Abstract
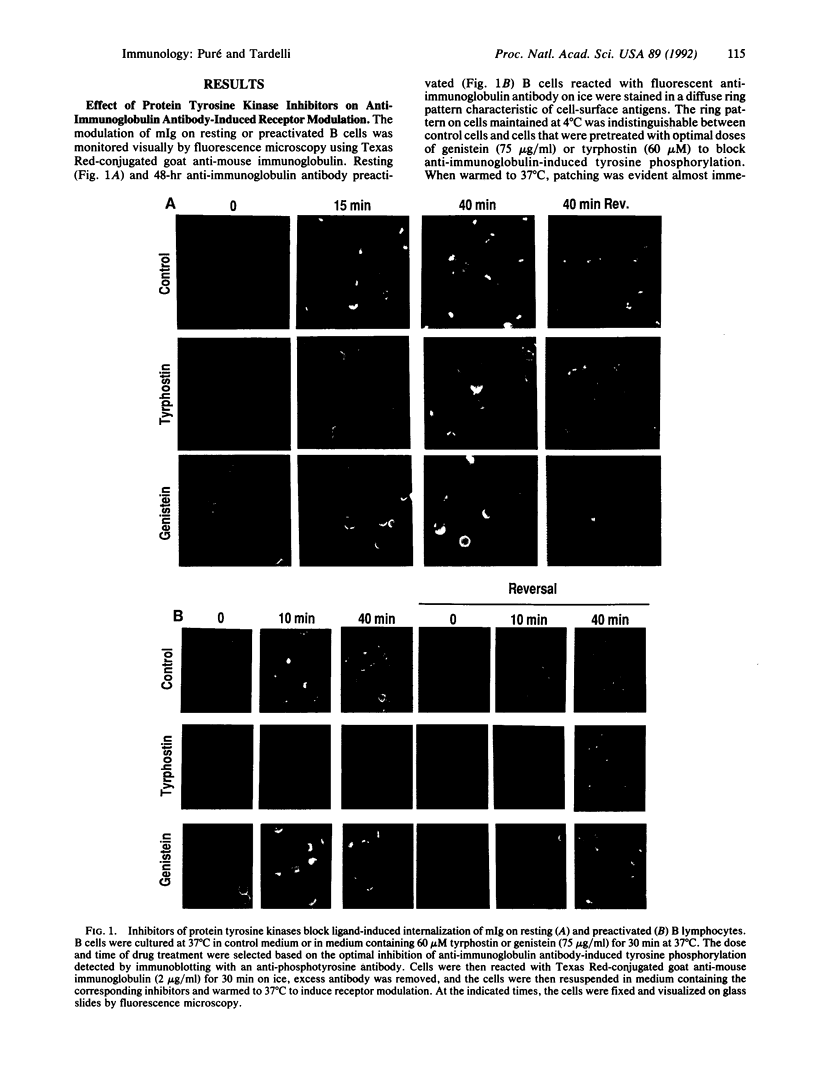
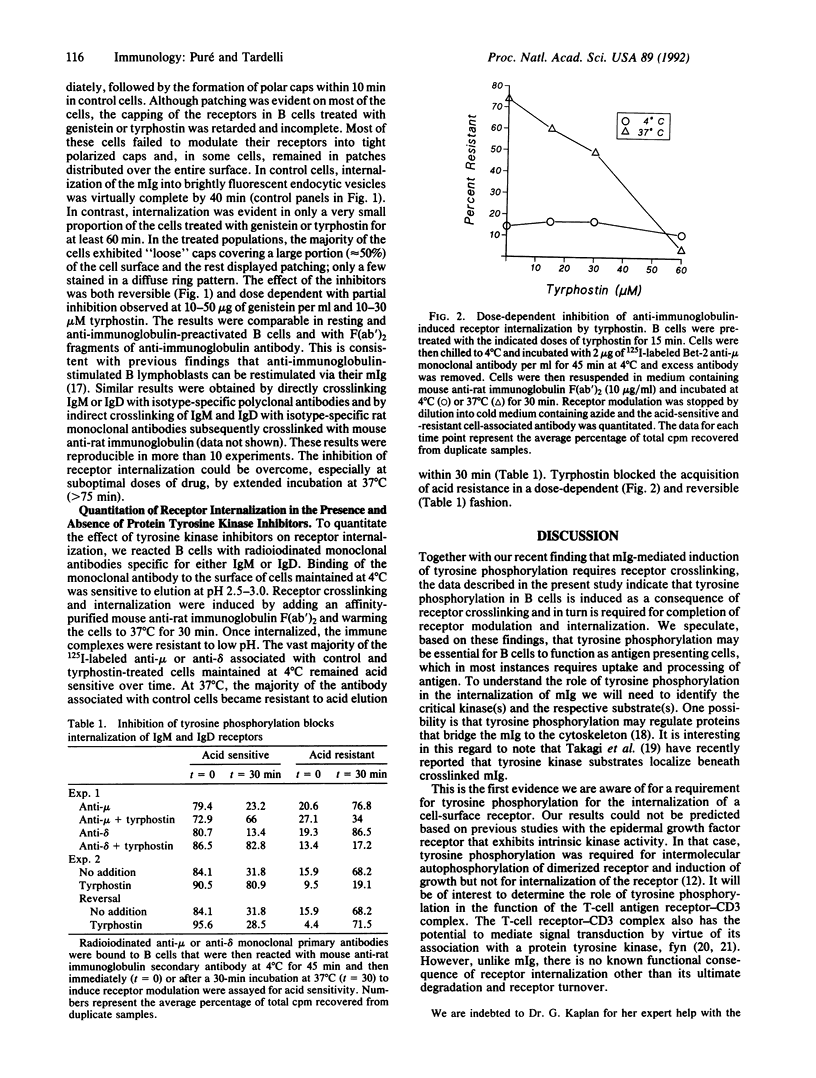
The membrane immunoglobulin (mIg) receptor for antigen mediates signal transduction in B lymphocytes. Multivalent ligand induces several early activation events including an increase in intracellular calcium concentration, hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol, and activation of protein kinase C. Most recently, it has been demonstrated that anti-immunoglobulin antibodies induce the rapid accumulation of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins and anti-phosphotyrosine immune complex-associated kinase activity, both of which require receptor crosslinking. Multivalent ligand binding of mIg also results in its association with detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal components and with a slight lag period, in a characteristic pattern of patching, followed by polar capping and finally internalization of the receptors. In this report, we demonstrate that two specific inhibitors of tyrosine phosphorylation, a tyrphostin and genistein, retard the modulation of mIg on the cell surface and inhibit ligand-induced receptor internalization. We conclude that in B cells, tyrosine phosphorylation occurs as the result of crosslinking mIg and is required for subsequent internalization of mIg-ligand complexes. This suggests that tyrosine phosphorylation may be important for B cells to function as specific antigen presenting cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland M. L., Simpson L., Isakson P. C., Pure E. T-independent and T-dependent steps in the murine B cell response to antiimmunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):506–519. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Hochman P. S., Unanue E. R. Ligand-induced association of surface immunoglobulin with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal matrix of the B lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1198–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. S., Cambier J. C. B lymphocyte antigen receptors (mIg) are non-covalently associated with a disulfide linked, inducibly phosphorylated glycoprotein complex. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):441–448. