Abstract
The study was designed to investigate whether endogenous sulfur dioxide (SO2) plays a role in vascular calcification (VC) in rats and its possible mechanisms. In vivo medial vascular calcification was induced in rats by vitamin D3 and nicotine for four weeks. In vitro calcification of cultured A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) was induced by calcifying media containing 5 mmol/L CaCl2. Aortic smooth muscle (SM) α-actin, runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and Smad expression was measured. VC rats showed dispersed calcified nodules among the elastic fibers in calcified aorta with increased aortic calcium content and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. SM α-actin was markedly decreased, but the osteochondrogenic marker Runx2 concomitantly increased and TGF-β/Smad signaling was activated, in association with the downregulated SO2/aspartate aminotransferase (AAT) pathway. However, SO2 supplementation successfully ameliorated vascular calcification, and increased SM α-actin expression, but inhibited Runx2 and TGF-β/Smad expression. In calcified A7r5 VSMCs, the endogenous SO2/AAT pathway was significantly downregulated. SO2 treatment reduced the calcium deposits, calcium content, ALP activity and Runx2 expression and downregulated the TGF-β/Smad pathway in A7r5 cells but increased SM α-actin expression. In brief, SO2 significantly ameliorated vascular calcification in association with downregulation of the TGF-β/Smad pathway.
Keywords: sulfur dioxide, vascular calcification, smooth muscle cell, transforming growth factor-β
1. Introduction
Vascular calcification (VC) is a common complication of aging, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes and chronic kidney disease. It is closely associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality and is an important risk factor for many cardiovascular diseases [1,2]. Recently, studies have shown that vascular calcification is a cell-mediated and highly regulated process similar to osteogenesis [3]. And it is the key point that vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) lose the expression of smooth-muscle lineage markers and express osteogenic markers [3].
As important vascular cells, VSMCs retain multi-potential capability. Under the influence of many factors, VSMCs can lose the expression of smooth-muscle lineage markers and transform into osteo-/chondrocytic-like cells, form matrix vesicle, and express the osteoblast related proteins. Then, the process of mineralization is activated [4]. Several molecules facilitate osteochondrogenic transition of VSMCs and vascular calcification, including Runx2/Cbfa1, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), Msx2, osterix, and Sox9, etc. Recent studies have shown that microRNA regulates several key checkpoints in the cellular processes involved in the process of VSMC phenotype transformation [4,5,6,7]. These findings suggest that the mechanism for VSMC trans-differentiation during the pathogenesis of vascular calcification is a complex multifactorial and tightly regulated process, and possibly related to the regulation of genes, molecules, and signaling pathways. However, the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms for vascular calcification are still not fully understood.
Endogenous sulfur dioxide (SO2) can be produced during the metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids. Aspartate aminotransferase (AAT) is considered to be a key enzyme during SO2 generation [8]. SO2 has many physiological functions such as regulating blood pressure, vasorelaxation and regulation on cardiac function [8,9,10,11,12]. SO2 also plays an important role in many pathophysiological processes of various vascular diseases including hypertension and pulmonary arterial hypertension [13,14]. Previously, our research team found that SO2 had regulatory effects on vascular remodeling [10], via the inhibition of vascular VSMC proliferation [13]. We found that SO2 exerted a negative regulation of VSMC proliferation by suppressing the Erk/MAPK pathway mediated by cAMP/PKA signaling [15]. Consequently, we speculated that SO2 might participate in the regulation of vascular calcification process.
Therefore, in the present study, we used in vivo and in vitro experiments to investigate if SO2 was involved in the regulation of vascular calcification and the possible underlying mechanisms.
2. Results
2.1. Establishment of the Rat Vascular Calcification Rat Model
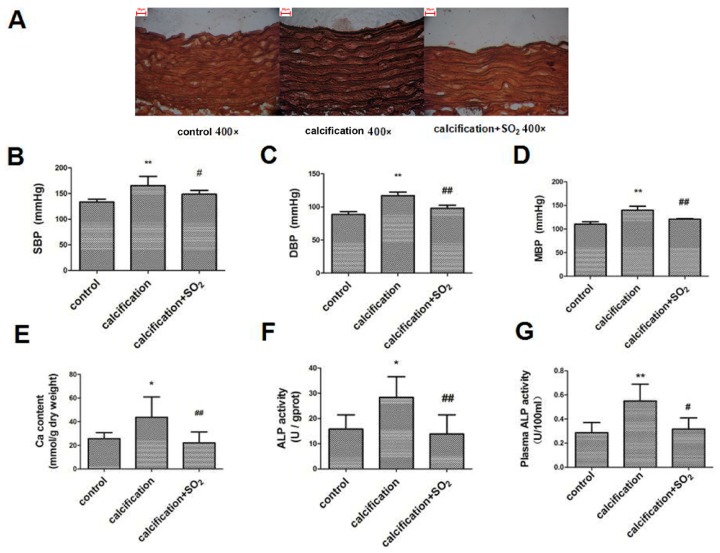
Von Kossa staining showed dispersed calcified nodules among the elastic fibers in calcified aortas but not in control aortas (Figure 1A). Compared with control group, SBP, DBP and MBP in calcification group were significantly increased (p < 0.01, p < 0.01 and p < 0.01) (Figure 1B–D) and the aortic calcium content was markedly increased (p < 0.05) (Figure 1E). In addition, the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in both aorta and plasma was increased (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05) (Figure 1F,G).
