Abstract
Hydatid disease continues to be a significant health problem in many parts of the world. It can occur in any part of the body, but liver is the commonest site of involvement. The disease may remain asymptomatic for years. Symptoms occur due to compression of local structures or complications like rupture and infection. The diagnosis is clear when typical radiological appearance is observed at the common sites of involvement. Complications give rise to atypical appearances. These coupled with unusual localizations pose diagnostic difficulty. The aim of this pictorial essay is to demonstrate the atypical manifestations of hydatid cysts – atypical either due to complications or the unusual site.
Keywords: Endocyst, hydatid cyst, liver, lung, pericyst
Introduction
Hydatid cyst is commonly caused by the larval stage of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. The life cycle of the worm involves two hosts. The definitive host is a dog and rarely some other carnivore. The adult worm lives in the proximal small bowel of the definitive host. Its ova are passed in the feces of the infected animal. Sheep ingests the ova by grazing on the contaminated grass and is the usual intermediate host. The humans get infected by contact with the dog or by ingestion of contaminated water and vegetables.[1] The ovum releases the larva called oncosphere in the duodenum, which enters the portal circulation by passing through the intestinal wall. Thus, it reaches the liver where it grows into a cyst.
The hydatid cyst has three layers: (i) The outer pericyst which consists of modified host cells that form a dense fibrous protective layer; (ii) the middle laminated layer which is acellular and impervious to bacteria, but allows the passage of nutrients; and (iii) the inner germinal layer where the scolices and laminated membrane are produced [Figure 1]. The middle laminated layer and the germinal layer form the true wall of the cyst and are usually referred to as the endocyst.[2] The thickness of these layers depends on the tissue in which the cyst is present. The layers tend to be thick in the liver, are less developed in muscle, and are absent in bone.[3]
Figure 1.
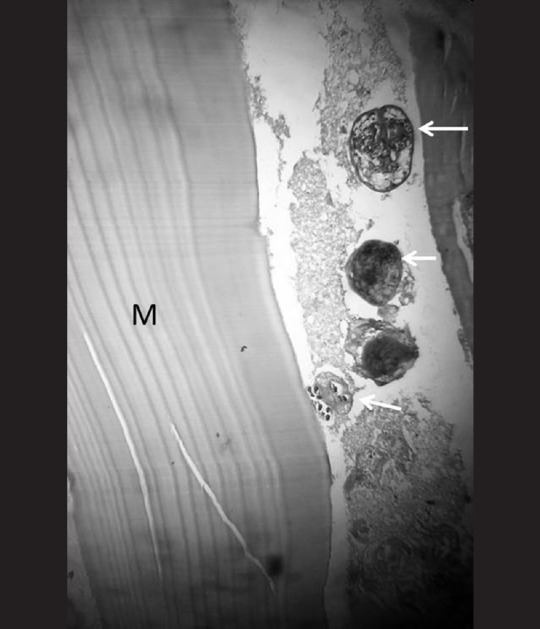
Hematoxylin and eosin stained section showing the wall of resected hepatic hydatid cyst. White arrows indicate daughter cysts with scolices. M = Middle laminated acellular layer
Hydatid disease involves the liver in approximately 75% of the cases, the lung in 15% of the cases, and other anatomic locations in 10% of the cases.[1] Based on the radiological appearance, hydatid cysts are classified into four types:
Type I- Simple cyst with no internal architecture with or without hydatid sand or septae
-
Type II- Cysts with daughter cysts and matrix
- IIa- Round daughter cysts arranged at the periphery
- IIb- Irregularly shaped daughter cysts occupying the entire mother cyst
- IIc- High attenuation oval or round mass with scattered calcification and occasional daughter cysts
Type III- Dead cyst with total calcification
Type IV- Complicated cyst with rupture and superinfection.[4]
Sites of Involvement
Liver
Ultrasound is the screening method of choice for hepatic hydatid cyst. Computed tomography (CT) has high sensitivity and specificity and is an important diagnostic tool to recognize complications.[3] A hydatid cyst is typically seen as a round or ovoid lesion with type I or II appearance [Figure 2]. It has water density and a high attenuation wall on unenhanced CT. Enhancement of the septae or cyst wall may be seen following contrast injection. There may be partial calcification of the cyst wall or internal matrix. This does not indicate death of the parasite. Later, dense complete calcification may occur and such a cyst is assumed to be inactive.[5] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the best modality to demonstrate the cystic component and biliary tree involvement. The cystic part is hypointense on T1-weighted images and markedly hyperintense on T2-weighted images. Presence of hypointense rim on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images is considered a characteristic sign of hydatid cyst.[6] It probably represents pericyst which is rich in collagen. Daughter cysts are seen as cystic structures which are hypointense relative to the intracystic fluid on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2 images. Irregularity of the cyst wall represents incipient detachment of the membranes.
