Abstract
Background and purpose — Obesity increases the risk of deep infection after total joint arthroplasty (TJA). Our objective was to determine whether there may be body mass index (BMI) and weight thresholds indicating a higher prosthetic joint infection rate.
Patients and methods — We included all 9,061 primary hip and knee arthroplasties (mean age 70 years, 61% women) performed between March 1996 and December 2013 where the patient had received intravenous cefuroxime (1.5 g) perioperatively. The main exposures of interest were BMI (5 categories: < 24.9, 25–29.9, 30–34.9, 35–39.9, and ≥ 40) and weight (5 categories: < 60, 60–79, 80–99, 100–119, and ≥ 120 kg). Numbers of TJAs according to BMI categories (lowest to highest) were as follows: 2,956, 3,350, 1,908, 633, and 214, respectively. The main outcome was prosthetic joint infection. The mean follow-up time was 6.5 years (0.5–18 years).
Results — 111 prosthetic joint infections were observed: 68 postoperative, 16 hematogenous, and 27 of undetermined cause. Incidence rates were similar in the first 3 BMI categories (< 35), but they were twice as high with BMI 35–39.9 (adjusted HR = 2.1, 95% CI: 1.1–4.3) and 4 times higher with BMI ≥ 40 (adjusted HR = 4.2, 95% CI: 1.8–9.7). Weight ≥ 100 kg was identified as threshold for a significant increase in infection from the early postoperative period onward (adjusted HR = 2.1, 95% CI: 1.3–3.6).
Interpretation — BMI ≥ 35 or weight ≥ 100 kg may serve as a cutoff for higher perioperative dosage of antibiotics.
About one half of patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and up to one third of patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty (THA) are obese, which increases the risk of prosthetic joint infection. Among the reasons for increased risk of infections in obese patients are the higher prevalence of comorbidities, complex surgery, and suboptimal tissue oxygen supply (Anaya and Dellinger 2006). Moreover, lower serum and tissue concentrations of prophylactic antibiotics have been measured (Forse et al. 1989, Brill et al. 2014), and there is concern about under-dosing of antibiotics during surgery in these patients (Janson and Thursky 2012). Antibiotic prophylaxis in TJA is most commonly performed with first- or second-generation cephalosporins. Weight-adjusted dosing has been recommended for cefazolin, but not for cefuroxime (Parvizi et al. 2013).
There is variation in the current literature regarding the obesity categories that are evaluated in relation to occurrence of infection, and this is often restricted to a comparison above and below a BMI of 30 (Haverkamp et al. 2011, Kerkhoffs et al. 2012), which may be too low as a cutoff. Determination of a threshold above which prosthetic joint infection rates after TJA increase is important to provide an efficient cutoff for optimization of perioperative treatment, particularly for adjustment of prophylactic antibiotic dosage (Bratzler et al. 2013). Such an assessment based on BMI (including World Health Organisation (WHO) classes of obesity (WHO 1995)) and on weight categories has not yet been performed for TJA.
Although it is often considered to be a modifiable risk factor, obesity is challenging to alter, especially with time constraints and in physically disabled patients. Adaptation of the dose of perioperative antibiotics to the severity of obesity may be even more important. Our objective was therefore to identify BMI and weight thresholds above which prosthetic joint infection rates increased in a cohort of primary TKA and THA patients treated with the same prophylactic antibiotic (cefuroxime, 1.5 g intravenously) prior to surgery, in accordance with current guidelines (Bratzler et al. 2013, Parvizi et al. 2013).
Patients and methods
Study design, study population, and data collection
Starting in March 1996, all patients undergoing THA and starting in April 1998, all patients undergoing TKA at our institution were enrolled in a prospective hospital-based cohort. For the present study, all primary TKAs and THAs treated with antibiotic prophylaxis consisting of cefuroxime (1.5 g intravenously) 30 min before surgery and operated upon between March 1996 and December 2013 were eligible. Of 9,173 eligible TJAs (5,735 THAs and 3,438 TKAs), 112 TJAs (1%) were excluded due to missing information on BMI. Overall, 9,061 TJAs were included: 5,661 THAs (63%) and 3,400 TKAs (37%). Mean age at surgery was 70 (18–96) years, mean BMI was 28 (14–60), mean weight was 76 (33–150) kg, and 5,498 TJAs (61%) were performed in women. The mean follow-up time was 6.5 (0.5–18) years. During the course of the study, 317 patients (4%) left the area and 1,555 (17%) died.
Surgery was performed under vertical laminar airflow by a large number of surgeons with varying levels of experience and training. Screening for MRSA carriage was not performed systematically, except for 2 periods between 2003 and 2005. Patients identified as MRSA-positive underwent topical decolonization treatment with nasal mupirocin (2%) twice a day for 5 days and whole-body washing with chlorhexidine soap (40 mg/mL) for 7 days.