Figure 1.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) prevents vascular calcification in vivo. (A) Von Kossa staining of rat thoracic aorta. In the calcification group, there were dispersed calcified nodules among the elastic fibers. In the calcification + SO2 group, Von Kossa staining showed dispersed calcified nodules among the elastic fibers disappeared. Scale bar, 20 μm; (B–D) Measurement of hemodynamics; (B) systolic blood pressure (SBP); (C) diastolic blood pressure (DBP); (D) mean blood pressure (MBP); (E) Quantification of calcium content of rat thoracic aortic tissue; (F) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity of rat thoracic aortic tissue; (G) Plasma ALP activity. ** p < 0.01 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification; ## p < 0.01 vs. calcification (n = 10 per group).
2.2. The SO2/AAT Pathway Is Downregulated in Calcified Arteries
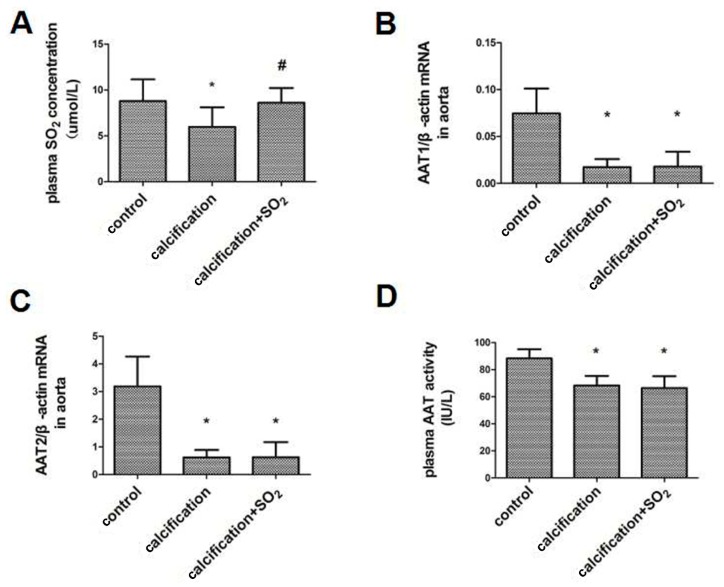
The plasma SO2 content was lower in the calcification group than in control group (p < 0.05) (Figure 2A). RT-PCR analysis revealed a reduced expression of AAT1 and AAT2 mRNAs, key enzymes for SO2 production, in the calcified aortas compared to the controls (p < 0.05, p < 0.05) (Figure 2B,C). Moreover, AAT activity in the plasma was decreased in the calcification model (p < 0.05) (Figure 2D). Thus, the endogenous SO2/AAT pathway was downregulated in calcified arteries.
Figure 2.
Endogenous SO2/aspartate aminotransferase (AAT) pathway in calcified arteries. (A) The plasma SO2 concentration; (B,C) The expression of AAT1 and AAT2 mRNA; (D) The plasma AAT activity. * p < 0.05 vs. control; # p < 0.01 vs. calcification (n = 10 per group).
2.3. SO2 Treatment Attenuated Vascular Calcification in Vivo
After treatment with SO2, Von Kossa staining showed dispersed calcified nodules among the elastic fibers disappeared in the calcification + SO2 group as compared with the calcification group (Figure 1A). SBP, DBP and MBP were significantly decreased in rats of calcification + SO2 group (p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.01, respectively) (Figure 1B–D). Furthermore, SO2 decreased the calcium content and ALP activity in both aorta homogenates and plasma (p < 0.01, p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively) (Figure 1E–G).
2.4. SO2 Attenuates Osteoblastic Differentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Vivo
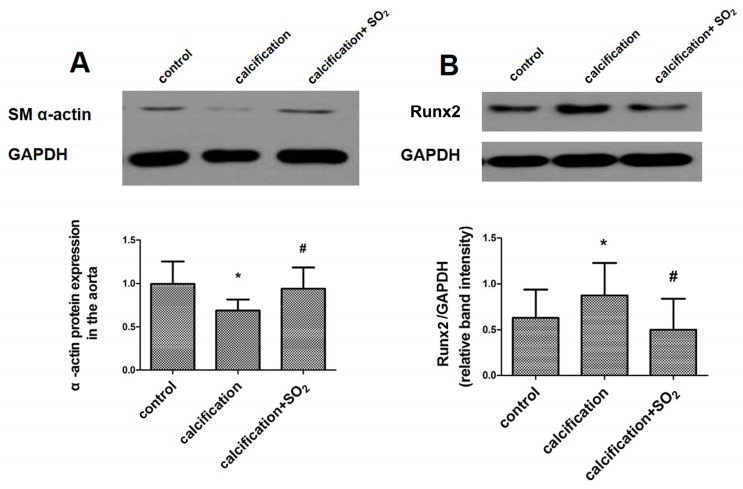
Compared with the normal vessels, the expression of the smooth muscle lineage marker SM α-actin was markedly decreased in aortas in the calcification group (p < 0.05, Figure 3A). In parallel, the level of the osteochondrogenic marker Runx2 concomitantly increased in aortas (p < 0.05, Figure 3B). However, SO2 treatment significantly prevented the upregulation of Runx2 and circumvented the reduction in the SM α-actin level (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, Figure 3A,B).