Figure 2.
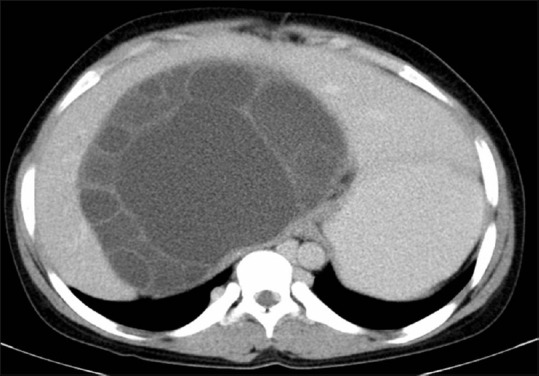
Type II hepatic hydatid cyst. CT scan shows a large fluid attenuation mass in the right and caudate lobe. Irregular shaped daughter cysts occupy almost the entire mother cyst
Complications of hepatic hydatid cyst are: (a) Infection, (b) rupture, (c) exophytic growth, and (d) portal vein involvement.
(a) Infection manifests on CT as hypodense mass with typical enhancing rim like any other hepatic abscess. Gas or air-fluid level may also be seen.
(b) Three types of cyst rupture have been described: Contained, communicating, or direct.[7]
Contained- Endocyst ruptures, but the pericyst remains intact. Detached endocyst is seen as serpentine linear membranes within the cyst. When there is complete detachment, crumpled endocyst floats freely in the cyst fluid, giving rise to the “water lily sign.”
Communicating- Passage of cyst contents into the biliary radicles that have been incorporated into the pericyst.
Direct- Spillage of hydatid material into the peritoneal or pleural cavity, abdominal wall, hollow viscera, etc.
Communicating rupture is indicated by direct and indirect signs. Direct sign is visible communication between the cyst and the biliary tree [Figure 3]. Indirect signs include deformity of the cyst indicated by loss of smooth round or oval shape, defect in the wall, and presence of beak-like projection extending from the cyst wall.[8] Intraductal areas of low signal intensity due to cyst material may also be seen on MRI.
Figure 3 (A-C).
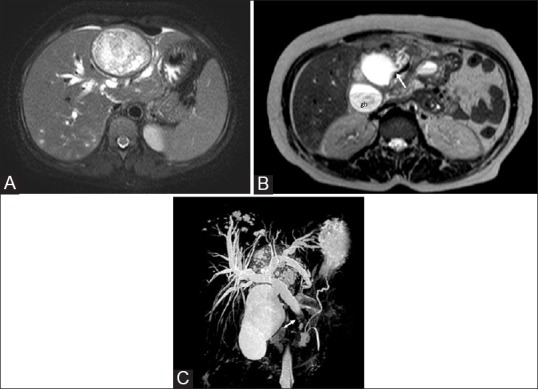
Hepatic hydatid cyst with biliary communication in a middle-aged female who presented with obstructive jaundice. (A) Axial T2W image shows a type II cyst seen as heterogeneous hyperintense mass with few daughter cysts in the left lobe of the liver. An intact dark rim of pericyst is seen. Intrahepatic biliary dilatation and small developing cysts in the posterior part of the right lobe are also seen (B) Axial T2W image through the inferior part of liver reveals cystobiliary communication (arrow), irregularity of cyst outline, and loss of dark rim (C) Coronal thick slab MR cholangiopancreatogram shows dilated intahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts with hypointense filling defect (arrow) due to hydatid material in the distal common bile duct. Gb = Gall bladder
Presence of fatty material, air-fluid level, and fat-fluid level in the hydatid cyst also suggests communication with biliary tree.[9] The fat is thought to arise from the lipid content of the bile [Figure 4].
Figure 4.
