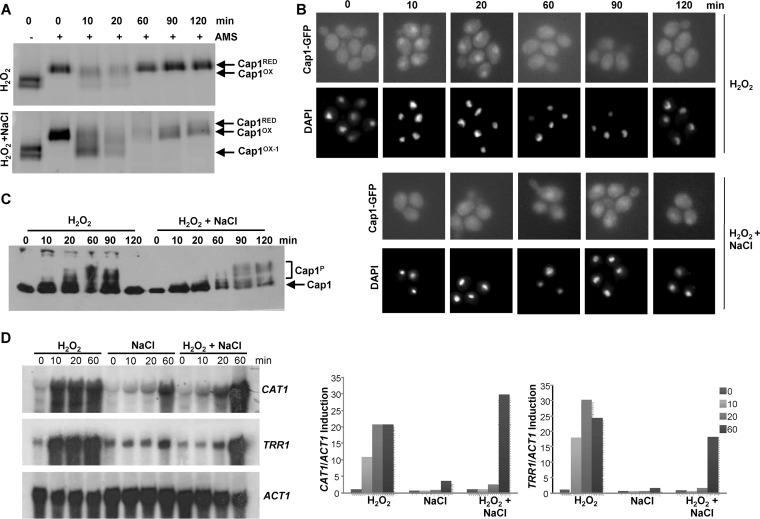
FIG 3 .
Combinatorial stress-mediated inhibition of Cap1 activation is transient. (A) Differential oxidation of Cap1 following combinatorial stress is not sustained. Cap1 oxidation was measured as described in the legend to Fig. 1E following exposure of Cap1-MH cells to 5 mM H2O2 or 5 mM H2O2 plus 1 M NaCl for the indicated times. (B) Cap1 nuclear accumulation is delayed following combinatorial stress. Cap1 localization was detected as described in the legend to Fig. 1B following treatment of Cap1-GFP cells for the indicated times with the stress treatments described above. (C) Cap1 phosphorylation is delayed following combinatorial stress treatment. Cap1 phosphorylation was detected as described in the legend to Fig. 1C, following treatment of Cap1-MH cells with the stress treatments described above for the indicated times. (D) The inhibition of Cap-dependent gene expression following combinatorial stress is transient. Northern blots were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1A, after wild-type cells were treated with the stress treatments described above for the indicated times (left panel). The levels of CAT1 and TRR1 mRNA were quantified relative to the ACT1 loading control (right panel).