Abstract
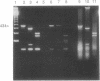
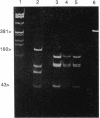
The identification of apparently fastidious microorganisms is often problematic. DNA from a rickettsia-like agent (called the ELB agent) present in cat fleas could be amplified by PCR with conserved primers derived from rickettsial 17-kDa common protein antigen and citrate synthase genes but not spotted fever group 190-kDa antigen gene. Alu I sites in both the 17-kDa and citrate synthase PCR products obtained with the rickettsia-like agent and Rickettsia typhi were different even though both agents reacted with monoclonal antibodies previously thought specific for R. typhi. The DNA sequence of a portion of the 17-kDa PCR product of the rickettsia-like agent differed significantly from all known rickettsial sequences and resembled the 17-kDa sequences of typhus more than spotted fever group rickettsiae. The rare stable transovarial maintenance of this rickettsia in cat fleas has important implications for the disease potential of cat fleas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. R., Schmidtmann E. T., Azad A. F. Infection of colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché), with a rickettsia-like microorganism. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Oct;43(4):400–409. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Tzianabos T. Comparative sequence analysis of a genus-common rickettsial antigen gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5199–5201. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5199-5201.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:553–569. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. F., Webb L., Carl M., Dasch G. A. Detection of rickettsiae in arthropod vectors by DNA amplification using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:557–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Tibbs C. W., Dobson M. E., Paparello S., Dasch G. A. Diagnosis of acute typhus infection using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):791–793. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilbeck P. M., Evermann J. F., Crawford T. B., Ward A. C., Leathers C. W., Holland C. J., Mebus C. A., Logan L. L., Rurangirwa F. R., McGuire T. C. Isolation of a previously undescribed rickettsia from an aborted bovine fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):814–816. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.814-816.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. E., Azad A. F., Dasch G. A., Webb L., Olson J. G. Detection of murine typhus infected fleas with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 May;40(5):521–528. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. New opportunistic infections--more opportunities. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1625–1627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhang-Azad A., Traub R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Rickettsia mooseri infection in the fleas Leptopsylla segnis and Xenopsylla cheopis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Nov;32(6):1392–1400. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Newhouse V. F. Natural history of Rickettsia rickettsii. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:287–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Anacker R. L., Peacock M. G., Hayes S. F., Lane R. S. Identification of an isolate of Rickettsia canada from California. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Nov;31(6):1216–1221. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Spruill C. L., Plikaytis B. D. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1576–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1576-1589.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Loutit J. S., Schmidt T. M., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. The agent of bacillary angiomatosis. An approach to the identification of uncultured pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1573–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Anderson B. E., McDade J. E. Detection of Rickettsia rickettsii DNA in clinical specimens by using polymerase chain reaction technology. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2866–2868. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2866-2868.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):63–65. doi: 10.1038/345063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L., Carl M., Malloy D. C., Dasch G. A., Azad A. F. Detection of murine typhus infection in fleas by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):530–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.530-534.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary A., Paperna I. Epitheliocystis disease in the striped bass Morone saxatilis from the Chesapeake Bay. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Oct;23(10):1404–1414. doi: 10.1139/m77-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]