Figure 3.
SO2 attenuates osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo. Western blot analysis of SM α-actin (A) and Runx2 (B) in rat thoracic aortic tissue. * p < 0.05 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification (n = 10 per group).
2.5. SO2 Inhibits Activation of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway during the Vascular Calcification Process
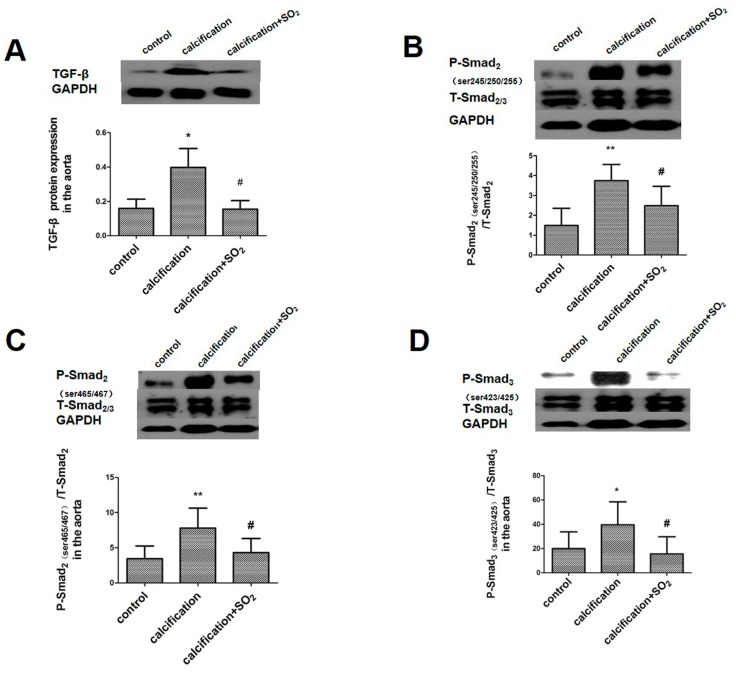
Compared with the control group, the expressions of TGF-β and its downstream signaling molecules P-Smad2 (ser245/250/255), P-Smad2 (ser465/467) and P-Smad3 (ser423/425) in the aortic homogenate were increased significantly (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, Figure 4). After treatment with SO2, however, the expression of these proteins was markedly decreased in rats of calcification group (p all< 0.05, Figure 4A–D).
Figure 4.
SO2 inhibits the activation of TGF-β signaling pathway during the process of vascular calcification in vivo. Western blot analysis of TGF-β (A); phospho-Smad2 (Ser245/250/255) (B); phospho-Smad2 (Ser465/467) (C); and phospho-Smad3 (Ser423/425) (D) in rat thoracic aortic tissue. * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification (n = 10 per group).
2.6. Establishment of the VSMC Calcification Model in Vitro
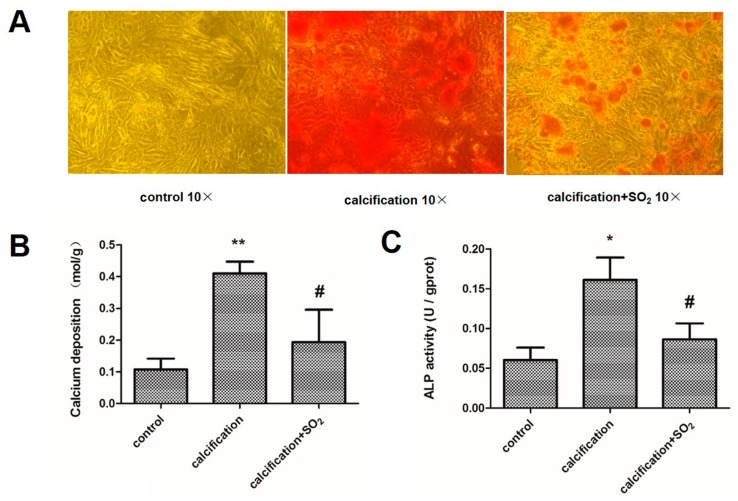
To further verify the above observation, we induced mineralization in incubated A7r5 cells in calcification media containing 5 mmol/L CaCl2. Compared with the control group, the VSMCs maintained in calcification medium showed development of granular calcium deposits throughout the cell culture (Figure 5A). Moreover, the calcium content and ALP activity of the cells were increased significantly (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, Figure 5B,C).
Figure 5.
SO2 prevents vascular smooth muscle cell calcification in vitro. (A) Alizarin Red S staining in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs); (B) Quantification of calcium content in A7r5 VSMCs; (C) ALP activity assay in A7r5 VSMCs. ** p < 0.01 vs. control; * p < 0.05 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 3) performed in triplicate.