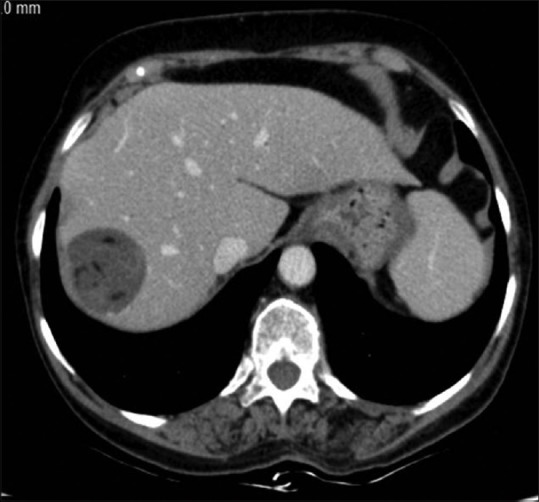
Lipid material in type II hepatic hydatid cyst. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image through the superior part of the liver shows well-defined cyst in the right lobe with fat attenuation areas within suggestive of biliary communication
(c) Complications may also arise due to exophytic growth of cyst. The most common routes are the bare area of liver and the gastrohepatic ligament. Involvement of diaphragm [Figure 5] and thoracic cavity may result. CT scan may reveal adherence to diaphragm, thickening and lobulation of cysts, rupture into the pleural cavity or pulmonary parenchyma, and chronic pleural fistula.[2]
Figure 5 (A and B).
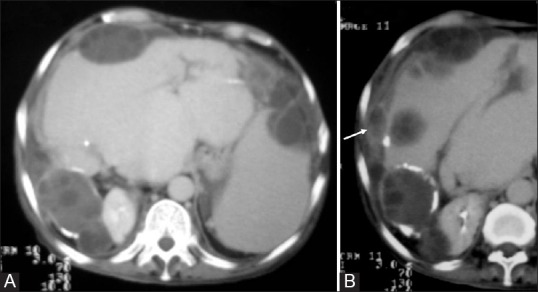
Disseminated abdominal hydatidosis. (A) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows multiple type II exophytic hydatid cysts in the liver. The posterior cyst shows calcification. Peritoneal hydatid with secondary splenic involvement is also evident (B) Diaphragm is thickened and shows areas of fluid attenuation (arrow)
(d) Portal vein involvement is very rare. It is due to compression by the cyst followed by thrombosis and cavernoma formation.
Spleen
Splenic hydatidosis is the third most common after the liver and lungs.[10] It is usually secondary to systemic dissemination or due to intraperitoneal spread from the ruptured hepatic hydatid cyst. The imaging characteristics are similar to those of hepatic cysts [Figure 6]. Identification of daughter cysts and detached floating membranes if present helps in the diagnosis. The differential diagnosis includes epidermoid cyst, pseudocyst, and lymphangioma.[11] Epidermoid is seen as a unilocular fluid attenuation mass with imperceptible walls. History of trauma and presence of thick calcified wall are suggestive of post-traumatic pseudocyst. Lymphangioma presents as an area of low attenuation that does not enhance. T1-weighted images may show high signal intensity if hemorrhage has occurred.
Figure 6.
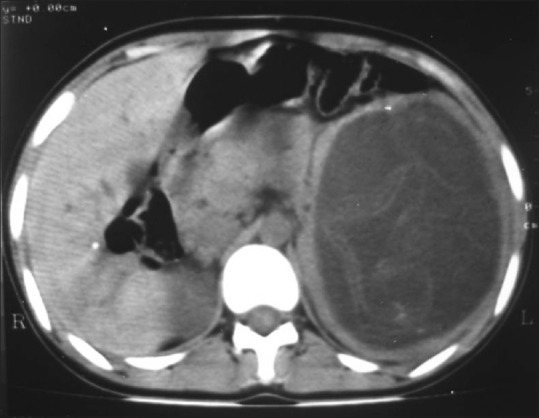
Splenic hydatid cyst. Axial unenhanced CT scan demonstrates replacement of the entire spleen by a cyst which shows linear tortuous structures within suggestive of ruptured endocyst. Speck of calcification is also seen in the anterior wall
Peritoneum
Peritoneal hydatid cysts are almost always secondary to hepatic hydatidosis. These are generally multiple and can occur anywhere in the peritoneal cavity. Presence of hepatic hydatid, multiple lesions in the peritoneum, and characteristic appearance of daughter cysts allow the diagnosis [Figure 7]. However, unilocular type I cysts are difficult to differentiate from mesenteric cyst and intestinal duplication cyst.[3]
Figure 7.
