Abstract
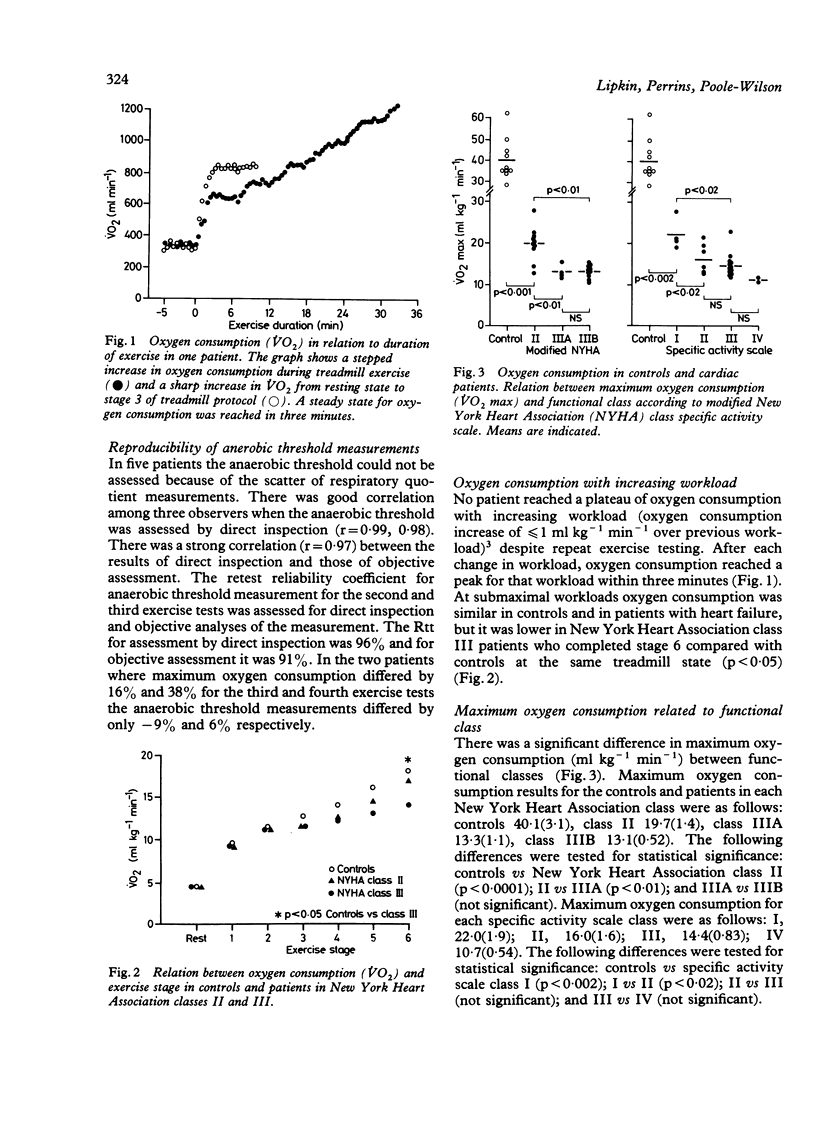
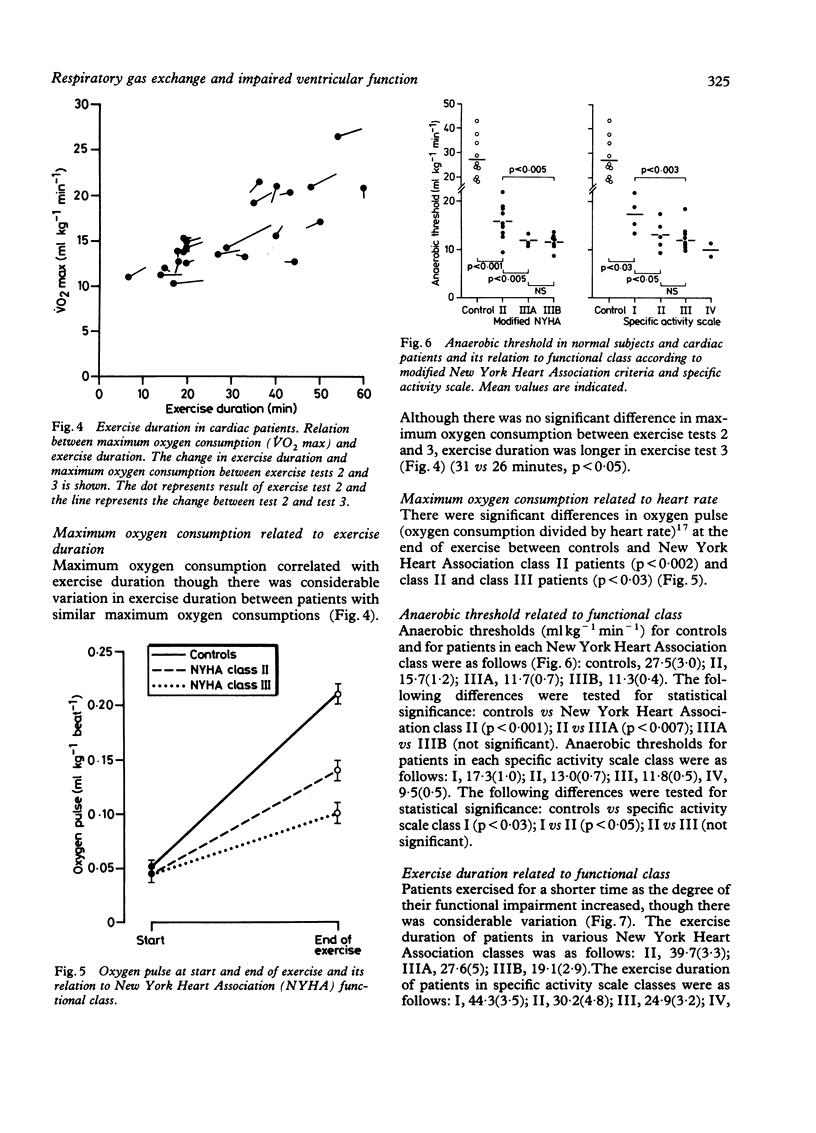
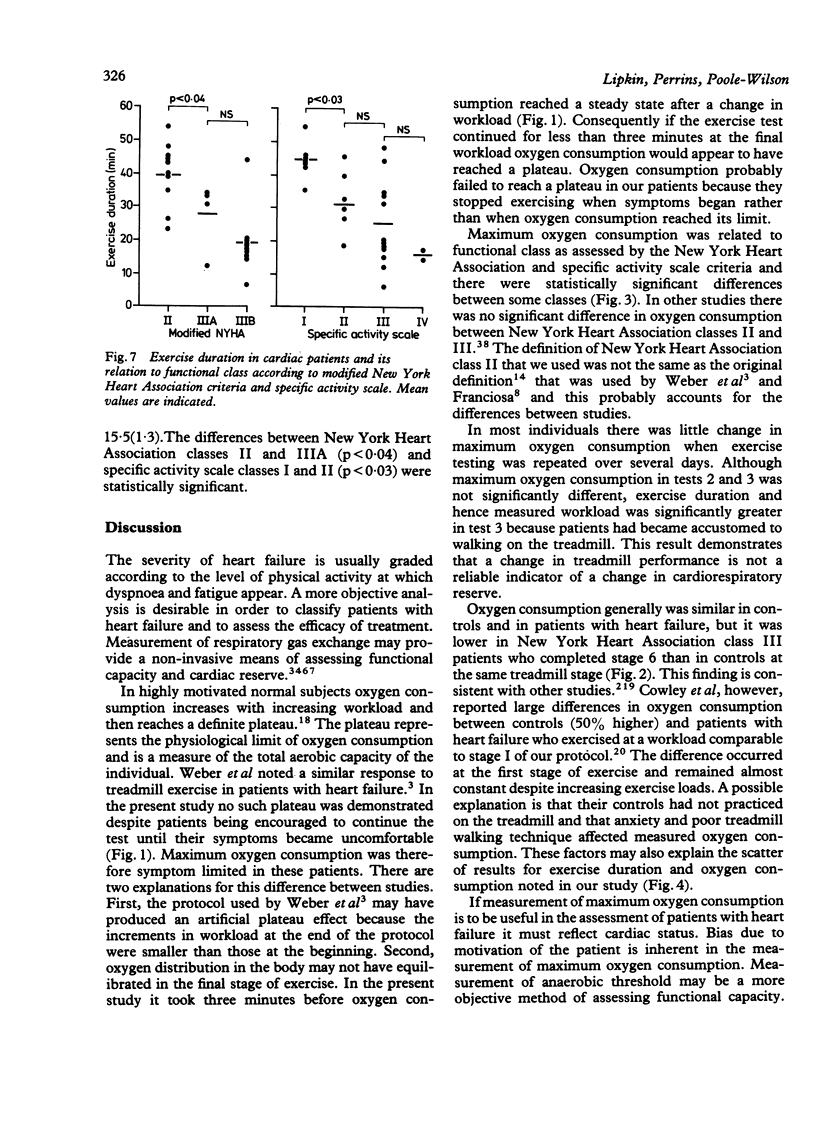
Respiratory gas exchange on exercise was evaluated as a non-invasive method of assessing patients with heart failure. Twenty four men (age 28-72) with symptomatic chronic stable heart failure (New York Heart Association class II-III) and ten controls aged 36-70 were studied. During treadmill exercise oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production were measured continuously by analysis of mixed expired gas with a computerised mass spectrometer. The anaerobic threshold was defined as the oxygen consumption at which carbon dioxide production increased disproportionately in relation to oxygen consumption. Oxygen consumption was stable at rest and increased on exercise, reaching a steady state within three minutes of any change in workload. The measurements of maximum oxygen consumption at the end of exercise and of anaerobic threshold were reproducible (retest reliability coefficients 90% and 91% respectively). There were significant differences in maximum oxygen consumption between functional classes. Similarly, there were significant differences in anaerobic threshold between classes, though there was considerable overlap. Measurement of oxygen consumption and anaerobic threshold provides an objective noninvasive assessment of patients with heart failure.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrand P. O. Measurement of maximal aerobic capacity. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Mar 25;96(12):732–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn E. H., Williams R. S., Wallace A. G. Exercise responses before and after physical conditioning in patients with severely depressed left ventricular function. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Feb 1;49(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)90504-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. J., Denison D. M. The measurement of metabolic gas exchange and minute volume by mass spectrometry alone. Respir Physiol. 1979 Feb;36(2):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(79)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan C. M., Brooks G. A. Endurance training affects lactate clearance, not lactate production. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):E83–E92. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.1.E83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa J. A. Exercise testing in chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1984 May 15;53(10):1447–1450. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(84)91041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa J. A., Leddy C. L., Wilen M., Schwartz D. E. Relation between hemodynamic and ventilatory responses in determining exercise capacity in severe congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Jan 1;53(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90696-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa J. A., Park M., Levine T. B. Lack of correlation between exercise capacity and indexes of resting left ventricular performance in heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Jan;47(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa J. A., Ziesche S., Wilen M. Functional capacity of patients with chronic left ventricular failure. Relationship of bicycle exercise performance to clinical and hemodynamic characterization. Am J Med. 1979 Sep;67(3):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90794-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Hashimoto B., Cook E. F., Loscalzo A. Comparative reproducibility and validity of systems for assessing cardiovascular functional class: advantages of a new specific activity scale. Circulation. 1981 Dec;64(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.6.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J., Jacobs I. Onset of blood lactage accumulation during muscular exercise as a threshold concept. I. Theoretical considerations. Int J Sports Med. 1982 Nov;3(4):190–201. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1026087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyal S. N., Whipp B. J., Huntsman D., Bray G. A., Wasserman K. Ventilatory responses to the metabolic acidosis of treadmill and cycle ergometry. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Jun;40(6):864–867. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.6.