Exposures
The exposures of interest were BMI and weight at the time of surgery. We classified BMI into 5 categories according to the WHO classification (1995): normal-weight (BMI < 25), overweight (BMI 25–29.9), obese class-I (BMI 30–34.9), obese class-II (BMI 35–39.9), and obese class-III (BMI ≥ 40). The final analysis was performed with only 2 BMI categories above and below the identified cutoff (< 35 and ≥ 35). Body weight was stratified in 5 categories: < 60, 60–79, 80–99, 100–119, and ≥ 120 kg. The final analysis was performed with only 2 categories (< 100 and ≥ 100 kg).
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the occurrence of prosthetic joint infection defined as (a) presence of a sinus tract that communicated with the joint; (b) intraoperative presence of purulence surrounding the prosthesis without any other known etiology; or (c) 2 or more intraoperative cultures, or a combination of preoperative aspiration and intraoperative cultures, that yielded the same organism (Osmon et al. 2013). Diagnosis, source of infection, and type of organism were ascertained by 2 infectious diseases specialists (DV and IU).
Covariates
The following variables were assessed at the time of surgery and used to perform adjusted analyses: sex, age at operation, American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) score, diabetes, etiology of osteoarthritis (primary vs. secondary), previous surgery, smoking status (ever-smoker vs. never-smoker), site of arthroplasty (hip vs. knee); use of antibiotic-laden cement (yes/no); and length of surgery (in min).
Data collection
Information concerning baseline characteristics and surgical intervention was documented by the operating surgeon on specifically designed data-collection forms. Information about comorbidities was retrieved from the anesthesia record and discharge summary. The treatment of any major complication performed at our hospital is routinely documented in the registry (Lübbeke et al. 2010). With our institution being a tertiary—and the only—public hospital in the “canton” (county), the vast majority of patients with TJA are referred and treated at our hospital in cases of prosthetic joint infection, reoperation, or revision for any other complication. Information on change of residence and death was obtained from the population registry of the “canton”.
Statistics
First, we measured incidence rates according to the 5 BMI categories. We calculated person-time at risk of prosthetic joint infection (originating from any source) as the length of the interval between the date of surgery and the date of infection, date of death, or end of follow-up (June 30, 2014 or date of change of residence in cases where the patient had moved out of the area). We also performed a Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with “prosthetic joint infection” as the endpoint. We then calculated incidence rates and incidence rate ratios (IRRs) according to the 2 BMI categories defined by the threshold identified (i.e. below it and above it). Adjusted HRs (interpreted as IRRs, and in the following named as such, were obtained using Cox regression analysis. We adjusted for sex, age, ASA score (1–2 vs. 3–4), diabetes, smoking status, etiology of OA, site of arthroplasty, use of antibiotic-laden cement, and length of surgery. There was a high correlation between the covariate “previous surgery” and “etiology of OA”, and the former was therefore not used in the adjusted analyses. Proportionality of hazards assumptions was assessed on log-minus-log plots of the cumulative incidence. All analyses were repeated for weight instead of BMI, in 5 categories and then in 2.
We performed 3 sensitivity analyses as follows. (1) In addition to the outcome prosthetic joint infection (originating from any source), we separately estimated the influence of weight on prosthetic joint infection originating from the surgical site and prosthetic joint infection originating from all other sources including those undetermined. (2) We re-evaluated the BMI and weight thresholds for the outcome prosthetic joint infection (any source) separately in the hip and knee cohorts. (3) We also did this separately in men and women.
Ethics
Ethical approval was obtained from the local ethics committee (CER 05-017 (05-041)).
Results
Over the study period, 111 prosthetic joint infections occurred, 68 of which were classified as postoperative infections and 16 of which were classified as hematogenous. In 27 patients, the origin could not be determined. The infections were diagnosed after a median of 11 months (IQR: 1–37).