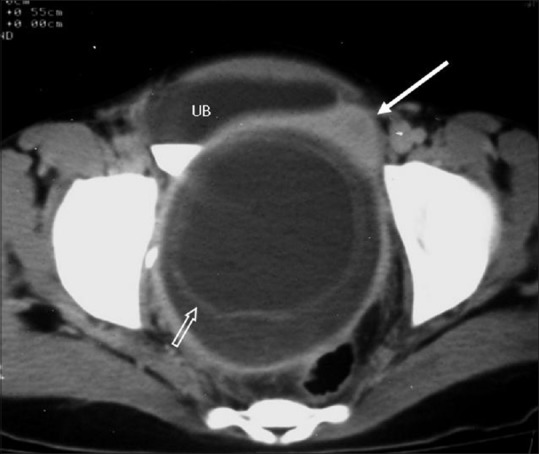
Peritoneal hydatid in a 12-year-old girl who presented with frequent micturition. Contrast-enhanced CT image shows a large cyst in the pelvis with a double-ring appearance due to detached endocyst (open arrow). Uterus is displaced to the left and anteriorly (white arrow). UB = Urinary bladder
Retroperitoneum
Retroperitoneal hydatid is rare, usually secondary to involvement of other organs, especially liver. The infection reaches the retroperitoneum by spontaneous rupture or by inoculation during surgery.[3] Visualization of daughter cysts helps in the diagnosis.[3] However, other appearances like unilocular cyst, cyst with detached membranes, partially or totally calcified cyst may be seen [Figure 8]. This needs to be differentiated from lymphangioma which appears as a large, thin-walled cystic mass that may involve more than one compartment of retroperitoneum. Other entities like mucinous cystadenoma, cystic teratoma, and pseudocyst can be differentiated based on age and other findings in the abdomen.
Figure 8 (A and B).
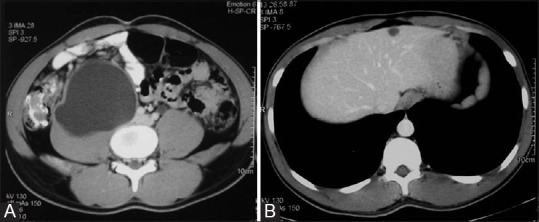
Retroperitoneal hydatid. (A) Contrast-enhanced CT scan of a 22-year-old man shows a unilocular cyst (type I) in the retroperitoneum abutting the right psoas muscle (B) Concomitant hepatic hydatid cyst is seen
Lung
Lung is the second most common site of involvement. Hydatid cyst can grow very large due to compressibility of lungs. It initially develops as type I cyst which may be round or oval. Daughter cysts are rarely seen. Erosion of the bronchiole included in the pericyst results in air between endocyst and pericyst, giving rise to the “crescent or meniscus sign.” Presence of crescent-like rim of air in the posterior part of cyst is sometimes seen and is termed the “inverse crescent sign.”[12] With continued leak, two layers may separate. The cyst shrinks and ruptures allowing the passage of air into the endocyst. An air-fluid level in the endocyst with air between the endocyst and pericyst constitute “the cumbo sign.” Air-fluid level with collapsed floating membranes can be seen inside the cyst – “water lily sign” [Figure 9]. All of the liquid content may be expelled to the bronchial tree – “dry cyst sign.”[13] Other complications of lung hydatid are secondary infection, rupture into lung parenchyma leading to consolidation, rupture into pleural cavity, and very rarely, pulmonary embolism.[3] In the absence of typical features, necrotic lung mass, metastasis, and intraparenhymal bronchogenic cyst should always be included in the differential diagnosis.
Figure 9 (A and B).
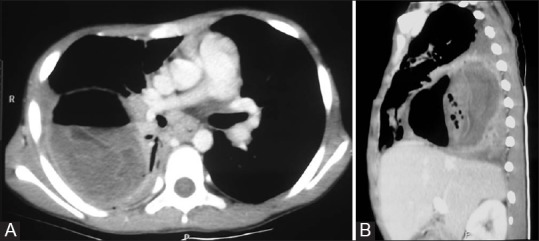
Ruptured lung hydatid. (A) Axial and (B) sagittal contrast-enhanced CT images of the thorax reveal a ruptured type IV hydatid cyst in the lower lobe of the right lung with water lily sign created by crumpled endocyst floating in the dependent part
Bone
Bone involvement is seen in 0.5-4% of cases.[14] Spine, pelvis, femur, tibia, humerus, skull, and ribs are the frequent sites involved.[14] Due to lack of pericyst formation, aggressive proliferation causes replacement of medulla, cortical destruction, and extension into soft tissues. Extraosseous cysts may calcify. The radiological appearance consists of areas of osteolysis with expansion, thinning, and destruction of cortex and extension into soft tissues [Figures 10–12]. Complications include deformity, pathological fracture, secondary infection, neurological deficit, compression of adjacent structures, and transarticular extension.[15]
Figure 10.