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura N., Nishijima H., Kojima S., Hashimoto F., Minami M., Yasuda H. Determination of anaerobic threshold for assessment of functional state in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 1983 Aug;68(2):360–367. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.68.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. A., Naughton J., Pietras R. J., Gunnar R. M. Treadmill exercise in assessment of the functional capacity of patients with cardiac disease. Am J Cardiol. 1972 Nov;30(7):757–762. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskamm H., Schnellbacher K., Samek L., Betz P. Does exercise testing with invasive measurements of cardiac output and pressure really contribute? Eur Heart J. 1983 Jan;4 (Suppl A):127–130. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/4.suppl_a.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN K., MCILROY M. B. DETECTING THE THRESHOLD OF ANAEROBIC METABOLISM IN CARDIAC PATIENTS DURING EXERCISE. Am J Cardiol. 1964 Dec;14:844–852. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(64)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman K., Whipp B. J. Excercise physiology in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Aug;112(2):219–249. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman K., Whipp B. J., Koyl S. N., Beaver W. L. Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Aug;35(2):236–243. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. T., Kinasewitz G. T., Janicki J. S., Fishman A. P. Oxygen utilization and ventilation during exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. Circulation. 1982 Jun;65(6):1213–1223. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.6.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Ferraro N., Weber K. T. Respiratory gas analysis during exercise as a noninvasive measure of lactate concentration in chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Jun;51(10):1639–1643. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Martin J. L., Ferraro N. Impaired skeletal muscle nutritive flow during exercise in patients with congestive heart failure: role of cardiac pump dysfunction as determined by the effect of dobutamine. Am J Cardiol. 1984 May 1;53(9):1308–1315. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



