Abstract
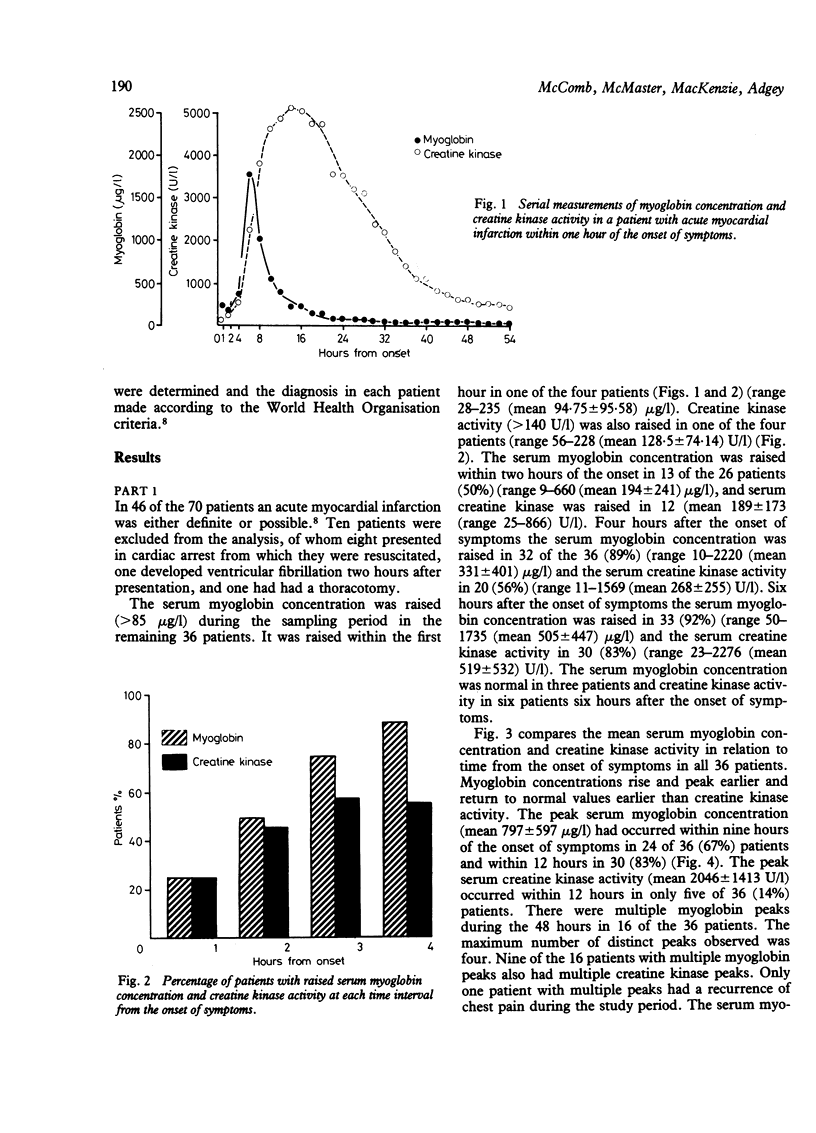
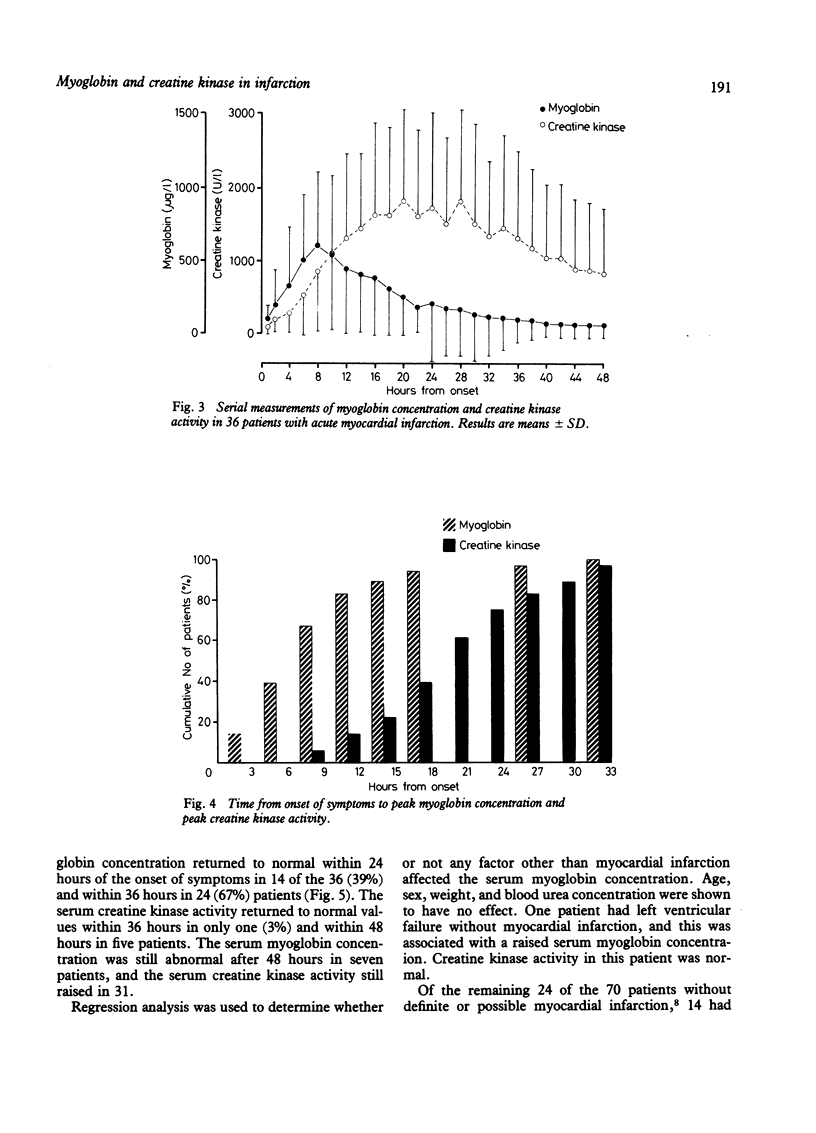
Serum myoglobin concentration and creatine kinase activity were measured serially in 70 consecutive patients presenting within four hours of the onset of symptoms of suspected acute myocardial infarction. Of 36 patients with definite or possible myocardial infarction (WHO criteria), the serum myoglobin concentration was raised (greater than 85 micrograms/l) one hour after the onset of symptoms in 25% and at four hours in 89%. Creatine kinase activity was raised (greater than 140 U/l) one hour after the onset in 25% and at four hours in only 56%. Within 12 hours of the onset of symptoms the myoglobin concentration reached a peak in 83% and the creatine kinase a peak in only 14%. Within 36 hours the myoglobin concentration fell to normal values in 67% while creatine kinase activity fell to normal values in only 3%. Four hours after the onset of symptoms the serum myoglobin concentration distinguished easily those patients with myocardial infarction from those without, whereas when creatine kinase values were used the sensitivity was poor but the specificity high. From the combined results of the two studies and using a single measurement of serum myoglobin concentration at six hours from the onset of symptoms to predict the diagnosis in 114 patients with suspected infarction, the sensitivity was 93% and specificity 89%.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMAKO T., KOGA J., KOBAYASHI A., URAKADO S., TOKUNAGA J. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE METABOLISM OF MYOGLOBIN. Kyushu J Med Sci. 1963 Oct;14:277–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. P., Fatches K. R., Carter I. W., Cloonan M. J., Wilcken D. E. Comparison of serum myoglobin and creatine kinase MB isoenzyme in early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Br Heart J. 1981 Apr;45(4):389–392. doi: 10.1136/hrt.45.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkeson G., Stone M. J., Waterman M., Ting R., Gomez-Sanchez C. E., Hull A., Willerson J. T. Detection of myoglobin by radioimmmunoassay in human sera: its usefulness and limitations as an emergency room screening test for acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1978 Jan;95(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(78)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNINGS R. B., SOMMERS H. M., SMYTH G. A., FLACK H. A., LINN H. Myocardial necrosis induced by temporary occlusion of a coronary artery in the dog. Arch Pathol. 1960 Jul;70:68–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISS A., REINHART W. Ueber den Nachweis des Myoglobins im Serum und im Harn nach Herzinfarkt. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1956 Mar 2;68(9):154–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser H., Spaar U., Sold G., Wolfrum D. I., Kreuzer H. Radioimmunologische Bestimmung von Human-Myoglobin in der Diagnostik des akuten Myokardinfarkts. Klin Wochenschr. 