There were 2,956 TJAs (33%) in normal-weight patients, 3,350 (37%) in overweight patients, 1,908 (21%) in obese class-I patients, 633 (7%) in obese class-II patients, and 214 TJAs (2%) in obese class-III patients. Higher BMI was significantly associated with younger age, more diabetes, higher ASA scores, more frequent primary OA, less ever-smokers, longer surgery time, and an increasing proportion of TKAs (p < 0.001 for all covariates) (Table 1). Except for the normal weight category, the proportion of women increased with increasing BMI. The percentage with surgery that lasted ≥ 180 min was similar in the 4 lower BMI categories (around 7%) and increased to 13% in those with BMI ≥ 40.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics according to the 5 BMI categories
| BMI | < 25 n = 2,956 | 25–29.9 n = 3,350 | 30–34.9 n = 1,908 | 35–39.9 n = 633 | ≥ 40 n = 214 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women (%) | 1,961 (66) | 1,833 (55) | 1,103 (58) | 427 (68) | 174 (81) |
| ASA score 3–4 (%) a | 663 (23) | 731 (22) | 534 (28) | 232 (37) | 110 (52) |
| Diabetes (%) | 172 (6) | 370 (11) | 326 (17) | 133 (21) | 54 (25) |
| Smoking status (%) b | |||||
| Never | 1,799 (61) | 2,110 (63) | 1,175 (62) | 436 (69) | 155 (72) |
| Former | 340 (11) | 494 (15) | 349 (18) | 98 (16) | 33 (15) |
| Current | 630 (21) | 515 (15) | 265 (14) | 68 (11) | 19 (9) |
| Missing | 187 (6) | 231 (7) | 119 (6) | 31 (5) | 7 (3) |
| Primary osteoarthritis (%) | 2,063 (70) | 2,755 (82) | 1,632 (85) | 570 (90) | 198 (93) |
| Knee arthroplasty (%) | 701 (24) | 1,255 (38) | 895 (47) | 392 (62) | 157 (73) |
| Use of antibiotic-laden cement (%) | 2,427 (82) | 2,826 (84) | 1671 (88) | 578 (91) | 193 (90) |
| Mean age at operation (SD), years | 70 (14) | 70 (11) | 69 (9.8) | 69 (9.3) | 67 (7.6) |
| Mean BMI (SD) | 22 (2.0) | 27 (1.4) | 32 (1.4) | 37 (1.4) | 44 (3.6) |
| Mean weight (SD), kg | 62 (9.4) | 76 (9.3) | 88 (11) | 98 (12) | 111 (13) |
| Mean length of surgery (SD), min | 111 (39) | 114 (35) | 119 (34) | 123 (31) | 132 (35) |
| Length of surgery ≥ 180 min (%) c | 220 (8) | 210 (6) | 140 (7) | 47 (7) | 28 (13) |
BMI: body mass index; ASA score: American Society of Anaesthesiology score: SD: standard deviation.
Information on ASA score missing, n = 50.
Information on smoking status missing, n = 575.
Information on length of surgery missing, n = 32.
BMI and prosthetic joint infection
33 prosthetic joint infections were diagnosed in patients with normal-weight, 37 in patients with over-weight, and 41 in obese patients. The incidence rates were similar between normal-weight patients (1.8 cases/1,000 person-years), overweight patients (1.7 cases/1,000 person-years), and obese class-I patients (1.6 cases/1,000 person-years), but the incidence of prosthetic joint infection increased to 3.3 cases/1,000 person-years in obese class-II patients and to 6.7 cases/1,000 person-years in obese class-III patients (Table 2). BMI ≥ 35 (obesity of class II and higher) was associated with more than twice the infection rate (crude IRR = 2.3, 95% CI: 1.5–3.8; p < 0.001) compared to a BMI of < 35 (Table 3). The effect was almost unchanged after adjustment for age, sex, ASA score, diabetes, smoking status, etiology of OA, length of surgery, use of antibiotic-laden cement, and arthroplasty site (adjusted IRR = 2.5, 95% CI: 1.5–4.3, p < 0.001). Stratification according to arthroplasty site revealed an adjusted IRR of 3.2 (95% CI: 1.6–6.3) after THA and of 2.1 (95% CI: 1.03–4.5) after TKA. Stratification according to sex gave an adjusted IRR of 2.2 (95% CI: 1.1–4.5) for women and of 2.8 (95% CI: 1.4–5.8) for men.
Table 2.
Incidence rates with crude and adjusted incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for prosthetic joint infection according to 5 BMI categories and 5 weight categories
| BMI | < 25 n = 2,956 | 25–29.9 n = 3,350 | 30–34.9 n = 1,908 | 35–39.9 n = 633 | ≥ 40 n = 214 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | 33 | 37 | 20 | 13 | 8 |
| Person-years | 18,726 | 22,194 | 12,575 | 3,925 | 1,202 |
| Incidence rate, cases/1,000 person-years | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 3.3 | 6.7 |
| Crude IRR (95% CI) | Ref. | 1.0 (0.6–1.5) | 0.9 (0.5–1.6) | 1.8 (1.0–3.5) | 3.5 (1.6–7.7) |
| Adjusted IRR (95% CI) a | Ref. | 1.0 (0.6–1.7) | 1.0 (0.6–1.8) | 2.1 (1.1–4.3) | 4.2 (1.8–9.7) |
| Weight, kg | < 60 n = 1,238 | 60–79 n = 4,259 | 80–99 n = 2,790 | 100–119 n = 665 | ≥ 120 n = 109 |
| Cases | 10 | 49 | 31 | 15 | 6 |
| Person-years | 7,704 | 28,425 | 17,921 | 3,932 | 640 |
| Incidence rate, cases/1,000 person-years | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 3.8 | 9.4 |
| Crude IRR (95% CI) | Ref. | 1.4 (0.7–2.7) | 1.4 (0.7–2.8) | 2.9 (1.3–6.4) | 7.1 (2.6–19.5) |
| Adjusted IRR (95% CI) a | Ref. | 1.4 (0.7–3.0) | 1.3 (0.6–2.9) | 2.5 (1.01–6.0) | 5.5 (1.8–16.6) |
BMI: body mass index; IRR: incidence rate ratio; CI: confidence interval.
