Abstract
Human tumors are believed to harbor a disabled p53 tumor suppressor pathway, either through direct mutation of the p53 gene or through aberrant expression of proteins acting in the p53 pathway, such as p14ARF or Mdm2. A role for Mdmx (or Mdm4) as a key negative regulator of p53 function in vivo has been established. However, a direct contribution of Mdmx to tumor formation remains to be demonstrated. Here we show that retrovirus-mediated Mdmx overexpression allows primary mouse embryonic fibroblast immortalization and leads to neoplastic transformation in combination with HRasV12. Furthermore, the human Mdmx ortholog, Hdmx, was found to be overexpressed in a significant percentage of various human tumors and amplified in 5% of primary breast tumors, all of which retained wild-type p53. Hdmx was also amplified and highly expressed in MCF-7, a breast cancer cell line harboring wild-type p53, and interfering RNA-mediated reduction of Hdmx markedly inhibited the growth potential of these cells in a p53-dependent manner. Together, these results make Hdmx a new putative drug target for cancer therapy.
Half of human tumors harbor the Trp53 mutation (20), whereas genetic or functional aberrations of genes that ultimately lead to disabled p53 function are common features of the remainder of human tumors (43). The mutual exclusivity of these widespread events underscores the central role of the p53 pathway in tumor suppression. A critical negative regulator of p53 is the Mdm2 protein, which directly blocks its transcriptional activity and stimulates its nuclear export and proteolytic degradation, acting as an E3 ubiquitin ligase (3, 11, 35, 41). Accordingly, Mdm2 was found to be overexpressed in human tumors and tumor cell lines as a consequence of gene amplification, increased transcript levels, or enhanced translation (26).
The Mdm2-related protein Mdmx (or Mdm4) is another key negative regulator of p53 function in vivo (9, 25, 28) and may similarly contribute to spontaneous tumor formation. Human Mdmx (Hdmx) maps in chromosomal region 1q32, a region frequently amplified in cancer (33, 42), and a low percentage of gliomas showed amplification of the Hdmx locus (34). Moreover, overexpression of the Hdmx protein was found in numerous tumor cell lines retaining wild-type p53 (32).
In contrast to Mdm2, Mdmx lacks ubiquitin ligase activity and is unable to target p53 for ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent proteolysis in vivo (24, 40). However, Mdmx binds p53 in its transactivation domain and is thereby able to inhibit its transcriptional activity. In addition, it was recently proposed that Mdmx blocks p300/CBP-mediated acetylation of p53 (36) on several lysine residues at its extreme COOH terminus, a modification likely to play a critical role in p53 tumor suppressor function (reviewed in reference 29).
Here, we show that Hdmx is an oncogene that becomes activated upon overexpression and that exerts its function by inhibiting p53-dependent transcription. A systematic screening of Hdmx expression or amplification in more than 500 human primary tumors of different origins revealed Hdmx overexpression in a wide spectrum of human tumors. In addition, we further demonstrate a role for Mdmx in regulating the acetylation status of p53 in vivo.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plasmids.
We cloned Flag-tagged Mdmx full-length cDNA and deletion mutants into vector pBABE-Puro by using BamHI/EcoRI sites. Plasmids pSUPER (pS) and pSUPER-p53 (pS-p53) were gifts from R. Agami. Two pSUPER-Hdmx (pS-Hx) plasmids were constructed as described previously (4) by inserting the following 19-nucleotide target sequences into the BglII and HindIII restriction sites of pS: 5′-GTGCAGAGGAAAGTTCCAC and 5′-TGAGTCAGTATCAGAGACG. Vectors pBABE(Puro)-E1A and pBABE(Puro)-RasV12 were provided by S. Lowe (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory). The expression vectors for hemagglutinin (HA)-p53, HA-Hdmx, HA-Hdmx-G, and pcDNA3.1-LacZ have been described elsewhere (6, 23). HA-Hdmx-E was identified by reverse transcription-PCR analysis of different human cells (6). Part of the Hdmx cDNA, spanning the coding region for the Hdmx-E protein, was cloned into pcDNA3.1. An N-terminal HA tag was added by PCR.
Cell cultures, transient transfection, and retrovirus infection.
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) of the C57BL/6 background, Phoenix Eco packaging cell lines, MCF-7 cells, and C33A cells were grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium with 10% fetal calf serum. H1299 cells were cultured in RPMI medium with 10% fetal calf serum. Transient transfection of MCF-7 cells with 4 μg of pS plasmids was performed by electroporation as previously described (4). For the acetylation assay, MCF-7 cells (100-mm dishes) were transfected by the calcium phosphate coprecipitation method. For retrovirus production, we transfected packaging cells with various plasmids and infected target cells as previously described (5). We used cells for experimentation (day 0) after selection for 4 days in the presence of 2 μg of puromycin ml−1.
Growth curves and immortalization assays.
The procedures used for growth curves and the immortalization assay were essentially those described previously (37). Low-passage MEFs were used in conjunction with retroviral infection. For growth curves, 105 cells were plated on 100-mm dishes and counted at daily intervals. Colony-forming ability was assayed with cells plated at a low density (3 × 103 cells/10-cm dish), cultured for 2 weeks, fixed, and stained (1% crystal violet in 35% methanol). The life span of MEFs was assayed by plating 3 × 105 cells on a 60-mm dish in quintuplicate and passaging them on a 3T3 protocol. The colony assay was performed with MCF-7 cells after transfection with 6 μg of pS plasmids and 300 ng of pBABE-Puro per 60-mm dish. At 40 h posttransfection, the cells were split 1:2, 1:5, and 1:10. The cells were provided with fresh medium containing 1 μg of puromycin ml−1 6 h later and refed every 2 to 3 days.
Focus formation and soft-agar assays.
Focus formation by infected MEFs was assayed with 106 cells plated on a 100-mm dish, cultured for 8 days, fixed in 70% ethanol, and stained with Giemsa stain. For soft-agar cloning, we used 20,000 puromycin-selected, infected cells in 0.5% agar to seed each well of a six-well plate in triplicate.
Antibodies, immunoprecipitation, and Western blot analysis.
