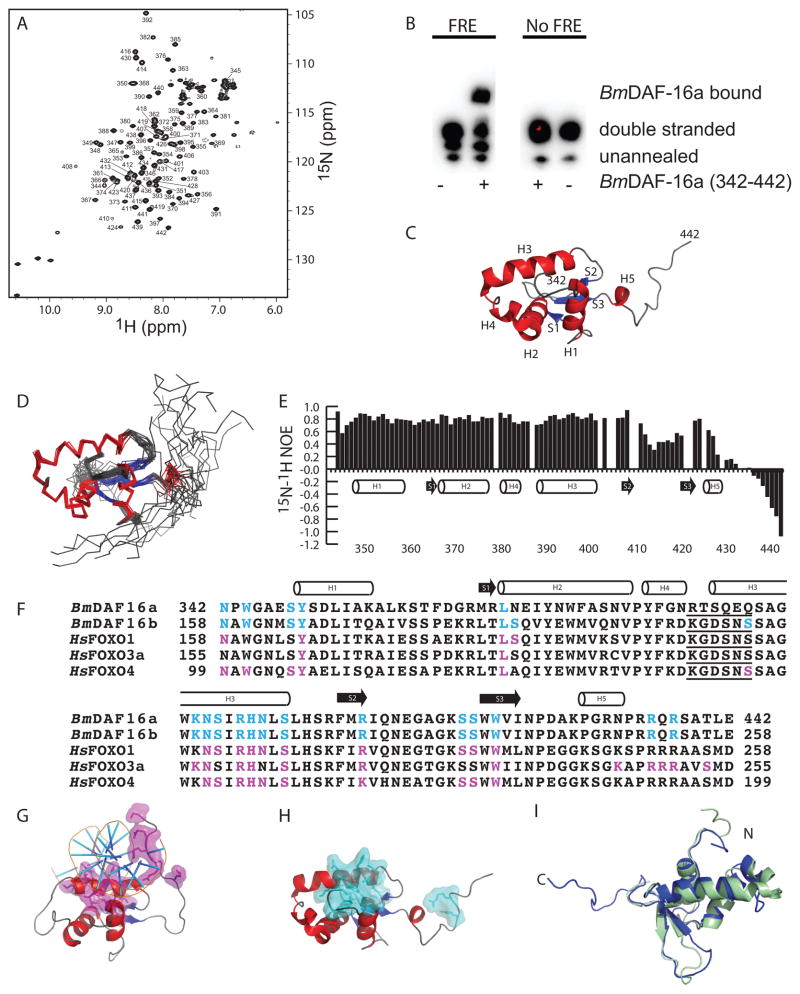
Figure 1. Residues in BmDAF-16a (342-442) are identical to FRE interacting residues in human FOXO proteins.
A) 15N-1H HSQC spectra of 500 μM [U-15N/13C] BmDAF-16a (342-442) with backbone amide assignments. B) Mobility shift assay showing Bm-DAF-16a (342-442) binds to DNA containing a canonical FRE sequence from C. elegans and does not bind DNA lacking an FRE sequence. C) The lowest energy structure of BmDAF-16a (342-442). D) Ensemble of 20 BmDAF-16a (342-442) structures. E) 15N-1H heteronuclear NOE values plotted versus BmDAF-16a (342-442) residue. F) Sequence alignment of BmDAF-16a and BmDAF-16b with the DNA binding domains of human FOXO1, FOXO3a, and FOXO4. FRE interacting residues in human FOXO1, FOXO3a, and FOXO4 are highlighted magenta12. Residues in BmDAF-16a and BmDAF-16b that are identical to DNA interacting residues of the human FOXO proteins are highlighted in cyan. The five amino acid insert consistent with FOXO domains, but not other FOX family members, is underlined12. G) Human FOXO3a bound to an FRE (PDB ID 2UZK)21. DNA interacting residues of FOXO3a are shown in magenta. H) Solution structure of BmDAF-16a (342-442) with residues identical to DNA interacting residues from human FOXO proteins shown in cyan. I) Superimposition of the Bm-DAF-16a (342-442) (blue) and FOXO4 (green, PDB ID 1E17).