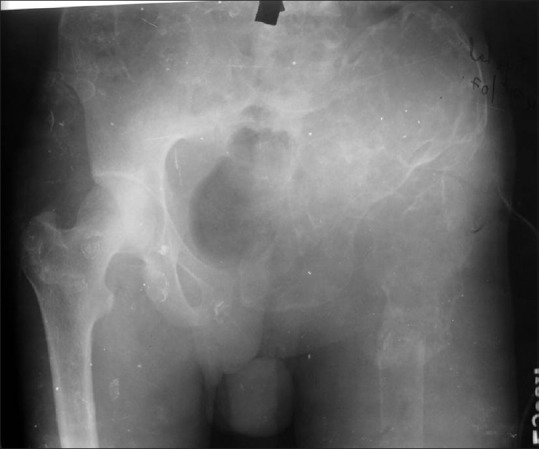
Radiograph of pelvis shows multiloculated, lytic lesion of left hemipelvis. Femoral head and proximal shaft are also involved with a pathological fracture of the shaft
Figure 12 (A and B).
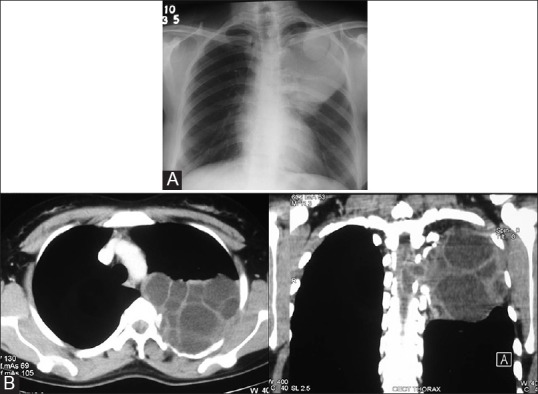
Costal echinococcosis with intraspinal extension in a 22-year-old female who presented with numbness of left lower limb. (A) Chest radiograph shows a homogenous opacity in the upper part of left hemithorax. A round, well-defined opacity is seen in its upper part. Erosion of posterior parts of fourth and fifth ribs is seen (B) CT images in the axial and coronal plane reveal a multiloculated cystic mass in the posterior left hemithorax with erosion of adjacent rib and extension into the spinal canal
Figure 11 (A and B).
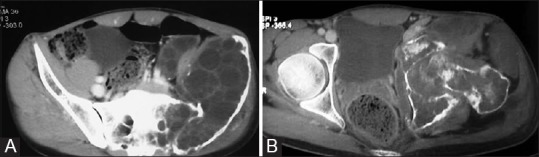
CT images of bone hydatid. (A) There is expansion of left iliac bone with destruction of anteromedial cortex by a multiloculated cystic mass. Transarticular extension to sacrum is also seen (B) Involvement of ischium, pubis, hip joint, and proximal femur is evident with extension into the adjacent muscles
Muscle
Skeletal muscle is a rare site as it does not favor the growth of hydatid cyst because of its contractility and high lactic acid level.[16] Muscles of the neck, trunk, thigh, or upper extremities and around the hip are generally involved, but any part can be involved.[15] Ultrasound done as part of initial workup of suspected soft tissue lesion may reveal findings typical of hydatid cyst. These vary from unilocular cyst to cyst with daughter vesicles, detached membranes, and water lily sign [Figures 13 and 14]. CT is helpful in the detection of osseous extension and cyst wall calcification.[17] Complicated cysts may simulate abscess, hematoma, metastases, or soft tissue tumors like myxoid liposarcoma. CT and MRI show rim enhancement in an abscess and variable enhancement in metastases and soft tissue tumors. Blood products are seen in hematoma on MRI.
Figure 13.