Adjustment was performed for age, sex, ASA score (ASA 1–2 vs. 3–4), presence of diabetes, smoking status, -etiology of OA (primary vs. secondary), site of arthroplasty, use of antibiotic-laden cement, and length of operation, using Cox regression analysis.
Table 3.
Incidence rates with crude and adjusted incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for prosthetic joint infection according to 2 BMI categories and 2 weight categories (above and below the threshold)
| BMI < 35 n = 8,214 | BMI ≥ 35 n = 847 | Weight < 100 kg n = 8,286 | Weight ≥ 100 kg n = 775 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | 90 | 21 | 90 | 21 |
| Person-years | 53,495 | 5,128 | 54,049 | 4,573 |
| Incidence rate, cases/1,000 person-years | 1.7 | 4.1 | 1.7 | 4.6 |
| Crude IRR (95% CI) | 2.3 (1.5–3.8, p < 0.001) | 2.6 (1.6–4.2, p < 0.001) | ||
| Crude IRR (95% CI) a | 2.4 (1.5–3.8, p < 0.001) | 2.6 (1.6–4.2, p < 0.001) | ||
| Adjusted IRR (95% CI) b | 2.5 (1.5–4.3, p < 0.001) | 2.1 (1.3–3.6, p = 0.003) | ||
BMI: body mass index; IRR: incidence rate ratio; CI: confidence interval.
Crude estimates only including the cases with complete covariate information.
Adjustment was performed for age, sex, ASA score (ASA 1–2 vs. 3–4), presence of diabetes, smoking status, -etiology of OA (primary vs. secondary), site of arthroplasty, use of antibiotic-laden cement, and length of operation, using Cox regression analysis.
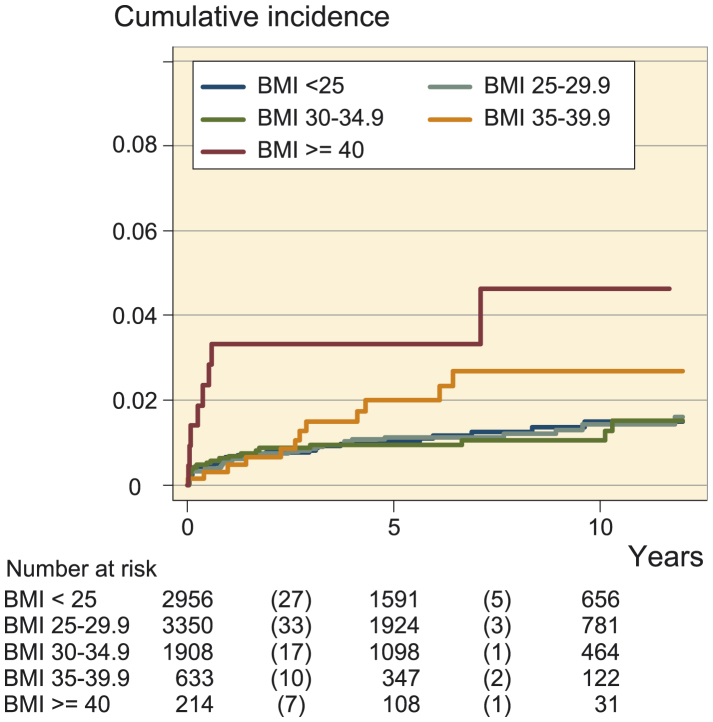
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (Figure 1) showed a similar cumulative incidence of infection in the normal-weight, overweight, and obese class-I categories, whereas the incidence increased in obese class-II patients, and was highest in obese class-III patients.
Figure 1.
Cumulative incidence of prosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty according to 5 categories of BMI.
Weight and prosthetic joint infection
The incidence rates were similar between patients with weight < 60 kg (1.3 cases/1,000 person-years), 60–79 kg (1.7 cases/1,000 person-years), and 80–99 kg (1.7 cases/1,000 person-years), but the incidence of prosthetic joint infection increased to 3.8 cases/1,000 person-years in the weight category 100–119 kg and to 9.4 cases/1,000 person-years in patients weighing ≥ 120 kg (Table 2). Weight ≥ 100 kg was associated with twice the infection rate (crude IRR = 2.6, 95% CI: 1.6–4.2; p < 0.001) compared to a weight of < 100 kg (Table 3). The effect was slightly attenuated after adjustment for age, sex, ASA score, diabetes, smoking status, etiology of OA, length of surgery, use of antibiotic-laden cement, and arthroplasty site (adjusted IRR = 2.1, 95% CI: 1.3–3.6; p = 0.003).
