Abstract
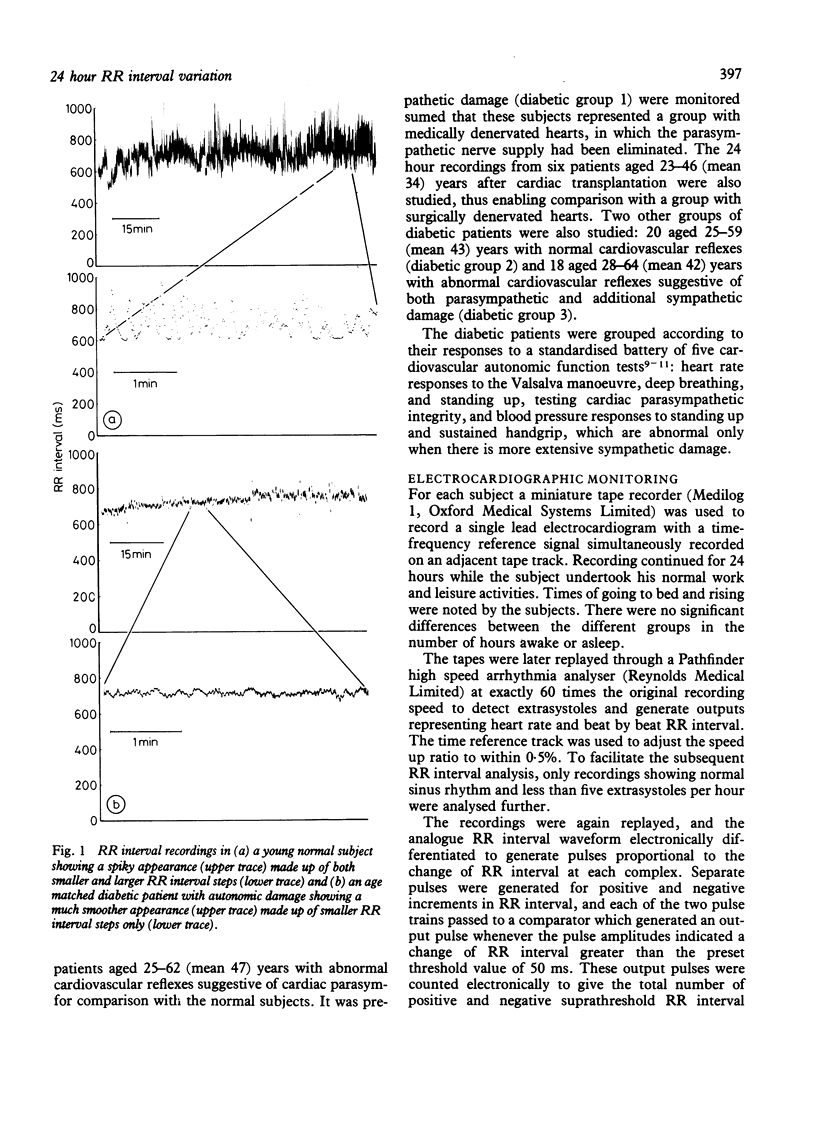
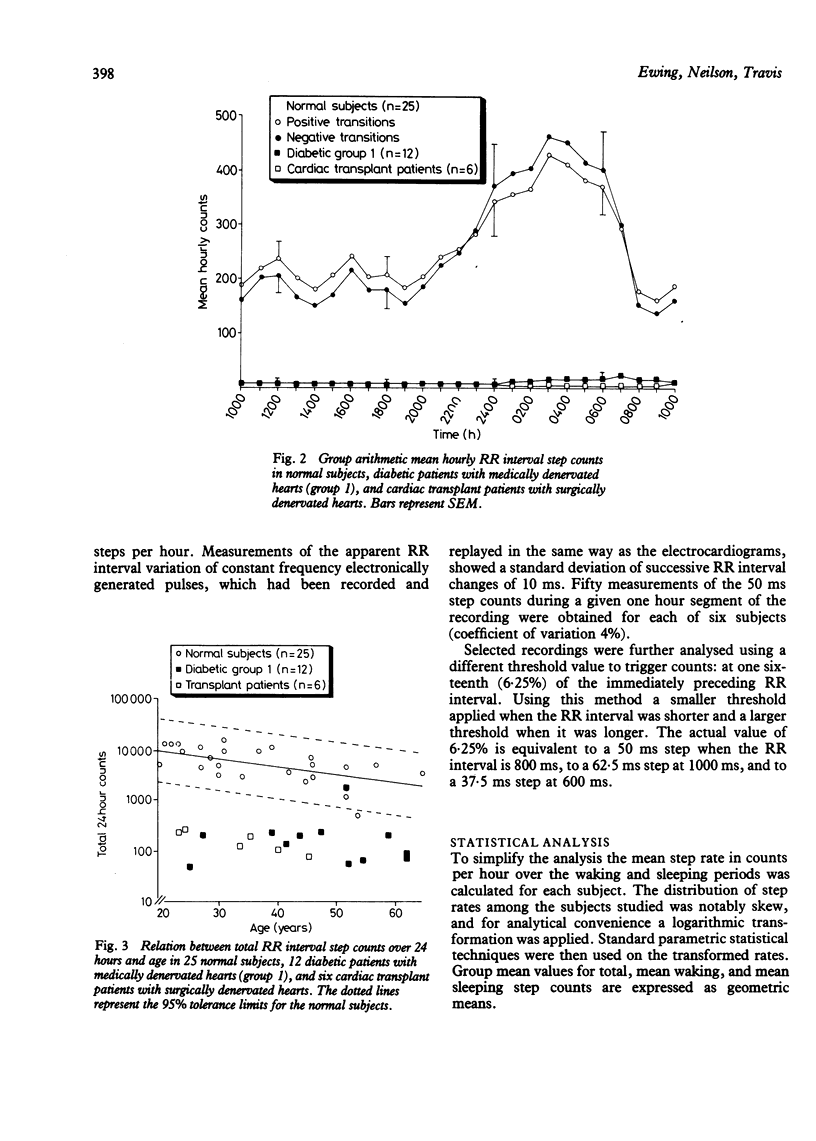
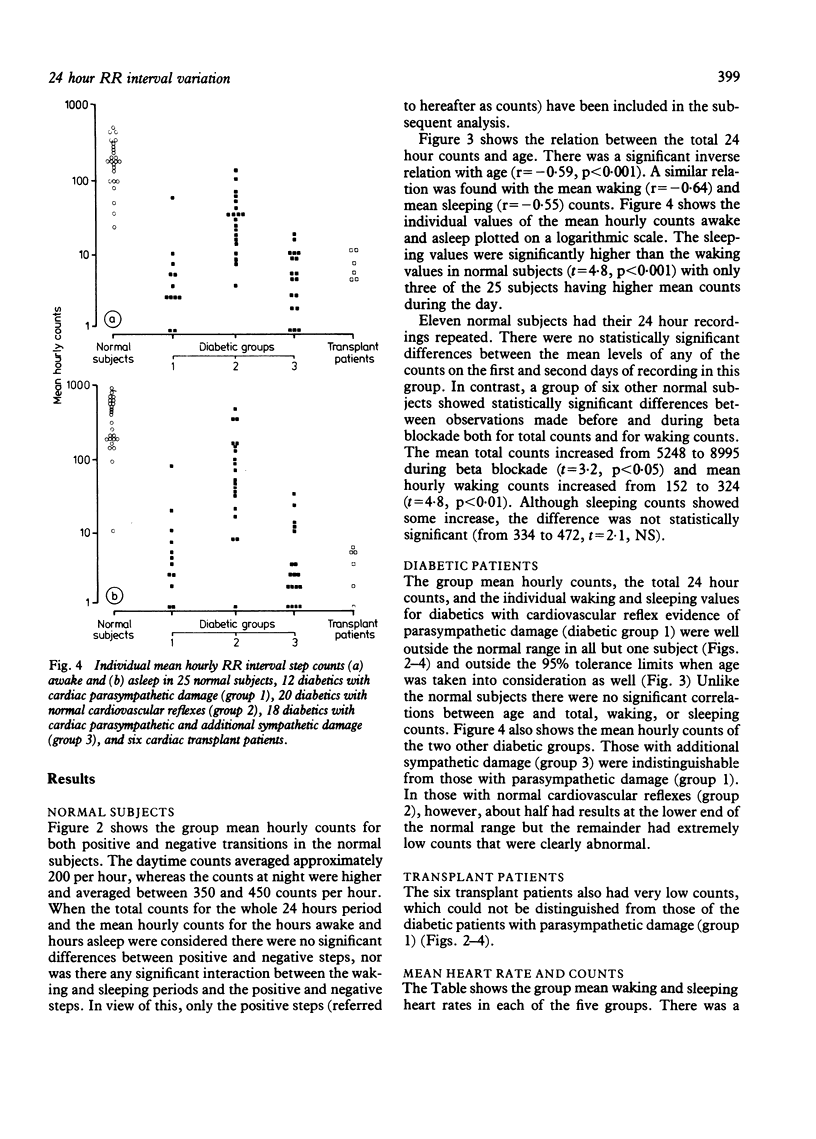
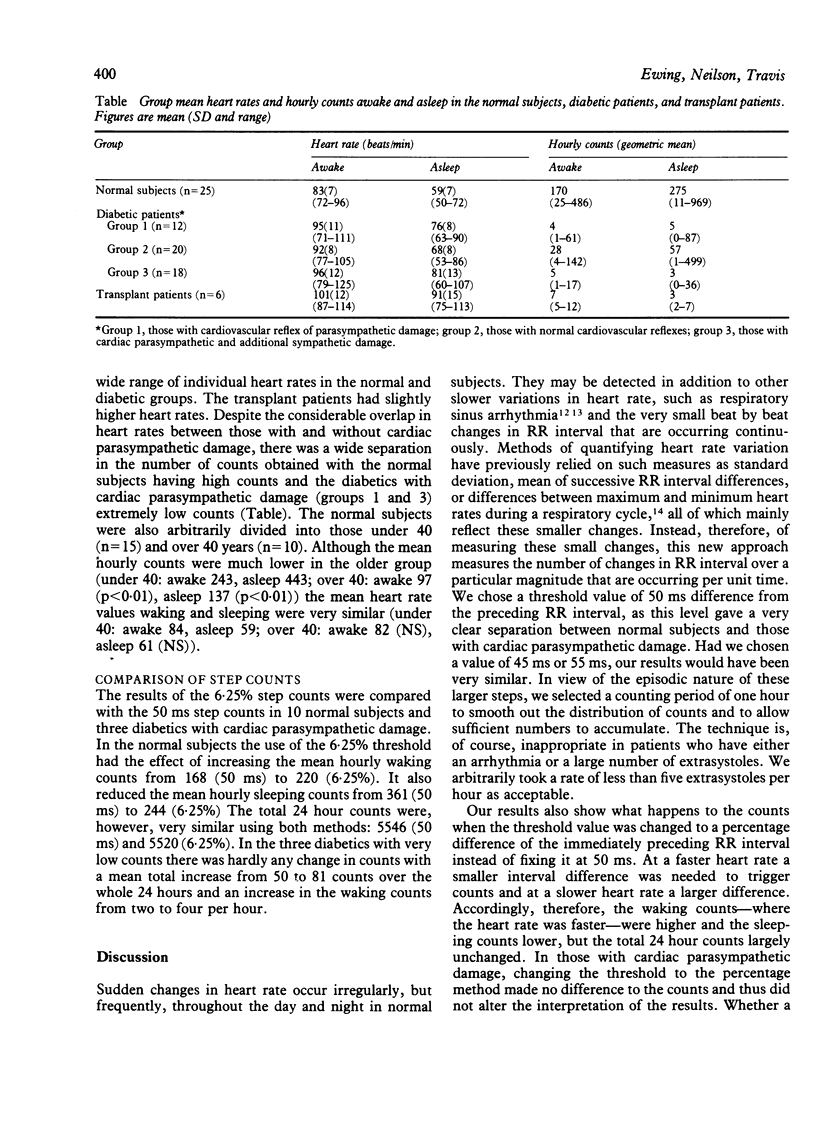
Cardiac parasympathetic activity was assessed using 24 hour electrocardiographic recordings by measuring the incidence of larger changes in successive RR intervals, which in normal subjects occur frequently but irregularly. In 25 normal subjects the mean number of times per hour in which the change in successive RR interval was greater than 50 ms was 150-250 during waking and 350-450 during sleeping. By contrast, 30 diabetics with medically denervated hearts (12 with cardiovascular reflex evidence of parasympathetic damage and 18 with additional sympathetic damage) and six cardiac transplant patients with surgically denervated hearts had extremely low counts. Additionally, of 20 diabetics with normal cardiovascular reflexes, about half had abnormally low counts, suggesting that this method is better than currently available reflex tests in detecting early cardiac parasympathetic damage. This technique provides a valid and sensitive way of monitoring cardiac parasympathetic activity over prolonged periods.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellavere F., Ewing D. J. Autonomic control of the immediate heart rate response to lying down. