lipid metabolites formed by cPLA2 and COX might modulate migration of tumor cells and cancer metastasis (41, 42). Depletion of cPLA2 levels inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor-induced migration and tube formation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (43), and cPLA2 inhibition suppressed pulmonary metastasis in a mouse model for pulmonary tumors (42). These studies suggest that the metabolites produced consequent to cPLA2 activation including PGE2 might play an important role in regulation of cell migration involving many cell types.
Our results support a model by which lipolytic stimulation in adipocytes induces macrophage migration via cPLA2α activation and PGE2 production. Moreover, the ATMs acutely recruited by PGE2 are mostly in the anti-inflammatory M2 state. This recruitment would help to limit the increase of local lipid concentration and lipotoxicity, unlike the chronic stimulation of ATM recruitment in obese WAT, which leads to inflammation. Dissection of the distinct cellular pathways that lead to differential ATM recruitment and activation should help identify attractive targets to limit obesity-associated inflammation and insulin resistance.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge assistance from Terri Pietka in the Adipocyte Biology and Molecular Nutrition Core and Dr. Adewole Okunade in the Clinical Research Core (Nutrition and Obesity Research Center at Washington University) and from Alice Tong in mouse husbandry.
Footnotes
Abbreviations:
- AA
- arachidonic acid
- adPLA2
- adipocyte phospholipase A2
- ATM
- adipose tissue macrophage
- CM
- conditioned medium
- COX
- cyclooxygenase
- cPLA2
- cytosolic phospholipase A2
- DAPI
- 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- EGFP-cPLA2α
- enhanced green fluorescent protein-tagged cPLA2α
- EP
- prostaglandin E receptor
- FC
- flow cytometry
- FSK
- forskolin
- LA
- linoleic acid
- OA
- oleic acid
- PA
- palmitic acid
- p-cPLA2α
- phospho-cPLA2α
- PGD2
- prostaglandin D2
- PGE2
- prostaglandin E2
- TAG
- triacylglycerol
- WAT
- white adipose tissue
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants DK033301, DK60022, DK097608, Nutrition and Obesity Research Center Grant P30-DK-056341, and Diabetes Research Center Grant P30-DK-020579; National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants 31371437 and 31570806; Czech Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports Grant LH14040; and a project funded by Priority Academic Programme Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
The online version of this article (available at http://www.jlr.org) contains a supplement.
REFERENCES
- 1.Frühbeck G., Méndez-Giménez L., Fernández-Formoso J. A., Fernández S., and Rodriguez A.. 2014. Regulation of adipocyte lipolysis. Nutr. Res. Rev. 27: 63–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nielsen T. S., Jessen N., Jorgensen J. O., Moller N., and Lund S.. 2014. Dissecting adipose tissue lipolysis: molecular regulation and implications for metabolic disease. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 52: R199–R222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Huh J. Y., Park Y. J., Ham M., and Kim J. B.. 2014. Crosstalk between adipocytes and immune cells in adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysregulation in obesity. Mol. Cells. 37: 365–371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fasshauer M., and Bluher M.. 2015. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 36: 461–470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hill A. A., Reid Bolus W., and Hasty A. H.. 2014. A decade of progress in adipose tissue macrophage biology. Immunol. Rev. 262: 134–152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cinti S., Mitchell G., Barbatelli G., Murano I., Ceresi E., Faloia E., Wang S., Fortier M., Greenberg A. S., and Obin M. S.. 2005. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 46: 2347–2355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ortega Martinez de Victoria E., Xu X., Koska J., Francisco A. M., Scalise M., Ferrante A. W. Jr., and Krakoff J.. 2009. Macrophage content in subcutaneous adipose tissue: associations with adiposity, age, inflammatory markers, and whole-body insulin action in healthy Pima Indians. Diabetes. 58: 385–393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kosteli A., Sugaru E., Haemmerle G., Martin J. F., Lei J., Zechner R., and Ferrante A. W. Jr. 2010. Weight loss and lipolysis promote a dynamic immune response in murine adipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 120: 3466–3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Capel F., Klimcakova E., Viguerie N., Roussel B., Vitkova M., Kovacikova M., Polak J., Kovacova Z., Galitzky J., Maoret J. J., et al. 2009. Macrophages and adipocytes in human obesity: adipose tissue gene expression and insulin sensitivity during calorie restriction and weight stabilization. Diabetes. 58: 1558–1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Michaud A., Pelletier M., Noel S., Bouchard C., and Tchernof A.. 2013. Markers of macrophage infiltration and measures of lipolysis in human abdominal adipose tissues. Obesity (Silver Spring). 21: 2342–2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shi H., Kokoeva M. V., Inouye K., Tzameli I., Yin H., and Flier J. S.. 2006. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 116: 3015–3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Suganami T., Tanimoto-Koyama K., Nishida J., Itoh M., Yuan X., Mizuarai S., Kotani H., Yamaoka S., Miyake K., Aoe S., et al. 2007. Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kappaB pathway in saturated fatty acid-induced inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27: 84–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhou D., Samovski D., Okunade A. L., Stahl P. D., Abumrad N. A., and Su X.. 2012. CD36 level and trafficking are determinants of lipolysis in adipocytes. FASEB J. 26: 4733–4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu Y., Zhou D., Abumrad N. A., and Su X.. 2010. ADP-ribosylation factor 6 modulates adrenergic stimulated lipolysis in adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 298: C921–C928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Patsouris D., Neels J. G., Fan W., Li P-P., Nguyen M. T. A., and Olefsky J. M.. 2009. Glucocorticoids and thiazolidinediones interfere with adipocyte-mediated macrophage chemotaxis and recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 284: 31223–31235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zeghari N., Vidal H., Younsi M., Ziegler O., Drouin P., and Donner M.. 2000. Adipocyte membrane phospholipids and PPAR-gamma expression in obese women: relationship to hyperinsulinemia. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 279: E736–E743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Balsinde J., Winstead M. V., and Dennis E. A.. 2002. Phospholipase A2 regulation of arachidonic acid mobilization. FEBS Lett. 531: 2–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wolf G. 2009. Adipose-specific phospholipase as regulator of adiposity. Nutr. Rev. 67: 551–554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pavicevic Z., Leslie C. C., and Malik K. U.. 2008. cPLA2 phosphorylation at serine-515 and serine-505 is required for arachidonic acid release in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Lipid Res. 49: 724–737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., and Davis R. J.. 1993. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 72: 269–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bertolini A., Ottani A., and Sandrini M.. 2002. Selective COX-2 inhibitors and dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: critical remarks. Curr. Med. Chem. 9: 1033–1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tang E. H., Cai Y., Wong C. K., Rocha V. Z., Sukhova G. K., Shimizu K., Xuan G., Vanhoutte P. M., Libby P., and Xu A.. 2015. Activation of prostaglandin E2–EP4 signaling reduces chemokine production in adipose tissue. J. Lipid Res. 56: 358–368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Red Eagle A., and Chawla A.. 2010. In obesity and weight loss, all roads lead to the mighty macrophage. J. Clin. Invest. 120: 3437–3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Trayhurn P., and Wood I. S.. 2005. Signalling role of adipose tissue: adipokines and inflammation in obesity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33: 1078–1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Guo L., Zhou D., Pryse K. M., Okunade A. L., and Su X.. 2010. Fatty acid 2-hydroxylase mediates diffusional mobility of Raft-associated lipids, GLUT4 level, and lipogenesis in 3T3–L1 adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 285: 25438–25447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lumeng C. N., Deyoung S. M., Bodzin J. L., and Saltiel A. R.. 2007. Increased inflammatory properties of adipose tissue macrophages recruited during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes. 56: 16–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Weisberg S. P., McCann D., Desai M., Rosenbaum M., Leibel R. L., and Ferrante A. W. Jr. 2003. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 112: 1796–1808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Iyer A., Fairlie D. P., Prins J. B., Hammock B. D., and Brown L.. 2010. Inflammatory lipid mediators in adipocyte function and obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 6: 71–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shimizu T. 2009. Lipid mediators in health and disease: enzymes and receptors as therapeutic targets for the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 49: 123–150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Strong P., Coleman R. A., and Humphrey P. P.. 1992. Prostanoid-induced inhibition of lipolysis in rat isolated adipocytes: probable involvement of EP3 receptors. Prostaglandins. 43: 559–566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Frolov A., Yang L., Dong H., Hammock B. D., and Crofford L. J.. 2013. Anti-inflammatory properties of prostaglandin E2: deletion of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 exacerbates non-immune inflammatory arthritis in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 89: 351–358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sokolowska M., Chen L. Y., Liu Y., Martinez-Anton A., Qi H. Y., Logun C., Alsaaty S., Park Y. H., Kastner D. L., Chae J. J., et al. 2015. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through EP4 receptor and intracellular cyclic AMP in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 194: 5472–5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kalinski P. 2012. Regulation of immune responses by prostaglandin E2. J. Immunol. 188: 21–28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lumeng C. N., Bodzin J. L., and Saltiel A. R.. 2007. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Invest. 117: 175–184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Norris P. C., Gosselin D., Reichart D., Glass C. K., and Dennis E. A.. 2014. Phospholipase A2 regulates eicosanoid class switching during inflammasome activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111: 12746–12751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Muthalif M. M., Benter I. F., Karzoun N., Fatima S., Harper J., Uddin M. R., and Malik K. U.. 1998. 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid mediates calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95: 12701–12706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vane J. R., Bakhle Y. S., and Botting R. M.. 1998. Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 38: 97–120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Klein T., Shephard P., Kleinert H., and Komhoff M.. 2007. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by cyclic AMP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1773: 1605–1618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sun H., Sheveleva E., and Chen Q. M.. 2008. Corticosteroids induce cyclooxygenase 1 expression in cardiomyocytes: role of glucocorticoid receptor and Sp3 transcription factor. Mol. Endocrinol. 22: 2076–2084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Anderson G. D., Hauser S. D., McGarity K. L., Bremer M. E., Isakson P. C., and Gregory S. A.. 1996. Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 reverses inflammation and expression of COX-2 and interleukin 6 in rat adjuvant arthritis. J. Clin. Invest. 97: 2672–2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Scott K. F., Sajinovic M., Hein J., Nixdorf S., Galettis P., Liauw W., de Souza P., Dong Q., Graham G. G., and Russell P. J.. 2010. Emerging roles for phospholipase A2 enzymes in cancer. Biochimie. 92: 601–610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jeong W. C., Kim K. J., Ju H. W., Back H. K., Kim H. K., Im S. Y., and Lee H. K.. 2010. Cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 metabolites play a critical role in pulmonary tumor metastasis in mice. Anticancer Res. 30: 3421–3427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang Q., Wang D., Singh N. K., Kundumani-Sridharan V., Gadiparthi L., Rao Ch. M., and Rao G. N.. 2011. Activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 downstream of the Src-phospholipase D1 (PLD1)-protein kinase C gamma (PKCgamma) signaling axis is required for hypoxia-induced pathological retinal angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 286: 22489–22498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.