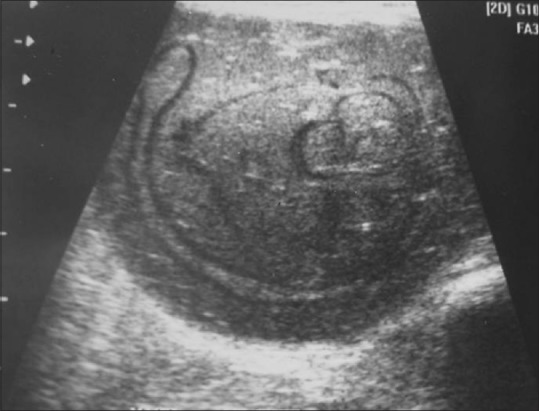
Ultrasound image of a 22-year-old female shows a type IV hydatid cyst in the thigh muscle. A well-defined hypoechoic mass with posterior enhancement and separated membranes within is seen
Figure 14.
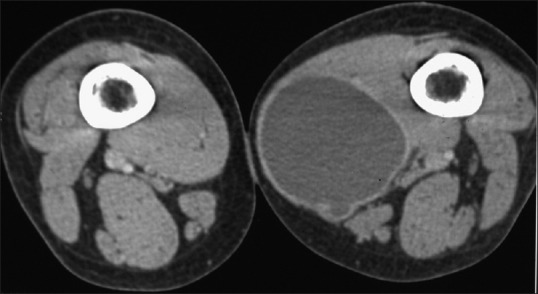
Contrast-enhanced CT image shows a non-enhancing hypodense mass in the adductor magnus. A daughter cyst is seen the posterior part
Brain
Involvement of brain is extremely rare. Hydatid cyst is mostly located in the middle cerebral arterial territory.[3] On CT scan, it is seen as unilocular cyst with attenuation similar to the cerebrospinal fluid [Figure 15]. Fine peripheral enhancement may be seen. Edema is absent. There may be erosion of adjacent calvarium. Atypical findings include edema, irregularity of cyst wall, multiple locules, heterogeneity of cyst content, and calcification.[4]
Figure 15 (A and B).
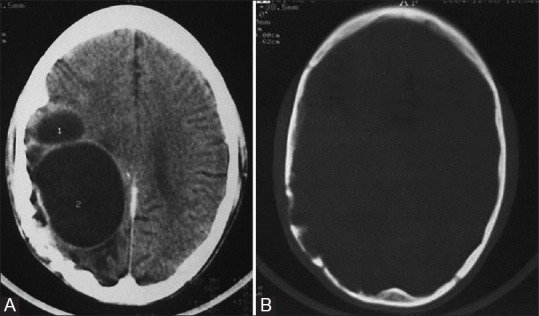
Recurrent hydatid cyst of brain. Contrast-enhanced CT images show (A) multiloculated hypodense mass with attenuation similar to cerebrospinal fluid in the right parietal lobe; minimal perilesional edema is also seen and (B) erosion of inner table of skull
Breast
Breast hydatid cyst is very rare. Diagnosis is difficult unless ultrasound reveals membranes or fluid level due to debris in the cyst [Figure 16]. Ring-shaped structures within a dense, well-circumscribed lesion on mammography are also suggestive of hydatid.[18] Presence of hydatid cysts in other organs adds to the diagnostic confidence.
Figure 16 (A and B).