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Jan;62(1):57–64. doi: 10.1042/cs0620057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckberg D. L. Human sinus arrhythmia as an index of vagal cardiac outflow. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Apr;54(4):961–966. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.4.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckberg D. L. Parasympathetic cardiovascular control in human disease: a critical review of methods and results. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):H581–H593. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.5.H581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Borsey D. Q., Bellavere F., Clarke B. F. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: comparison of measures of R-R interval variation. Diabetologia. 1981 Jul;21(1):18–24. doi: 10.1007/BF03216217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Campbell I. W., Clarke B. F. Assessment of cardiovascular effects in diabetic autonomic neuropathy and prognostic implications. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 2):308–311. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Clarke B. F. Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 2;285(6346):916–918. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6346.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. J., Hume L., Campbell I. W., Murray A., Neilson J. M., Clarke B. F. Autonomic mechanisms in the initial heart rate response to standing. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Nov;49(5):809–814. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.5.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagraeus L., Linnarsson D. Autonomic origin of heart rate fluctuations at the onset of muscular exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1976 May;40(5):679–682. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.5.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander A. P., Bouman L. N. Cardiac acceleration in man elicited by a muscle-heart reflex. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Feb;38(2):272–278. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett S., Lamb J. F., Travis P. Sudden large and periodic changes in heart rate in healthy young men after short periods of exercise. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 23;285(6349):1154–1156. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6349.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona P. G., Jih F. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: noninvasive measure of parasympathetic cardiac control. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):801–805. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaan A. The antagonistic cardiac nerves and heart rate. J Physiol. 1935 Feb 9;83(3):332–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