The primary antibodies used were as follows: anti-Flag M2 mouse monoclonal antibody, anti-Flag rabbit polyclonal antibody, antivinculin mouse monoclonal antibody (clone hVIN-1), anti-γ-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody (clone GTU-88), and anti-α-tubulin mouse monoclonal antibody (clone DM1A) (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.); anti-p53 sheep polyclonal antibody Ab-7 and anti-p21WAF1 mouse monoclonal antibody Ab-1 (Oncogene Research Products, Cambridge, Mass.); anti-p53 goat polyclonal antibody FL393-G, anti-p53 mouse monoclonal antibodies DO-1 and PAb1801, and anti-p21 rabbit polyclonal antibody F5 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, Calif.); anti-acetyl-K373/K382 p53 antibody (Upstate Biotechnology Incorporated, Lake Placid, N.Y.); anti-phospho-p53 (Ser-15) (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, Mass.); anti-HA monoclonal antibody (BabCO, Richmond, Calif.); anti-p19ARF rabbit polyclonal antibody R562 (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom); anti-acetyl-p53 K379 (a kind gift from E. Appella); anti-Mdm2 mouse monoclonal antibodies 4B2 and 2A10; anti-Mdmx rabbit polyclonal antibody Si23; and anti-Hdmx mouse monoclonal antibody 6B1A.
For immunoprecipitation experiments, total cell extracts from trypsinized embryos or lysates of infected MEFs were obtained as previously described (25). To determine endogenous Mdm2 expression levels or p53 acetylation status in MEFs, immunoprecipitation was performed with 1 mg of extracts and a mixture of anti-Mdm2 antibodies (2A10, 4B2, and SMP14) or agarose-conjugated PAb421, respectively.
To detect p300-mediated acetylation of p53, transfected MCF-7 cells were treated with trichostatin A (TSA) (500 nM) for 6 h at 40 h after transfection. The cells were washed twice with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline and lysed in Giordano buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 250 mM NaCl, 0.1% Triton X-100, 5 mM EDTA) containing 10% glycerol and supplemented with protease inhibitors and TSA. Anti-p53 immunoprecipitation was performed with 800 μg of total lysates and anti-p53 FL393-G. Western blot analysis was performed as described previously (18, 23, 25).
ISH, FISH, immunohistochemical (IHC), and TMA analyses of Hdmx.
A total of 460 formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human tumor samples, including the most common tumor types, were analyzed. Samples were obtained from Ospedale Maggiore, Novara, Italy; Ospedale Civile, Vimercate, Italy; and the European Institute of Oncology, Milan, Italy. For each sample, two 0.6-mm cylinders from a previously selected tumor area and two from a normal counterpart were included. Hdmx mRNA expression was assessed by in situ hybridization (ISH) with [35S]UTP-labeled antisense and sense riboprobes. As a probe for fluorescence ISH (FISH), we used a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone (RP11-430C7) localized on chromosomal region 1q32 and containing the entire Hdmx locus and a BAC clone (RP11-1064P9) localized on chromosomal region 12q14 and containing the Mdm2 locus. The BAC clones were labeled with Cy3-dUTP and subsequently hybridized to metaphases spreads and tissue microarrays (TMAs). Immunostaining for p53 and Hdmx on paraffin sections was performed with mouse monoclonal antibodies DO-1 and PAb1801 and the 6B1A hybridoma supernatant, respectively.
RESULTS
Mdmx oncogenic activity in tissue cultures.
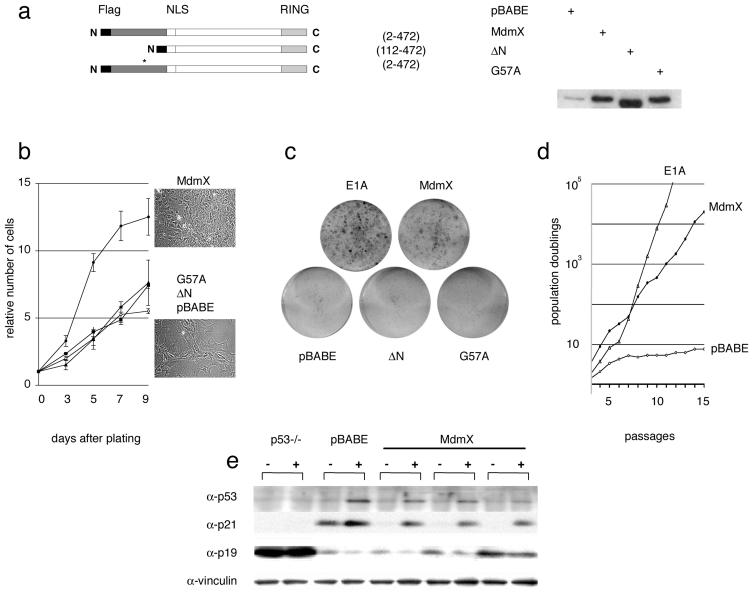
We first decided to analyze the effect of retrovirus-mediated enforced expression of Mdmx on the proliferation and life span of explanted MEFs. When wild-type MEFs are placed in cultures, their proliferative capacity dwindles with passages and eventually ceases. This permanent cell cycle arrest, the so-called senescence phenotype, results from cumulative trauma imposed by tissue culturing per se and is the consequence of the progressive activation of p53 function (39). Cells lacking functional p53 have an increased growth rate and a greater ability to proliferate at a low density (15). Similarly, wild-type MEFs with retrovirus-mediated enforced Mdmx expression (Fig. 1a) proliferated significantly faster and to a higher cell density than did control cells (Fig. 1b) and were capable of forming colonies when plated at a very low density (Fig. 1c). Moreover, the same cells continuously grew for more than 20 passages in a defined 3T3 culture protocol (Fig. 1d), while mock-infected MEFs entered senescence after about 7 passages. Enforced Mdmx expression therefore immortalizes early-passage wild-type MEFs.
FIG. 1.