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. S., Hager E. J., Friedrich R. J., Cambier J. C. IgM antigen receptor complex contains phosphoprotein products of B29 and mb-1 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Park D. J., Rhee S. G., Fearon D. T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C induced by membrane immunoglobulin in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defranco A. L., Raveche E. S., Asofsky R., Paul W. E. Frequency of B lymphocytes responsive to anti-immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1523–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Yaish P., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins I: synthesis and biological activity of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1989 Oct;32(10):2344–2352. doi: 10.1021/jm00130a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Matsuuchi L., Kelly R. B., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of components of the B-cell antigen receptors following receptor crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3436–3440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakson P. C., D'Angelo D., Schetz J., Tardelli L., Puré E. Anti-Ig-stimulated B lymphoblasts can be restimulated via their surface Ig. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3901–3908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey E. K., Casten L. A., Niebling W. L., Margoliash E., Pierce S. K. Time dependence of B cell processing and presentation of peptide and native protein antigens. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3309–3314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyall R. M., Zilberstein A., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A., Schlessinger J. Tyrphostins inhibit epidermal growth factor (EGF)-receptor tyrosine kinase activity in living cells and EGF-stimulated cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14503–14509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Yaish P., Chorev M., Gilon C., Braun S., Levitzki A. Inhibition of insulin-dependent lipogenesis and anti-lipolysis by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1671–1676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi S., Daibata M., Last T. J., Humphreys R. E., Parker D. C., Sairenji T. Intracellular localization of tyrosine kinase substrates beneath crosslinked surface immunoglobulins in B cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):381–388. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaish P., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Blocking of EGF-dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):933–935. doi: 10.1126/science.3263702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]