Abstract
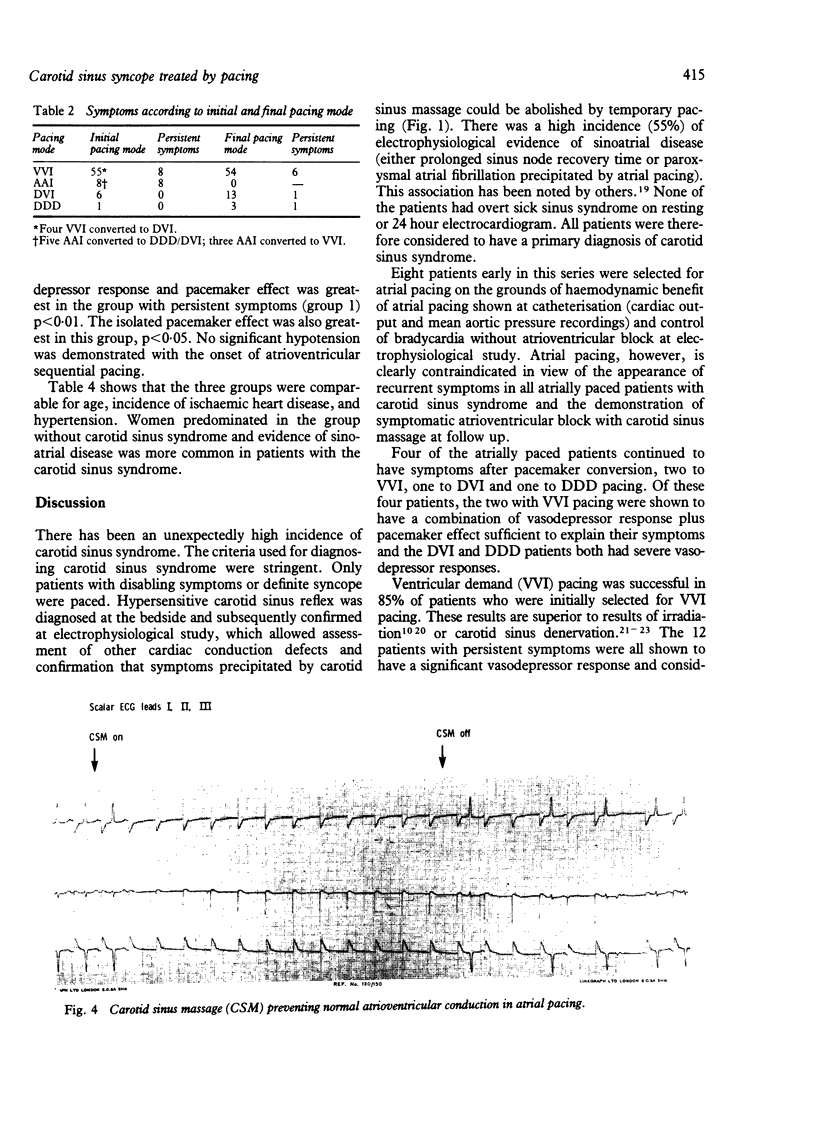
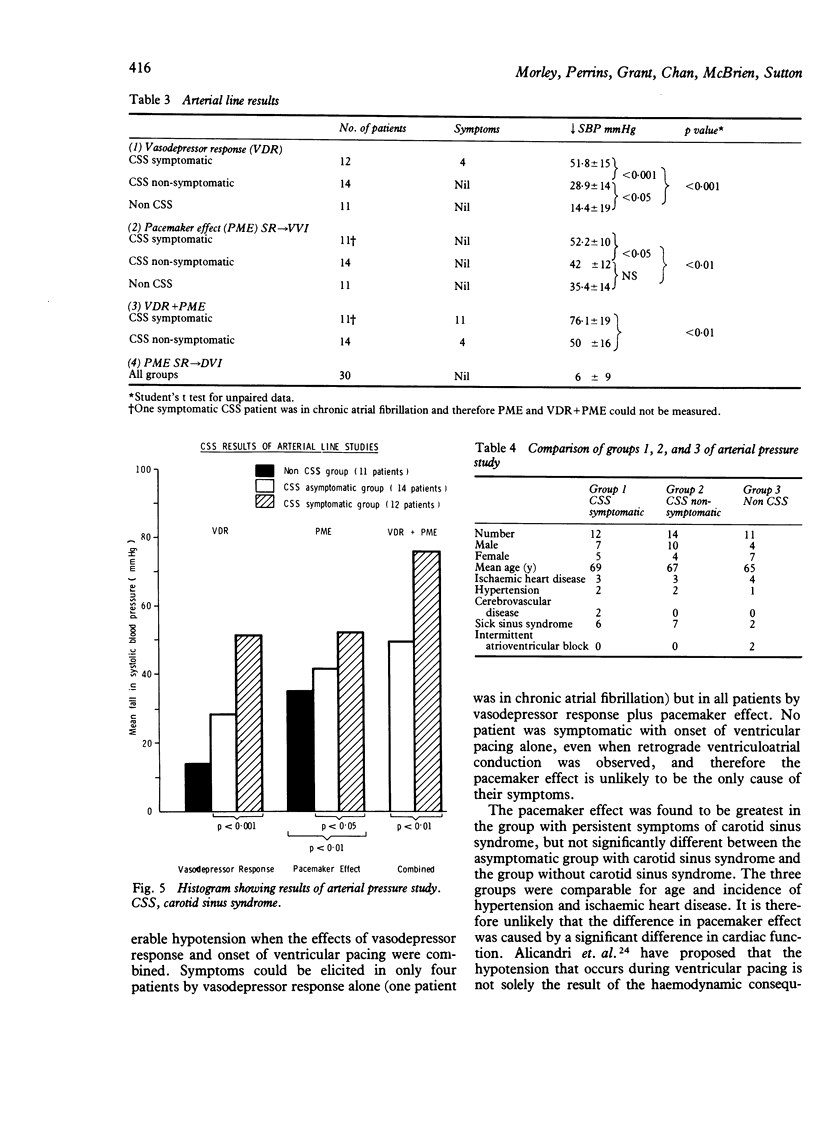
Seventy patients have been paced for carotid sinus syndrome over four years. Twelve patients had persistent symptoms despite adequate ventricular pacing. Patients with persistent symptoms were found to have a significant vasodepressor response, a significant hypotensive response to ventricular pacing (pacemaker effect), and a severe hypotensive response to carotid sinus massage with introduction of ventricular pacing, which reproduced symptoms in all patients. A group of 14 asymptomatic paced carotid sinus patients was found to have a significantly lower vasodepressor response, pacemaker effect, and combined vasodepressor response plus pacemaker effect than the group with persistent symptoms. Atrioventricular sequential pacing was shown to eliminate the hypotensive effect of ventricular pacing and is considered to be the treatment of choice for patients with carotid sinus syndrome who have both cardioinhibitory and significant vasodepressor responses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARP C. R., DAVISON H. M., ATWATER J. S. Carotid sinus syndrome. J Med Assoc Ga. 1950 May;39(5):196–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alicandri C., Fouad F. M., Tarazi R. C., Castle L., Morant V. Three cases of hypotension and syncope with ventricular pacing: possible role of atrial reflexes. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Jul;42(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90998-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt J. O., Brambring P., Hindorf K., Röhnelt M. The afferent discharge pattern of atrial mechanoreceptors in the cat during sinusoidal stretch of atrial strips in situ. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):33–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. B., Stephens M. R., Davies A. G. Carotid sinus hypersensitivity in patients presenting with syncope. Br Heart J. 1979 Nov;42(5):583–586. doi: 10.1136/hrt.42.5.