Immortalization in the absence of concomitant p19ARF or p53 loss in early-passage MEFs with enforced Mdmx expression. MEFs were infected with recombinant retroviruses encoding Flag-tagged Mdmx (amino acids 2 to 472), Mdmx ΔN (N-terminal deletion of the p53-binding domain; amino acids 112 to 472), Mdmx G57A, or puromycin resistance only (pBABE). (a) The Mdmx proteins from infected MEFs were detected by Western blotting with anti-Mdmx polyclonal antibody Si-23. The asterisk indicates the position of the G57A mutation. (b) Growth curves for infected MEFs; each 100-mm dish was seeded with 105 cells. The numbers represent the means and standard deviations for two independently infected MEF cultures. Cells were photographed at a magnification of about ×30 after 7 days in cultures. (c) Colony formation assay. Infected MEFs were plated at a very low density (3 × 103 cells/100-mm dish). (d) Proliferation of control (pBABE and E1A) or Mdmx-infected MEFs on a 3T3 schedule. The accumulated number of population doublings is shown on a log scale on the y axis. (e) Mdmx-immortalized clones were UV-C irradiated (30 J/m2), and cell extracts were prepared 24 h after treatment and subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Passage 4 MEFs infected with pBABE alone and p53-null MEFs are shown as control cells; vinculin served as a loading control.
Mdm2 residue G58 is critical for the interaction of Mdm2 with the p53 protein (10). Since structural similarities between the p53-binding pockets of Mdmx and Mdmx exist (2), we mutagenized residue G57 of Mdmx (corresponding to Mdm2 G58) and showed by coimmunoprecipitation experiments that this mutation (G57A) inhibits p53 binding (unpublished data). Importantly, substitution of this residue as well as deletion of the entire N-terminal p53-binding site (ΔN mutant) of Mdmx inhibited its growth-promoting effect (Fig. 1b and c), clearly indicating that direct binding of Mdmx to p53 is essential for this function.
The assumption that Mdmx can immortalize MEFs by interfering with p53-induced senescence would predict that these cells do not show selective pressure for the loss of p53 or p19ARF expression, almost invariantly observed during spontaneous immortalization (19, 45). Direct immunoblotting analysis showed high levels of p19ARF in Mdmx-infected cultures immediately after infection and selection (data not shown). As expected from previous observations (30), p19ARF expression was significantly elevated in the p53-null fibroblasts used here as control cells (Fig. 1e). Despite variable p19ARF levels among the various Mdmx-immortalized clones analyzed (the results for three different clones are shown in Fig. 1e), the protein was readily detectable in every clone, suggesting that the p19ARF-encoding locus was intact. A striking reduction of CDKN1A (p21), a p53-responsive gene product that negatively regulates progression through the cell cycle (7, 44), was observed in Mdmx-immortalized cells, confirming impaired p53 activity under these culture conditions. Although basal p53 levels were almost undetectable in these cells, treatment with UV-C induced p53 stabilization, Ser-15 phosphorylation (data not shown), and upregulation of p21 expression (Fig. 1e). Together, these data suggest that enforced Mdmx expression allows primary cell immortalization without p19ARF or p53 loss of expression or p53-inactivating mutations.
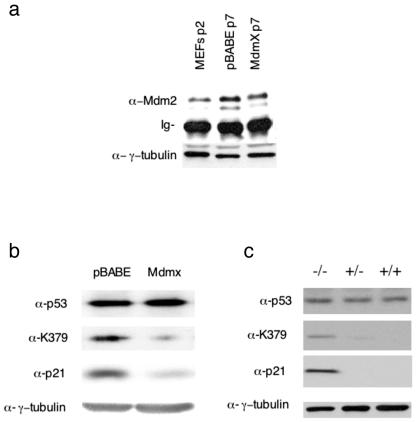
Next, we wanted to gain insights into the mechanism by which Mdmx inhibits p53 function. Since Mdm2 levels were slightly lower in Mdmx-overexpressing MEFs than in mock-infected cells (Fig. 2a), Mdmx-induced immortalization is not due to increased Mdm2 protein expression. This lower level of Mdm2 expression can be explained by impairment of the p53-mediated transcriptional activation of the Mdm2 gene. It was recently shown that, in transfection assays, Mdmx can prevent p300-induced acetylation of p53 (36), a finding which might explain the inhibition of p53-induced transcription by Mdmx. In agreement with this observation, the pool of acetylated endogenous p53 was dramatically reduced in late-passage Mdmx-overexpressing MEFs, while robust p53 K379 acetylation could be detected in control (pBABE-infected) cells (Fig. 2b). Interestingly, p53 levels were largely unaffected in Mdmx-infected cells and, in agreement with decreased transcriptional activity, marked downregulation of p21 was observed. In addition, striking p53 K379 acetylation could be detected in extracts prepared from Mdmx-deficient embryos and to a much lesser extent in Mdmx+/− embryos (Fig. 2c). Again, the total level of p53 did not appear to be significantly affected but, as was previously shown, the expression of p21 was strongly increased in the absence of Mdmx expression (Fig. 2b) (25). Since it has been suggested that acetylation plays a significant role in p53-dependent transcriptional activation (14, 38, 1), these observations provide a putative mechanism for the inhibitory effect of Mdmx on p53 activity.
FIG. 2.
Mdmx/Hdmx regulates p53 acetylation. (a) Immunoprecipitation of Mdm2 from passage 7 infected MEFs with a mixture of 2A10, 4B2, and SMP14, followed by Western blot analysis with the mouse monoclonal anti-Mdm2 antibody 2A10. Mdm2 levels in extracts from early-passage, noninfected MEFs were also determined. Total lysates were analyzed with an anti-γ-tubulin antibody to show equal input in the immunoprecipitations. Ig, immunoglobulin. (b) Immunoprecipitation of p53 from passage 7 infected MEFs, followed by Western blot analysis with either a pan-p53 antibody (Ab7) or an antibody specifically recognizing acetylated lysine-379 of murine p53 [PabLys(Ac)379m]. (c) Immunoprecipitation of p53 from pooled lysates of Mdmx−/−, Mdmx+/−, and Mdmx+/+ embryos. Immunoprecipitates were first analyzed with the antibody specifically recognizing acetylated lysine-379 of murine p53 [PabLys(Ac)379m] and then analyzed, after stripping, with the pan-p53 antibody (Ab7). Total lysates were also analyzed with anti-p21 and anti-γ-tubulin antibodies.