1979 Mar 1;57(5):225–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01477491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubasik N. P., Guiney W., Warren K., D'Souza J. P., Sine H. E., Brody B. B. Radioimmunoassay of serum myoglobin: evaluation and modification of a commercial kit and assessment of its usefulness for detecting acute myocardial infarction. Clin Chem. 1978 Nov;24(11):2047–2049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComb J. M., McMaster E. A. Serum myoglobin after cardiac catheterisation. Br Heart J. 1982 Apr;47(4):353–356. doi: 10.1136/hrt.47.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxley D. K., Bolton M. R., Shaeffer C. W. Myoglobin in myocardial infarction. Results in a coronary-care-unit population. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;72(2):137–141. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosano T. G., Sanders L. A., Johnson E. S., Kenny M. A., Clayson K. J., Strandjord P. E. Myoglobin concentrations and muscle-enzyme activities in serum after myocardial infarction and cardiac arrhythmia. Clin Chem. 1977 May;23(5):868–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J., Waterman M. R., Harimoto D., Murray G., Willson N., Platt M. R., Blomqvist G., Willerson J. T. Serum myoglobin level as diagnostic test in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Br Heart J. 1977 Apr;39(4):375–380. doi: 10.1136/hrt.39.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J., Waterman M. R., Poliner L. R., Templeton G. H., Buja L. M., Willerson J. T. Myoglobinemia is an early and quantitative index of acute myocardial infarction. Angiology. 1978 May;29(5):386–392. doi: 10.1177/000331977802900506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J., Willerson J. T., Gomez-Sanchez C. E., Waterman M. R. Radioimmunoassay of myoglobin in human serum. Results in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1334–1339. doi: 10.1172/JCI108211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C., Bendz R. Myoglobin, creatine kinase and its isoenzyme MB in serum after acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Cardiol. 1978 Nov;8(4-5):515–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvén C. The kinetics of myoglobin in old volunteers and in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Oct;38(6):561–565. doi: 10.1080/00365517809108820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommaso C. L., Salzeider K., Arif M., Klutz W. Serial myoglobin vs. CPK analysis as an indicator of uncomplicated myocardial infarction size and its use in assessing early infarct extension. Am Heart J. 1980 Feb;99(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(80)90759-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