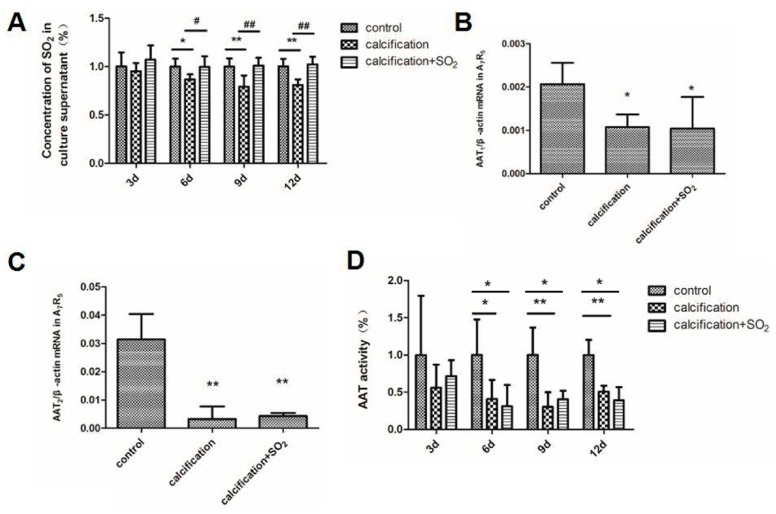
2.7. The Expression of the SO2/AAT Pathway in Calcified VSMCs
On the 3rd day, there were no differences in the culture supernatant SO2 content between the control group and the calcification group (p > 0.05). But on the 6th, 9th and 12th day the culture supernatant SO2 content in the calcification group was significantly reduced compared with that in the control group (p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.01, Figure 6A). In the calcified cells, the expression of AAT1 and AAT2 mRNAs were significantly reduced (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, Figure 6B,C). Compared with the control group, the AAT activity did not alter after 3 days of the incubation with calcification media containing 5 mmol/L CaCl2 (p < 0.05), but on the 6th, 9th or 12th day the AAT activity was significantly decreased (p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.01, Figure 6D).
Figure 6.
Change of endogenous SO2/AAT pathway in calcification VSMCs in vitro. (A) The SO2 concentration in A7r5 cell supernatants; (B,C) The expression of AAT1and AAT2 mRNA in A7r5 VSMCs; (D) The AAT activity in A7r5 cell supernatant. * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification; ## p < 0.01 vs. calcification. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 3) performed in triplicate.
2.8. SO2 Treatment Attenuates Cell Calcification in Vitro
Compared with the calcification group, Alizarin red S staining showed the granular calcium deposits disappeared after treatment with SO2 (Figure 5A). With treatment of SO2, the calcium content and ALP activity were lower than those in the calcified VSMCs (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, Figure 5B,C).
2.9. SO2 Inhibits Osteoblastic Differentiation of VSMCs in Vitro
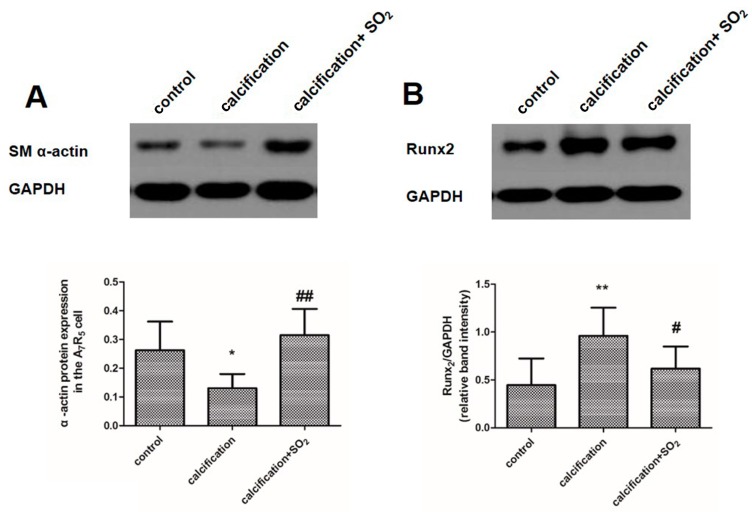
In the calcified cells, the expression of SM α-actin was significantly decreased, while the level of osteochondrogenic marker Runx2 was markedly increased (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, Figure 7A,B). But SO2 treatment significantly prevented the upregulation of Runx2 and circumvented the reduction in SM α-actin level (p < 0.01, p < 0.05, Figure 7A,B).
Figure 7.
SO2 inhibits osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Western blot analysis of SM α-actin (A) and Runx2 (B) in A7r5 VSMCs. * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification; ## p < 0.01 vs. calcification. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 3) performed in triplicate.
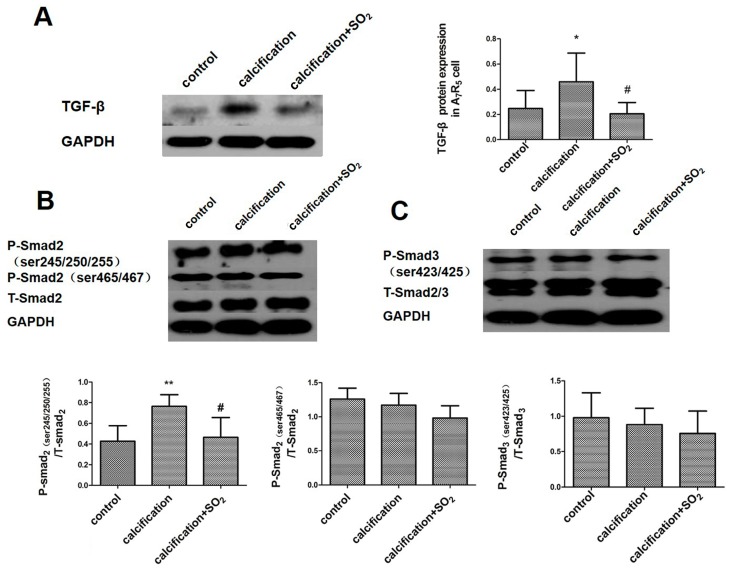
2.10. SO2 Inhibits Activation of the TGF-β Signaling Pathway during the Process of VSMCs Calcification
The expression of TGF-β (Figure 8A) and its downstream signaling molecules P-Smad2 (ser245/250/255) in the calcified cells was increased significantly (p < 0.01, Figure 4D), but the P-Smad2 (ser465/467) and P-Smad3 (ser423/425) expression had no significant differences compared with the control group (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, Figure 8B,C). With treatment of SO2, however, the expression of TGF-β and P-Smad2 (ser245/250/255) was decreased significantly (p < 0.05, p < 0.05, Figure 8A,B) but the P-Smad2 (ser465/467) and P-Smad3 (ser423/425) expression did not change in the calcification group (p all > 0.05, Figure 8B,C).