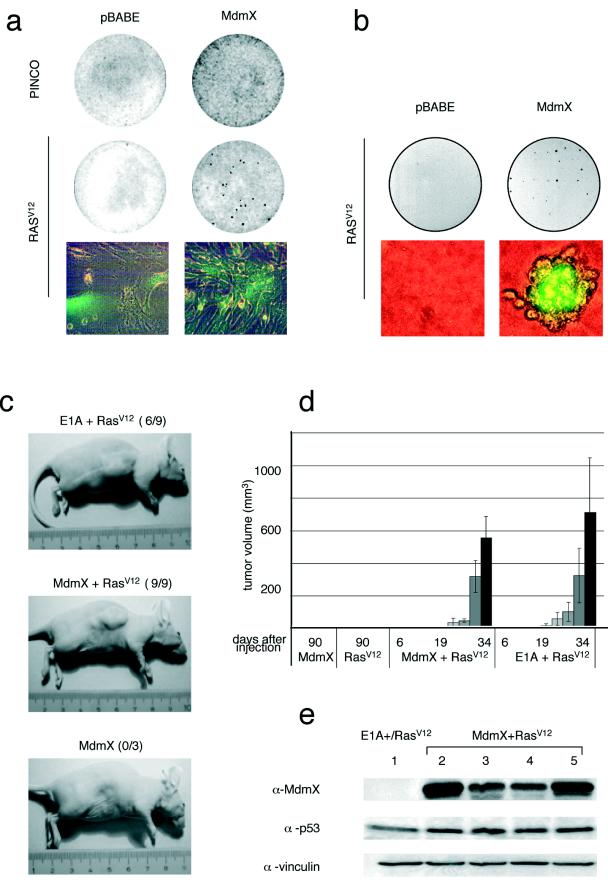
High-efficiency transformation of MEFs by an oncogenic Ras allele, HRasV12, requires a loss of p53 function (15, 16, 21). Therefore, we evaluated whether Mdmx could cooperate with HRasV12 in the neoplastic transformation of MEFs (Fig. 3). Indeed, Mdmx/HRasV12-expressing cells were no longer contact inhibited (Fig. 3a) and efficiently grew anchorage independently (Fig. 3b). Moreover, MEFs expressing Mdmx/HRasV12 as well as E1A/HRasV12-expressing control cells formed tumors within 3 weeks when subcutaneously injected into nude mice (Fig. 3c and d). Western blotting analysis confirmed that tumor development occurred without a loss of p19ARF (data not shown), p53, or Mdmx, since these proteins were detectable in Mdmx/HRasV12-expressing cells before injection into mice (Fig. 3e, lane 2), in the formed tumors (lanes 3 and 4), and in the tumor-derived cell cultures (lane 5).
FIG. 3.
Mdmx bypasses HRasV12-induced senescence and cooperates with HRasV12 in neoplastic transformation. (a) Coinfected MEFs overexpressing Mdmx and either EGFP (PINCO) or HRasV12 plus EGFP (RasV12) were plated for a focus formation assay. (b) MEFs from panel a were used to seed soft agar. After 2 weeks, foci were photographed at magnifications of ×5 and ×100. (c) Animals were injected with MEFs expressing RasV12, Mdmx, Mdmx/RasV12, or E1A/RasV12 at 6 to 8 weeks of age and were inspected for the presence of tumors 3 weeks later. (d) The mean tumor size was estimated at regular intervals after injection. Nine out of nine mice injected with Mdmx/RasV12-expressing MEFs and six out of nine mice injected with E1A/RasV12-expressing MEFs developed tumors. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (e) Cell extracts were prepared from an E1A/RasV12-expressing tumor mass (lane 1), from Mdmx/RasV12-infected MEFs before injection into nude mouse flanks (lane 2), from two different tumors (lanes 3 and 4), and from cells cultured ex vivo from another tumor mass (lane 5) and were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Vinculin served as a loading control.
Hdmx is overrepresented in a fraction of human primary tumors and amplified in a subset of primary breast cancers.
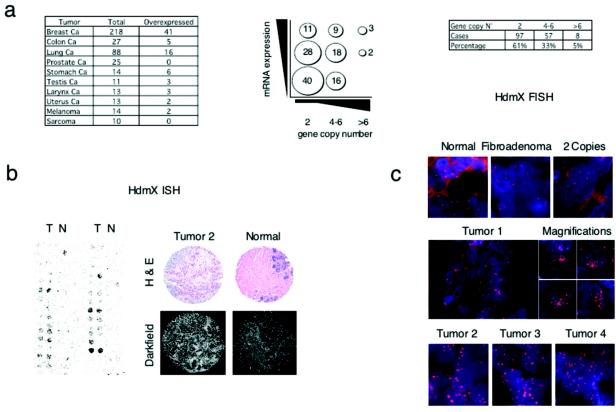
Since the above results suggest that aberrant expression of Mdmx/Hdmx contributes to tumorigenesis, we analyzed levels of Hdmx mRNA expression by ISH analysis with TMAs of hundreds of primary human tumor samples (Fig. 4a and b). We observed high levels of Hdmx expression (defined as levels at least three- to fivefold higher than those in matched controls) in 19% of breast (41 of 218), 19% of colon (5 of 27), and 18% of lung (16 of 88) cancers (Fig. 4a).
FIG. 4.
Hdmx is overexpressed in human primary tumors and amplified in a subset of breast cancers. (a) Correlation between numbers of copies of the Hdmx locus as shown by FISH (x axis) and Hdmx mRNA levels (y axis). (b) The expression of Hdmx mRNA levels was determined by ISH with TMAs. The left panels show a representative portion of ISH for Hdmx with a breast cancer TMA. The bright-field panels show the morphology of tissue samples as revealed by hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) counterstaining. The dark-field panels show ISH analysis of Hdmx expression levels in breast invasive carcinoma and in normal mammary gland. (c) Subset of primary breast tumors showing amplification of Hdmx gene copy numbers as determined by FISH analysis. (Top panel, from left to right) Normal breast tissue sample, fibroadenoma, and carcinoma containing normal copy numbers for the Hdmx gene. (Middle and bottom panels) Representative breast carcinoma tissues showing significant amplification of the Hdmx locus (>6 to 8 copies).
