The DEPDC5 gene (OMIM #614191), mapped to 22q12.2-q12.3, encodes the DEP domain-containing protein 5. DEPDC5 has been associated with a variety of familial epilepsies, including familial focal epilepsy with variable foci, autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy, familial temporal lobe epilepsy, epileptic spasms, and cortical dysplasia.1–4 Notably, DEPDC5 has never been linked to increased risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). We report a family with epilepsy due to DEPDC5 mutation and 2 definite cases of SUDEP within this family.
Case report.
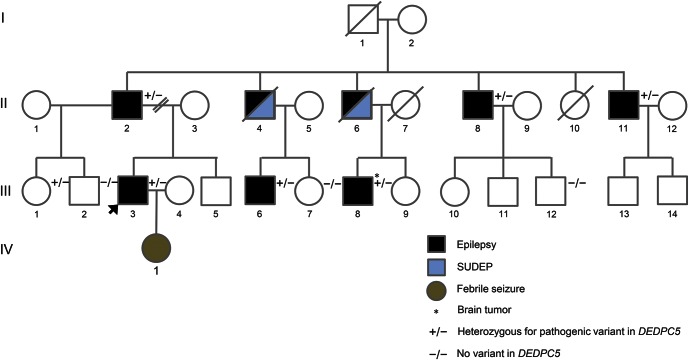
We studied a 4-generation nonconsanguineous French-Canadian family with 9 affected individuals. Of note, all but one are male. The index case (III.3, figure) is a 39-year-old man who started having seizures at the age of 13 years. His seizures were characterized by a “dream-like” aura followed by loss of consciousness and tonic–clonic movements. Initially, seizures were mainly diurnal; in his mid-20s, they became exclusively nocturnal. He currently experiences 2–5 seizures a year on dual therapy with carbamazepine and clobazam. EEGs showed interictal epileptiform discharges over the right anterior temporal region. Brain MRI was normal.
Figure. Pedigree of the reported family.
SUDEP = sudden unexpected death in epilepsy.
Individuals II.4 and II.6 had definite autopsy-confirmed SUDEP at the ages of 58 and 50 years, respectively. Patient II.4 presented with nocturnal generalized tonic–clonic (GTC) seizures at the age of 9 years; he was initially treated with phenytoin, but his seizures persisted throughout life with an average of one seizure per month. A few months before his sudden death, he was switched to lacosamide because of phenytoin side effects. He was never compliant with his treatment in adulthood. Patient II.6 had GTC seizures since 2 years of age, with poor compliance to antiepileptic therapy during his entire life. Postmortem examination revealed hemorrhagic pulmonary congestion and bitten tongue.
Seizure history in this family is summarized in table e-1 at Neurology.org/ng. All patients were cognitively intact. There was no history of any cardiac symptomatology, cardiovascular risk factors, or definite cardiac condition.
Genetic analysis of the index case revealed a pathogenic heterozygous variant in the DEDPC5 gene (p.Gln216*, c.646C>T; ENST00000536766) resulting in a premature stop codon. The index case was also tested for genes associated with SUDEP, none of which showed mutations (table e-2).
All living affected relatives (except for individual IV.1) and 4 healthy family members were clinically evaluated and had DEPDC5 Sanger sequenced. All affected patients and individual III.1 were found to carry the same DEPDC5 pathogenic variant as the index case (figure).
Discussion.
SUDEP represents a rare but important cause of mortality in patients with epilepsy. In a Finnish long-term follow-up study of community-based pediatric epilepsy that included 220 patients, there were only 3 cases of SUDEP5 (compared with 2 SUDEP cases in this family with 9 affected individuals; χ2 = 8.46, p = 0.003). While the exact pathophysiology underlying SUDEP remains poorly understood, there are consistently associated risk factors: GTC seizures, polytherapy, early onset of epilepsy, duration of seizure disorder, nocturnal seizures, and full-scale IQ less than 70.6,7 It is worth mentioning that SUDEP does occur in patients who do not present with risk factors; indeed, the 2 individuals with SUDEP reported here were cognitively intact and not on polytherapy.
