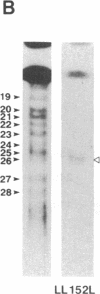
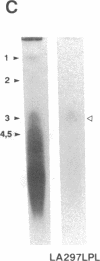
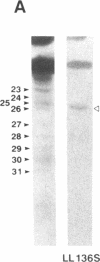
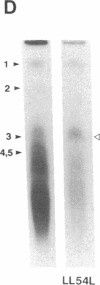
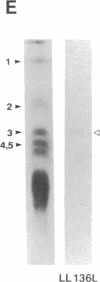
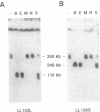
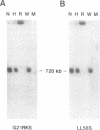
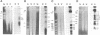Abstract
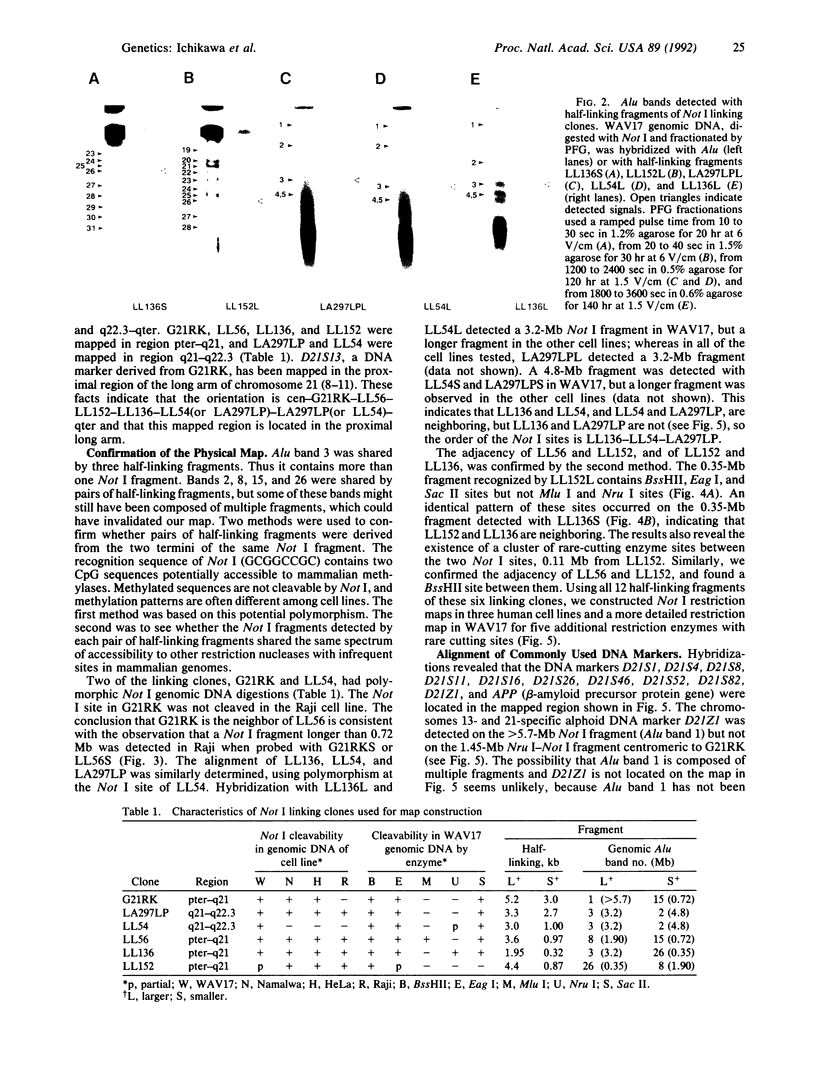
Human chromosome 21 is the smallest of the 22 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. Hybridization of the human repetitive sequence Alu to pulsed-field gel-fractionated Not I-digested genomic DNA from a human-mouse hybrid cell line containing chromosome 21 as the sole human component identified chromosome 21 Not I restriction fragments. A Not I restriction map of regions of the chromosome was constructed, by identifying neighboring Alu bands with Not I linking clones. This approach simplifies the task of physical mapping and avoids ambiguities in Not I fragment assignments that arise from gel-to-gel mobility variations. A contiguous map was constructed with six Not I linking clones that covers at least the proximal one-third of the long arm of chromosome 21 and spans 20 megabases. A more detailed restriction map revealed 11 likely CpG islands in this region and localized 11 additional DNA markers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borrow J., Goddard A. D., Sheer D., Solomon E. Molecular analysis of acute promyelocytic leukemia breakpoint cluster region on chromosome 17. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2218500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Harper K., Bonthron D., Krumlauf R., Polkey A., Pembrey M. E., Williamson R. Use of a chromosome 21 cloned DNA probe for the analysis of non-disjunction in Down syndrome. Hum Genet. 1984;66(1):54–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00275186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deaven L. L., Van Dilla M. A., Bartholdi M. F., Carrano A. V., Cram L. S., Fuscoe J. C., Gray J. W., Hildebrand C. E., Moyzis R. K., Perlman J. Construction of human chromosome-specific DNA libraries from flow-sorted chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):159–167. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Cremer T., Slagboom P., Bakker E., Scholl H. P., Hager H. D., Stevenson A. F., Cornelisse C. J., Pearson P. L. Two subsets of human alphoid repetitive DNA show distinct preferential localization in the pericentric regions of chromosomes 13, 18, and 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(4):193–201. doi: 10.1159/000132229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Chikashige Y., Smith C. L., Niwa O., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. Construction of a Not I restriction map of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2801–2818. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountain J. W., Wallace M. R., Bruce M. A., Seizinger B. R., Menon A. G., Gusella J. F., Michels V. V., Schmidt M. A., Dewald G. W., Collins F. S. Physical mapping of a translocation breakpoint in neurofibromatosis. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1085–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.2543076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Watkins P., Münke M., Drabkin H., Jones C., Patterson D. Partial physical map of human chromosome 21. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):623–637. doi: 10.1007/BF01535316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A. M., Haynes A. R., Owen M. J., Farrall M., James L. A., Lai L. Y., Mullan M. J., Roques P., Rossor M. N., Williamson R. Predisposing locus for Alzheimer's disease on chromosome 21. Lancet. 