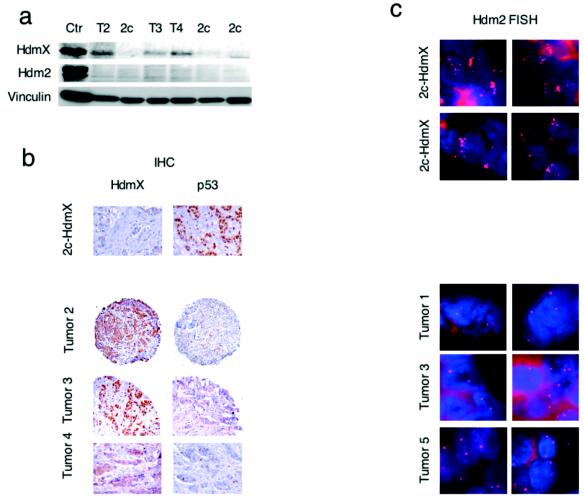
Since Hdmx maps in a region frequently amplified in human breast cancers (33, 42), we evaluated Hdmx gene copy numbers by FISH analysis with TMAs of a large number of primary breast tumors. In normal breast tissue or benign breast lesions (i.e., breast fibroadenoma), we observed two copies of the Hdmx locus (Fig. 4c). In contrast, we found Hdmx amplification (defined as more than 6 to 8 copies per cell) in 5% (8 of 162) of all samples analyzed, with lesion samples carrying up to 20 copies of the gene (Fig. 4c, middle and bottom panels). Notably, tumors with Hdmx gene amplification showed the highest degree of Hdmx RNA expression, as indicated by mRNA ISH (Fig. 4a). Western blotting (Fig. 5a) and IHC analysis (Fig. 5b) of the same tumor biopsy samples confirmed Hdmx overexpression at the protein level. Analysis of p53 levels showed elevated p53 protein concentrations (defined as >10% of cells showing staining) in 17% of the samples tested, but none of the 8 Hdmx-amplified tumors was shown to have high p53 protein concentrations by IHC analysis (Fig. 5b) or by Western blotting (data not shown). Sequencing of the p53 gene after PCR amplification of exons 4 to 9 (hosting 95% of all reported p53 mutations in human cancers) confirmed the absence of mutations. Moreover, FISH analysis with an Hdm2-specific probe revealed multiple copies of the Hdm2 gene in 3 of the 80 samples analyzed but only two copies per cell in all Hdmx-amplified tumors (Fig. 5c). Together, the data strongly suggest mutual exclusivity between Hdmx or Hdm2 gene amplification and p53 mutations.
FIG. 5.
Tumors showing Hdmx amplification overexpress Hdmx protein and retain wild-type p53 and two copies of Hdm2. (a) High levels of Hdmx protein were detected in tumors showing amplification of the Hdmx locus with 6B1A (Hdmx) or 4B2 (Hdm2) antibodies. Ctr, control; T2, T3, and T4, tumors 2, 3, and 4, respectively; 2c, two copies. (b) Detection of Hdmx and p53 by IHC analysis of selected breast tumor samples with 6B1A (Hdmx) or PAb1801 (p53) antibodies. (c) Hdm2 FISH (two fields per tumor) analysis of breast cancer samples. (Bottom panels) Samples carrying multiple copies of Hdmx. (Top panels) Hdm2 amplification in two samples carrying normal Hdmx copy numbers.
RNA interference-mediated reduction of Hdmx protein levels in breast cancer cell line MCF-7 affects cell growth in a p53-dependent manner.
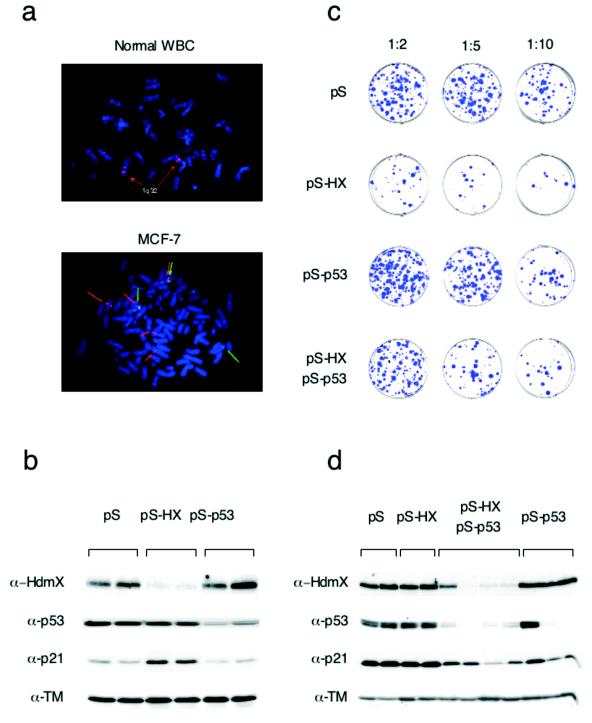
To evaluate the biological significance of Hdmx amplification in breast tumorigenesis, we used wild-type p53-expressing breast tumor cell line MCF-7, which contains multiple copies of the Hdmx gene (five copies) (Fig. 6a) and expresses a high level of Hdmx protein (32). To test whether a high level of expression of Hdmx in these cancer cells is required for long-term growth and whether this expression occurs through the inhibition of p53, we specifically inhibited the expression of Hdmx, p53, or both by RNA interference. MCF-7 cells were transiently transfected with the pS empty vector, a combination of two pS-Hx vectors, or a pS-p53 vector (4). Western blot analysis showed efficient suppression of endogenous Hdmx and p53 expression in pS-Hx- and pS-p53-transfected cells, respectively (Fig. 6b). Notably, the suppression of endogenous Hdmx expression did not significantly affect p53 levels, but p21 levels were increased, suggesting the activation of p53 function.
FIG. 6.