Several genes have been associated with SUDEP in human and/or animal studies (table e-2). These genes are associated with cardiac arrhythmias and/or severe epilepsies (usually in the setting of epileptic encephalopathies), neither of which apply to this family's phenotype. Based on the clinical histories of both SUDEP cases, it is unlikely that these patients carried mutations in genes previously associated with SUDEP.
An alternative hypothesis would be that patients II.4 and II.6 actually had sudden cardiac deaths instead of SUDEP. This is also highly unlikely because they had never presented any cardiac symptomatology or cardiovascular risk factors such as obesity, cigarette smoking, dyslipidemia, hypertension, or excessive alcohol intake.
This study has limitations. First, the deceased patients were not tested for SUDEP susceptibility genes; thus, we could not rule out the possibility of a second genetic variant segregating in this family. Second, a potential adverse reaction of lacosamide, a drug known to be associated with PR interval prolongation and occasionally death,8 cannot be completely ruled out—even in the poor medication compliance scenario related by patient II.4's family.
The findings in this family suggest that DEPDC5 mutations may be a risk factor for SUDEP, but future studies are necessary to elucidate this association. Our report should serve as an initial cautionary note, and this particular genetic diagnosis might be highly consequential. Elucidation of the basic mechanisms connecting defective DEPDC5 to its clinical outcomes will be of major importance.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgment: The authors thank Dr. Enkeleida Brunga for performing genetic testing of the participants.
Footnotes
Supplemental data at Neurology.org/ng
Author contributions: Fábio A. Nascimento: study concept and design, acquisition of data, data analysis and interpretation, drafting manuscript. Felippe Borlot: acquisition of data, drafting the manuscript. Patrick Cossette: acquisition of data. Berge A. Minassian: revising manuscript. Danielle M. Andrade: study concept and design, study supervision, revising manuscript, final approval. All authors accept responsibility for conduct of the research.
Study funding: This study was funded by Genome Canada and the Ontario Brain Institute (OBI).
Disclosure: Fábio A. Nascimento reports no disclosures. Felippe Borlot has received funding for travel or speaker honoraria from BioMarin and has received research support from the University of Toronto. Patrick Cossette has received research support from UCB Pharma, CIHR, Genome Canada, Genome Quebec, and the Savoy Foundation. Berge A. Minassian has received funding for travel and/or speaker honoraria from UCB Pharma and receives license and royalty payments for patents held with regard to diagnostic testing of the following genes: EPM2A, EPM2B, MECP2, VMA21. Danielle M. Andrade has served on scientific advisory boards for Esai and has received research support from the Ontario Brain Institute, University of Toronto, Krembil Neurosciences Centre, and Toronto Western Hospital Foundation. Go to Neurology.org/ng for full disclosure forms. The Article Processing Charge was paid by the authors.
References
- 1.Dibbens LM, de Vries B, Donatello S, et al. Mutations in DEPDC5 cause familial focal epilepsy with variable foci. Nat Genet 2013;45:546–551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Scheffer IE, Heron SE, Regan BM, et al. Mutations in mammalian target of rapamycin regulator DEPDC5 cause focal epilepsy with brain malformations. Ann Neurol 2014;75:782–787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baulac S, Ishida S, Marsan E, et al. Familial focal epilepsy with focal cortical dysplasia due to DEPDC5 mutations. Ann Neurol 2015;77:675–683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Carvill GL, Crompton DE, Regan BM, et al. Epileptic spasms are a feature of DEPDC5 mTORopathy. Neurol Genet 2015;1:e17. 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sillanpää M, Jalava M, Kaleva O, Shinnar S. Long-term prognosis of seizures with onset in childhood. N Engl J Med 1998;338:1715–1722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nilsson I, Farahmand BY, Persson PG, Thiblin I, Tomson T. Risk factors for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: a case-control study. Lancet 1999;353:888–893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Walczak TS, Leppik IE, D'Amelio M, et al. Incidence and risk factors in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: a prospective cohort study. Neurology 2001;56:519–525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zaccara G, Perucca P, Loiacono G, Giovannelli F, Verrotti A. The adverse event profile of lacosamide: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Epilepsia 2013;54:66–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.