1989 Feb 18;1(8634):352–355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91725-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Skraastad M. I., Bergen A. A., Wapenaar M. C., Bakker E., Millington-Ward A., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. The X chromosome shows less genetic variation at restriction sites than the autosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):438–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Croyle M. L., Cox D. R. Isolation and regional mapping of DNA sequences unique to human chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):963–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Engels W. R. Base ratio, DNA content, and quinacrine-brightness of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3382–3386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Rykowski M. C. Human genome organization: Alu, lines, and the molecular structure of metaphase chromosome bands. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE J., GAUTIER M., TURPIN R. Etude des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 16;248(11):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Sistonen P., Miao J., Hästbacka J., Norio R., de la Chapelle A. Localization of a gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy to chromosome 21q22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3696–3699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew M. K., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 2. Effect of pulse time and electric field strength and implications for models of the separation process. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9210–9216. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., James L. A., Hardy J. A., Williamson R., Goate A. M. Physical mapping around the Alzheimer disease locus on the proximal long arm of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):316–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Abad J. P., Wang D. N., Ohki M., Cantor C. R., Smith C. L. Construction and characterization of a NotI linking library of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):618–630. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90444-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Oishi N., Furuya H., Yoshioka K., Yamada T., Ogawa S., Wong C. W., Glenner G. G., Sakaki Y. A HindIII polymorphism detected by the cDNA encoding amyloid beta protein of Alzheimer's disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6309–6309. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Ichikawa H., Miyoshi H., Ohki M., Kobayashi H., Maseki N., Kaneko Y. Molecular assignment of a translocation breakpoint in acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21). Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1991 May;3(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., Figlewicz D. A., Pericak-Vance M. A., Haines J. L., Rouleau G., Jeffers A. J., Sapp P., Hung W. Y., Bebout J., McKenna-Yasek D. Linkage of a gene causing familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to chromosome 21 and evidence of genetic-locus heterogeneity. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slate D. L., Shulman L., Lawrence J. B., Revel M., Ruddle F. H. Presence of human chromosome 21 alone is sufficient for hybrid cell sensitivity to human interferon. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):319–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.319-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Approaches to physical mapping of the human genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):115–122. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gibbons K. T., Tricoli J. V., Landes G., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6075–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao G. H., Grzeschik K. H., Scherer G. Anonymous DNA sequence from chromosome 21 showing a three allele insertion/deletion RFLP (HGM 9 provisional no. D21S82). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5499–5499. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]