The RNA interference-mediated reduction of Hdmx protein levels reduces the colony-forming efficiency of a breast cancer cell line in a p53-dependent manner. (a) FISH analysis of normal white blood cells (WBC) and MCF-7 cells. (Top panel) The probe (BAC clone RP11-430C7) recognizes the Hdmx locus on chromosome 1q32. (Bottom panel) MCF-7 cells harbor multiple copies of the Hdmx locus (red arrows) and three copies of a neighboring, more telomeric region (BAC clone 14B15) (green arrows). (b) MCF-7 cells were transiently transfected by electroporation as described previously (4) with 4 μg of the indicated plasmids and harvested 40 h later. Lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. Blots were probed with antitropomyosin (α-TM) as a loading control. (c) MCF-7 cells were transfected with pBABE-Puro and either pS, pS-Hx, or pS-p53 alone or pS-Hx together with pS-p53; the final DNA amount was adjusted to a total of 6 μg with pS. (d) Puromycin-resistant colonies were isolated and established as cell lines. The expression of Hdmx, p53, p21, and tropomyosin (loading control) was analyzed by Western blotting.
MCF-7 cells then were transfected with the same vectors together with a dominant selectable marker (pBABE-Puro) and plated at different densities on selective medium to evaluate their growth potential. MCF-7 cells efficiently formed puromycin-resistant colonies when stably cotransfected with pS or pS-p53 (Fig. 6c) or with pS-Mx (data not shown). In contrast, transfection with pS-Hx dramatically reduced the number of colonies formed (Fig. 6c). Strikingly, cotransfection of pS-p53 largely rescued the antiproliferative effect of Hdmx downregulation, indicating that the growth of MCF-7 cells depends on Hdmx overexpression and its ability to keep p53 activity low under normal growth conditions.
Finally, we derived monoclonal stable cell lines from the puromycin-resistant colonies and analyzed Hdmx and p53 expression (Fig. 6d). The downregulation of Hdmx expression was observed in a high percentage (50 to 60%) of pS-Hx- and pS-p53-transfected, puromycin-resistant cell lines, always in correlation with a decrease in p53 expression. Importantly, Hdmx protein levels were unaffected in the cell lines established from the rare pS-Hx-transfected colonies. These cell lines therefore were probably derived from background puromycin-resistant colonies that had not simultaneously integrated the pS-Hx plasmid. These data indicate that Hdmx expression can be stably reduced only when p53 expression is simultaneously reduced, reinforcing the notion that growth inhibition following interference with Mdmx/Hdmx expression is p53 dependent. This conclusion is supported by the observation that transfection of pS-Hx in p53-negative H1299 cells did not affect cell growth (data not shown).
DISCUSSION
We demonstrate here that increased and constitutive Mdmx expression in primary cells causes immortalization and neoplastic transformation in combination with oncogenic HRasV12. Hdmx is overexpressed in a sizable fraction of human primary cancers and is amplified in about 5% of the breast tumors tested, all of which retain wild-type p53. Importantly, we show that the breast cancer cell line MCF-7 loses its ability to grow when depleted of Hdmx and that this effect is strictly dependent on the presence of wild-type p53. Together, these data demonstrate that Hdmx directly contributes to human tumor formation by impeding the ability of p53 to exert its tumor suppressor function.
The molecular mechanism that prevents p53 activation in the presence of high levels of Mdmx/Hdmx is largely unknown. Transient overexpression studies with various cell lines have suggested that Mdmx inhibits Mdm2-mediated p53 degradation (24, 40). However, it was later proposed that when expressed at lower levels, Mdmx facilitates Mdm2-dependent p53 degradation by rendering Mdm2 protein sufficiently stable to function at its full potential (13). In primary cells expressing constitutively elevated Mdmx protein levels, no increase in Mdm2 expression levels was observed, and p53 expression levels were not significantly affected, suggesting that the inhibition of p53 activity in this cellular setting does not require p53 degradation. Furthermore, data presented here clearly indicate that the direct binding of Mdmx to p53 is necessary for the inhibition of p53 function.
We show here a key role for Mdmx in the regulation of p53 acetylation in both physiological and overexpression contexts. Previous studies proposed a key role for this modification in p53-mediated transcriptional activation. If this model holds true, then the inhibition of p53 acetylation by Mdmx provides a simple explanation for impaired p53 activity in the presence of high Mdmx concentrations. However, the relevance of p53 acetylation for its activity is still a matter of debate (8, 27; for a review, see reference 29), and it was recently proposed that p53 acetylation could simply be a consequence of the recruitment of the coactivators p300/CBP. The recruitment of p300/CBP appears, however, to be essential for p53-dependent transcription, at least of the p21 promoter, by elevating the level of histone acetylation around p53 target promoters (22). Thus, the binding of Mdmx to p53 could either prevent the recruitment of p300 or inhibits its acetyltransferase activity. A competition of p300 and Hdmx for p53 binding is compatible with previous observations. Hdmx contacts p53 at about amino acids 22 and 23 (2), and a p53 mutant lacking the 23 N-terminal amino acids does not interact with p300/CBP (22), indicating overlapping binding sites. In addition, the phosphorylation of Ser-15, Thr-18, and Ser-20 after DNA damage helps the release of Mdm2 (and presumably Mdmx) and simultaneously greatly increases the recruitment of p300/CBP to p53 (12). Moreover, p53 acetylation itself could also be important in facilitating recruitment of the coactivators p300/CBP (1). One could therefore speculate that the oncogenic potential of Mdmx/Hdmx resides in the abilities to prevent the recruitment of p300/CBP to the p53 transactivation domain and, as a consequence, to inhibit the essential functions of these coactivators in p53-dependent transcription.
To determine the domain(s) of Mdmx/Hdmx involved in the regulation of p53 acetylation, we made use of two Hdmx splicing variants, Hdmx-G and Hdmx-E. As recently described, Hdmx-G lacks the p53-binding domain (6). Hdmx-E is the human homolog of Mdmx-S (31) lacking exon 6 through alternative splicing. It essentially encodes only the p53-binding domain (see supplementary information at http://www.dmbr.ugent.be/lmbc/contents/mcb_vol24_july2004). The effect of these variants on p300-induced K373/K382 acetylation of exogenous p53 was tested in transient transfection assays with MCF-7 cells (see supplementary information at http://www.dmbr.ugent.be/lmbc/contents/mcb_vol24_july2004). Cells were either mock treated or treated with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor TSA (500 nM) for 6 h before harvesting. In the absence of TSA treatment, p53 acetylation was hardly detectable, whereas in the presence of TSA treatment, both Hdmx and Hdmx-E inhibited the p300-mediated acetylation of p53. These results suggest that the p53-binding domain of Hdmx is necessary and sufficient to interfere with p300-induced p53 acetylation.