With only prosthetic joint infections originating from the surgical site (n = 68) as outcome, the unadjusted and adjusted IRRs for the weight threshold of 100 kg were 3.6 (95% CI: 2.1–6.3) and 3.4 (95% CI:1.8–6.2). With only prosthetic joint infections from all other sources including undetermined origin as outcome (n = 43), the unadjusted and adjusted IRRs were 1.2 (95% CI: 0.4–3.5) and 0.8 (95% CI: 0.3–2.5). Stratification according to arthroplasty site gave an adjusted IRR of 2.5 (95% CI: 1.3–4.9) after THA and of 1.9 (95% CI: 0.9-4.2) after TKA. Stratification according to sex revealed an adjusted IRR of 2.8 (95% CI: 1.2–6.5) for women and of 1.9 (95% CI: 1.03–3.7) for men.
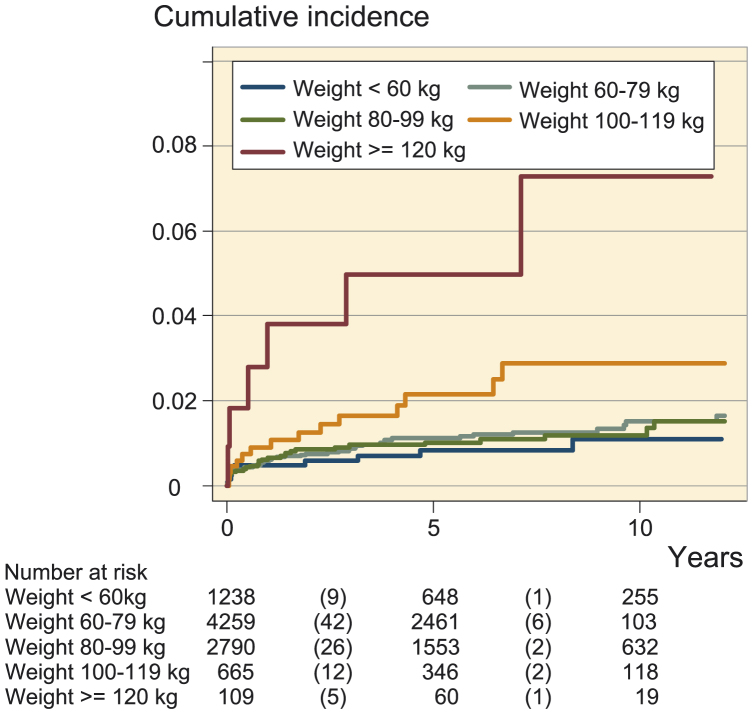
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (Figure 2) showed a similar cumulative incidence of infection in the weight categories < 60kg, 60–79 kg, and 80–99 kg, whereas the incidence increased in those weighing 100–119 kg and was highest in those weighing ≥ 120 kg. The difference in incidence of infection was observed already in the first months after surgery (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Cumulative incidence of prosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty according to 5 categories of body weight.
Figure 3.
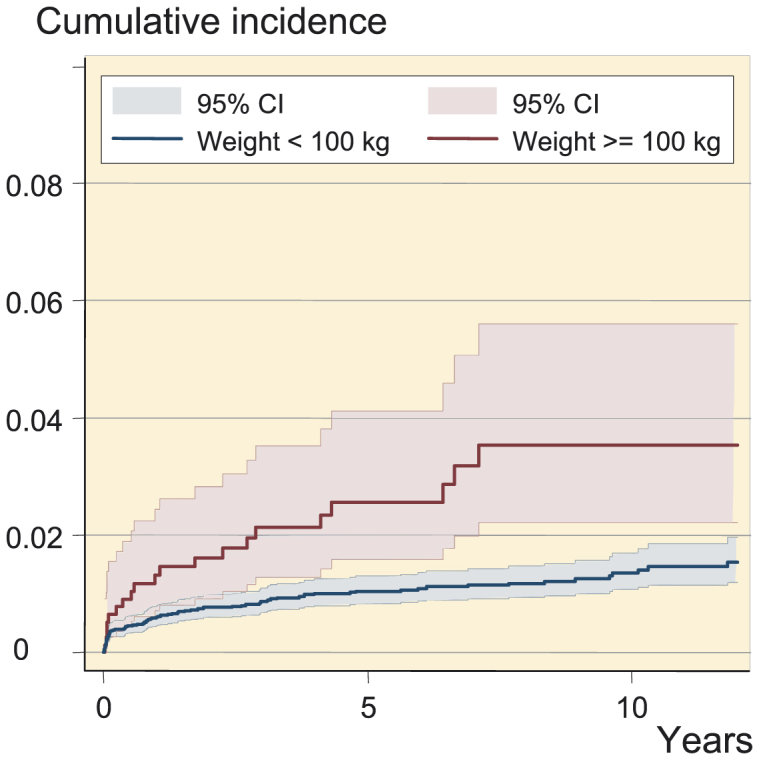
Cumulative incidence of prosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty according to 2 categories of body weight.