Figure 8.
SO2 inhibited the activation of TGF-β signaling pathway during the process of VSMCs calcification in vitro. Western blot analysis of TGF-β (A) and Smads (B,C) in A7r5 VSMCs. * p < 0.05 vs. control; ** p < 0.01 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. calcification. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 3) performed in triplicate.
3. Discussion
More and more studies have shown that vascular calcification is a cell-mediated, active, and highly regulated process. This process may be associated with many mechanisms including the disorder of calcium-phosphorus metabolism, osteoblast phenotype transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells and imbalance of promoter/inhibitors of vascular calcification [3]. But the exact mechanisms are still unclear. SO2 is a new endogenous gaseous transmitter [8]. Our group found that SO2 could be produced endogenously in the cardiovascular system and we showed the presence of the key enzyme AAT in various organs and tissues of rats [8]. We also found that SO2 has marked cardiovascular, physiological and pathophysiological significance [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,16,17,18,19,20].
In our study, we established the calcification model in vivo and in vitro, and investigated the endogenous SO2/AAT pathway. We found that the expression of the endogenous SO2/AAT pathway was downregulated in the calcification model both in vivo and in vitro. Interestingly, SO2 supplementation could significantly increase the plasma level of SO2 and inhibit vascular calcification. Meanwhile, SO2 suppressed VSMC calcification, exhibiting loss of granular calcium deposits in calcified VSMCs and decreased calcium content and ALP activity. These results suggest that the downregulated endogenous SO2/AAT pathway is involved in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification. Since AAT is a key enzyme during SO2 generation, AAT level did not change after the addition of SO2 derivatives, as we expected. This is because SO2 as a product by the enzyme AAT would not necessarily induce a significant change in the protein level of AAT itself [13].
The osteoblast transformation of VSMCs was known as a key process of calcification. In the process of calcification, VSMCs can lose the expression of smooth-muscle lineage markers, acquire osteoblast-like phenotype and express osteogenic markers [2,4]. We found that the expression of the smooth-muscle lineage marker SM α-actin was markedly decreased, whereas the level of the osteochondrogenic marker Runx2 was concomitantly increased in calcified aortas and cells. However, SO2 treatment significantly prevented the upregulation of Runx2 and circumvented the reduction in SM α-actin level. These results indicated that SO2 could inhibit the trans-differentiation of VSMCs. Collectively, the results demonstrated that bone mineralization and osteoblast transformation of VSMCs were present during the calcification process in association with the downregulation of the SO2/AAT pathway. Interestingly, we found that SO2 could prevent the bone mineralization and the development of an osteogenic phenotype in VSMCs. These findings suggested that SO2 played an important role in vascular calcification likely by inhibiting the bone mineralization and osteoblast transformation of VSMCs.
Then, we further explored the possible mechanism by which SO2 inhibited vascular calcification. TGF-β regulates cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis by autocrine or paracrine signaling via cell surface receptor signal transduction pathways and plays an important role in regulating extracellular matrix synthesis. Studies have shown that TGF-β1 exists in calcified aortic valve and can regulate interstitial cell calcification of aortic valve via an apoptosis mechanism [21,22]. Other studies have shown that TGF-β can regulate vascular calcification and the differentiation of VSMCs in vivo [23,24]. TGF-β transmits cytoplasmic signals into the intracellular domain via its type I and II receptors. The activated type II receptor combines with the type I receptor to form a heterotrimer which consists of type II receptor-ligand-type I receptors. The activated type II receptor phosphorylates Smad2 and Smad3 (receptor-regulated Smad proteins, R-Smad) and transmits cytoplasmic signals into intracellular signals. The activated phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3 combine with Smad4 (common mediated Smad, co-Smad) and translocate into the nucleus to regulate the transcription of many genes [25]. In our study, we found that the expression of TGF-β was increased and meanwhile the phosphorylation of its downstream signal molecules Smad2/3 was reinforced in calcified vascular tissues and cells. It was suggested that the activation of the TGF-β signal pathway was enhanced in the process of vascular calcification. We also found that the increased expression of TGF-β and phosphorylation of its downstream signal molecules were inhibited after treatment with SO2. Studies have shown that Runx2 is a key regulatory factor for vascular calcification and Runx2/Cbfa1 is a key regulatory factor for the phenotypic transformation of smooth muscle cells and matrix calcification under the hyperphosphate condition. The upregulation of the Runx2/Cbfa1 expression is crucial for the osteogenesis/ chondrogenesis phenotypic transformation and the start of the process of calcification, which was seen in the process of vascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease [26]. Another study showed that Runx2, as a common and important target gene of the TGF-β and BMP signal pathway, together with receptor-activated Smad protein, could stop C2C12 cell myogenic differentiation and induce its osteoblast differentiation [27]. In our study, we found that the expression of TGF-β was increased and its phosphorylation of downstream signal molecules was reinforced together with the upregulation of Runx2 expression in the calcified vascular tissues and cells. However, SO2 inhibited the upregulation of the expression of TGF-β and the enhancement of its downstream signal molecule phosphorylation, and the expression of Runx2 was reduced. These findings suggest that the TGF-β signal pathway is probably involved in the inhibition of vascular calcification by SO2.