A recent report suggested that Mdm2 promotes p53 deacetylation by recruiting an HDAC1-containing complex (17). To investigate whether this suggestion would hold true for Hdmx, we tested the ability of Hdmx isoforms to be coimmunoprecipitated with HDAC1. In contrast to both Hdmx and Hdmx-G, Hdmx-E could not be found in a complex with HDAC1 (see supplementary information at http://www.dmbr.ugent.be/lmbc/contents/mcb_vol24_july2004). Since the latter is able to reverse p300-mediated p53 acetylation, this result suggests that, in contrast to what has been proposed for Mdm2, complex formation between HDAC1 and Hdmx does not appear to be a prerequisite for the inhibition of p300-dependent p53 acetylation. However, our data do not exclude the possibility that the recruitment of HDAC1 in vivo has a further impact on p53 acetylation or the levels of acetylation of other relevant proteins present in the p53-containing complex, such as Mdm2.
Our data suggest that the Hdmx-E spliced variant, which essentially encodes only the p53-binding domain, is at least equally as potent as full-length Hdmx in interfering with p300 recruitment and p53-mediated transcriptional activation. This suggestion is consistent with the observation that the mouse counterpart of Hdmx-E, Mdmx-S, was reported to act as a strong inhibitor of p53-mediated transcriptional activation (31). It will therefore be of interest to determine the levels of expression of Hdmx-E and full-length Hdmx in our collection of human primary tumors.
In conclusion, our findings indicate that increased Hdmx expression directly contributes to the development of human cancer and therefore represents a new and promising target for cancer therapy. In particular, agents that downregulate Hdmx protein levels or inhibit the Hdmx-p53 interaction will be expected to sensitize cancer cells to p53 tumor suppressor function.
Acknowledgments
We thank Micaela Quarto and Marco Bianchi for generation of the TMAs and for ISH and IHC analyses; Manuela Nebuloni, Renzo Boldorini, and Giuseppe Viale for providing tumor material; Giuseppe Ossolengo and Daniele Piccini for antibody purification; Manuela Capillo for help with mice; Elena Belloni for bioinformatics; and Adrian Bracken for helpful discussions. We also thank E. Appella for providing the agarose-conjugated PAb421 and PabLys(Ac)379m antibodies and R. Agami for the gifts of plasmids pS and pS-p53.
J.-C. Marine is a Chercheur Qualifié from the Fonds National pour la Recherche Scientifique. D. Danovi is a recipient of a fellowship from Fondazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (FIRC). P. de Graaf and E. Meulmeester were supported by grants from the Association for International Cancer Research and the Dutch Cancer Society, respectively. This work was supported in part by grants from FB Insurance, FIRC, AICR, Fédération Belge contre le Cancer, and the Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology.
REFERENCES
- 1.Barlev, N. A., L. Liu, N. H. Chehab, K. Mansfield, K. G. Harris, T. D. Halazonetis, and S. L. Berger. 2001. Acetylation of p53 activates transcription through recruitment of coactivators/histone acetyltransferases. Mol. Cell 8:1243-1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bottger, V., A., Bottger, C., Garcia-Echeverria, Y. F., Ramos, A. J. van der Eb, A. G. Jochemsen, and D. P. Lane. 1999. Comparative study of the p53-mdm2 and p53-MDMX interfaces. Oncogene 18:189-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boyd, S. D., K. Y. Tsai, and T. Jacks. 2000. An intact HDM2 RING-finger domain is required for nuclear exclusion of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:563-568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brummelkamp, T. R., R. Bernards, and R. Agami. 2002. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296:550-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Colombo, E., J. C. Marine, D. Danovi, B. Falini, and P. G. Pelicci. 2002. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:529-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.De Graaf, P., N. A. Little, Y. F. Ramos, E. Meulmeester, S. J. Letteboer, and A. G. Jochemsen. 2003. Hdmx protein stability is regulated by the ubiquitin ligase activity of Mdm2. J. Biol. Chem. 278:38315-38324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.el-Deiry, W. S., T. Tokino, V. E. Velculescu, D. B. Levy, R. Parsons, J. M. Trent, D. Lin, W. E. Mercer, K. W. Kinzler, and B. Vogelstein. 1993. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75:817-825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Espinosa, J. M., and B. M. Emerson. 2001. Transcriptional regulation by p53 through intrinsic DNA/chromatin binding and site-directed cofactor recruitment. Mol. Cell 8:57-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Finch, R. A., D. B. Donoviel, D. Potter, M. Shi, A. Fan, D. D. Freed, C. Y. Wang, B. P. Zambrowicz, R. Ramirez-Solis, A. T. Sands, and N. Zhang. 2002. mdmx is a negative regulator of p53 activity in vivo. Cancer Res. 62:3221-3225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Freedman, D. A., C. B. Epstein, J. C. Roth, and A. J. Levine. 1997. A genetic approach to mapping the p53 binding site in the MDM2 protein. Mol. Med. 3:248-259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Geyer, R. K., Z. K. Yu, and C. G. Maki. 2000. The MDM2 RING-finger domain is required to promote p53 nuclear export. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:569-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Grossman, S. R. 2001. p300/CBP/p53 interaction and regulation of the p53 response. Eur. J. Biochem. 268:2773-2778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gu, J., H. Kawai, L. Nie, H. Kitao, D. Wiederschain, A. G. Jochemsen, J. Parant, G. Lozano, and Z. M. Yuan. 2002. Mutual dependence of MDM2 and MDMX in their functional inactivation of p53. J. Biol. Chem. 277:19251-19254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gu, W., and R. G. Roeder. 1997. Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal domain. Cell 90:595-606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Harvey, M., A. T. Sands, R. S. Weiss, M. E. Hegi, R. W. Wiseman, P. Pantazis, B. C. Giovanella, M. A. Tainsky, A. Bradley, and L. A. Donehower. 1993. In vitro growth characteristics of embryo fibroblasts isolated from p53-deficient mice. Oncogene 8:2457-2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hicks, G. G., S. E. Egan, A. H. Greenberg, and M. Mowat. 1991. Mutant p53 tumor suppressor alleles release ras-induced cell cycle growth arrest. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1344-1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ito, A., Y., Kawaguchi, C. H., Lai, J. J., Kovacs, Y., Higashimoto, E., Appella, T. P., Yao. 2002. MDM2-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of p53 is required for its degradation. EMBO J. 21:6236-6245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kalkhoven, E., H. Teunissen, A. Houweling, C. P. Verrijzer, and A. Zantema. 