The organisms identified, sources of infection, and Gram stain according to the BMI and weight thresholds identified are presented in Table 4.
Table 4.
Breakdown of source of infection, type of organism, and Gram staining result according to BMI and weight thresholds
| BMI < 35 n = 8,214 | BMI ≥ 35 n = 847 | p-value | Weight < 100 kg n = 8,286 | Weight ≥ 100 kg n = 775 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 90 (81) | 21 (19) | 90 (81) | 21 (19) | ||
| Source of infection (%) a | ||||||
| Surgical site infection | 52 (58) | 16 (76) | 0.3 | 51 (57) | 17 (81) | 0.1 |
| Other sources b | 15 (17) | 1 (5) | 15 (17) | 1 (5) | ||
| Undetermined | 23 (25) | 4 (19) | 24 (26) | 3 (14) | ||
| Gram-positive (%) | 70 (78) | 14 (67) | 0.7 c | 68 (78) | 14 (67) | 0.2 c |
| MSSA | 21 (29) | 2 (14) | 19 (28) | 3 (21) | ||
| MRSA | 10 (13) | 3 (21) | 9 (13) | 3 (21) | ||
| MSCNS | 8 (12) | 0 (0) | 8 (12) | 0 (0) | ||
| MRCNS | 11 (16) | 3 (21) | 11 (16) | 3 (21) | ||
| Other | 20 (29) | 6 (43) | 21 (31) | 5 (36) | ||
| Gram-negative (%) | 14 (15) | 4 (19) | 11 (13) | 6 (28) | ||
| Gram-pos. & Gram-neg. (%) | 2 (2) | 1 (5) | 3 (3) | 0 (0) | ||
| Unknown Gram status (%) | 4 (5) | 2 (9) | 5 (6) | 1 (5) |
BMI: body mass index; MS: methicillin-sensitive; MR: methicillin-resistant; SA: Staphyloccoccus aureus; CNS: coagulase-negative staphylococcus.
In 27 cases, the source of infection could not be determined.
Other sources included: skin infection, urinary tract infection, gastrointestinal tract infection, endocarditis, -cholecystitis, and acute prostatitis.
Comparison of Gram-pos. and Gram-neg. infections. Simultaneous Gram-pos. and Gram-neg. infections and -infections of unknown Gram status were excluded.
Discussion
We found similar prosthetic joint infection rates in the categories normal-weight, overweight, and obese class-I, with a substantial increase thereafter, indicating that BMI ≥ 35 may be a useful threshold value. Similarly, no change in the rate of prosthetic joint infection was observed in the 3 weight categories up to 100 kg, but there was a substantial and exponential increase after that—starting in the immediate postoperative period. This indicates that 100 kg may be a useful weight threshold. Above these thresholds, more than twice the incidence rate of prosthetic joint infection was found in primary TJA patients treated with antibiotic prophylaxis that uniformly consisted of 1.5 g cefuroxime intravenously.
We are not aware of any study that has evaluated thresholds for BMI-adjusted (including all 3 WHO classes of obesity) and weight-adjusted dosage in the context of infection prevention after TJA. A number of studies have assessed the role of BMI in infection occurrence after hip and knee arthroplasty using a BMI of 30 (Haverkamp et al. 2011, Kerkhoffs et al. 2012), 35 (Namba et al. 2013), or 30–39 and 40 (Andrew et al. 2008, Dowsey and Choong 2008, Bordini et al. 2009) as cutoff. Only Chesney et al. (2008) reported prosthetic joint infections according to the 3 obesity classes. However, the number of infections was too small to be able to make any firm conclusions. All but 1 study (Bordini et al. 2009) found a higher infection risk with an effect estimate 2 to 4 times higher for obese patients than for non-obese patients (with a cutoff BMI of 30).
Namba et al. (2013) evaluated risk factors associated with prosthetic joint infection in 56,216 primary TKAs that were followed for a maximum of 105 months. The authors identified BMI ≥ 35 as an important risk factor, among others. Their HR and 95% CI comparing BMI ≥ 35 and BMI < 35 was lower (1.5, 95% CI: 1.2–1.9) and more precise than ours (2.1; 95% CI: 1.04–4.3), which was partly due to their larger sample size. In that study, the dosage of antibiotic prophylaxis with cefazolin was not specified, so it is not clear whether their somewhat lower effect estimate could be related to weight-based antibiotic prophylaxis with cefazolin, as indicated in a previous paper by the same authors (Namba et al. 2005).