However, the present study has limitations. It is known that vascular calcification is related to arterial hypertension and to the decreased vascular compliance, with subsequent elevated systolic blood pressure [28]. Several studies showed that administration of vitamin D3 plus nicotine could induce severe medial calcification of the aorta and produce a significant increase in blood pressure of rats [29,30]. Our present study demonstrated that SO2 treatment markedly attenuated vascular calcification and decreased blood pressure in rats. However, the attenuation in blood pressure by SO2 might be related not only to the inhibition of vascular calcification, but also to the vasorelaxation induced by SO2 [8]. Also, previous studies indicated that the multi-organ calcification including cardiac and renal calcification could be induced by vitamin D3 plus nicotine [30]. Therefore, we could not exclude the possibility that attenuation of blood pressure might also be associated with the inhibitory effect of SO2 on the cardiac and renal calcification and these issues need to be further elucidated. In addition, in the present study we measured arterial blood pressure under anaesthesia. It is known that the blood pressure is affected by anaesthetic depth although the control group was used to ensure the equivalent levels of anaesthesia in the present study.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the Animal Model
All animal care and experimental protocols were performed in accordance with the Guide to The Care and Use of Experimental Animals issued by the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats (180–200 g) were provided by the Animal Research Center of Peking University First Hospital. All animals used in this work received humane care in compliance with the animal care guidelines of the institute and the study was approved by the Experimental Animal Ethic Committee of Peking University First Hospital. Thirty rats were randomly divided into three groups: control group (n = 10), calcification group (n = 10) and SO2 treatment (calcification + SO2) group (n = 10). Rats in calcification group and SO2 treatment group were subjected to vitamin D3 (300,000 IU /kg in arachis oil, intramuscularly) plus nicotine (25 mg/kg in 5 mL peanut oil, orally) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 9 am on day 1 and nicotine was re-administered at 7 pm [31]. Starting from second day, rats of calcification + SO2 group were given intraperitoneal injection of SO2 donor for 28 days. Na2SO3/NaHSO3 was freshly dissolved in physiological (0.9%) saline at 0.54 mmol/kg:0.18 mmol/kg before injection. We injected rats in the calcification and control groups with the same volume of physiological saline.
4.2. A7r5 VSMC Culture and Calcification Inducement
Rat A7r5 VSMCs were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). A7r5 cells (5 × 103) were seeded in 6-well plates and the next day we started our treatment for 12 days. Calcification of A7r5 VSMCs was induced by calcifying media containing 5 mmol/L CaCl2 for 12 days with media changes every 2 days [2]. Smooth muscle cells in calcification + SO2 group were treated with 50 μmol/L SO2 with media changes every 2 days.
4.3. Measurement of Hemodynamic Features in Vivo
After 28 days treatment, all rats were anesthetized intraperitoneally with sodium pentobarbital (45 mg/kg). A silicone catheter filled with heparin saline (500 U/mL) was inserted into the right carotid arteries to measure systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and mean blood pressure (MBP). The catheter was connected to a Multi-Lead Physiological Monitor (BL-420F, Chengdu TME Technology, Chengdu, China). The anaesthesia and the surgery conducted were blinded to the group identity of the rats.
4.4. Sample Preparation
Plasma was collected from the rats, centrifuged, and stored at −80 °C. Rat aorta was rapidly isolated. A consistent location of thoracic aorta from each rat was fixed in 4% polyoxymethylene for morphometric analysis. The rest of the aorta was frozen and stored in liquid nitrogen.
4.5. Quantification of Calcium Content
Calcium content in the aorta was measured as described [29]. The aortas were dried at 55 °C and weighed. Then dissolved in HNO3, dried in an oven at 180 °C and re-dissolved with the blank solution (27 nmol/L KCl and 27 μmol/L LaCl3 in deionized water). The calcium levels were determined by colorimetry through a reaction with the o-cresolphthalein complexon method (Calcium Kit, BioSino Bio-technology and Science Inc., Beijing, China) and were normalized by aortic dry weight.
For calcium content in the A7r5 VSMCs [2], A7r5 VSMCs were grown in 6-well plates and treated with growth medium or calcifying medium for 12 days. After removing the culture medium, cells were washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and treated with 0.6 N HCl overnight at 4 °C. Then, the HCL supernatant was harvested and the total protein of cells was extracted. The calcium content in the HCL supernatant was determined by a calcium kit and was normalized by protein concentration.
4.6. ALP Activity Assay
Plasma and aortic tissue homogenate ALP activity was measured colorimetrically as the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl phosphate by ALP assay kit (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). ALP activity was measured and the results were normalized to levels of total protein.
