Abstract
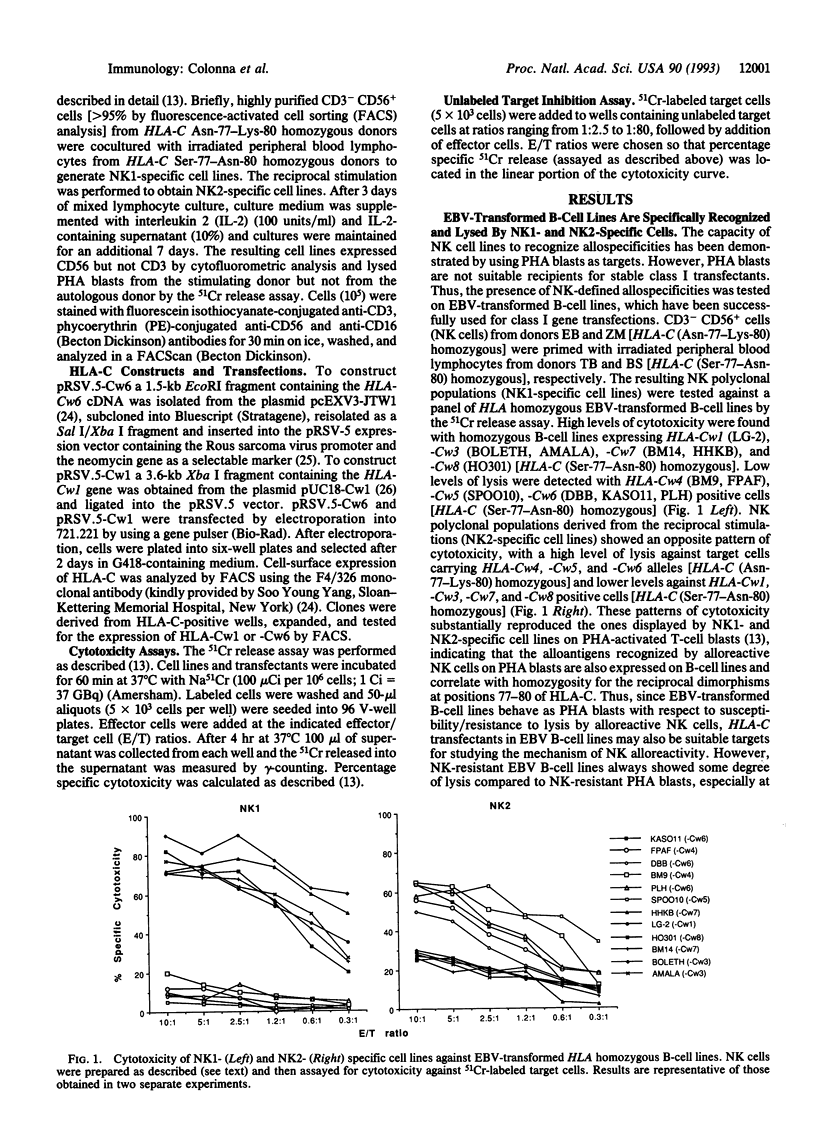
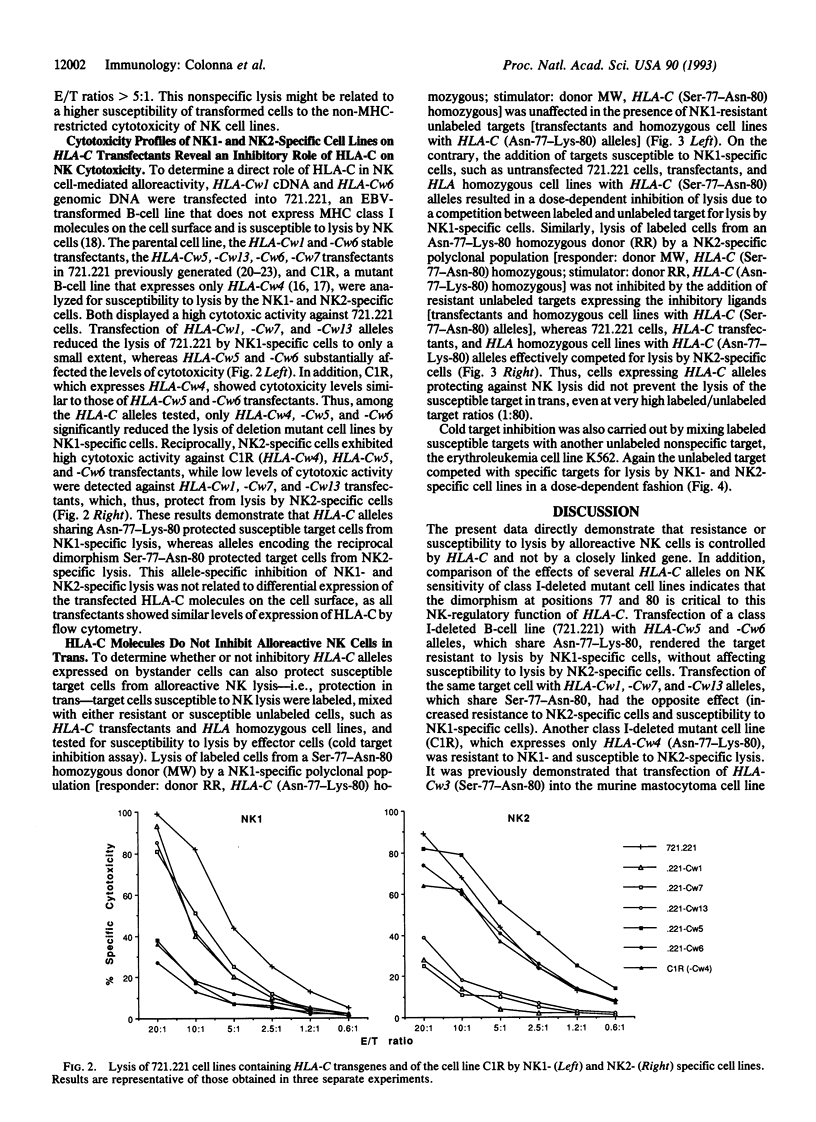
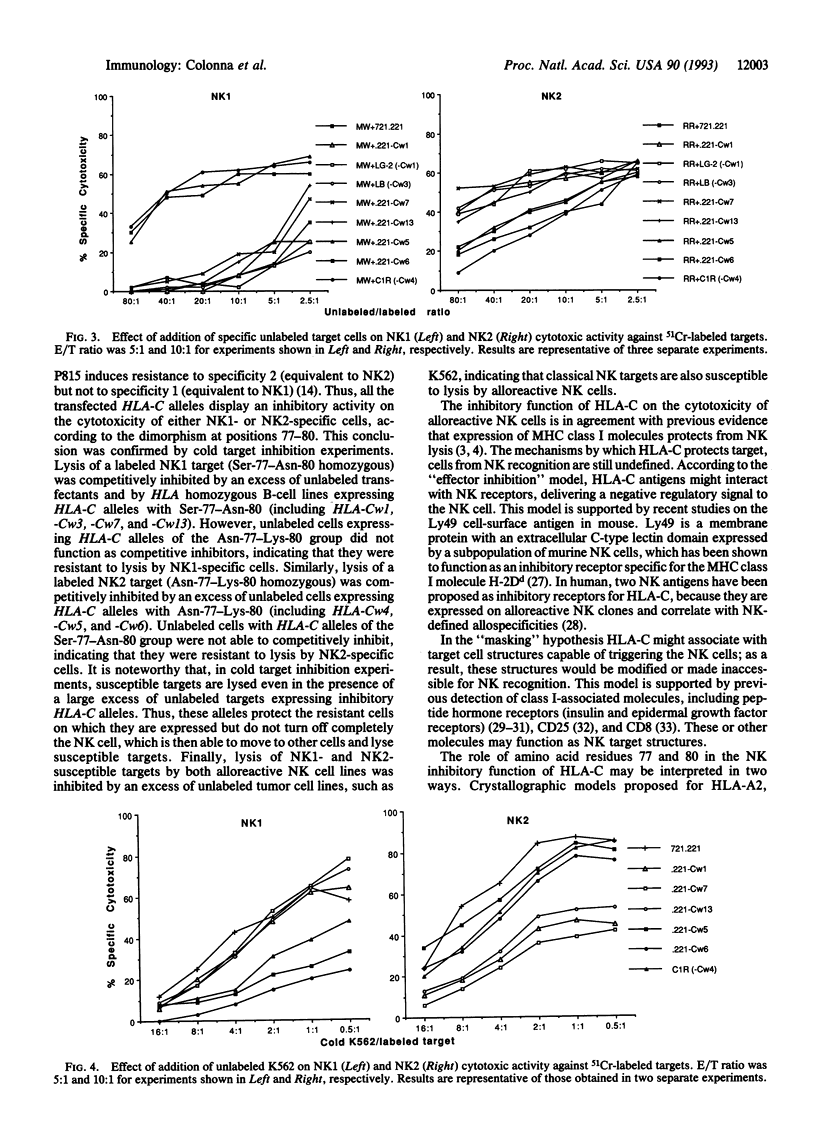
Natural killer (NK) cells recognize alloantigens on normal cells. One of these alloantigens correlates with homozygosity for a dimorphism of HLA-C at positions 77-80, which is shared by a number of HLA-C alleles. A second allelic alloantigen correlates with homozygosity for the alternative HLA-C dimorphism, which is shared by the remaining HLA-C alleles. Moreover, NK1- and NK2-specific NK cell lines can be generated by mixed leukocyte cultures in which donor and stimulator are homozygous for the alternative dimorphisms at positions 77-80 of HLA-C. In the present work, the role of HLA-C in NK cell-mediated allorecognition was directly investigated by analyzing the effects produced by transfection of several HLA-C alleles on NK sensitivity of class I-deleted mutant cell lines. Transfection of cells with HLA-C alleles encoding Asn-77-Lys-80 (including HLA-Cw4, -Cw5, and -Cw6) inhibited the lysis of the targets by NK1-specific NK cells, whereas HLA-C alleles encoding Ser-77-Asn-80 (including HLA-Cw1, -Cw7, and -Cw13) protected the targets from NK2-specific NK cells. Thus, HLA-C alleles are the dominant inhibitory ligands that protect targets from lysis by these allospecific NK cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender J. R., Pardi R., Engleman E. T-cell receptor-negative natural killer cells display antigen-specific cytotoxicity for microvascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6949–6953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer J. G., Marsh S. G., Albert E. D., Bodmer W. F., Dupont B., Erlich H. A., Mach B., Mayr W. R., Parham P., Sasazuki T. Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 1991. Hum Immunol. 1992 May;34(1):4–18. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(92)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushkin Y., Demaria S., Le J. M., Schwab R. Physical association between the CD8 and HLA class I molecules on the surface of activated human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3985–3989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capps G. G., Robinson B. E., Lewis K. D., Zúiga M. C. In vivo dimeric association of class I MHC heavy chains. Possible relationship to class I MHC heavy chain-beta 2-microglobulin dissociation. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Stuber G., Andrée S., Franksson L., Klein E., Beretta A., Siccardi A. G., Kärre K. Reduced expression of major histocompatibility complex class I free heavy chains and enhanced sensitivity to natural killer cells after incubation of human lymphoid lines with beta 2-microglobulin. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):1752–1756. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick B. S., Sambhara S. R., Sasakura Y., Miller R. G. Effect of class I MHC binding peptides on recognition by natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3150–3156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Colonna M., Viale O., Pende D., Di Donato C., Reinharz D., Amoroso A., Jeannet M., Guardiola J., Moretta A. Susceptibility or resistance to lysis by alloreactive natural killer cells is governed by a gene in the human major histocompatibility complex between BF and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9794–9797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Pende D., Viale O., Di Donato C., Tripodi G., Orengo A. M., Guardiola J., Moretta A., Moretta L. Evidence of a natural killer (NK) cell repertoire for (allo) antigen recognition: definition of five distinct NK-determined allospecificities in humans. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):709–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Pende D., Viale O., Tambussi G., Ferrini S., Biassoni R., Longo A., Guardiola J., Moretta A., Moretta L. Specific recognition of human CD3-CD16+ natural killer cells requires the expression of an autosomic recessive gene on target cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):47–52. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Pende D., Viale O., Than A., Di Donato C., Orengo A. M., Biassoni R., Verdiani S., Amoroso A., Moretta A. Involvement of HLA class I alleles in natural killer (NK) cell-specific functions: expression of HLA-Cw3 confers selective protection from lysis by alloreactive NK clones displaying a defined specificity (specificity 2). J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):963–971. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Viale O., Pende D., Malnati M., Biassoni R., Melioli G., Moretta A., Long E. O., Moretta L. Specific lysis of allogeneic cells after activation of CD3- lymphocytes in mixed lymphocyte culture. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2403–2408. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna M., Brooks E. G., Falco M., Ferrara G. B., Strominger J. L. Generation of allospecific natural killer cells by stimulation across a polymorphism of HLA-C. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.8493555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna M., Spies T., Strominger J. L., Ciccone E., Moretta A., Moretta L., Pende D., Viale O. Alloantigen recognition by two human natural killer cell clones is associated with HLA-C or a closely linked gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7983–7985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Due C., Simonsen M., Olsson L. The major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chain as a structural subunit of the human cell membrane insulin receptor: implications for the range of biological functions of histocompatibility antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6007–6011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Grahovac B., Schendel D., Stevanović S., Gnau V., Jung G., Strominger J. L., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific peptide ligand motifs of HLA-C molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):12005–12009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.12005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi F., Meneveri R., Gullberg M., Lopalco L., Rossi G. B., Lanza P., De Santis C., Brattsand G., Buttò S., Ginelli E. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 mimics a hidden monomorphic epitope borne by class I major histocompatibility complex heavy chains. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):53–62. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güssow D., Rein R. S., Meijer I., de Hoog W., Seemann G. H., Hochstenbach F. M., Ploegh H. L. Isolation, expression, and the primary structure of HLA-Cw1 and HLA-Cw2 genes: evolutionary aspects. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(5):313–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00404424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlhofer F. M., Ribaudo R. K., Yokoyama W. M. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):66–70. doi: 10.1038/358066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie W. R., Myers N. B., Connolly J. M., Gorka J., Lee D. R., Hansen T. H. The specific binding of peptide ligand to Ld class I major histocompatibility complex molecules determines their antigenic structure. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):449–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. In search of the 'missing self': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90097-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Rosen-Bronson S., Karp D. R., Malnati M., Sekaly R. P., Jaraquemada D. Efficient cDNA expression vectors for stable and transient expression of HLA-DR in transfected fibroblast and lymphoid cells. Hum Immunol. 1991 Aug;31(4):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90092-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The three-dimensional structure of HLA-B27 at 2.1 A resolution suggests a general mechanism for tight peptide binding to MHC. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrigal J. A., Belich M. P., Benjamin R. J., Little A. M., Hildebrand W. H., Mann D. L., Parham P. Molecular definition of a polymorphic antigen (LA45) of free HLA-A and -B heavy chains found on the surfaces of activated B and T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1085–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Kang S. H., Lee H. W., Trapani J. A., Dupont B., Yang S. Y. Isolation and expression of a cDNA clone encoding HLA-Cw6: unique characteristics of HLA-C encoded gene products. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(5):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00352842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Bottino C., Pende D., Tripodi G., Tambussi G., Viale O., Orengo A., Barbaresi M., Merli A., Ciccone E. Identification of four subsets of human CD3-CD16+ natural killer (NK) cells by the expression of clonally distributed functional surface molecules: correlation between subset assignment of NK clones and ability to mediate specific alloantigen recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1589–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Ploegh H. L. Allele and locus-specific differences in cell surface expression and the association of HLA class I heavy chain with beta 2-microglobulin: differential effects of inhibition of glycosylation on class I subunit association. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):801–810. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L., Gamble S., Rothstein L., Gramm C., Benacerraf B. Dissociation of beta 2-microglobulin leads to the accumulation of a substantial pool of inactive class I MHC heavy chains on the cell surface. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90093-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M., Cousin J. L., Fehlmann M. Cross-linking of insulin receptors to MHC antigens in human B lymphocytes: evidence for selective molecular interactions. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2293–2298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schendel D. J., Reinhardt C., Nelson P. J., Maget B., Pullen L., Bornkamm G. W., Steinle A. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes show HLA-C-restricted recognition of EBV-bearing cells and allorecognition of HLA class I molecules presenting self-peptides. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2406–2414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabl E., Stockinger H., Majdic O., Gaugitsch H., Lindley I. J., Maurer D., Hajek-Rosenmayr A., Knapp W. Activated human T lymphocytes express MHC class I heavy chains not associated with beta 2-microglobulin. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Schlessinger J., Edidin M. Interaction between major histocompatibility complex antigens and epidermal growth factor receptors on human cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):725–731. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Gnarra J. R., Baniyash M., Leonard W. J. Possible association between IL-2 receptors and class I HLA molecules on T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3512–3515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., DeMars R. Production of human cells expressing individual transferred HLA-A,-B,-C genes using an HLA-A,-B,-C null human cell line. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3320–3328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. H., Barber B. H. The conformational flexibility of class I H-2 molecules as revealed by anti-peptide antibodies specific for intracytoplasmic determinants: differential reactivity of beta 2-microglobulin "bound" and "free" H-2Kb heavy chains. Mol Immunol. 1990 Feb;27(2):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90112-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Crumpton M. J. Molecular structure of human histocompatibility antigens: the HLA-C series. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):580–585. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyer R., Damotte M., Delovitch T. L., Trucy J., Jordan B. R., Strachan T. Complete nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding a functional human class I histocompatibility antigen (HLA-CW3). EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):879–885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Spits H., Ploegh H. L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinle A., Nössner E., Schendel D. J. Isolation and characterization of a genomic HLA-Cw6 clone. Tissue Antigens. 1992 Mar;39(3):134–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1992.tb01923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Dawson J. R. Target structures involved in natural killing (NK): characteristics, distribution, and candidate molecules. Crit Rev Immunol. 1991;10(5):393–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Howell D. N., Salter R. D., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1657–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Salter R. D., Alexander J., Ward F. E., Ruiz R. E., Cresswell P., Dawson J. R. Class I-induced resistance to natural killing: identification of nonpermissive residues in HLA-A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5989–5992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Salter R. D., Cresswell P., Dawson J. R. Peptide-induced modulation of target cell sensitivity to natural killing. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Bianchi E., Bass H., Suzuki T., Bender J., Pardi R., Brenner C. A., Larrick J. W., Engleman E. G. Natural killer lines and clones with apparent antigen specificity. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):457–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibensky D., DeMars R., Holowachuk E. W., Delovitch T. L. Sequence and gene transfer analyses of HLA-CwBL18 (HLA-C blank) and HLA-Cw5 genes. Implications for the control of expression and immunogenicity of HLA-C antigens. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):348–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibensky D., Decary F., Delovitch T. L. HLA-C genes are transcribed in HLA-C blank individuals. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(3):220–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00346590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M., Seaman W. E. The Ly-49 and NKR-P1 gene families encoding lectin-like receptors on natural killer cells: the NK gene complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:613–635. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemmour J., Little A. M., Schendel D. J., Parham P. The HLA-A,B "negative" mutant cell line C1R expresses a novel HLA-B35 allele, which also has a point mutation in the translation initiation codon. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