The link between obesity and infection may be explained by several factors, but under-dosing of antibiotics is probably the most important to consider (Falagas and Karageorgopoulos 2010). Therapeutic under-dosing in obese patients has been reported for vancomycin (Bauer et al. 1998) and cefazolin (Forse et al. 1989, Brill et al. 2014). Data regarding cefuroxime, which is frequently used for infection prophylaxis during TJA, are limited to 1 study that evaluated soft tissue penetration of a single dose of 1.5 g cefuroxime intravenously in 6 highly obese patients undergoing abdominal surgery (Barbour et al. 2009). The authors suggested that “concentrations in the interstitial space fluid of soft tissues following a single 1.5-g dose may be high enough to prevent infections with Gram-positive organisms but may be insufficient to prevent infections with Gram-negative organisms”.
Other factors that may lead to a higher infection risk in obese patients include the thickness of the subcutaneous adipose tissue at the surgical site (Fujii et al. 2010) (predisposing to infection because of poorer perfusion and lower tissue oxygen tension), enhanced risk of hematoma, and higher tension in the wound leading to dehiscence (Wilson and Clark 2003). In addition, the sometimes technically more challenging intervention in obese patients can lead to soft tissue injuries and prolonged surgery. It has also been demonstrated that adipose tissue produces mediators that can influence the immune system and possibly impair its function (Marti et al. 2001). Finally, nasal Staphyloccocus aureus colonization, which is associated with a greater risk of surgical site infection (Kalmeijer et al. 2000), may be more frequent in obese patients.
Bratzler et al. (2013) recently stated, “Conclusive recommendations for weight-based dosing for antimicrobial prophylaxis in obese patients cannot be made because data demonstrating clinically relevant decreases in SSI rates from the use of such dosing strategies instead of standard doses in obese patients are not available in the published literature”, but our findings could be helpful in defining a dosing strategy for perioperative cefuroxime prophylaxis in TJA. Several authorities and expert groups have already suggested doubling the dose of cephalosporins in highly obese patients undergoing clean high-risk surgery, considering the favorable safety profile of this agent, the low cost, and the low risk of adverse effects (Anaya and Dellinger 2006, Falagas and Karageorgopoulos 2010, Alexander et al. 2011). Nevertheless, our understanding of the influence of obesity on antibiotic pharmacokinetics is still limited and many factors—such as lean body mass and altered adipose tissue blood flow—must be considered. Moreover, clinical studies are needed to evaluate the impact of the double-dosing strategy on prosthetic joint infection rates in highly obese patients.
In addition to the improvement of antibiotic dosage, the identification of BMI and weight thresholds may also facilitate comparison between studies, improve case-mix adjustment, and optimize preoperative preparation.
Our findings were obtained from a large prospective cohort of TJA patients, who were all treated with cefuroxime at the same dosage. We performed a time-to-event-analysis, adjusted for the main potential confounders, and tested the robustness of the results in sensitivity analyses. However, there were limitations. Firstly, our findings relate to the use of cefuroxime and may not be applicable to patients receiving a different antibiotic. Secondly, prosthetic joint infection is a serious complication requiring treatment in a hospital. As our institution is the only public hospital in the area, the proportion of patients living in the area but seeking treatment elsewhere in the case of prosthetic joint infection is very low. Nevertheless, we may still have missed a few infections. However, the missing information can be expected to be unrelated to BMI. Thirdly, there was no information available on serum/tissue concentrations of cefuroxime, and as a consequence we cannot directly relate antibiotic concentrations to BMI/weight and to prosthetic joint infection. However, there is a growing body of literature to suggest that there may be an element of under-dosing in the pathogenesis of surgical site infections (Forse et al. 1989, Barbour et al. 2009, Janson and Thursky 2012, Brill et al. 2014). Fourthly, adequate antibiotic prophylaxis timing and re-dosing are important, but this information was not systematically available. Even so, it appears unlikely that timing of antibiotic prophylaxis may depend on BMI or weight. Moreover, concerning re-dosing, the number of patients with an intervention exceeding 180 min was low and did not vary according to BMI. Finally, information on nasal S. aureus colonization was not available.
In conclusion, after primary TJA more than double the rate of prosthetic joint infection was found in patients with a BMI of ≥ 35 and in those weighing ≥ 100 kg. Infection rates were similar in the BMI and weight categories below those thresholds. Given the multifactorial relationship between obesity and infection, the identification of differences according to the severity of obesity may help to better target preventive interventions. One of these might be a weight-based dosage adaptation for the antibiotic prophylaxis with cefuroxime, consisting of doubling of dosage with a weight of 100 kg or greater. Whether or not the higher prophylactic single-shot dose would ultimately reduce the risk of infection in obese patients undergoing TJA remains to be determined.