4.7. Von Kossa Staining and Alizarin Red S Staining
Von Kossa staining of thoracic aortic ring calcification was performed as described previously [16]. A consistent location of thoracic aorta was used for all rats [32]. And the Alizarin red staining of A7r5 VSMCs was carried out in accordance with the predecessors [2].
4.8. Real-Time PCR Analysis
Total RNA from aortic tissue or A7r5 VSMCs was isolated with the use of TRIZOL reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and reverse-transcribed into single-strand cDNA using oligo (dT) 15 primer and M-MLV reverse transcriptase. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed with an ABI 7300 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA) and the amplification conditions were 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. Primers for rat AAT1 were: 5′-CCAGGGAGCTCGGATCGT-3′ (sense), and 5′-GCCATTGTCTTCACGTTTCCTT-3′ (antisense); primers for rat AAT2 were 5′-GAGGGTCGGAGCCAGCTT-3′ (sense), and 5′-TTTCCCCAGGATGGTTTGG-3′ (antisense); and primers for rat β-actin were 5′-ACCCGCGAGTACAACCTTCTT-3′ (sense) and 5′-TATCGTCATCCATGGCGAACT-3′ (antisense).
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
Extracts containing equal amounts of total protein from rat arteries or A7r5 VSMCs were resolved by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were incubated with primary antibody and secondary antibody. The immunofluorescence signal was exposed to X-ray film (Kodak Scientific, New Haven, CT, USA), and then quantified by using AlphaImager (San Leandro, CA, USA).
4.10. Determination of SO2 Content in Plasma and Cell Supernatant
Samples obtained from plasma and cell supernatant were prepared and the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Agilent 1200 series, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with fluorescence determination to determine the SO2 concentration [13,14].
4.11. AAT Activity Assay
AST/GOT Determination Kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Biological Engineer Academy, Nanjing, China) was used to detect AAT activity in plasma and cell supernatant. The samples were prepared according to the introduction.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. Statistical comparisons were performed with SPSS 20.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Comparisons between more than two groups involved one-way ANOVA followed by LSD test, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
In our study, we observed a downregulation of the endogenous SO2/AAT pathway in the process of vascular calcification and the downregulated SO2/AAT pathway was likely involved in the development of vascular calcification. Mechanistically, we suggested that SO2 inhibited vascular calcification, likely in association with inhibition of the TGF-β signal pathway. These findings are meaningful for understanding the mechanisms for vascular calcification and also to provide new thoughts and potential strategies for the prevention and therapy of vascular calcification.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81400311 and 31130030) and by the Major Basic Research Development Program of China (Nos. 2012CB517806 and 2013CB933801).
Author Contributions
Junbao Du, Hongfang Jin and Chaoshu Tang conceived and designed the experiments; Zhenzhen Li, Yaqian Huang, Yongfen Qi and Angie Dong Liu performed the experiments; Zhenzhen Li, Yaqian Huang, Yongfen Qi, Hongfang Jin, Junbao Du and Chaoshu Tang analyzed the data; Hongfang Jin, Yongfen Qi, Angie Dong Liu and Chaoshu Tang contributed reagents. Junbao Du, Hongfang Jin, Yaqian Huang, Zhenzhen Li and Angie Dong Liu wrote the paper. All authors discussed and confirmed the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Shanahan C.M., Crouthamel M.H., Kapustin A., Giachelli C.M. Arterial calcification in chronic kidney disease: Key roles for calcium and phosphate. Circ. Res. 2011;109:697–711. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Du Y., Wang Y., Wang L., Liu B., Tian Q.Y., Liu C.J., Zhang T., Xu Q.B., Zhu Y., Ake O., et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein inhibits vascular smooth muscle calcification by interacting with bone morphogenetic protein-2. Circ. Res. 2011;108:917–928. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Towler D.A., Demer L.L. Thematic series on the pathobiology of vascular calcification: An introduction. Circ. Res. 2011;108:1378–1380. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Leopold J.A. MicroRNAs regulate vascular medial calcification. Cells. 2014;3:963–980. doi: 10.3390/cells3040963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Qiao W., Chen L., Zhang M. MicroRNA-205 regulates the calcification and osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014;33:1945–1953. doi: 10.1159/000362971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cui R.R., Li S.J., Liu L.J., Yi L., Liang Q.H., Zhu X., Liu G.Y., Liu Y., Wu S.S., Liao X.B., et al. MicroRNA-204 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell calcification in vitro and in vivo. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012;96:320–329. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liao X.B., Zhang Z.Y., Yuan K., Liu Y., Feng X., Cui R.R., Hu Y.R., Yuan Z.S., Gu L., Li S.J., et al. MiR-133a modulates osteogenic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology. 2013;154:3344–3352. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Du S.X., Jin H.F., Bu D.F., Zhao X., Geng B., Tang C.S., Du J.B. Endogenously generated sulfur dioxide and its vasorelaxant effect in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008;29:923–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen S.S., Tang C.S., Jin H.F., Du J.B. Sulfur dioxide acts as a novel endogenous gaseous signaling molecule in the cardiovascular system. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2011;124:1901–1905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang X.B., Jin H.F., Tang C.S., Du J.B. The biological effect of endogenous sulfur dioxide in the cardiovascular system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011;670:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang R.Y., Du J.B., Sun Y., Chen S., Tsai H.J., Yuan L., Li L., Tang C.S., Jin H.F. Sulfur dioxide derivatives depress l-type calcium channel in rat cardiomyocytes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011;38:416–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang Q., Meng Z. The vasodilator mechanism of sulfur dioxide on isolated aortic rings of rats: Involvement of the K+ and Ca2+ channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009;602:117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.11.