2002. The PHD-type zinc finger is an integral part of the CBP acetyltransferase domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:1961-1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kamijo, T., F. Zindy, M. F. Roussel, D. E. Quelle, J. R. Downing, R. A. Ashmun, G. Grosveld, and C. J. Sherr. 1997. Tumor suppression at the mouse INK4a locus mediated by the alternative reading frame product p19ARF. Cell 91:649-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Levine, A. J. 1997. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lin, H. J., V. Eviner, G. C. Prendergast, and E. White. 1995. Activated H-ras rescues E1A-induced apoptosis and cooperates with E1A to overcome p53-dependent growth arrest. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:4536-4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liu, G., T. Xia, and X. Chen. 2003. The activation domains, the proline-rich domain, and the C-terminal basic domain in p53 are necessary for acetylation of histones on the proximal p21 promoter and interaction with p300/CREB-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 278:17557-17565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Meulmeester, E., R. Frenk, R. Stad, P. de Graaf, J. C. Marine, K. H. Vousden, and A. G. Jochemsen. 2003. Critical role for a central part of Mdm2 in the ubiquitylation of p53. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23:4929-4938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Migliorini, D., D. Danovi, E. Colombo, R. Carbone, P. G. Pelicci, and J. C. Marine. 2002. Hdmx recruitment into the nucleus by Hdm2 is essential for its ability to regulate p53 stability and transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:7318-7323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Migliorini, D., E. L. Denchi, D. Danovi, A. Jochemsen, M. Capillo, A. Gobbi, K. Helin, P. G. Pelicci, and J. C. Marine. 2002. Mdm4 (Mdmx) regulates p53-induced growth arrest and neuronal cell death during early embryonic mouse development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:5527-5538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Momand, J., H. H. Wu, and G. Dasgupta. 2000. MDM2—master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Gene 242:15-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nakamura, S., J. A. Roth, and T. Mukhopadhyay. 2000. Multiple lysine mutations in the C-terminal domain of p53 interfere with MDM2-dependent protein degradation and ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:9391-9398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Parant, J., A. Chavez-Reyes, N. A. Little, W. Yan, V. Reinke, A. G. Jochemsen, and G. Lozano. 2001. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm4-null mice by loss of Trp53 suggests a nonoverlapping pathway with MDM2 to regulate p53. Nat. Genet. 29:92-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Prives, C., and J. L. Manley. 2001. Why is p53 acetylated? Cell 107:815-818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Quelle, D. E., F. Zindy, R. A. Ashmun, and C. J. Sherr. 1995. Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell 83:993-1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rallapalli, R., G. Strachan, B. Cho, W. E. Mercer, and D. J. Hall. 1999. A novel MDMX transcript expressed in a variety of transformed cell lines encodes a truncated protein with potent p53 repressive activity. J. Biol. Chem. 274:8299-8308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ramos, Y. F., R. Stad, J. Attema, L. T. Peltenburg, A. J. van der Eb, and A. G. Jochemsen. 2001. Aberrant expression of HDMX proteins in tumor cells correlates with wild-type p53. Cancer Res. 61:1839-1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ried, T., K. E. Just, H. Holtgreve-Grez, S. du Manoir, M. R. Speicher, E. Schrock, C. Latham, H. Blegen, A. Zetterberg, T. Cremer, et al. 1995. Comparative genomic hybridization of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded breast tumors reveals different patterns of chromosomal gains and losses in fibroadenomas and diploid and aneuploid carcinomas. Cancer Res. 55:5415-5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Riemenschneider, M. J., C. B. Knobbe, and G. Reifenberger. 2003. Refined mapping of 1q32 amplicons in malignant gliomas confirms MDM4 as the main amplification target. Int. J. Cancer 104:752-757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Roth, J., M. Dobbelstein, D. A. Freedman, T. Shenk, and A. J. Levine. 1998. Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the hdm2 oncoprotein regulates the levels of the p53 protein via a pathway used by the human immunodeficiency virus rev protein. EMBO J. 17:554-564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sabbatini, P., and F. McCormick. 2002. MDMX inhibits the p300/CBP-mediated acetylation of p53. DNA Cell Biol. 21:519-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sage, J., G. J. Mulligan, L. D. Attardi, A. Miller, S. Chen, B. Williams, E. Theodorou, and T. Jacks. 2000. Targeted disruption of the three Rb-related genes leads to loss of G(1) control and immortalization. Genes Dev. 14:3037-3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sakaguchi, K., J. E. Herrera, S. Saito, T. Miki, M. Bustin, A. Vassilev, C. W. Anderson, and E. Appella. 1998. DNA damage activates p53 through a phosphorylation-acetylation cascade. Genes Dev. 12:2831-2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sherr, C. J., and R. A. DePinho. 2000. Cellular senescence: mitotic clock or culture shock? Cell 102:407-410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stad, R., N. A. Little, D. P. Xirodimas, R. Frenk, A. J. van der Eb, D. P. Lane, M. K. Saville, and A. G. Jochemsen. 2001. Mdmx stabilizes p53 and Mdm2 via two distinct mechanisms. EMBO Rep. 2:1029-1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tao, W., and A. J. Levine. 1999. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of oncoprotein Hdm2 is required for Hdm2-mediated degradation of p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:3077-3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tirkkonen, M., M. Tanner, R. Karhu, A. Kallioniemi, J. Isola, and O. P. Kallioniemi. 1998. Molecular cytogenetics of primary breast cancer by CGH. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 21:177-184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vousden, K. H., and X. Lu. 2002. Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2:594-604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xiong, Y., G. J. Hannon, H. Zhang, D. Casso, R. Kobayashi, and D. Beach. 1993. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature 366:701-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zindy, F., D. E. Quelle, M. F. Roussel, and C. J. Sherr. 1997. Expression of the p16INK4a tumor suppressor versus other INK4 family members during mouse development and aging. Oncogene 15:203-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]