We thank all the orthopedic surgeons at the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology who have provided information to the registry since 1996, and also Carole Bandi, Lamia Blatter-Sellak, Flavia Renevey, and Christophe Baréa for their invaluable help with data management and data entry for this study.
The Division of Orthopaedic Surgery received financial institutional support from the “Fondation pour la Recherche Ostéo-articulaire” for the Geneva Arthroplasty Registry. The source of funding had no role in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data, in the preparation of the manuscript, and in its submission for publication.
No competing interests declared.
AL: study design, data collection, statistical analyses, interpretation of data, and writing and revision of the manuscript. MZ: literature review, data collection, statistical analysis, interpretation of data, and writing of the manuscript. DV, HHM, PC, and IU: data collection. SH: literature review, interpretation of data, and manuscript revision. PH: data collection and interpretation of data.
References
- Alexander J W, Solomkin J S, Edwards M J.. Updated recommendations for control of surgical site infections. Ann Surg 2011; 253(6): 1082–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anaya D A, Dellinger E P.. The obese surgical patient: a susceptible host for infection. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2006; 7(5): 473–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew J G, Palan J, Kurup H V, Gibson P, Murray D W, Beard D J.. Obesity in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2008; 90(4): 424–429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A, Schmidt S, Rout W R, Ben-David K, Burkhardt O, Derendorf H.. Soft tissue penetration of cefuroxime determined by clinical microdialysis in morbidly obese patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2009; 34(3): 231–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer L A, Black D J, Lill J S.. Vancomycin dosing in morbidly obese patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1998; 54(8): 621–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordini B, Stea S, Cremonini S, Viceconti M, De Palma R, Toni A.. Relationship between obesity and early failure of total knee prostheses. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2009; 10: 29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratzler D W, Dellinger E P, Olsen K M, Perl T M, Auwaerter P G, Bolon M K, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2013; 70(3): 195–283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill M J, Houwink A P, Schmidt S, Van Dongen E P, Hazebroek E J, van Ramshorst B, et al. Reduced subcutaneous tissue distribution of cefazolin in morbidly obese versus non-obese patients determined using clinical microdialysis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2014; 69(3): 715–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney D, Sales J, Elton R, Brenkel I J.. Infection after knee arthroplasty a prospective study of 1509 cases. J Arthroplasty 2008; 23(3): 355–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowsey M M, Choong P F.. Obesity is a major risk factor for prosthetic infection after primary hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2008; 466(1): 153–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falagas M E, Karageorgopoulos D E.. Adjustment of dosing of antimicrobial agents for bodyweight in adults. Lancet 2010; 375(9710): 248–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forse R A, Karam B, MacLean L D, Christou N V.. Antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery in morbidly obese patients. Surgery 1989; 106(4): 750–6; discussion 756-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T, Tsutsumi S, Matsumoto A, Fukasawa T, Tabe Y, Yajima R, et al. Thickness of subcutaneous fat as a strong risk factor for wound infections in elective colorectal surgery: impact of prediction using preoperative CT. Dig Surg 2010; 27(4): 331–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkamp D, Klinkenbijl M N, Somford M P, Albers G H, van der Vis H M.. Obesity in total hip arthroplasty–does it really matter? A meta-analysis. Acta Orthop 2011; 82(4): 417–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson B, Thursky K.. Dosing of antibiotics in obesity. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2012; 25(6): 634–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmeijer M D, van Nieuwland-Bollen E, Bogaers-Hofman D, de Baere G A.. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus is a major risk factor for surgical-site infections in orthopedic surgery. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2000; 21(5): 319–323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoffs G M, Servien E, Dunn W, Dahm D, Bramer J A, Haverkamp D.. The influence of obesity on the complication rate and outcome of total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis and systematic literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2012; 94(20): 1839–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbeke A, Garavaglia G, Barea C, Hoffmeyer P.. Why do we need hospital-based registries? The Geneva Hip Arthroplasty Registry. Zürich, EFORT; 2010: 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Marti A, Marcos A, Martinez J A.. Obesity and immune function relationships. Obes Rev 2001; 2(2): 131–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba R S, Paxton L, Fithian D C, Stone M L.. Obesity and perioperative morbidity in total hip and total knee arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplasty 2005; 20(7 Suppl 3): 46–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba R S, Inacio M C, Paxton E W.. Risk factors associated with deep surgical site infections after primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 56,216 knees. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2013; 95(9): 775–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmon D R, Berbari E F, Berendt A R, Lew D, Zimmerli W, Steckelberg J M, et al. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 56(1): 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvizi J, Gehrke T, Chen A F.. Proceedings of the International Consensus on Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Bone Joint J 2013; 95-B(11): 1450–1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 1995; 854: 1–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J A, Clark J J.. Obesity: impediment to wound healing. Crit Care Nurs Q 2003; 26(2): 119–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]