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun Y., Tian Y., Prabha M., Liu D., Chen S., Zhang R., Liu X., Tang C., Tang X., Jin H., et al. Effects of sulfur dioxide on hypoxic pulmonary vascular structural remodeling. Lab. Investig. 2010;90:68–82. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2009.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jin H.F., Du S.X., Zhao X., Wei H.L., Wang Y.F., Liang Y.F., Tang C.S., Du J.B. Effects of endogenous sulfur dioxide on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008;29:1157–1166. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu D., Huang Y., Bu D., Liu A.D., Holmberg L., Jia Y., Tang C., Du J., Jin H. Sulfur dioxide inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing the Erk/MAP kinase pathway mediated by cAMP/PKA signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5 doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li W., Tang C., Jin H., Du J. Regulatory effects of sulfur dioxide on the development of atherosclerotic lesions and vascular hydrogen sulfide in atherosclerotic rats. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215:323–330. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.12.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liang Y., Liu D., Ochs T., Tang C., Chen S., Zhang S., Geng B., Jin H., Du J. Endogenous sulfur dioxide protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury and increases myocardial antioxidant capacity in rats. Lab. Investig. 2011;91:12–23. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen S., Du J., Liang Y., Ochs T., Liu D., Zhu L., Tang X., Tang C., Jin H. Sulfur dioxide inhibits excessively activated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with myocardial injury. Heart Vessels. 2012;27:505–516. doi: 10.1007/s00380-011-0192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang X.B., Huang X.M., Ochs T., Li X.Y., Jin H.F., Tang C.S., Du J.B. Effect of sulfur dioxide preconditioning on rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011;106:865–878. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang S., Du J., Jin H., Li W., Liang Y., Geng B., Li S., Zhang C., Tang C. Endogenous sulfur dioxide aggravates myocardial injury in isolated rat heart with ischemia and reperfusion. Transplantation. 2009;87:517–524. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318195fe82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jian B., Narula N., Li Q.Y., Mohler E.R., III, Levy R.J. Progression of aortic valve stenosis: TGF-β1 is present in calcified aortic valve cusps and promotes aortic valve interstitial cell calcification via apoptosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003;75:457–465. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(02)04312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kanno Y., Into T., Lowenstein C.J., Matsushita K. Nitric oxide regulates vascular calcification by interfering with TGF-signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008;77:221–230. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Watson K.E., Boström K., Ravindranath R., Lam T., Norton B., Demer L.L. TGF-β1 and 25-hydroxycholesterol stimulate osteoblast-like vascular cells to calcify. J. Clin. Investig. 1994;93:2106–2113. doi: 10.1172/JCI117205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Grainger D.J., Metcalfe J.C., Grace A.A., Mosedale D.E. Transforming growth factor-β dynamically regulates vascular smooth muscle differentiation in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 1998;111:2977–2988. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.19.2977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeon H.S., Jen J. TGF-β signaling and the role of inhibitory Smads in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010;5:417–419. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ce3afd. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Speer M.Y., Li X., Hiremath P.G., Giachelli C.M. Runx2/Cbfa1, but not loss of myocardin, is required for smooth muscle cell lineage reprogramming toward osteochondrogenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010;110:935–947. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee K.S., Kim H.J., Li Q.L., Chi X.Z., Ueta C., Komori T., Wozney J.M., Kim E.G., Choi J.Y., Ryoo H.M., et al. Runx2 is a common target of transforming growth factor β1 and bone morphogenetic protein 2, and cooperation between Runx2 and Smad5 induces osteoblast-specific gene expression in the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;20:8783–8792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.23.8783-8792.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Scheiber D., Veulemans V., Horn P., Chatrou M.L., Potthoff S.A., Kelm M., Schurgers L.J., Westenfeld R. High-dose menaquinone-7 supplementation reduces cardiovascular calcification in a murine model of extraosseous calcification. Nutrients. 2015;7:6991–7011. doi: 10.3390/nu7085318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu Y., Zhou Y.B., Zhang G.G., Cai Y., Duan X.H., Teng X., Song J.Q., Shi Y., Tang C.S., Yin X.H., et al. Cortistatin attenuates vascular calcification in rats. Regul. Pept. 2010;159:35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2009.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kieffer P., Robert A., Capdeville-Atkinson C., Atkinson J., Lartaud-Idjouadiene I. Age-related arterial calcification in rats. Life Sci. 2000;66:2371–2381. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00567-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cai Y., Xu M.J., Teng X., Zhou Y.B., Chen L., Zhu Y., Wang X., Tang C.S., Qi Y.F. Intermedin inhibits vascular calcification by increasing the level of matrix γ-carboxyglutamic acid protein. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010;85:864–873. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ameer O.Z., Salman I.M., Avolio A.P., Phillips J.K., Butlin M. Opposing changes in thoracic and abdominal aortic biomechanical properties in rodent models of vascular calcification and hypertension. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014;307:H143–H151. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00139.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]