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREELEY H. P., SMEDAL M. I., MOST W. The treatment of the carotid-sinus syndrome by irradiation. N Engl J Med. 1955 Jan 20;252(3):91–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195501202520304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWN B., LEVINE S. A. The carotid sinus. Clinical value of its stimulation. Circulation. 1961 May;23:766–789. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.23.5.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel W. J., Hayakawa H., Allen H. N., Danzig R., Kermaier A. I. Assessment of sinus node function in patients with the sick sinus syndrome. Circulation. 1972 Oct;46(4):761–769. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.46.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. K., Yap V. U., Fields J., Thomsen J. H. Carotid sinus syncope induced by malignant tumors in the neck. Emergence of vasodepressor manifestations following pacemaker therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Nov;139(11):1281–1284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz D. I., Gerein A. N., Miyagishima R. T. Permanent demand pacing for hypersensitive carotid sinus syndrome. Can Med Assoc J. 1973 May 5;108(9):1131–1134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponsonnaille J., Heiligenstein D., Pailloncy M., Marcheix J. C., Gras H. Les syncopes par hyperréflectivité sino-carotidienne. Intérêt et limite de la stimulation cardiaque. Nouv Presse Med. 1980 Apr 5;9(16):1175–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklaroff H. J. Carotid sinus hypersensitivity--asystole and hypertension in the same patient. Am Heart J. 1979 Jun;97(6):815–815. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(79)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trout H. H., 3rd, Brown L. L., Thompson J. E. Carotid sinus syndrome: treatment by carotid sinus denervation. Ann Surg. 1979 May;189(5):575–580. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197905000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P. F., Crawley I. S., Dorney E. R. Carotid sinus hypersensitivity and syncope. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Sep;42(3):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90934-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]