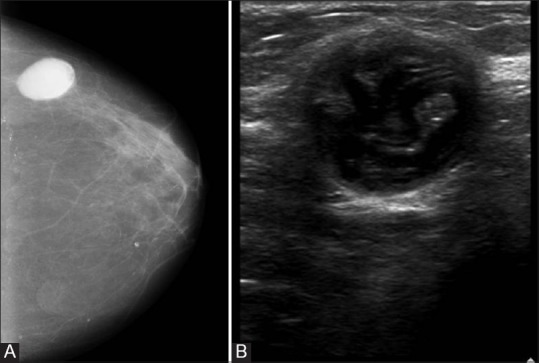
Breast hydatid. (A) Mammogram of right breast shows a smooth, well-circumscribed mass in the outer quadrant. An arc-like differential density is noted within (B) Sonogram reveals a well-defined cystic mass with curvilinear structures suggestive of hydatid membranes
Hydatid cyst can occur in other anatomic sites also. These include the heart, pericardium, orbit, mediastinum, kidney, adrenal glands, and subcutaneous space. Involvement of kidney is seen in about 3% and that of orbit in less than 1% of cases.[3] It is even rarer in other locations. Imaging appearances are similar to those described for other organs. The orbital hydatid is typically unilocular, may be extra or intraconal.[19] Thus, hydatid cyst should be included in the differential diagnosis of cystic masses of a specific organ, even when the typical appearance of cyst with multiple daughter cysts is not seen. This is particularly important if the patient belongs to an endemic region and has cystic lesions in the liver or lung.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Beggs I. The radiology of hydatid disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985;145:639–48. doi: 10.2214/ajr.145.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pedrosa I, Saiz A, Arrozola I, Ferreirós J, Pedrosa CS. Hydatid disease: Radiologic and pathologic features and complications. Radiographics. 2000;20:795–817. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.20.3.g00ma06795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Polat P, Kantarci M, Alper F, Suma S, Koruyucu MB, Okur A. Hydatid disease from head to toe. Radiographics. 2003;23:475–94. doi: 10.1148/rg.232025704. quiz 536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.von Sinner W, te Strake L, Clark D, Sharif H. MR imaging of hydatid disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157:741–5. doi: 10.2214/ajr.157.4.1892028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shah DS, Parikh H, Shah B, Bhanuprakash S, Shah J. Imaging appearances of hydatid cyst. Ind J Radiol Imag. 2006;4:533–5. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marani SA, Canossi GC, Nicoli FA, Alberti GP, Monni SG, Casolo PM. Hydatid disease: MR imaging study. Radiology. 1990;175:701–6. doi: 10.1148/radiology.175.3.2343117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marti-Bonmati L, Menor Serrano F. Complications of hepatic hydatid cysts: Ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance diagnosis. Gastrointest Radiol. 1990;15:119–25. doi: 10.1007/BF01888753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Erden A, Ormeci N, Fitoz S, Erden I, Tanju S, Genç Y. Intrabiliary rupture of hepatic hydatid cysts: Diagnostic accuracy of MR Cholangiopancreatography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:W84–9. doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.2068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mendez Montero JV, Arrazola Garcia J, Lopez Lafuente J, Antela Lopez J, Mendez Fernandez R, Saiz Ayala A. Fat-fluid level in hepatic hydatid cyst: A new sign of rupture into the biliary tree? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167:91–4. doi: 10.2214/ajr.167.1.8659428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ilica AT, Kocaoglu M, Zeybek N, Guven S, Adaletli I, Basgul A, et al. Extrahepatic abdominal hydatid disease caused by Echinococcus granulosus: Imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:337–43. doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.2255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Urrutia M, Mergo PJ, Ros LH, Torres GM, Ros PR. Cystic masses of the spleen: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1996;16:107–29. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.16.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koul PA, Koul AN, Wahid A, Mir FA. CT in pulmonary hydatid disease: Unusual appearances. Chest. 2000;118:1645–7. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.6.1645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Erdem CZ, Erdem LO. Radiological characteristics of pulmonary hydatid disease in children: Less common radiological appearances. Eur J Radiol. 2003;45:123–8. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(02)00054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Torricelli P, Martinelli C, Biagini R, Ruggieri P, De Cristofaro R. Radiographic and computed tomographic findings in hydatid disease of bone. Skeletal Radiol. 1990;19:435–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00241799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Belzunegui J, Maíz O, López L, Plazaola I, González C, Figueroa M. Hydatid disease of bone with adjacent joint involvement. A radiological follow-up of 12 years. Br J Rheumatol. 1997;36:133–5. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guthrie JA, Lawton JO, Chalmers AG. Case report: The MR appearances of primary intramuscular hydatid disease. Clin Radiol. 1996;51:377–9. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(96)80122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kerimoglu U, Kapicioglu S, Emlik D, Arazi M, Ural O. Case 161: Hydatid disease with water lily sign manifesting as a soft-tissue mass in the calf of a child. Radiology. 2010;256:1007–10. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10081066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vega A, Ortega E, Cavada E, Garijo F. Hy datid cyst of the breast: Mammographic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162:825–6. doi: 10.2214/ajr.162.4.8140999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Turgut AT, Turgut M, Koºar U. Hydatidosis of the orbit in Turkey: Results from review of the literature 1963-2001. Int Ophthalmol. 2004;25:193–200. doi: 10.1007/s10792-004-6739-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


